View Assertion Errors On LambdaTest
While handling GET requests in your Selenium scripts, many times the assertion might fail. To view these assertion errors as exceptions and handle them better, you can now use the Lambda Exceptions feature.
What Are Lambda Exceptions?
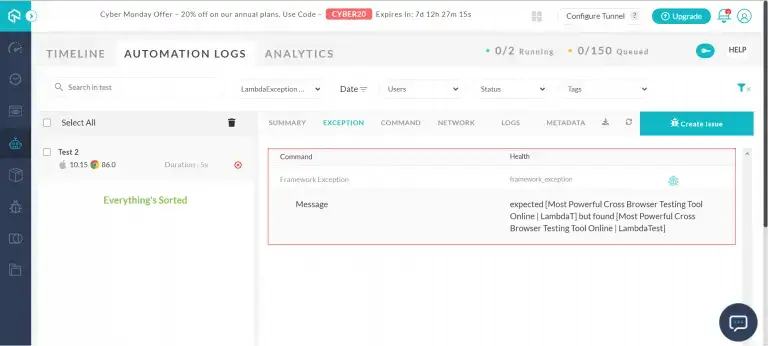
Lambda Exception is the feature of LambdaTest, by which you can easily manage and handle your GET request errors, like AssertionError. By using this feature, the error gets displayed as an exception in the Exception tab of your test.
For example:
How To Use Lambda Exception?
While performing assertions on GET requests, if the assertion fails, an AssertionError exception is thrown. Refer the below Java syntax to catch this error and push it to LambdaTest using Lambda Exceptions.
try {
// some GET request
Assert.assertEquals(ActualValue, ExpectedValue);
} catch (AssertionError e) {
Status = "failed";
exceptionCapture.add(e.getMessage());
((JavascriptExecutor) driver).executeScript("lambda-exceptions", exceptionCapture);
}
In the above syntax, when the AssertionError is caught in the catch block, the exception message is added in the form of an array of Strings. This message is then pushed to LambdaTest using the Lambda Exceptions feature, as shown via the JavascriptExecutor command.
Lambda Exception Demo
For demo purpose, we will create a script to:
- Visit www.lambdatest.com
- Fetch the title
- Assert the title with expected value
View Exception on LambdaTest Using Lambda Exception
Below is the complete code for this script, using TestNG framework in Java.
package com.lambdatest;
import java.net.MalformedURLException;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import org.openqa.selenium.By;
import org.openqa.selenium.JavascriptExecutor;
import org.openqa.selenium.NoSuchElementException;
import org.openqa.selenium.remote.DesiredCapabilities;
import org.openqa.selenium.remote.RemoteWebDriver;
import org.testng.Assert;
import org.testng.annotations.AfterSuite;
import org.testng.annotations.BeforeSuite;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
public class LambdaException {
private static RemoteWebDriver driver;
private static String Status="failed";
@BeforeSuite
public void setup() throws MalformedURLException {
try {
String username = System.getenv("LT_USERNAME");
String authkey = System.getenv("LT_ACCESS_KEY");
String hub = "@hub.lambdatest.com/wd/hub";
DesiredCapabilities caps = new DesiredCapabilities();
caps.setCapability("browser", "Chrome");
caps.setCapability("version", "86");
caps.setCapability("platform", "MacOS Catalina");
caps.setCapability("build", "LambdaException Demo");
caps.setCapability("name", "Test 2");
caps.setCapability("network", true);
caps.setCapability("visual", true);
caps.setCapability("video", true);
caps.setCapability("console", true);
System.out.println("Desired Caps: " + caps);
driver = new RemoteWebDriver(new URL("https://" + username + ":" + authkey + hub), caps);
}
catch(Exception e)
{
System.out.println(e);
}
}
@Test
public static void testAssertionError() {
ArrayList<String> exceptionCapture = new ArrayList<>();
try {
driver.get("https://www.lambdatest.com");
String ExpectedTitle = "Most Powerful Cross Browser Testing Tool Online | LambdaT";
String TitleValue = driver.getTitle();
if (TitleValue.equals(ExpectedTitle)) {
Status = "passed";
}
Assert.assertEquals(TitleValue, ExpectedTitle);
} catch (AssertionError e) {
Status = "failed";
exceptionCapture.add(e.getMessage());
((JavascriptExecutor) driver).executeScript("lambda-exceptions", exceptionCapture);
}
}
@AfterSuite
public void tearDown() {
driver.executeScript("lambda-status=" + Status);
driver.quit();
}
}
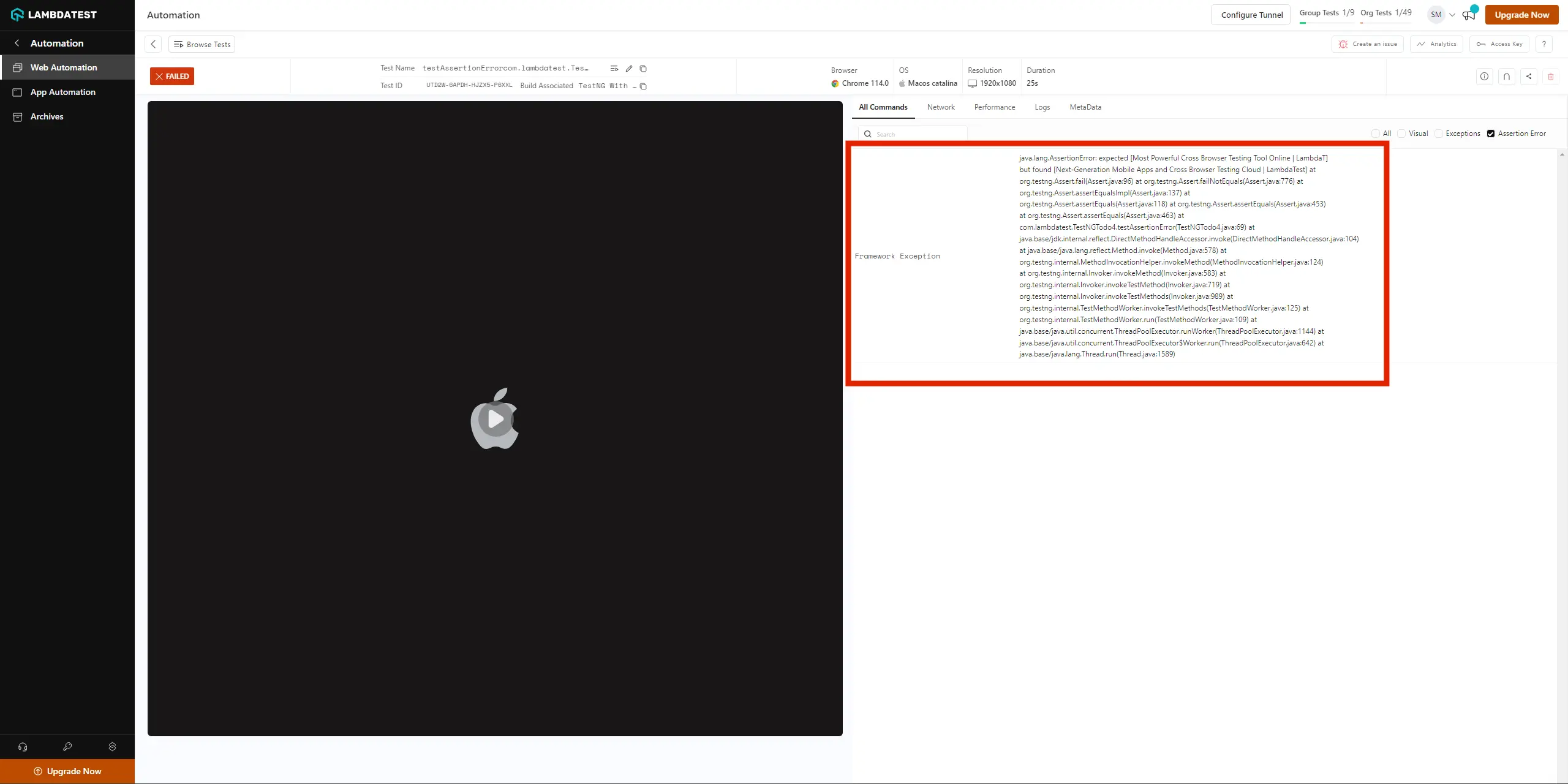
Upon executing the above test as a TestNG script, you will notice that the test will fail. It is because we have provided an incorrect value in the ExpectedTitle variable, for demo purposes. So when you open the test view of this test and navigate to the Exception tab, you will find a message displaying this error, as shown below:
View StackTrace on LambdaTest Using Lambda Exception
You can even view the complete StackTrace on the LambdaTest platform, using the Lambda Exceptions feature. For this, you need to convert the StackTrace to String and print it in the form of an array of Strings. Below is the complete script to print the StackTrace, using the TestNG framework in Java:
package com.lambdatest;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.io.StringWriter;
import java.net.MalformedURLException;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import org.openqa.selenium.By;
import org.openqa.selenium.JavascriptExecutor;
import org.openqa.selenium.NoSuchElementException;
import org.openqa.selenium.remote.DesiredCapabilities;
import org.openqa.selenium.remote.RemoteWebDriver;
import org.testng.Assert;
import org.testng.annotations.AfterSuite;
import org.testng.annotations.BeforeSuite;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
public class LambdaException {
private static RemoteWebDriver driver;
private static String Status="failed";
@BeforeSuite
public void setup() throws MalformedURLException {
try {
String username = System.getenv("LT_USERNAME");
String authkey = System.getenv("LT_ACCESS_KEY");
String hub = "@hub.lambdatest.com/wd/hub";
DesiredCapabilities caps = new DesiredCapabilities();
caps.setCapability("browser", "Chrome");
caps.setCapability("version", "86");
caps.setCapability("platform", "MacOS Catalina");
caps.setCapability("build", "LambdaException Demo");
caps.setCapability("name", "Print StackTrace");
caps.setCapability("network", true);
caps.setCapability("visual", true);
caps.setCapability("video", true);
caps.setCapability("console", true);
System.out.println("Desired Caps: " + caps);
driver = new RemoteWebDriver(new URL("https://" + username + ":" + authkey + hub), caps);
}
catch(Exception e)
{
System.out.println(e);
}
}
@Test
public static void testAssertionError() {
ArrayList<String> exceptionCapture = new ArrayList<>();
try {
driver.get("https://www.lambdatest.com");
String TitleValue = driver.getTitle();
String ExpectedTitle = "Most Powerful Cross Browser Testing Tool Online | LambdaT";
if (TitleValue.equals(ExpectedTitle)) {
Status = "passed";
}
Assert.assertEquals(TitleValue, ExpectedTitle);
} catch (AssertionError e) {
Status = "failed";
StringWriter sw = new StringWriter();
PrintWriter printWriter = new PrintWriter(sw);
PrintWriter pw = printWriter;
e.printStackTrace(pw);
String sStackTrace = sw.toString();
exceptionCapture.add(sStackTrace);
((JavascriptExecutor) driver).executeScript("lambda-exceptions", exceptionCapture);
}
}
@AfterSuite
public void tearDown() {
driver.executeScript("lambda-status=" + Status);
driver.quit();
}
}
Upon executing the above test as a TestNG script, it will provide you the same result as the view exception section, because we have provided an incorrect value in the ExpectedTitle variable, for demo purposes. So when you open the test view of this test and navigate to the Exception tab, you will find the complete StackTrace, as shown below:
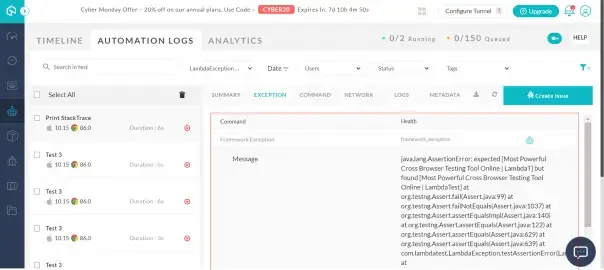
Below is the complete StackTrace printed on the LambdaTest platform, generated from above script.
java.lang.AssertionError: expected [Most Powerful Cross Browser Testing Tool Online | LambdaT] but found [Most Powerful Cross Browser Testing Tool Online | Lambdatest] at
org.testng.Assert.fail(Assert.java:99) at
org.testng.Assert.failNotEquals(Assert.java:1037) at
org.testng.Assert.assertEqualsImpl(Assert.java:140) at
org.testng.Assert.assertEquals(Assert.java:122) at
org.testng.Assert.assertEquals(Assert.java:629) at
org.testng.Assert.assertEquals(Assert.java:639) at
com.lambdatest.LambdaException.testAssertionError(LambdaException.java:66) at
java.base/jdk.internal.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0(Native Method) at
java.base/jdk.internal.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(NativeMethodAccessorImpl.java:64) at
java.base/jdk.internal.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.java:43) at
java.base/java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Method.java:564) at
org.testng.internal.MethodInvocationHelper.invokeMethod(MethodInvocationHelper.java:132) at
org.testng.internal.TestInvoker.invokeMethod(TestInvoker.java:599) at
org.testng.internal.TestInvoker.invokeTestMethod(TestInvoker.java:174) at
org.testng.internal.MethodRunner.runInSequence(MethodRunner.java:46) at
org.testng.internal.TestInvoker$MethodInvocationAgent.invoke(TestInvoker.java:822) at
org.testng.internal.TestInvoker.invokeTestMethods(TestInvoker.java:147) at
org.testng.internal.TestMethodWorker.invokeTestMethods(TestMethodWorker.java:146) at
org.testng.internal.TestMethodWorker.run(TestMethodWorker.java:128) at
java.base/java.util.ArrayList.forEach(ArrayList.java:1511) at
org.testng.TestRunner.privateRun(TestRunner.java:764) at
org.testng.TestRunner.run(TestRunner.java:585) at
org.testng.SuiteRunner.runTest(SuiteRunner.java:384) at
org.testng.SuiteRunner.runSequentially(SuiteRunner.java:378) at
org.testng.SuiteRunner.privateRun(SuiteRunner.java:337) at
org.testng.SuiteRunner.run(SuiteRunner.java:286) at
org.testng.SuiteRunnerWorker.runSuite(SuiteRunnerWorker.java:53) at
org.testng.SuiteRunnerWorker.run(SuiteRunnerWorker.java:96) at
org.testng.TestNG.runSuitesSequentially(TestNG.java:1218) at
org.testng.TestNG.runSuitesLocally(TestNG.java:1140) at
org.testng.TestNG.runSuites(TestNG.java:1069) at
org.testng.TestNG.run(TestNG.java:1037) at
org.testng.remote.AbstractRemoteTestNG.run(AbstractRemoteTestNG.java:115) at
org.testng.remote.RemoteTestNG.initAndRun(RemoteTestNG.java:251) at
org.testng.remote.RemoteTestNG.main(RemoteTestNG.java:77)
That’s it! You can now easily handle and manage exceptions using the Lambda Exceptions feature. If you still have any doubt, please feel free to reach out to us via 24/7 chat support or by mailing to us on support@lambdatest.com. Happy testing! 🙂
