Playwright Testing With Cucumber.js
Cucumber.js is a JavaScript-based open-source framework for web automation testing. It runs on Node.js and latest web browsers. Cucumber.js allows you to write and execute tests in Gherkin - a non-technical and human-readable language.
LambdaTest enables you to run Playwright tests with Cucumber.js test runner on a browser farm of 40+ real browser and operating system combinations. This guide will outline the fundamentals of getting started with Playwright testing on the LambdaTest platform using the Cucumber.js test runner.
Prerequisites
Note: All the code samples in this documentation can be found in the LambdaTest's Repository on GitHub. You can either download or clone the repository to quickly run your tests.
View on GitHub
-
Clone the LambdaTest-Playwright repository on your system.
-
Install the npm dependencies.
npm install
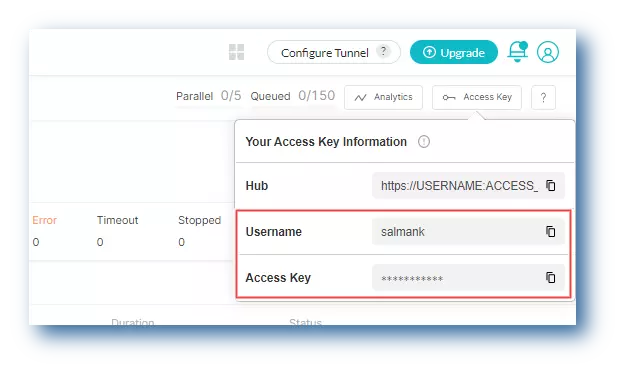
- In order to run your Playwright tests with Playwright test runner, you will need to set your LambdaTest username and access key in the environment variables. Click the Access Key button at the top-right of the Automation Dashboard to access it.
Windows
set LT_USERNAME="YOUR_LAMBDATEST_USERNAME"
set LT_ACCESS_KEY="YOUR_LAMBDATEST_ACCESS_KEY"
macOS/Linux
export LT_USERNAME="YOUR_LAMBDATEST_USERNAME"
export LT_ACCESS_KEY="YOUR_LAMBDATEST_ACCESS_KEY"
Running Playwright Tests With Cucumber.js
In your setup.js file, specify your LambdaTest Username and LambdaTest Access Key, add the browserName, browserVersion, and platform.
const { setWorldConstructor, World, Before, After} = require("@cucumber/cucumber");
const { chromium } = require('playwright')
class CustomWorld extends World{
async setTestStatus(status, remark) {
await page.evaluate(_ => {}, `lambdatest_action: ${JSON.stringify({ action: 'setTestStatus', arguments: { status, remark } })}`)
}
}
Before(async (scenario) => {
const capabilities = {
'browserName': 'Chrome', // Browsers allowed: `Chrome`, `MicrosoftEdge`, `pw-chromium`, `pw-firefox` and `pw-webkit`
'browserVersion': 'latest',
'LT:Options': {
'platform': 'Windows 10',
'build': 'Playwright Sample Build with Cucumber Runner',
'name': scenario.pickle.name,
'user': process.env.LT_USERNAME,
'accessKey': process.env.LT_ACCESS_KEY,
'network': true,
'video': true,
'console': true,
'tunnel': false, // Add tunnel configuration if testing locally hosted webpage
'tunnelName': '' // Optional
}
}
// Create page and browser globals to be used in the scenarios
global.browser = await chromium.connect({
wsEndpoint: `wss://cdp.lambdatest.com/playwright?capabilities=${encodeURIComponent(JSON.stringify(capabilities))}`
})
const context = await global.browser.newContext();
global.page = await context.newPage();
})
After(async () => {
await global.browser.close()
})
setWorldConstructor(CustomWorld);
Pass the below command to run the test.
npm run test
Visit the LambdaTest Automation dashboard to view the results of your executed test with Playwright test runner.
Testing With Cucumber.js When Migrating To LambdaTest
- In your
setup.jsfile, add before and after code block for setting up and closing the remote browsers.
Before(async (scenario) => {
const capabilities = {
'browserName': 'Chrome', // Browsers allowed: `Chrome`, `MicrosoftEdge`, `pw-chromium`, `pw-firefox` and `pw-webkit`
'browserVersion': 'latest',
'LT:Options': {
'platform': 'Windows 10',
'build': 'Playwright Sample Build with Cucumber Runner',
'name': scenario.pickle.name,
'user': process.env.LT_USERNAME,
'accessKey': process.env.LT_ACCESS_KEY,
'network': true,
'video': true,
'console': true,
'tunnel': false, // Add tunnel configuration if testing locally hosted webpage
'tunnelName': '' // Optional
}
}
// Create page and browser globals to be used in the scenarios
global.browser = await chromium.connect({
wsEndpoint: `wss://cdp.lambdatest.com/playwright?capabilities=${encodeURIComponent(JSON.stringify(capabilities))}`
})
const context = await global.browser.newContext();
global.page = await context.newPage();
})
After(async () => {
await global.browser.close()
})
setWorldConstructor(CustomWorld);
- In the class CustomWorld, create a function
setTestStatusthat will mark your test passed or failed on the LambdaTest platform.
class CustomWorld extends World{
async setTestStatus(status, remark) {
await page.evaluate(_ => {}, `lambdatest_action: ${JSON.stringify({ action: 'setTestStatus', arguments: { status, remark } })}`)
}
}
- After any assertions in your script mark the test status as passed as shown below:
try {
assert.equal(title,
"How to use HyperExecute for scalable and reliable web automation testing | LambdaTest",
"Page title does not match");
await this.setTestStatus("passed", "Title matched");
} catch (e) {
await this.setTestStatus("failed", e);
throw(e);
}
- After that, you can run your test.
