Migrating From Sauce Labs To LambdaTest
LambdaTest and Sauce Labs both offer the cloud-based Selenium Grid. Hence, you can easily migrate your existing Selenium test automation scripts (or suites) from Sauce Labs to LambdaTest.
[Note: This guide covers the migration of tests running on the cloud grid that uses Selenium 4 and Selenium 3]Authentication
Firstly, you need to change the authentication in your configuration settings of your test suite. For running tests on LambdaTest Selenium Grid, you need to have a valid user_name and access_key to perform tests on our Grid. In case you do not have an account on LambdaTest, visit the LambdaTest signup page and create a new account.
When migrating your Selenium 4 tests from BrowserStack to LambdaTest, the following updates are required in your existing code:
-
Get LambdaTest Credentials: You can find these credentials under Account Settings > Password & Security and copy your Username and Access Key, then add them to the .env file to keep them safe from public exposure.
-
Create .env file: Securely store your LambdaTest credentials, create a .env file in the root of your project and add the following values:
- Sauce Labs Selenium Grid Credentials
- LambdaTest Selenium Grid Credentials
public static final String user_name = "SauceLabs_UserName";
public static final String access_key = "SauceLabs_AccessKey";
LT_USERNAME="<your_username>"
LT_ACCESS_KEY="<your_access_key>"
Once the .env file is set up, ensure your test framework correctly reads these variables at runtime. This helps keep your authentication secure and avoids hard-coding credentials within your scripts. With the credentials in place, you’re now ready to update your Hub URL for LambdaTest execution.
Changes in Hub URL
You need to now change the hub URL in the configuration settings of your test suite. Hub URL is of type String and it defines the Hub location to which the Selenium tests would be submitted for execution.
- Sauce Labs Selenium Grid URL
- LambdaTest Selenium Grid URL
@ondemand.us-west-1.saucelabs.com:443/wd/hub
@hub.lambdatest.com/wd/hub
Configuring Selenium 4 Tests on LambdaTest
Migrating your existing tests running on Sauce Labs Cloud to LambdaTest Selenium cloud can be done with just a few lines of change. In this guide, we will see how you can use LambdaTest desired capabilities in your tests, authenticate your test session, and run tests on the browsers in our cloud.
LambdaTest Automation Capabilities
Capabilities generator let you configure the desired capabilities (or capabilities) which are configuration options that let you set the following:
- Desired browser
- Desired browser version
- Desired platform (or operating system)
Optionally, you can also choose the Selenium version and other advanced options present in the Selenium Capabilities Generator. For this migration guide, we have only restricted to the three capabilities listed above.
To generate capabilities use LambdaTest Capabilities Generator to define key automation testing parameters, such as browser, version, operating system, and additional test settings.
For the migration, we have considered Java-based Selenium automation tests. Shown below are the screenshots of capabilities generator of Sauce Labs and LambdaTest:
- Sauce Labs Capabilities
- LambdaTest Capabilities
SafariOptions browserOptions = new SafariOptions();
browserOptions.setPlatformName("macOS 15");
browserOptions.setBrowserVersion("latest");
Map<String, Object> sauceOptions = new HashMap<>();
sauceOptions.put("username", "YOUR_USERNAME");
sauceOptions.put("accessKey", "YOUR_ACCESS_KEY");
sauceOptions.put("build", "<your build id>");
sauceOptions.put("name", "<your test name>");
sauceOptions.put("armRequired", true);
browserOptions.setCapability("sauce:options", sauceOptions);
SafariOptions browserOptions = new SafariOptions();
browserOptions.setPlatformName("MacOS Tahoe");
browserOptions.setBrowserVersion("26");
HashMap<String, Object> ltOptions = new HashMap<String, Object>();
ltOptions.put("username", "<your_username>");
ltOptions.put("accessKey", "<your_access_key>");
ltOptions.put("w3c", true);
browserOptions.setCapability("LT:Options", ltOptions);
Configuring Selenium 3 Tests on LambdaTest
Migrating your existing tests running on Sauce Labs Cloud to LambdaTest Selenium cloud can be done with just a few lines of change. In this guide, we will see how you can use LambdaTest desired capabilities in your tests, authenticate your test session, and run tests on the browsers in our cloud.
LambdaTest Automation Capabilities
Capabilities generator let you configure the desired capabilities (or capabilities) which are configuration options that let you set the following:
- Desired browser
- Desired browser version
- Desired platform (or operating system)
Optionally, you can also choose the Selenium version and other advanced options present in the Selenium Capabilities Generator. For this migration guide, we have only restricted to the three capabilities listed above.
To generate capabilities use LambdaTest Capabilities Generator to define key automation testing parameters, such as browser, version, operating system, and additional test settings.
For the migration, we have considered Java-based Selenium automation tests. Shown below are the screenshots of capabilities generator of Sauce Labs and LambdaTest:
- Sauce Labs Capabilities
- LambdaTest Capabilities
SafariOptions browserOptions = new SafariOptions();
browserOptions.setCapability("platformName", "macOS 15");
browserOptions.setCapability("browserVersion", "latest");
Map<String, Object> sauceOptions = new HashMap<>();
sauceOptions.put("build", "<your build id>");
sauceOptions.put("name", "<your test name>");
sauceOptions.put("username", "YOUR_USERNAME");
sauceOptions.put("accessKey", "YOUR_ACCESS_KEY");
sauceOptions.put("armRequired", true);
browserOptions.setCapability("sauce:options", sauceOptions);
DesiredCapabilities capabilities = new DesiredCapabilities();
capabilities.setCapability("browserName", "Safari");
capabilities.setCapability("browserVersion", "26");
HashMap<String, Object> ltOptions = new HashMap<String, Object>();
ltOptions.put("username", "<your_username>");
ltOptions.put("accessKey", "<your_access_key>");
ltOptions.put("platformName", "MacOS Tahoe");
ltOptions.put("visual", true);
ltOptions.put("video", true);
capabilities.setCapability("LT:Options", ltOptions);
Hands On Guide - LambdaTest Migration
Let’s walk through a practical example demonstrating how to migrate a Selenium 4 test to LambdaTest. In this scenario, we launch the latest Chrome browser on a Windows 10 machine.
Test Scenario:
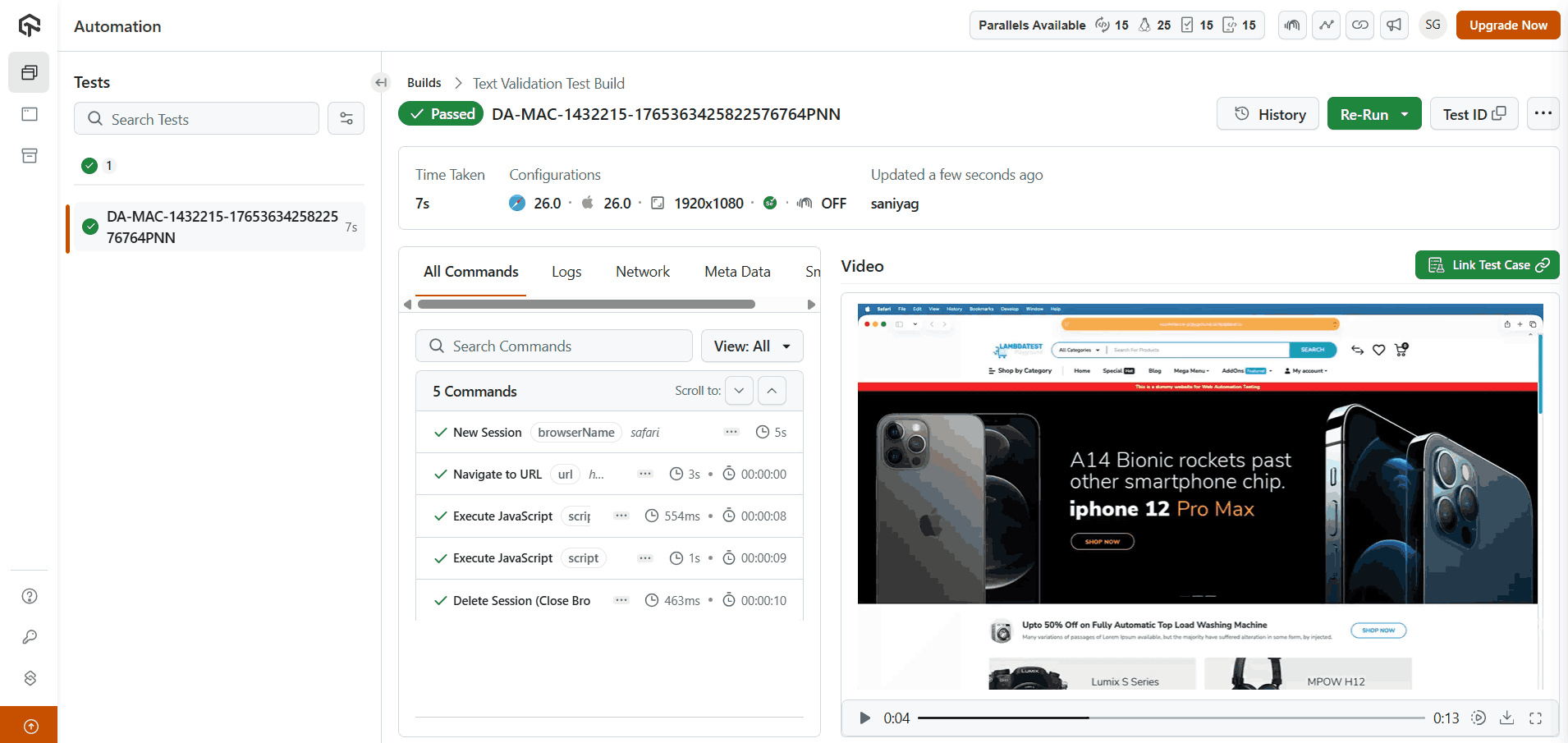
This test script performs a basic text validation on the website LambdaTest eCommerce Playground and shows the expected execution results when running the test in the LambdaTest cloud.
- LambdaTest Execution With Selenium 4 Capabilities
- LambdaTest Execution With Selenium 3 Capabilities
// TextValidationTest.java
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.remote.RemoteWebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.JavascriptExecutor;
import org.openqa.selenium.safari.SafariOptions;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class TextValidationTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String username = System.getenv("LT_USERNAME") == null ?
"Your LT Username" : System.getenv("LT_USERNAME");
String authkey = System.getenv("LT_ACCESS_KEY") == null ?
"Your LT AccessKey\n" : System.getenv("LT_ACCESS_KEY");
String GRID_URL = "https://" + username + ":" + authkey + "@hub.lambdatest.com/wd/hub";
SafariOptions browserOptions = new SafariOptions();
browserOptions.setPlatformName("MacOS Tahoe");
browserOptions.setBrowserVersion("26");
HashMap<String, Object> ltOptions = new HashMap<String, Object>();
ltOptions.put("username", "<your_username>");
ltOptions.put("accessKey", "<your_access_key>");
ltOptions.put("project", "Text Validation Test");
ltOptions.put("build", "Text Validation Test Build");
ltOptions.put("w3c", true);
browserOptions.setCapability("LT:Options", ltOptions);
WebDriver driver = new RemoteWebDriver(new URL(GRID_URL), browserOptions);
try {
driver.get("https://ecommerce-playground.lambdatest.io/");
String expectedText = "This is a dummy website for Web Automation Testing";
boolean isTextPresent = driver.getPageSource().contains(expectedText);
if (isTextPresent) {
((JavascriptExecutor) driver).executeScript("lambda-status=passed");
System.out.println("✔ Text validation PASSED");
} else {
((JavascriptExecutor) driver).executeScript("lambda-status=failed");
System.out.println("✘ Text validation FAILED");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
((JavascriptExecutor) driver).executeScript("lambda-status=pass");
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
driver.quit(); // 🔹 Correctly placed – runs even if test fails
}
}
}
// TextValidationTest.java – Selenium 3 Configuration
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.remote.DesiredCapabilities;
import org.openqa.selenium.remote.RemoteWebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.JavascriptExecutor;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class TextValidationTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String username = System.getenv("LT_USERNAME") == null ?
"Your LT Username" : System.getenv("LT_USERNAME");
String authkey = System.getenv("LT_ACCESS_KEY") == null ?
"Your LT AccessKey" : System.getenv("LT_ACCESS_KEY");
String GRID_URL = "https://" + username + ":" + authkey + "@hub.lambdatest.com/wd/hub";
DesiredCapabilities capabilities = new DesiredCapabilities();
capabilities.setCapability("browserName", "Safari");
capabilities.setCapability("browserVersion", "26");
HashMap<String, Object> ltOptions = new HashMap<String, Object>();
ltOptions.put("username", "<your_username>");
ltOptions.put("accessKey", "<your_access_key>");
ltOptions.put("platformName", "MacOS Tahoe");
ltOptions.put("visual", true);
ltOptions.put("video", true);
capabilities.setCapability("LT:Options", ltOptions);
WebDriver driver = new RemoteWebDriver(new URL(GRID_URL), capabilities);
try {
driver.get("https://ecommerce-playground.lambdatest.io/");
String expectedText = "This is a dummy website for Web Automation Testing";
boolean isTextPresent = driver.getPageSource().contains(expectedText);
if (isTextPresent) {
((JavascriptExecutor) driver).executeScript("lambda-status=passed");
System.out.println("✔ Text validation PASSED");
} else {
((JavascriptExecutor) driver).executeScript("lambda-status=failed");
System.out.println("✘ Text validation FAILED");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
((JavascriptExecutor) driver).executeScript("lambda-status=pass");
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
driver.quit(); // 🔹 Correctly placed – runs even if test fails
}
}
}
Result
Visit LambdaTest Web Automation dashboard to view your test execution result.