HyperExecute Deployment on Amazon Marketplace
One of the biggest challenges developers and testers face is the speed of test execution and the lack of smart test orchestration. But, so far, customers had only two options—depend on traditional cloud-based grids that haven't really innovated to fulfill present demands or build their own in-house infrastructure.
Existing test execution solutions are inherently slow because of lots of network hops that happen during each test, triggered test scenarios are first sent to the automation hub, which in turn are scheduled to run on the best-suited automation node resulting in unnecessary latency. Also, multiple network hops with separated components result in increased test flakiness.
On the other hand, local setups don't have the smart features that can be offered on the cloud. It has always been a trade-off for customers.
HyperExecute by LambdaTest
HyperExecute by LambdaTest is a lightning-quick intelligent end-to-end test execution and orchestration platform that is framework and language-agnostic. It is up to 70% faster than any cloud-based test execution grid. HyperExecute reduces developer friction and interrupts and ultimately helps businesses release features/products quicker.
-
HyperExecute achieves in-house-like performance by merging all the components into a single execution environment, thereby ensuring all the components 'talk' to each other just like they do in a local network.
-
High-performing, highly scalable, and with intelligent features, the platform takes care of executing your tests in the least time possible so that you can focus on crafting your test cases. With smart features such as auto-grouping, auto-retry, and fail-fast mechanisms, HyperExecute takes away all the pain to run tests leaving the developers/testers to focus on other important tasks.
-
Through a simple YAML file, HyperExecute allows one to group and distribute tests intelligently across runner environments. This intelligent test orchestration takes into account past test run data, and automatically reorders the test runs to surface failures faster and thus cuts down developer feedback time.
-
HyperExecute ensures that all test execution data is available on a single platform, thereby allowing teams to truly analyze the quality of their builds through insightful automatic reports generated for each build run.
HyperExecute's other noteworthy features include artifacts management, automatic tunnel management, customizable test environments, dependency caching, etc.
Data Processing and Storing by LambdaTest
LambdaTest processes and stores two categories of data from its Customers while providing LambdaTest Services.
-
LambdaTest Account data: The first category of data is any Personally Identifiable Information (PII) other than 'Test execution data' provided by the Customer during the Services. This includes PII related to employees, users, or customer personnel. We refer to this data as 'LambdaTest Account data.' It may include names, email addresses, and contact numbers.
-
Test execution data: The second category of data is any information, including PII, that is stored, processed, or transmitted via the LambdaTest platform by, or on behalf of, our Customers. We refer to this data as 'Test execution data.'
The Test execution data consists of the data that our Customers upload to our Platform or that our Platform accesses during the testing of applications. It may include reports, tests, networks, browser process logs, other artifacts, authentication information, licensing information, and test execution metadata (e.g., test status, duration, name, browsing sessions, search history), as well as other information that Customers may provide during testing.
In general, 'Test execution data' refers to data that is stored or processed for the delivery of the Services we provide as a data processor. This data may also include backup storage. It is important to note that 'Test execution data' does not necessarily contain any identifiable PII or sensitive data regarding customer personnel, customers, end-users, or other third parties.
Please note that LambdaTest does not collect, nor does it require, any identifiable PII or sensitive data by default for its functioning.
From a privacy perspective, the customer is considered the controller of Test execution data, while LambdaTest acts as a processor. This means that throughout the time a customer subscribes to services with LambdaTest, the Customer retains ownership of and control over the Test execution data in their account.
'Test execution data' encompasses data stored for the delivery of services we provide as a data processor, including data stored for backup purposes.
Data to be Processed by LambdaTest while using the HyperExecute Platform
The following data will be processed by LambdaTest when using the HyperExecute Platform:
-
Selenium test data: This includes selenium logs, Selenium video logs, Selenium test network logs captured from browsers, and selenium process logs. These will be stored on LambdaTest.
-
LambdaTest authentication and Licensing information: Authentication and licensing information related to LambdaTest will be stored on LambdaTest's platform to control the test concurrency.
-
Web browsers and selenium drivers: LambdaTest curates and stores publicly available web browsers and selenium drivers in their public storage. The HyperExecute environment for customers will regularly download these web browsers and selenium drivers from LambdaTest's public storage.
-
Test execution metadata: Metadata related to test execution, such as test status, duration, and name, will be stored on LambdaTest's servers. This data is used to power dashboards for customers, providing insights into test execution.
-
Alerts from HyperExecute services: HyperExecute services running inside the customer's environment may send alerts to LambdaTest in case of failures. These alerts will not contain any critical or sensitive details. The data sent will include information such as error type, service, and time. This data is used to provide prompt technical support to the customer.
-
Software updates: LambdaTest will roll out frequent software updates for the HyperExecute Platform. Customers can apply these updates at their convenience.
-
Customer's critical data: All critical data, including test scripts, terminal logs, and test dependencies, will remain within the customer's environment and will not leave their perimeter. LambdaTest does not process or store this data.
Please note that LambdaTest prioritizes data privacy and security and ensures that sensitive customer data remains protected and within the customer's control.
Data Deletion Process
LambdaTest follows the following data deletion process:
-
All test execution data from the executed virtual machines (VMs) is deleted as soon as the test is completed. This means that each time a test is run, a new clean and sanitized machine is used, and the VM where the test was executed is deleted immediately after the test ends.
-
LambdaTest stores encrypted test execution result data, including logs, videos, and screenshots, that are generated during test runs on LambdaTest's platform. By default, this data is retained for 60 days.
-
Customers have the ability to request the deletion of all data corresponding to a person. This can be done by contacting LambdaTest via email and explicitly requesting the deletion. LambdaTest aims to process such requests within a turnaround time of 48 hours.
LambdaTest prioritizes data privacy and provides mechanisms for data deletion to ensure compliance with data protection regulations and to meet customer requirements.
Deployment with the AWS Marketplace Offer
Prerequisites
Before deploying the CloudFormation template for HyperExecute through the AWS Marketplace, ensure that the following prerequisites are met:
-
Region with min 3 availability zones: Make sure you are running the CloudFormation in a region that supports a minimum of 3 availability zones. The currently supported regions are us-east-1, us-east-2, us-west-2, eu-central-1, ap-south-1, and ap-southeast-2.
-
Elastic IPs (EIPs): HyperExecute requires 3 Elastic IPs for each availability zone (AZ). Ensure that you have sufficient quota for EIPs in your AWS account. You can refer to the EIP Limits to check your quota.
-
EC2 quota limits: The CloudFormation template will create EC2 instances as part of a Managed NodeGroup, with a minimum requirement of 5 nodes, and an Auto Scaling Group with a maximum size based on your concurrency license. Make sure to increase your EC2 quota limits accordingly.
Steps to Deploy
To deploy the CloudFormation template on AWS, follow these steps:
Step 1: Download the CloudFormation template named hyperexecute_deployment.yaml from the AWS Marketplace.
Step 2: Navigate to the AWS CloudFormation console and choose Create Stack .
Step 3: On the Create Stack page, select the option Template is ready and click on the Upload a template file" option.
Step 4: Browse for the main template file hyperexecute_deployment.yaml and click Next.
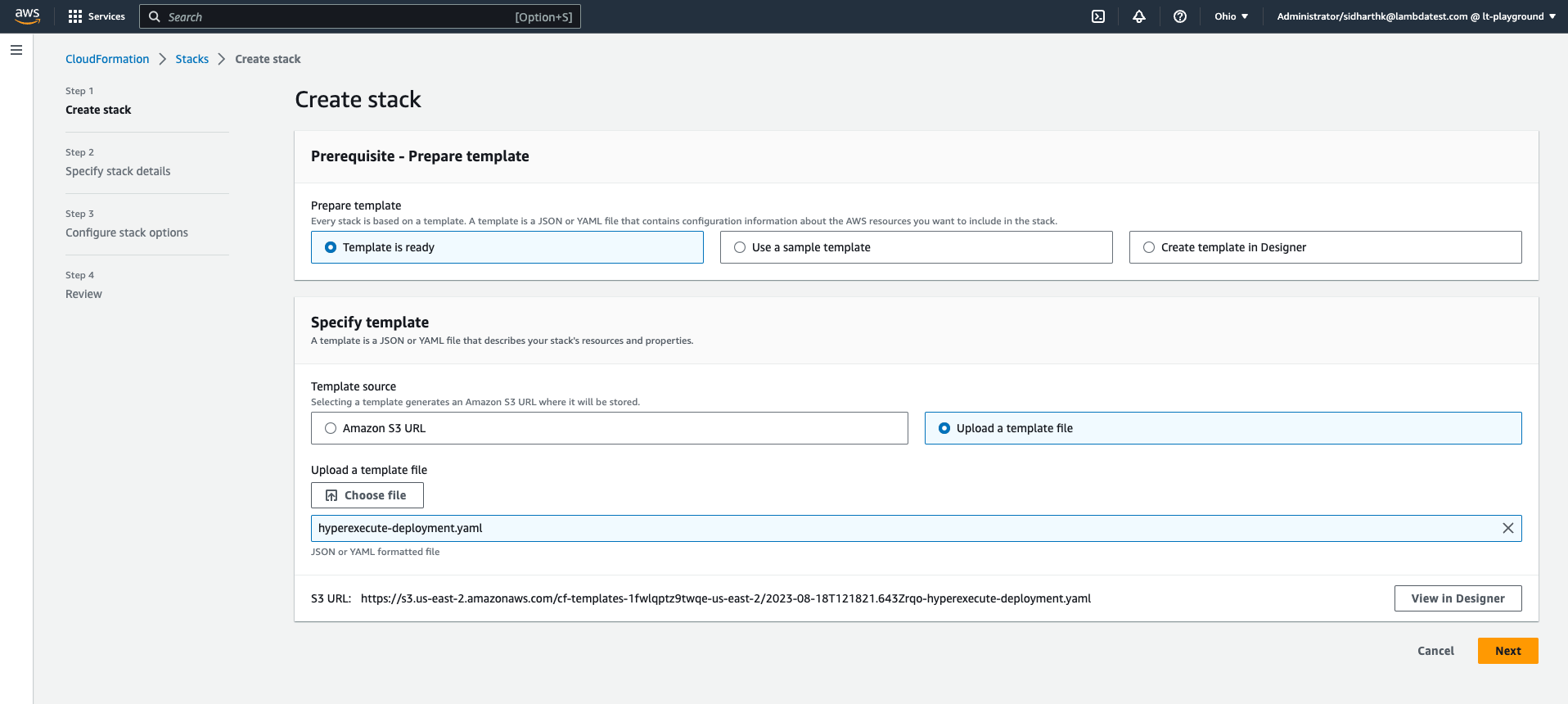
Step 5: On the Specify Stack details page, provide a name for the stack (deployment) and provide the necessary configuration details. Refer to the configuration parameters details sections for guidance.
Step 6: On the next page, under the Configure stack option, change the Stack failure options to preserve the successfully provisioned resources. This helps in preserving the created resources and troubleshooting issues in case of a stack failure.
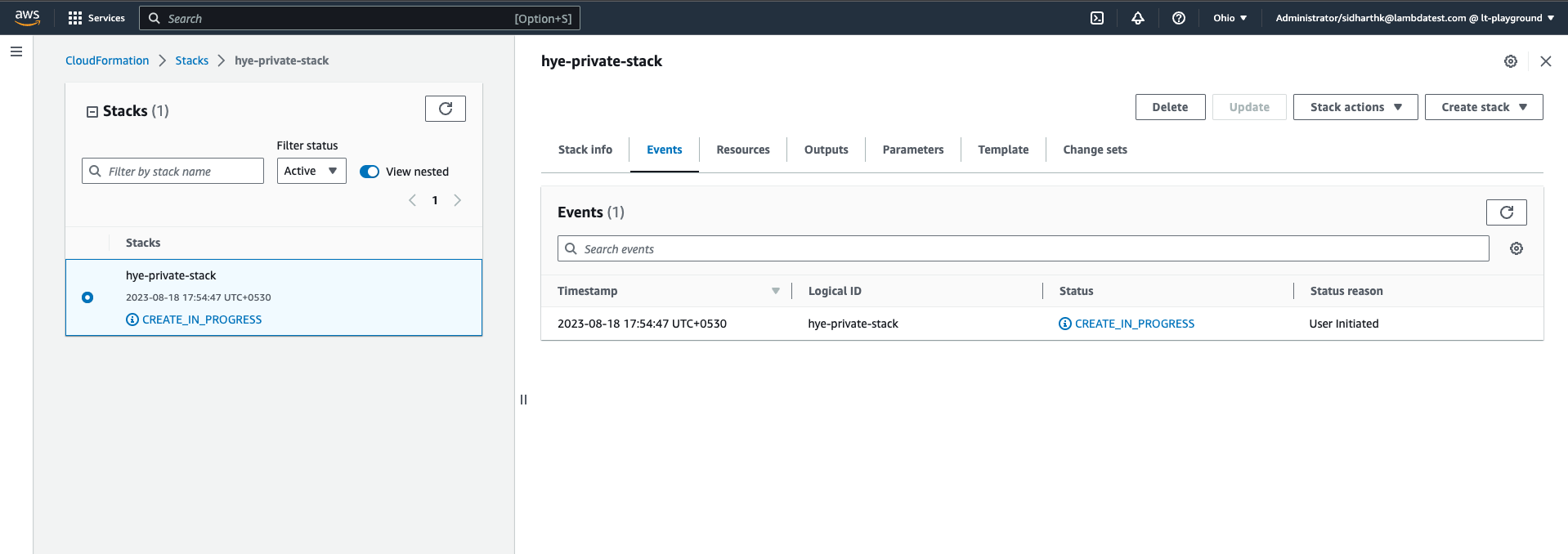
Step 7: Click Next to review all the details, and then initiate the launch to deploy the HyperExecute CloudFormation stack.
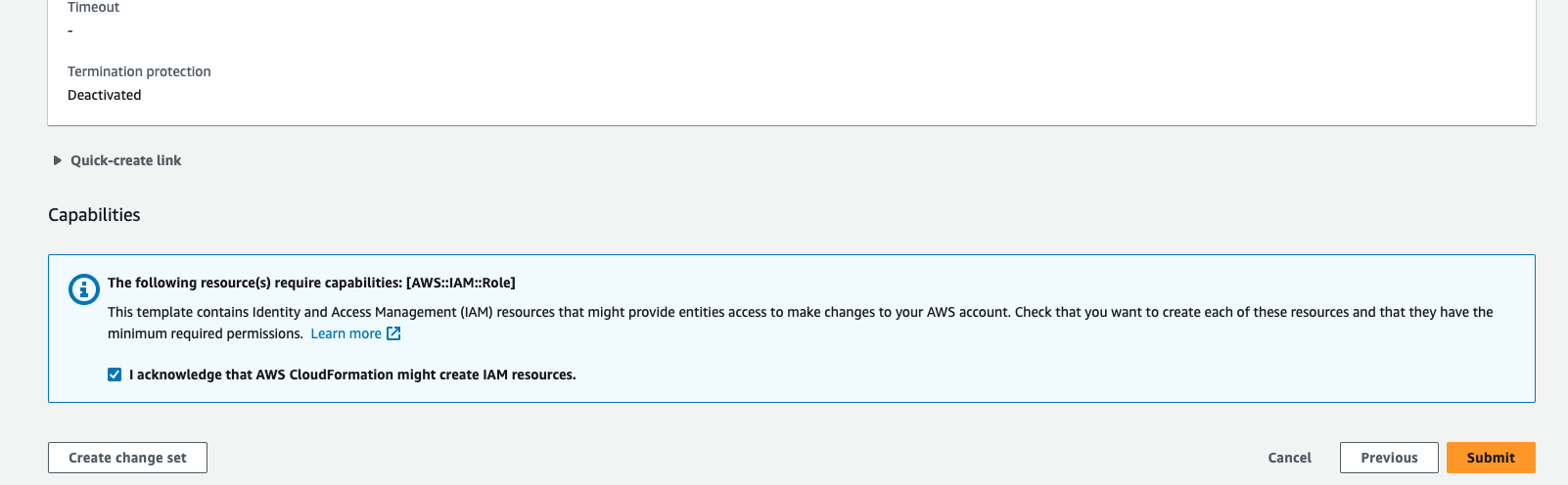
By following these steps, you can deploy the HyperExecute CloudFormation template from the AWS Marketplace and set up the required infrastructure for your testing needs.
Configuration Parameters
Please provide the following configuration details based on the type of installation you want to perform:
User Details
In the User Details section, provide the following details as required:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| EmailID | Your valid email ID to set up a LambdaTest account. If you already have a LambdaTest Account, you can specify that email ID. |
| ManagedAppName | Provide a unique ManagedAppName to be used for the application environment in the cluster. It must be between 5 to 20 characters long and can only contain lowercase letters. |
VPC Configuration
In the VPC Configuration, provide the following details as required:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| VpcCidr | The VPC CIDR block. Must be a valid IP CIDR range of the form x.x.x.x/x. Default Value: 10.10.0.0/16 |
| AvailabilityZones | List of Availability Zones to use for the subnets in the VPC. You must select three Availability Zones in the specified order. |
EKS Configuration
In the EKS Configuration, provide the following details as required:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| ManagedNodeGroupInstanceType | Specify the instance types for a node group. Default Value: m5.xlarge |
| SpotNodes | Enable Spot Nodes for the EKS cluster. Default Value: No |
| IngressLBType | Type of Ingress Load Balancer to create for the EKS Cluster. Private Load Balancer will only be accessible within the VPC. |
VMS Autoscaling Group
In the VMS Autoscaling Group, provide the following details as required:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| VMInstanceType | Specify the instance types for an EC2 Auto Scaling Group. |
| SpotVMs | Enable Spot EC2 instances for the Auto Scaling Group. Default Value: No |
| KeyPairName | Name of an existing EC2 key pair for SSH access to the instances in the Auto Scaling Group. |
Other Configuration
In the Other Configuration, provide the following details as required:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| RedisClusterNodeType | The ElasticCache node type. Default value: cache.t3.small |
| DebugMode | Enable debug mode for your environment to run preview images in your EKS cluster. Default Value: No |
| WindowsJumpHost | Enable a Windows jump host for accessing your Windows machines in your Auto Scaling Group. Default Value: No |
Accessing HyperExecute after deployment
Once the CloudFormation template is successfully deployed, you can access HyperExecute and perform the following steps:
Step 1: Login into the EC2 instance named "HyperExecute-Admin-Bastion" using either SSM (Session Manager) or the SSH key provided in the Configuration Parameters. Note that SSH access is allowed by default within the VPC.
Step 2: Log in to the AWS environment and access the Kubernetes cluster by running the following command on AWS CLI:
aws eks --region <region_name> update-kubeconfig --name <cluster_name>
Replace <region_name> with the appropriate region and <cluster_name> with the name of your cluster.
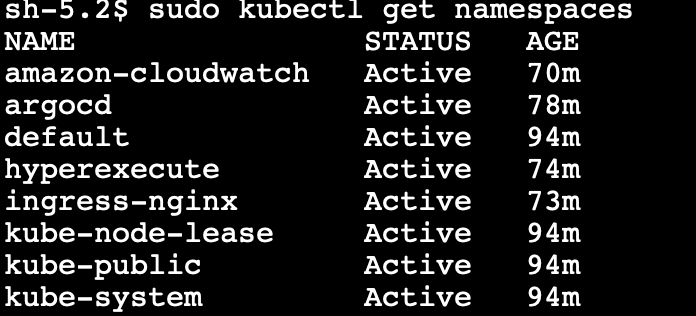
Step 3: Execute the command:
kubectl get namespaces
This command will provide a list of namespaces created.
Step 4: Execute the command:
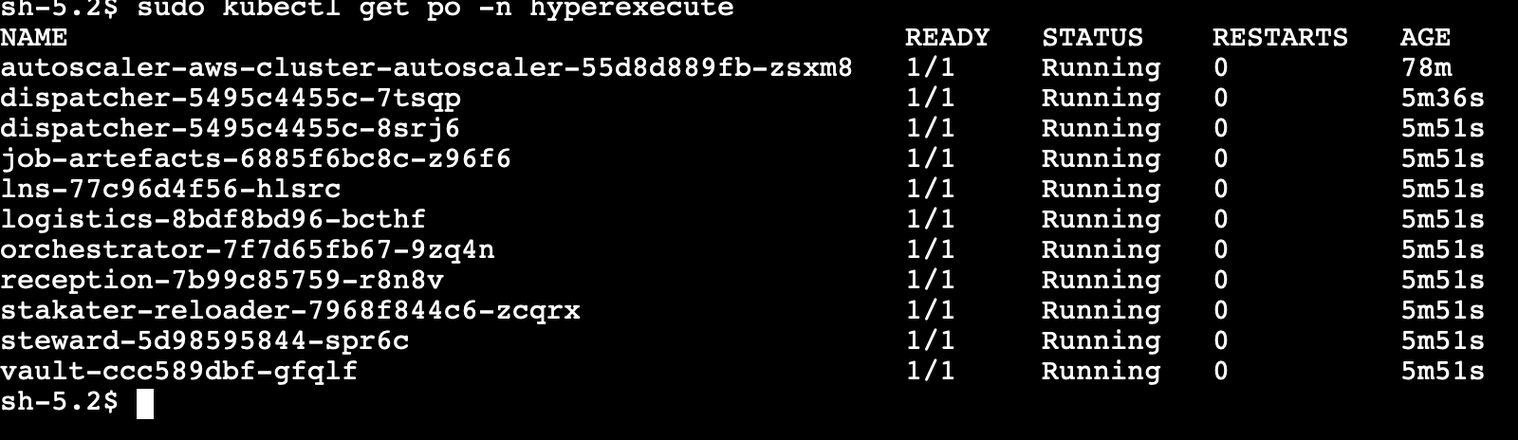
kubectl get po -n hyperexecute
This command will provide a list of pods created under the hyperexecute namespace.
Step 5: Access the Private Cloud deployment using the provided link.
Step 6: If the emailID you used to setup this deployment is not an existing user on LambdaTest then check your Email, there should be a email titled Create Password - LambdaTest, generate a new password using the link provided in the email.
Step 7: Login using your email and password and run jobs using the HyperExecute CLI. For further details about HyperExecute, refer to the documentation.
Cleanup the environment
If you wish to clean up the resources created during the deployment, follow these steps:
-
Ensure that the objects inside the S3 bucket created by the CloudFormation template with the name
${AWS::StackName}-${AWS::AccountId}-hyperexecute-bucketare deleted before the bucket can be deleted. -
Delete the images in the ECR (Elastic Container Registry) repository with the name
${ManagedAppName}-hyperexecute-private-cloudbefore deleting the repository. -
Delete the root stack from CloudFormation. This will delete all the nested stacks and their resources.
-
CloudWatch log groups are not deleted by default. Manually navigate to CloudWatch and delete the log groups starting with the following regex patterns:
/aws/lambda/*-ClusterCreatorFunction-*/aws/lambda/*-ClusterOIDCURLFunction-*/aws/lambda/*-HyePrivateCloudFunction-*/aws/containerinsights/${ManagedAppName}-hyperexecute-eks-cluster/*
-
If you have used the secrets feature in HyperExecute, the secrets with the regex pattern
hyperexecute-secrets-*will not be deleted. Manually navigate to AWS Secret Manager and delete the secrets.
Make sure to follow these cleanup steps to remove the resources associated with the HyperExecute deployment.
