Advanced LambdaTest Tunnel Features
LambdaTest Tunnel feature allows you to test your private server URLs or locally hosted web-apps or websites on 3000+ real browsers through LambdaTest. However, sometimes corporate firewalls and proxy settings may have restricted you to leverage the LambdaTest Tunnel binary. Not anymore though, as we’ve come up with a new binary for LambdaTest Tunnel. LambdaTest Tunnel follows various protocols such as Web Socket, HTTPS, SSH(Secure Shell) etc. to help you establish a secure and unique tunnel connection between your system and LambdaTest cloud servers.
You can download the LambdaTest Tunnel binary that will help you establish a secure connection through corporate firewalls between your computer and LambdaTest cloud servers for a testing locally hosted website or web-applications. You can test plain HTML, CSS, PHP, Python or other similar web files saved on your local system, over combinations of operating systems, browsers, and screen resolutions that are available on LambdaTest.
| Download Links |
|---|
| Windows |
| macOS |
| Linux |
| FreeBSD |
Executing LambdaTest Tunnel for Client Connection
After you download the zip file for your operating system, extract it in a folder and open you command line there. Once you have your terminal routed to the correct directory where the LambdaTest Tunnel binary file is placed, you need to execute the below command.
LT --user {Your Registered Email ID} --key {Your LambdaTest Access Key} --tunnelName {any random string}
So for example, if your details are as below:
| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| example@lambdatest.com | |
| LambdaTest Access Key | 123asd123 |
| Tunnel Name | SampleTunnel |
Then your command would be:
LT --user example@lambdatest.com --key 123asd123 --tunnelName SampleTunnel
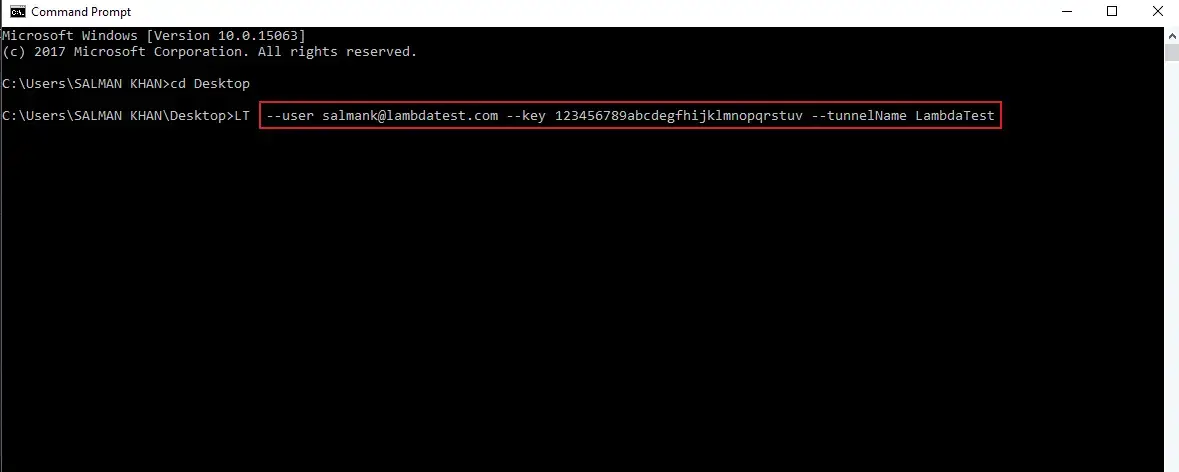
Once you execute the command, you will successfully establish a client connection using the LambdaTest Tunnel. You will find the command logs to state, that you are now ready to test.
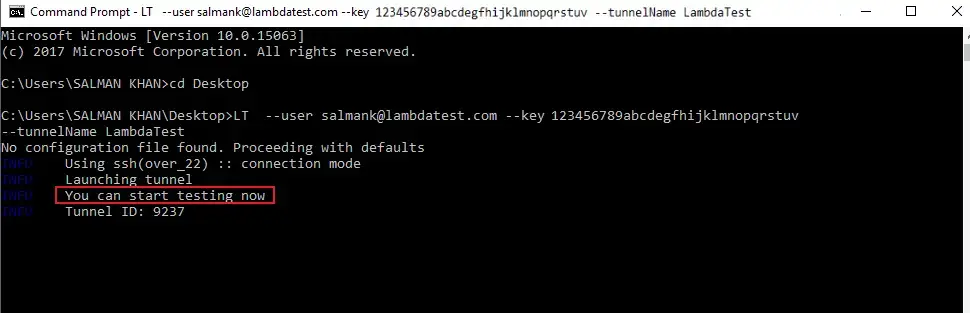
What Makes The New LambdaTest Tunnel Binary Special?
Well, other than the fact that you can now establish a connection through your corporate firewalls with the new LambdaTest Tunnel binary. Here are a couple things to top it off -
Auto Update Functionality
Earlier, for every version update in out LambdaTest Tunnel, you were compelled to download the latest binary from our platform and over write it over the outdated version in your computer. Well, now this new binary will take care of that. Every time you execute this binary, it will check for the latest version available and will update itself automatically, in case it gets outdated.
Default Port 443
Now, by default, everything will run over the port 443 to ensure a secure web browser communication through http protocol over TLS/SSL.
Leverage .lt.yaml file
With this new LambdaTest Tunnel binary, you can declare your LambdaTest authentication credentials in a YAML file configuration and keep it in the same directory as the LT binary file. That way, you won’t have to pass the environment variables in the cmd every time you wish to configure the LambdaTest Tunnel. Once you specify these variables in the .lt.yaml file, you will just have to execute the binary file through cmd LT.exe and the YAML file will automatically configure a secure LambdaTest Tunnel connection by auto detecting the variables specified in the YAML file.
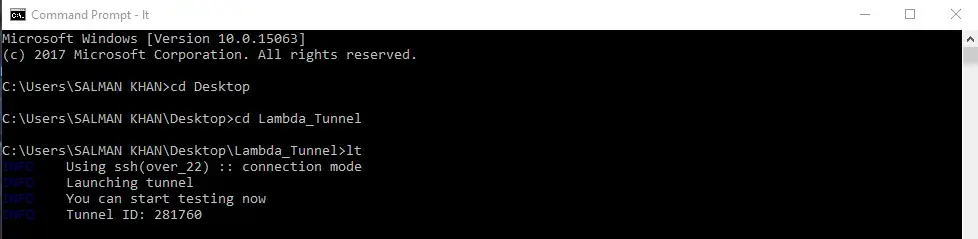
Here is an example of the .lt.yaml file.
User: salmank
Key: 123456789abcdefghijklmnopqrstuv
TunnelName: LambdaTest
Note: You will need to replace this file with your credentials and it has to be named exactly "
.lt.yaml". Once you specify the proxy information as environment variable, it gets auto detected.
Similarly, you can go ahead and pass any other variables by just specifying them in the YAML file. For example, if you wish to have verbose variable passed on for detailed logs while the binary is being configured. You will add the verbose flag in your YAML file:
User: salmank
Key: 123456789abcdefghijklmnopqrstuv
TunnelName: LambdaTest
Verbose: True
Now, when you trigger the binary file through cmd. You will have your verbose logs populated automatically, without you having to specify the variable every time.
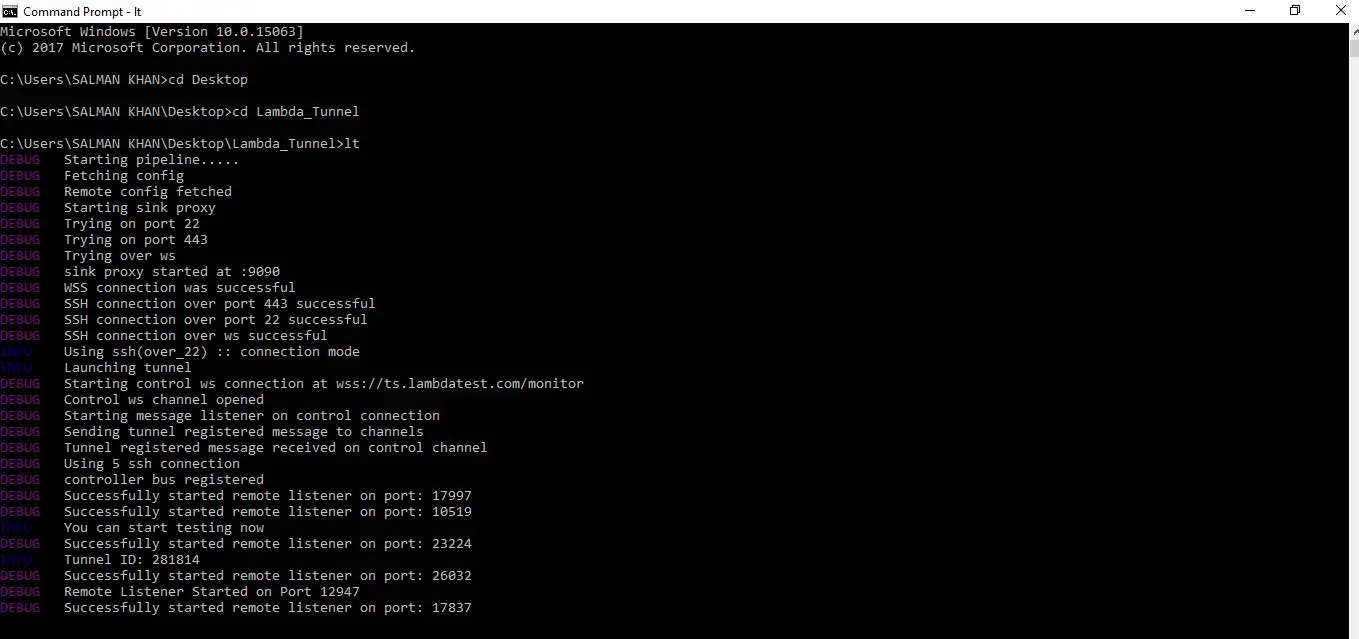
Local Testing By MITM (Man-In-The-Middle)
The MITM(Man-in-the-middle) mode enables you to test websites using self-signed certificates on your local system or internal network. It happens very often that you may try to test a website on the localhost which may not have valid SSL certificates before the website is made live. In such cases, you may receive the below error.
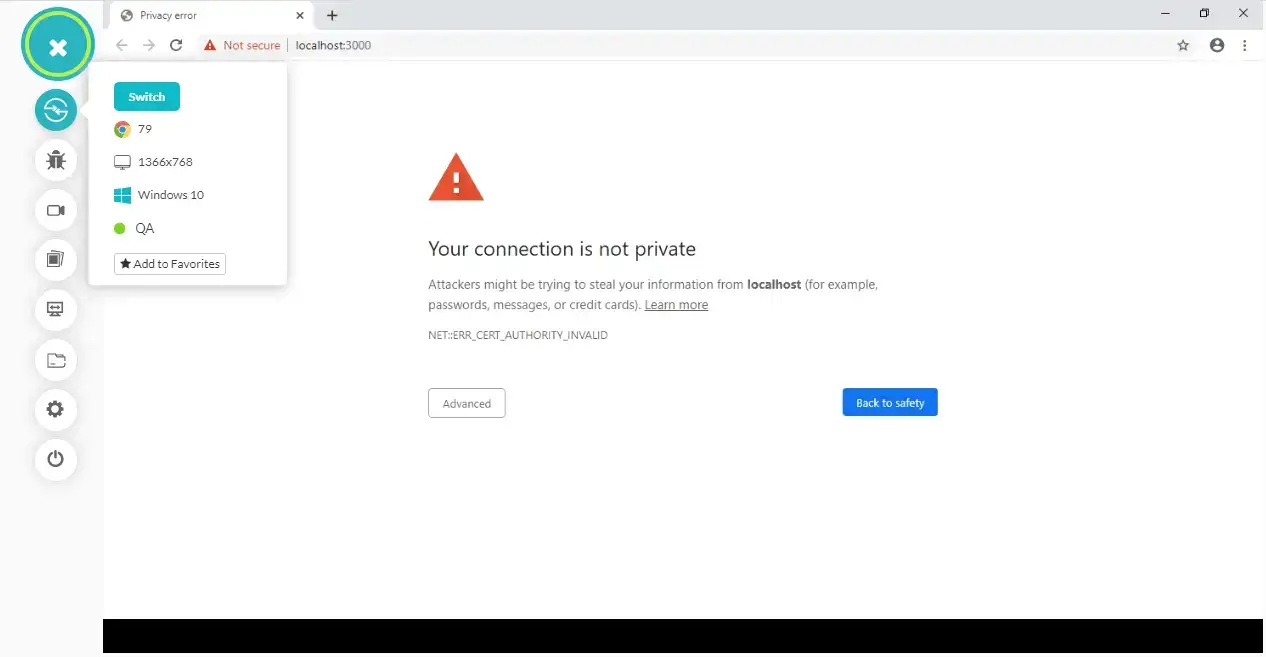
You can test such websites by leveraging the MITM mode. The command will look like this:
LT --user salmank@lambdatest.com --key 123456789abcdefghijklmnopqrstuv --tunnelName LambdaTest --mitm
Here is a screenshot of the same website that was throwing an error earlier but can now be tested by running the MITM mode.
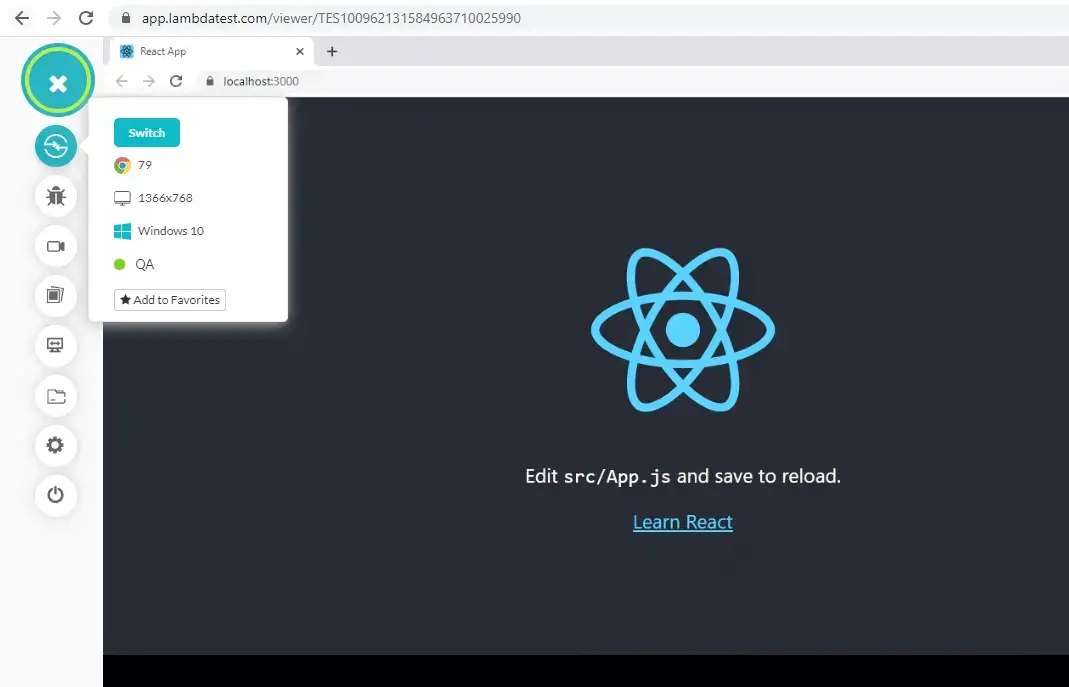
Using The Tunnel InfoAPIs
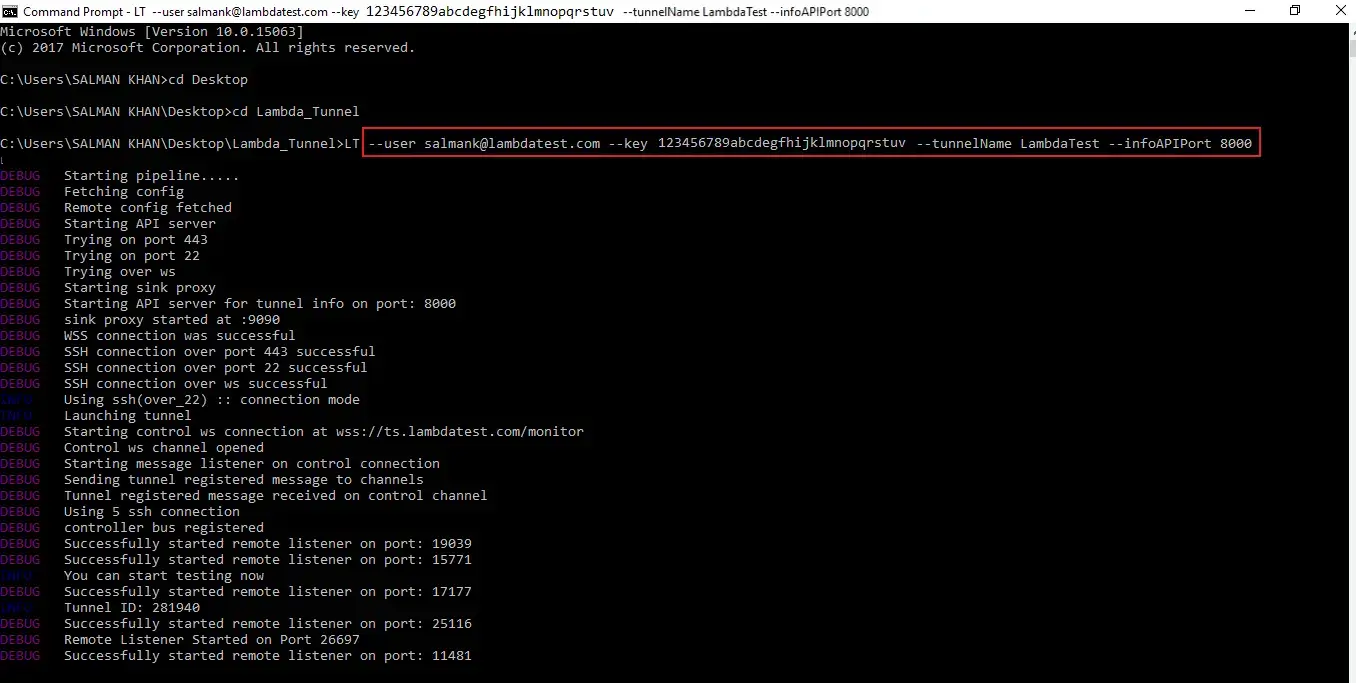
By using the tunnel Info APIs, you can fetch the current status of the tunnel and can use it to stop the tunnel. You can fetch the current tunnel status using the Info API on the tunnel. Suppose the InfoAPI is available on the host over port 8000, then use the below command to infuse the InfoAPI in the tunnel.
LT --user salmank@lambdatest.com --key 123456789abcdefghijklmnopqrstuv --tunnelName LambdaTest --infoAPIPort 8000
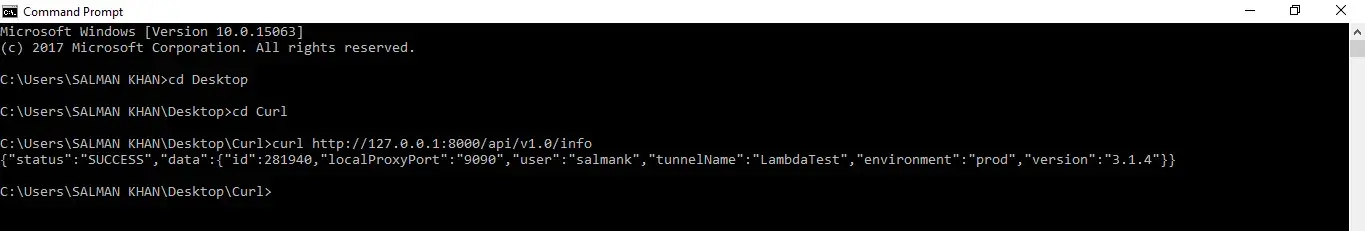
In order to fetch the current tunnel status, execute the below command:
curl http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/v1.0/info
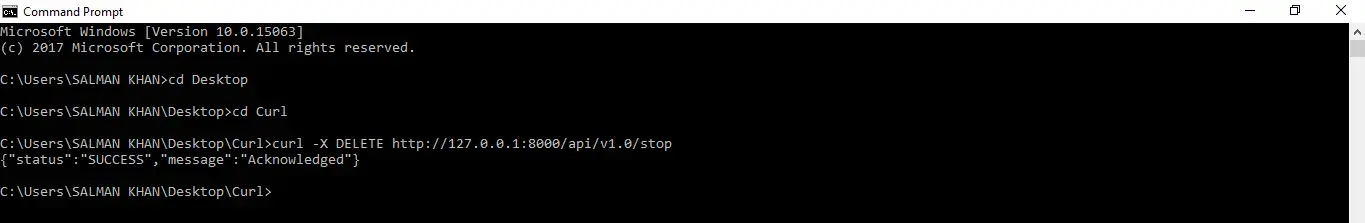
To stop the current tunnel, execute the below command:
curl -X DELETE http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/v1.0/stop
Tunnel Logs
The --log-level flag in the LambdaTest CLI is used to specify the desired log level for tunnel logs. This feature enables users to control the verbosity of logs generated during tunnel operations, making it easier to debug or monitor activities as needed.
--log-level YOUR_LOG_LEVEL
Supported Log Levels:
- info : Provides informational messages about the general operation of the tunnel.
- warn : Highlights potential issues that might not immediately affect functionality but require attention.
- debug : Outputs detailed logs, including diagnostic information, for troubleshooting purposes.
- error : Displays error messages when something goes wrong in the tunnel operation.
- fatal : Shows critical issues that cause the tunnel to terminate unexpectedly.
AllowHost In Tunnel
With the latest tunnel binary release we have introduced the capability to provide the domains which will be resolved from tunnel binary and the rest of the urls will be resolved from our servers. This can speed up the execution of test as the latency will be reduced by transferring data from the tunnel client. You may also use this to restrict the traffic flowing from user’s network.
Usage:
–allowHosts <comma_separated_domains>
LT --user <username> --key <accessKey> –allowHosts google.com,apple.com,amazon.com
Explanation: When this flag is used only requests for provided domains will be routed via tunnel and resolved from the user's network. Requests for domains other than mentioned will be resolved from Lambdatest’s network.
Tunnel Arguments
You can find all the arguments for LambdaTest Tunnel by running the below command in your command line:
LT --help
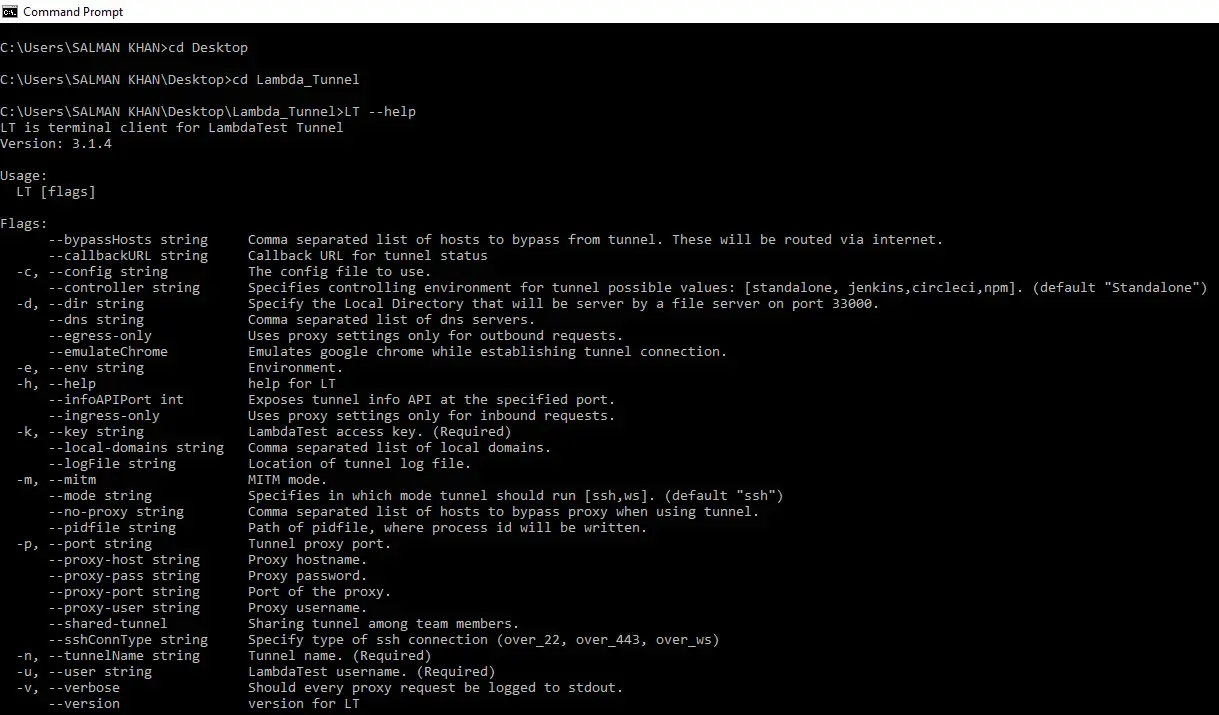
Note: For all modifiers/arguments, refer to the list of LambdaTest Tunnel Modifiers.
That was all you need to know for configuring a client connection through LambdaTest Tunnel. In case you have any questions, feel free to share them with us through our 24/7 chat support or drop us an email to support@lambdatest.com. Happy testing! 🙂
