Architecture
TAS Terminology
-
Action: Action is a term to signify generic execution triggered by the TAS server in response to a webhook or any other request. Job, Task, pre-processing, and post-processing, FTM, Culprit finding, git-bisect are different kinds of action.
-
Task: An action triggered for running activities for a particular commit. This includes fetching dependencies, discovering tests, running tests, and publishing results.
-
FTM: Flaky test management is a type of Task that gets triggered on special events such as new test introduction, test updates, etc. The TAS server will conduct Flaky test management tasks just like any other actions and will spawn containers for them.
-
Job: The collection of tasks is called a job.
Major Components
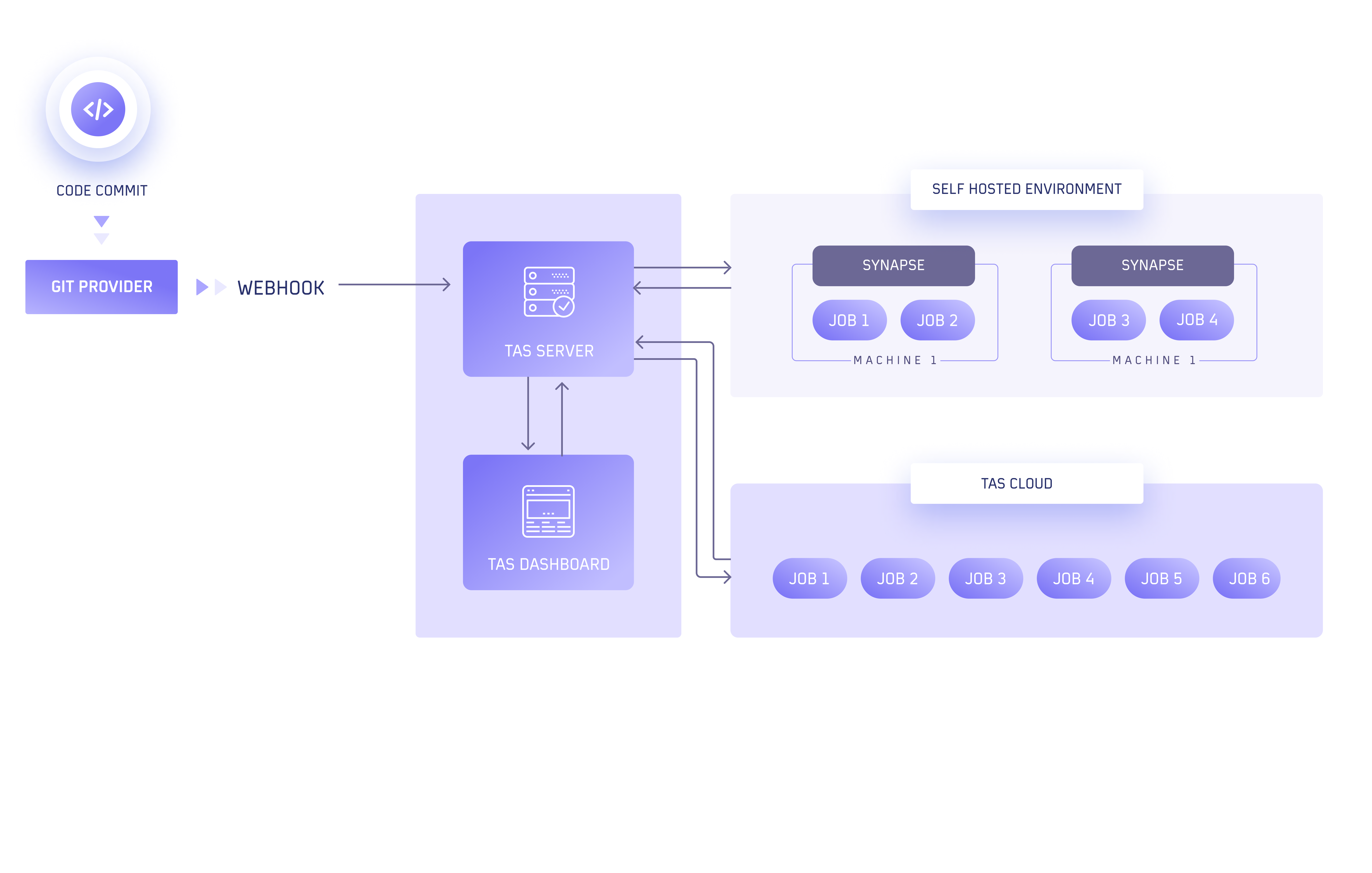
TAS Server
TAS server consists of multiple components.
The first component is responsible for receiving webhooks from git providers and queueing actions to be taken as a response to events received.
The second component runs the business logic by executing an action in response to the request/event received. The action can be triggering a build, run pre or post-processing of a build, execute FTM etc. It triggers every action in a separate container.
Nucleus
This component is the driving agent of the container executed to run the actions scheduled by the TAS server. All actions are executed on Linux containers and the nucleus manages the lifecycle of the container. Synapse The role of this component is to connect on-prem/local runners to LamdaTest Server and be able to run actions for a particular repository on self-hosted infrastructure instead of using LambdaTest infra to run containers.
Synapse
The role of this component is to connect on-prem/local runners to LamdaTest Server and be able to run actions for a particular repository on self-hosted infrastructure instead of using LambdaTest infra to run containers.
Process Flow
- TAS server receives a git event webhook from git event provider (github/gitlab/bitbucket)
- TAS server processes the webhook information and determines if the request should run on a Self-Hosted Environment or TAS Cloud.
- For Self-Hosted Environment
- An event is sent to synapse connection (if available)
- Synapse requests task information from TAS Server
- Synapse runs container for action on the local system
- For TAS Cloud
- TAS queues the action in the relevant queue depending on the license type
- Queued actions will schedule containers for each action
- For Self-Hosted Environment
