Auto Split Strategy
The Smart Auto Split Strategy enables you to distribute tests across multiple virtual machines efficiently. This strategy ensures optimal utilization of concurrency by allowing you to split tests based on various levels, such as files, modules, and scenarios.
Key Benefits of Auto Split Strategy
- Efficient distribution of tests across nodes.
- Fine-grained control over test distribution.
- Maximization of concurrency for faster results.
Without HyperExecute Auto Split
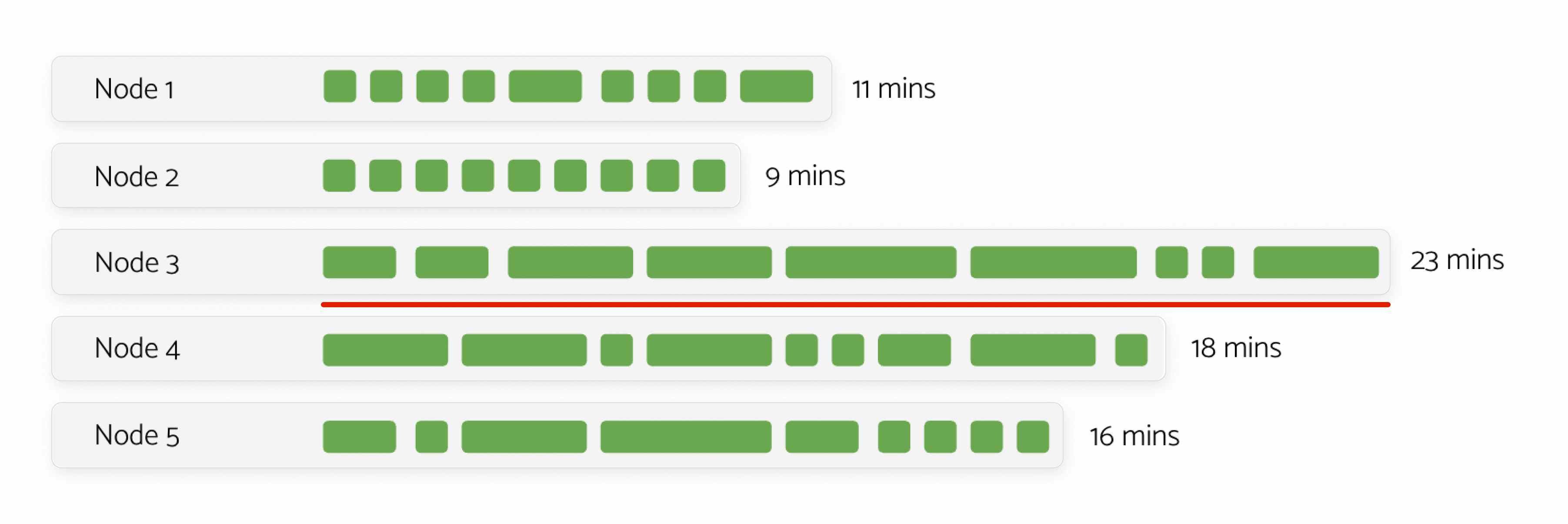
With HyperExecute Auto Split

HyperExecute provides flexibility to distribute tests at file level, scenario level, module level, and practically anything, provided you have a way to list down all the possible values of the entity that has to be distributed.
Enabling Auto-Test Splitting
For enabling auto-test splitting, set the autosplit key to true in the HyperExecute YAML file.
autosplit: true
Along with that, you need to provide testDiscovery and testRunnerCommand parameters as well.
Configuration Parameters
1. testDiscovery Parameter
- It is used to list down all the values to be distributed. HyperExecute will execute the testDiscovery command verbatim and expects distinct values to be on separate lines. It can be as simple as a list of files on different lines.
- This can be used later to split tests over files, modules, or any level supported by your language and framework.
- It is used for locating/discovering the tests that are a part of the project. You can use the combination of grep, awk, sed, or any valid command to locate the tests that you intend to run.
- For NodeJS, usually at file level, for Python at class level, in Java at class and module level. For Cucumber based frameworks at scenario level or feature level or at tag level.
2. testRunnerCommand Parameter
It is used to run a single item from the testDiscovery. You need to add $test in the testRunnerCommand for interpolating one of the values from the testDiscovery.
It tells the system how to run a single test entity in isolation. This entity could be a file, module, feature or scenario. Test runner command will run over each of the values extracted from the testDiscovery command.
Sample Commands
A few samples are given below:
# The following command (or value) when assigned to testDiscoverer key searches for the scenarios by matching the string Scenario [or Scenario Outline] in the .feature files located in the *src* directory of the project.
testDiscovery:
type: raw
mode: dynamic
command: grep -nri 'Scenario:\^|Scenario Outline:' src -ir --include=\*.feature | awk '{print $1}' | sed 's/\.\///g' | sed 's/\(.*\):/\1 /'
testDiscovery:
type: raw
mode: dynamic
command: grep 'class name' testng.xml | awk '{print$2}' | sed 's/name=//g' | sed 's/\x3e//g'
Concurrency Control
The concurrency key indicates the total number of concurrent sessions that can run in parallel. With both of these commands (testDiscovery and testRunnerCommand), HyperExecute intelligently distributes tests over multiple virtual machines as specified by the concurrency directive in the YAML file. Autosplit mode provides fine grain control over the test distribution.
For example, assume that the total number of test scenarios [discovered via testDiscovery] are 27 and concurrency is set to 7. In this case, HyperExecute would allocate 7 nodes for running the 27 tests in parallel.
concurrency: 7
The Test Execution Tasks [1..7] run in parallel whereas tests within each Task, run in a serial manner. Considering the above test scenario, this is how the tests would be executed on HyperExecute:
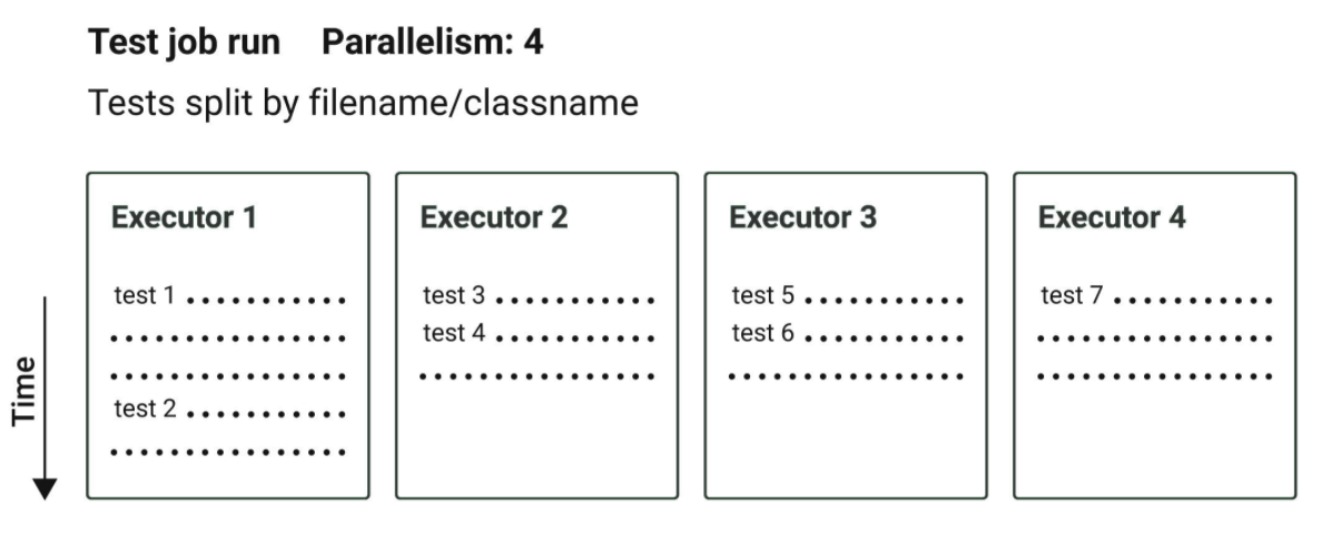
- Test Executor - 1: 4 tests (running in a sequence)
- Test Executor - 2: 4 tests (running in a sequence)
- Test Executor - 3: 4 tests (running in a sequence)
- Test Executor - 4: 4 tests (running in a sequence)
- Test Executor - 5: 4 tests (running in a sequence)
- Test Executor - 6: 4 tests (running in a sequence)
- Test Executor - 7: 3 tests (running in a sequence)