Perform Headless Browser Testing On Cloud Selenium Grid
Performing automated tests on the Headless browsers can be challenging as it does not contain any UI. LambdaTest now allows you to perform Headless browser testing easily on its cloud-based Selenium Grid. In this document, you will learn how to enable and perform Headless browser testing on the LambdaTest platform.
Enabling The Headless Browser Testing On LambdaTest
For Headless browser testing on LambdaTest, you need to enable the desired capability of Headless browsing – ‘headless’. You can enable this capability using any one of the two methods mentioned below:
Enable Headless Browser Testing On Desired Capabilities Generator
Visit the Desired Capabilities Generator. Under the Browser Specific Capabilities, you can find a toggle button to enable Headless browsing. Just switch the button to true.
Enable Headless Browser Testing Via Code
While writing the desired capabilities in your code, you can enable Headless browser testing, by adding the below syntax:
capabilities.setCapability("headless",true);
Below is the complete code for a sample desired capabilities in various languages:
Java
DesiredCapabilities capabilities = new DesiredCapabilities();
capabilities.setCapability("browser", "Chrome");
capabilities.setCapability("version", "86");
capabilities.setCapability("platform", "MacOS Catalina");
capabilities.setCapability("build", "your build name");
capabilities.setCapability("name", "your test name");
// Capability setting to enable Headless browser testing
caps.setCapability("headless",true);
C#
DesiredCapabilities capabilities = new DesiredCapabilities();
capabilities.SetCapability("user","username")
capabilities.SetCapability("accessKey","access_key")
capabilities.SetCapability("build", "your build name");
capabilities.SetCapability("name", "your test name");
capabilities.SetCapability("platform", "MacOS Catalina");
capabilities.SetCapability("browserName", "Chrome");
capabilities.SetCapability("version","86.0");
// Capability setting to enable Headless browser testing
capabilities.setCapability("headless",true);
PHP
$capabilities = array(
"build" => "your build name",
"name" => "your test name",
"platform" => "MacOS Catalina",
"browserName" => "Chrome",
"version" => "86.0",
"headless" => true
)
Ruby
capabilities = Selenium::WebDriver::Remote::Capabilities.new
capabilities["build"] = "your build name"
capabilities["name"] = "your test name"
capabilities["platform"] = "MacOS Catalina"
capabilities["browserName"] = "Chrome"
capabilities["version"] = "86.0",
capabilities["headless"] = true
JavaScript
var capabilities = {
"build" : "your build name",
"name" : "your test name",
"platform" : "MacOS Catalina",
"browserName" : "Chrome",
"version" : "86.0",
"headless" : true
}
Python
capabilities = {
"build" : "your build name",
"name" : "your test name",
"platform" : "MacOS Catalina",
"browserName" : "Chrome",
"version" : "86.0",
"headless" : True
}
Perform Headless Browser Testing on LambdaTest
Below is a example to perform Headless browser testing. For demo purpose, we have used TestNG framework of Java language.
package com.lambdatest;
import java.net.MalformedURLException;
import java.net.URL;
import org.openqa.selenium.By;
import org.openqa.selenium.remote.DesiredCapabilities;
import org.openqa.selenium.remote.RemoteWebDriver;
import org.testng.Assert;
import org.testng.annotations.AfterSuite;
import org.testng.annotations.BeforeSuite;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
public class HeadlessAutomation {
private static RemoteWebDriver driver;
private static String Status="failed";
@BeforeSuite
public void setup() throws MalformedURLException {
try {
String username = System.getenv("LT_USERNAME");
String authkey = System.getenv("LT_ACCESS_KEY");
String hub = "@hub.lambdatest.com/wd/hub";
DesiredCapabilities caps = new DesiredCapabilities();
caps.setCapability("browser", "Chrome");
caps.setCapability("version", "86");
caps.setCapability("platform", "MacOS Catalina");
caps.setCapability("build", "Headless Automation");
caps.setCapability("name", "Headless Automation");
caps.setCapability("network", true);
caps.setCapability("visual", true);
caps.setCapability("video", true);
caps.setCapability("console", true);
// Capability setting to enable Headless browsing
caps.setCapability("headless",true);
System.out.println("Desired Caps: " + caps);
driver = new RemoteWebDriver(new URL("https://" + username + ":" + authkey + hub), caps);
}
catch(Exception e)
{
System.out.println(e);
}
}
@Test
public static void testAssertion() {
try {
driver.get("https://opensource-demo.orangehrmlive.com/"); //define the url
String pageTitle = driver.getTitle(); //get the title of the webpage
System.out.println("The title of this page is ===> " +pageTitle);
Assert.assertEquals("OrangeHRM", pageTitle); //verify the title of the webpage
driver.findElement(By.id("txtUsername")).clear();//clear the input field before entering any value
driver.findElement(By.id("txtUsername")).sendKeys("Admin");//enter the value of username
driver.findElement(By.id("txtPassword")).clear();
driver.findElement(By.id("txtPassword")).sendKeys("admin123");//enter the value of password
driver.findElement(By.id("btnLogin")).click(); //click Login button
System.out.println("Successfully logged in");
Status = "passed";
}
catch(Exception e)
{
Status = "failed";
}
}
@AfterSuite
public void tearDown() {
driver.executeScript("lambda-status=" + Status);
driver.quit();
}
}
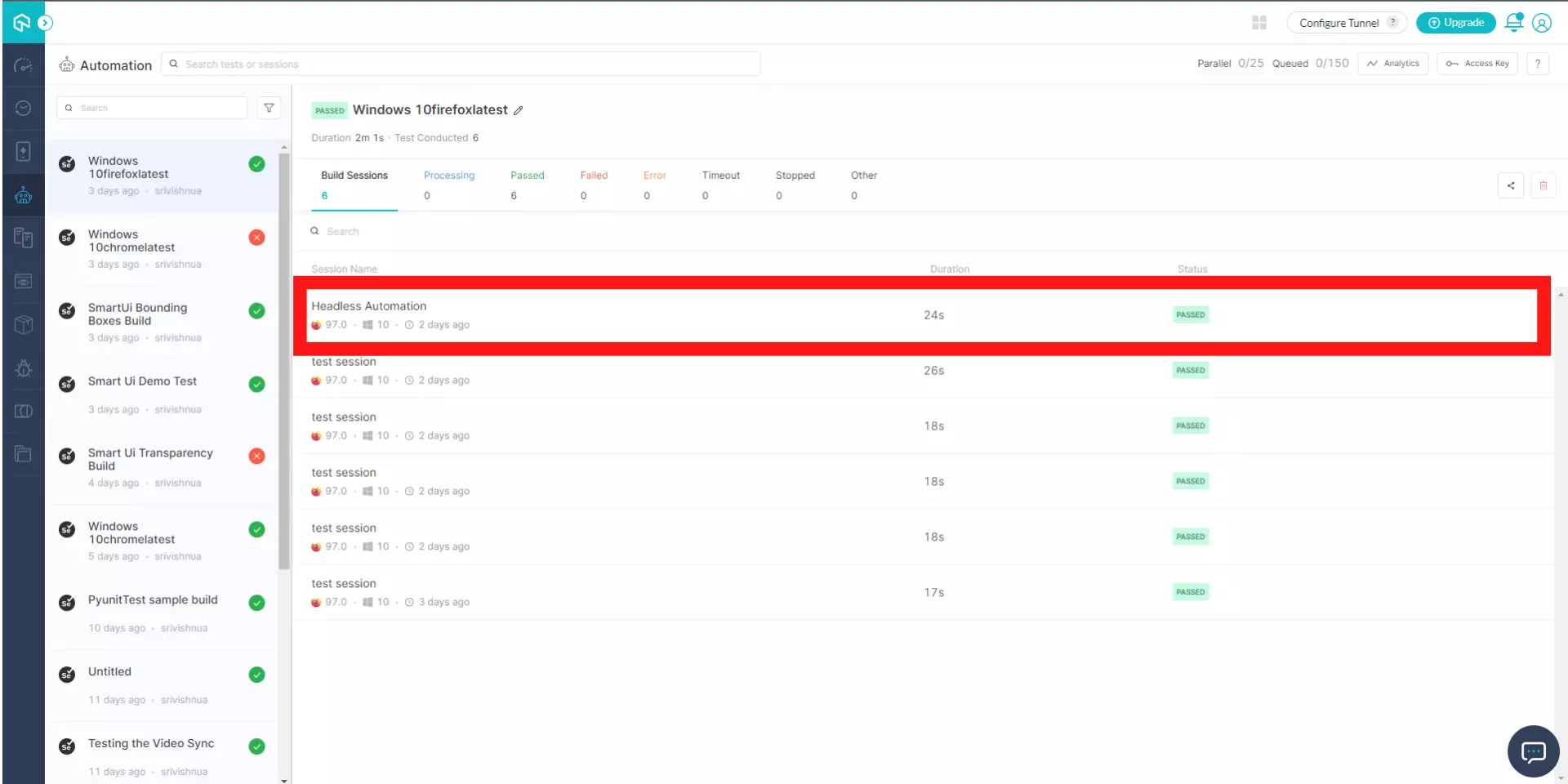
Upon executing the above code, the test will run on your LambdaTest successfully. You can view the status of the test on your Automation dashboard.
That's it folks! If you have any doubt or questions, feel free to contact our experts at 24/7 Customer chat support or mail us at support@lambdatest.com. Happy testing! 🙂
