Variables in KaneAI
Variables are placeholders that store values, which can be reused across different parts of a test case. In automation, using variables helps make the tests more flexible, reusable, and maintainable. Instead of hardcoding values in test steps, you can define variables, assign them values, and reference them throughout your tests. This reduces redundancy and makes the tests easier to modify, especially when dealing with frequently changing parameters like URLs, credentials, or device configurations. Variables can be accessed directly from https://kaneai.lambdatest.com/variables.
Using variables enables you to:
- Avoid repetitive entries in test cases.
- Get values from within the application under test & store it in variable to validate the accuracy of data.
- Increase the reusability and adaptability of test scripts, especially useful for parameters that might change frequently, such as URLs, credentials, or environmental settings.
Types of variables
-
String Variables: Store simple text values. They can be used for things like usernames, or any textual data. String variables can be created via KaneAI or manually within the session.
-
JSON Variables: Store structured data in the form of key-value pairs. JSON variables are especially useful for passing complex objects such as API responses. JSON variables are auto-generated from API calls and DB queries used in KaneAI and cannot be created manually.
Scope of variables
Local Variables
Local variables can only be defined using natural language or used as a part of an operation when an instruction is provided by the user. They are only accessible within the specific test case where they are defined. They help ensure that values are isolated and can be used temporarily within a specific context. A local variable can be converted to a global or an environment variable within the authoring session of KaneAI.
Global Variables
Global variables are accessible across multiple test cases within the entire organisation. They allow values to be reused in multiple places, enhancing consistency and reducing redundancy. Any variable which is converted from local to global has an option to persist value across sessions if the value changes within a session. More details about persist check are added below.
Environment Variables
Environment variables are variables that are typically set for a specific environment (e.g., staging, production). They are useful for managing values like URLs, or credentials that differ based on the environment in which the tests are being executed. Using environment variables you can execute your test on multiple environments easily. More details about environments are added below.
How to create & edit variables
Variables can be created using the following three methods:
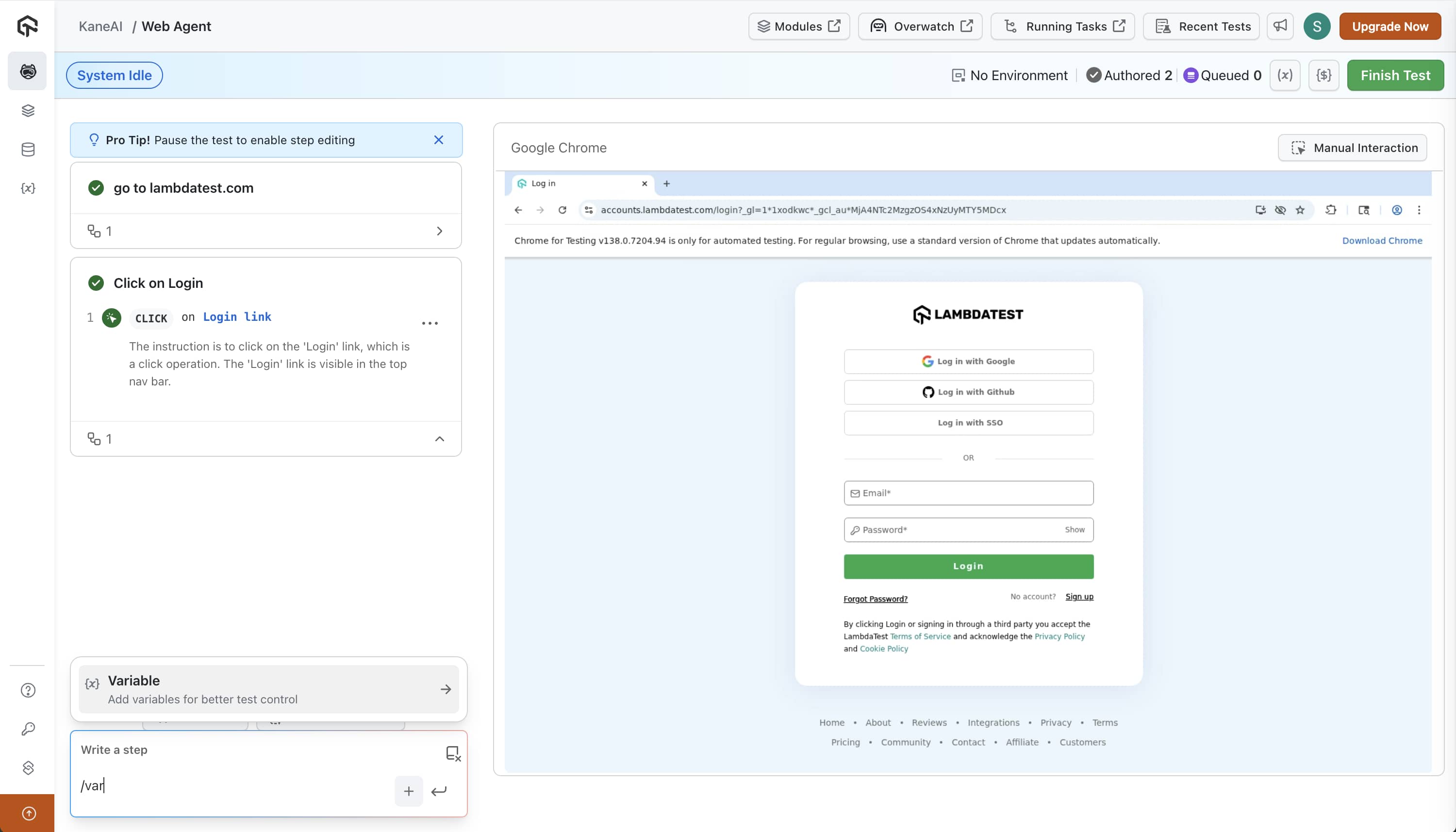
Using Slash "/" Command in authoring session
You can define variables directly by using the / command in the step input and select "Add a variable" option. You are allowed to create global and environment variables using this approach and define their values.
The value of variables can be edited by clicking on the variables listing icon on the top right.
Using Natural Language in authoring session
KaneAI allows you to create variables using natural language. For instance, you can write:
Set username as John
This will automatically create a local variable {{username}} with the value "John".
For such local variables, only the scope of the variable can be changed to a global with an option to enable the persist check which ensures that the value when updated in one session or test execution gets persistes across sessions and test executions.
Via UI from Variables page
By visiting the variables page, you can click on "Create new" option and add relevant details and scope. You can list of all global and environment variables on this page. You can edit the session value for the variables here which will lead to updation of the value in all new test executions and sessions for that variable.
How to leverage variables during authoring
Variables can be used to enhance your test cases, making them more dynamic.
Syntax for Assertions
Variable usage can be done using the {{ prefix to list all existing variables in the KaneAI session input box. When making assertions in your test case, you can use variables for inputing a value or as part of the assertion logic.
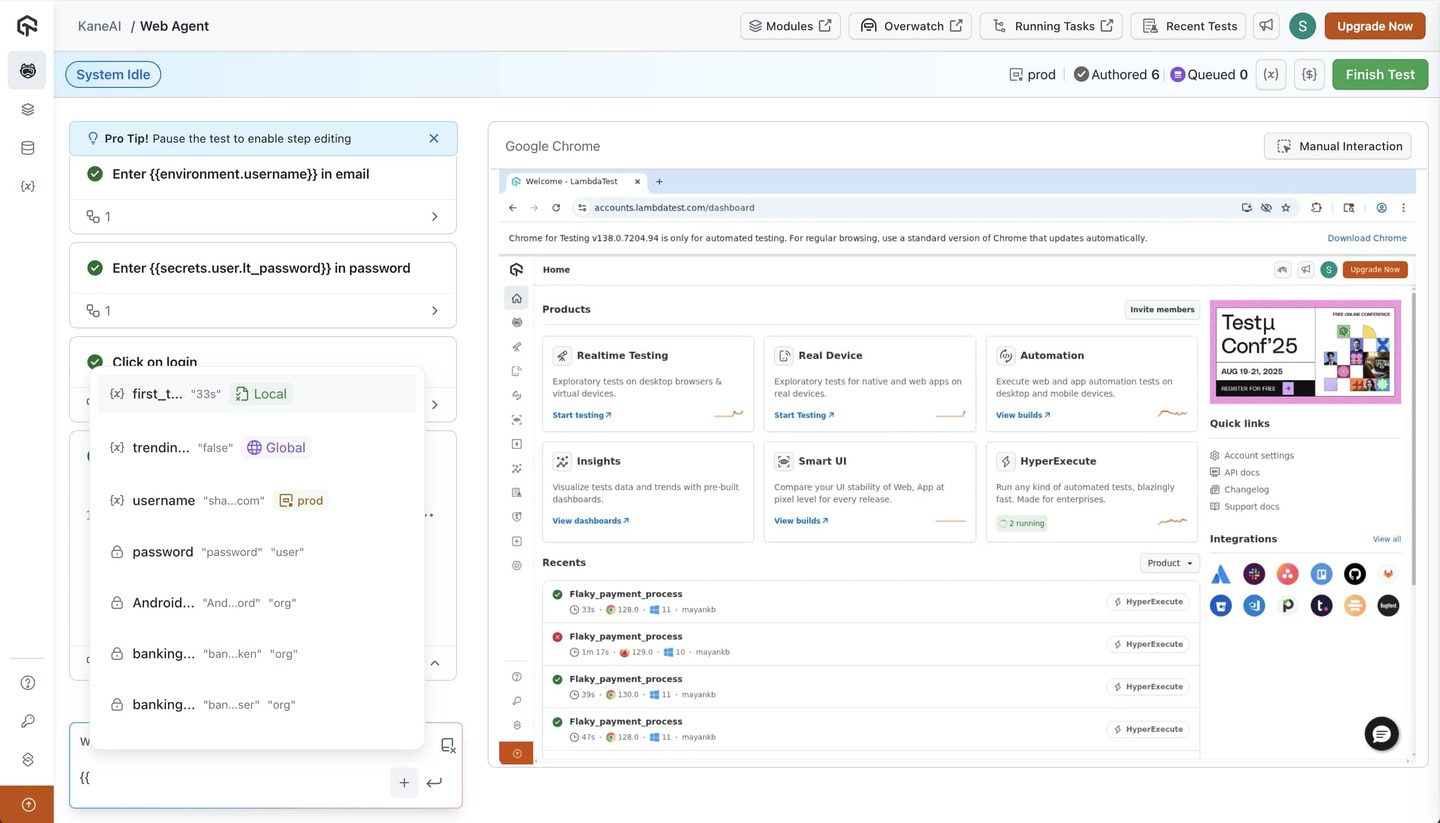
String variables example:
Enter {{username}} in user input field
This will input the value of the username variable in the user input field.
assert {{username}} contains 'John'
This will assert if the username variable contains the value "John".
JSON variables example:
JSON variables are generated from the response of an API used via the slash command or from the DB query output. We can use JSON variables to reach a particular object which might be inside the JSON hierarchy via the UI when the {{ prefix is used in the input box inside the KaneAI session. For instance, we can assert that the email field inside the API variable response matches "john.doe@example.com".
assert {{api_variable.response.email}} is 'john.doe@example.com'
Here is a video to further explain the JSON variables usage:
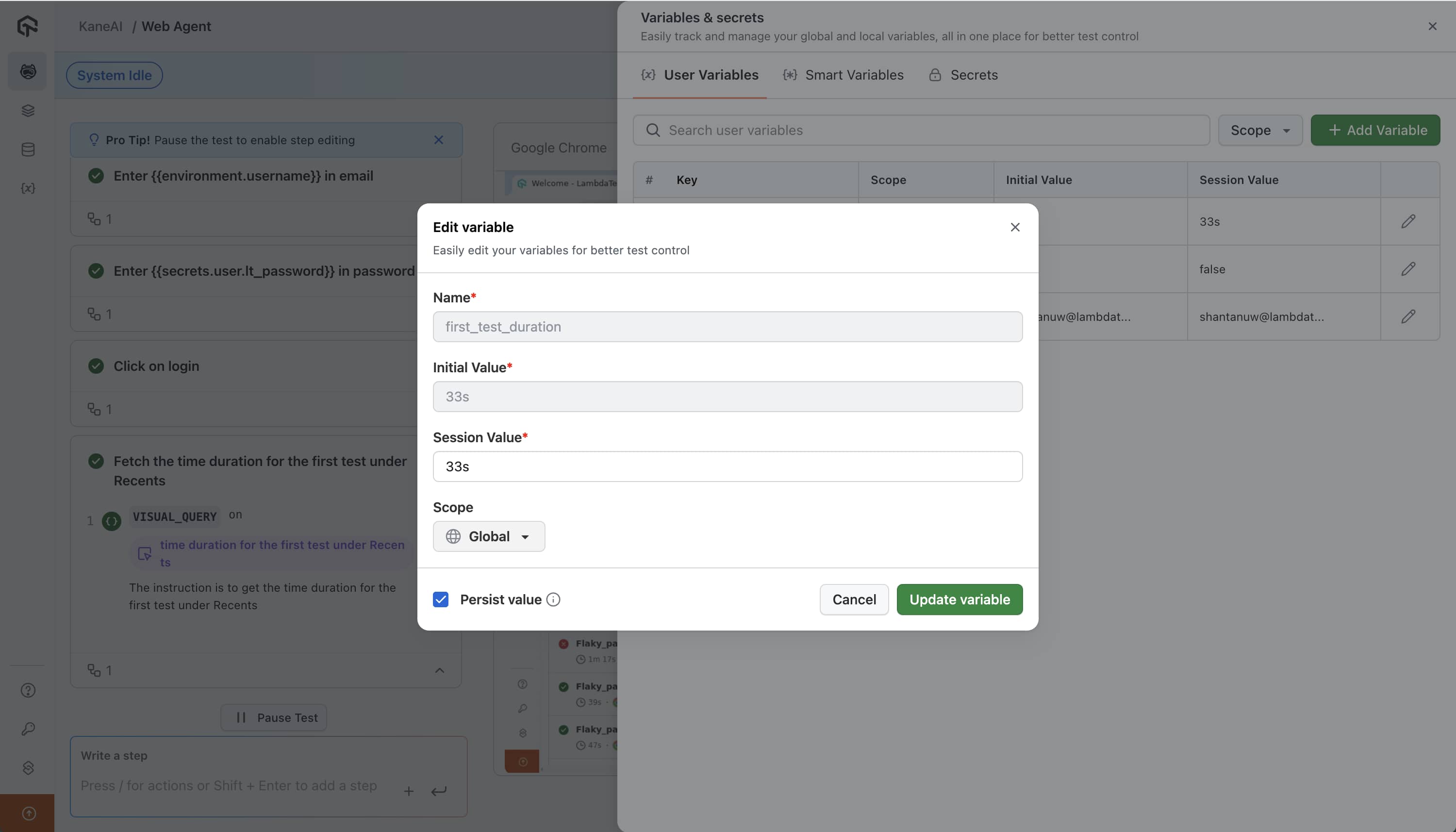
Persist Value in Variables
Persist value check is a mechanism used to ensure that variables retain their values across multiple test executions. This is important for situations where a variable’s value should be preserved between test cases and test executions to ensure consistency. For example, if you fetch a value from the AUT in a test while authoring, you may want to persist it for the other test cases even during test executions.
The persist check option becomes available only when you change a variable's scope from local to global.
Environments
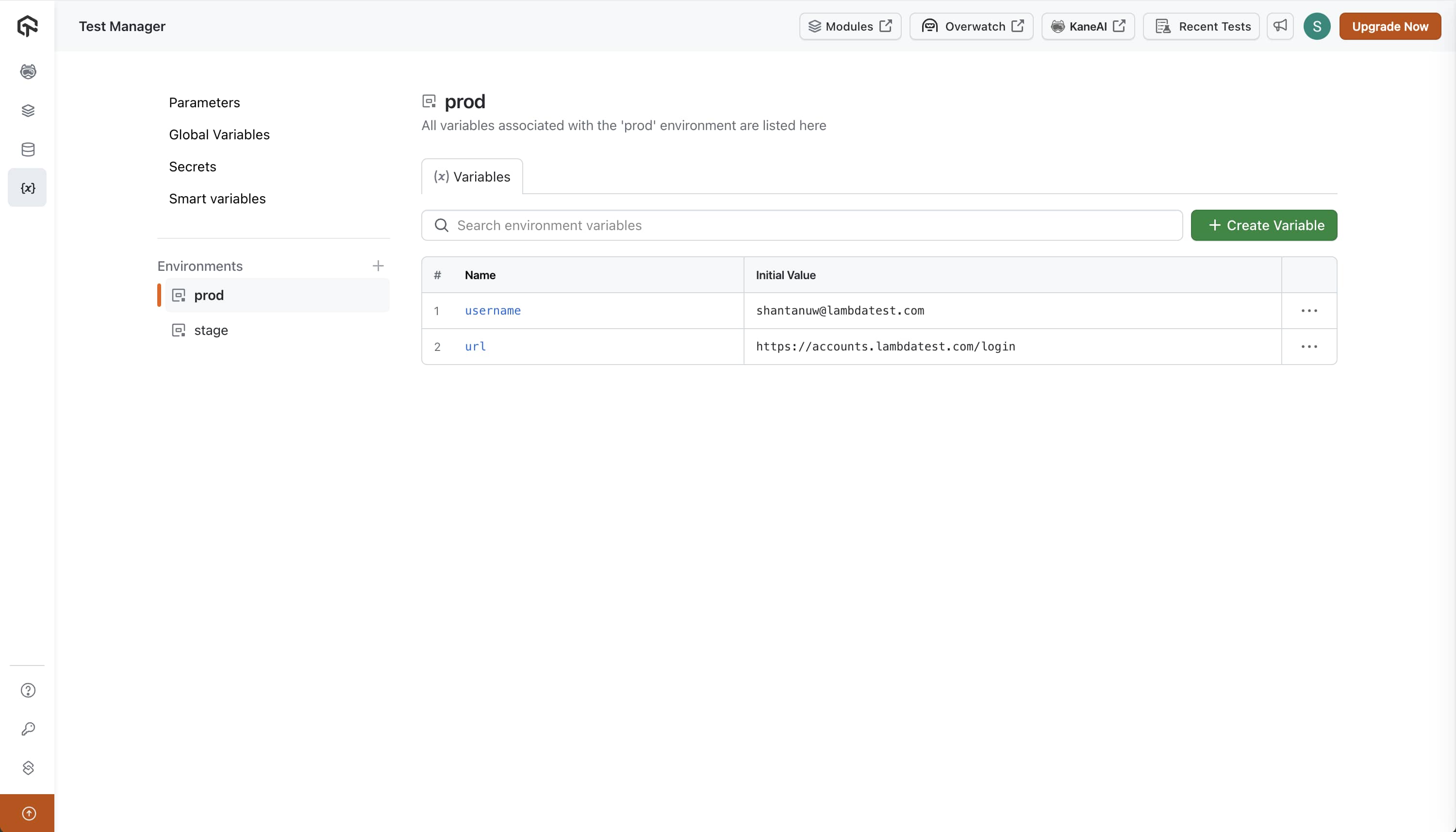
What are Environments?
Environments in KaneAI refer to the different configurations under which the tests are executed. Environments typically represent different stages of deployment (e.g., development, staging, production). Each environment can have its own set of variables tailored to the respective deployment scenario.
How to Use Environments During Test Runs
Once a test case is authored using environment variables, it can then be executed in any environment as long as the variables used in the test case, exist in the requested environment.
Leveraging UI
While executing a test run or scheduling one, you can choose which environment they want to execute a test run on. All the test cases inside a test run can be executed on a single environment only at a point of time.
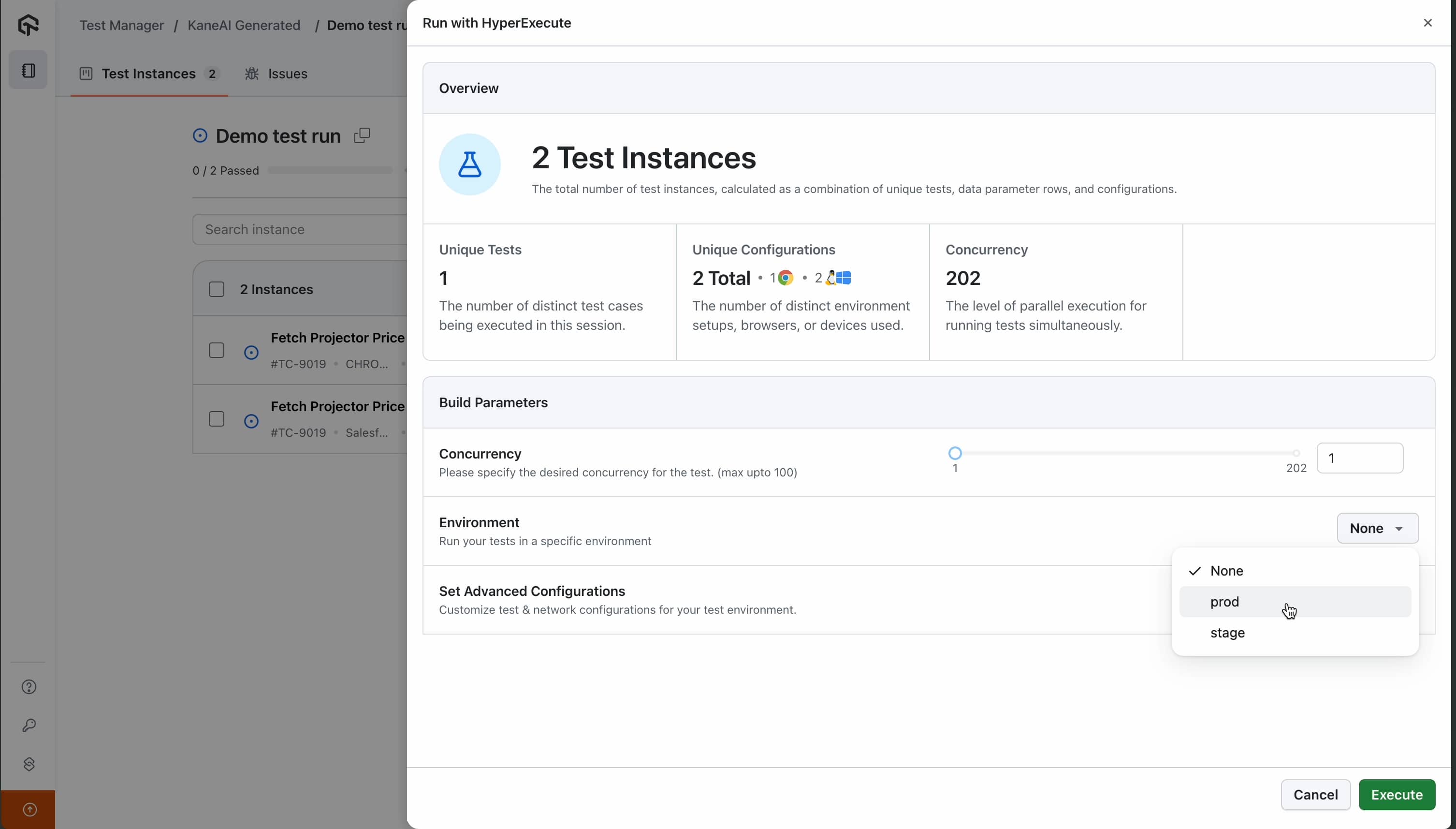
Leveraging API
You can pass environment name programmatically when initiating test runs via the API. This allows you to automate the execution of tests in different environments without manual intervention. For instance,
curl --location 'https://test-manager-api.lambdatest.com/api/atm/v1/hyperexecute' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--header 'Authorization: Basic <Base64Auth>' \
--data '{
"test_run_id": "YOUR_TEST_RUN_ID", #enter test run id
"concurrency": 1,
"environment": "staging" #Optional
This will run the test case in the "staging" environment.
If you have any feedback or suggestions, feel free to reach out at support@lambdatest.com with your comments.
