REST API testing works best when you validate status codes, response bodies, headers, and schemas together, use clear test data, separate environments, mock external services, automate recurring checks, and include both positive and negative scenarios. You verify proper functioning by confirming the API responds with the correct format, handles errors gracefully, enforces authentication, returns consistent data, and maintains stability under different conditions.
The biggest challenges usually come from managing dynamic data, handling chained requests, dealing with authentication tokens, testing asynchronous flows, setting up stable environments, mocking external dependencies, maintaining versioned APIs, and keeping tests reliable when multiple services change rapidly. Coordinating updates between backend and frontend teams also adds complexity.
API testing covers validation testing, functional testing, security checks, error handling tests, load and stress testing, regression checks, and schema validation. Split testing compares different API versions or logic paths. Load testing examines performance under volume. Parallel testing runs multiple API tests at the same time to improve speed. Model-based testing uses predefined workflows or state models to generate and validate API behaviors automatically.
Common API bugs include incorrect status codes, wrong response formats, broken data structures, missing fields, incorrect business logic, authentication failures, authorization leaks, rate-limit issues, improper error messages, timeout problems, and inconsistent behavior between environments.
Yes, you can integrate Rest Assured with LambdaTest's Automation and HyperExecute on an MCP server. This setup lets you scale API automation, use smart orchestration, collect logs and reports, and pair it with Copilot for quick script generation.
A 15-day plan works best when you split the work into requirement review, endpoint mapping, environment preparation, writing core functional tests, adding negative tests, validating authentication flows, running performance checks, and completing regression coverage, followed by consolidation, reporting, and automation setup.
A strong guideline covers naming conventions, environment details, authentication methods, test data rules, schema validation standards, error-handling expectations, logging rules, automation patterns, versioning practices, performance expectations, security considerations, and reporting formats.
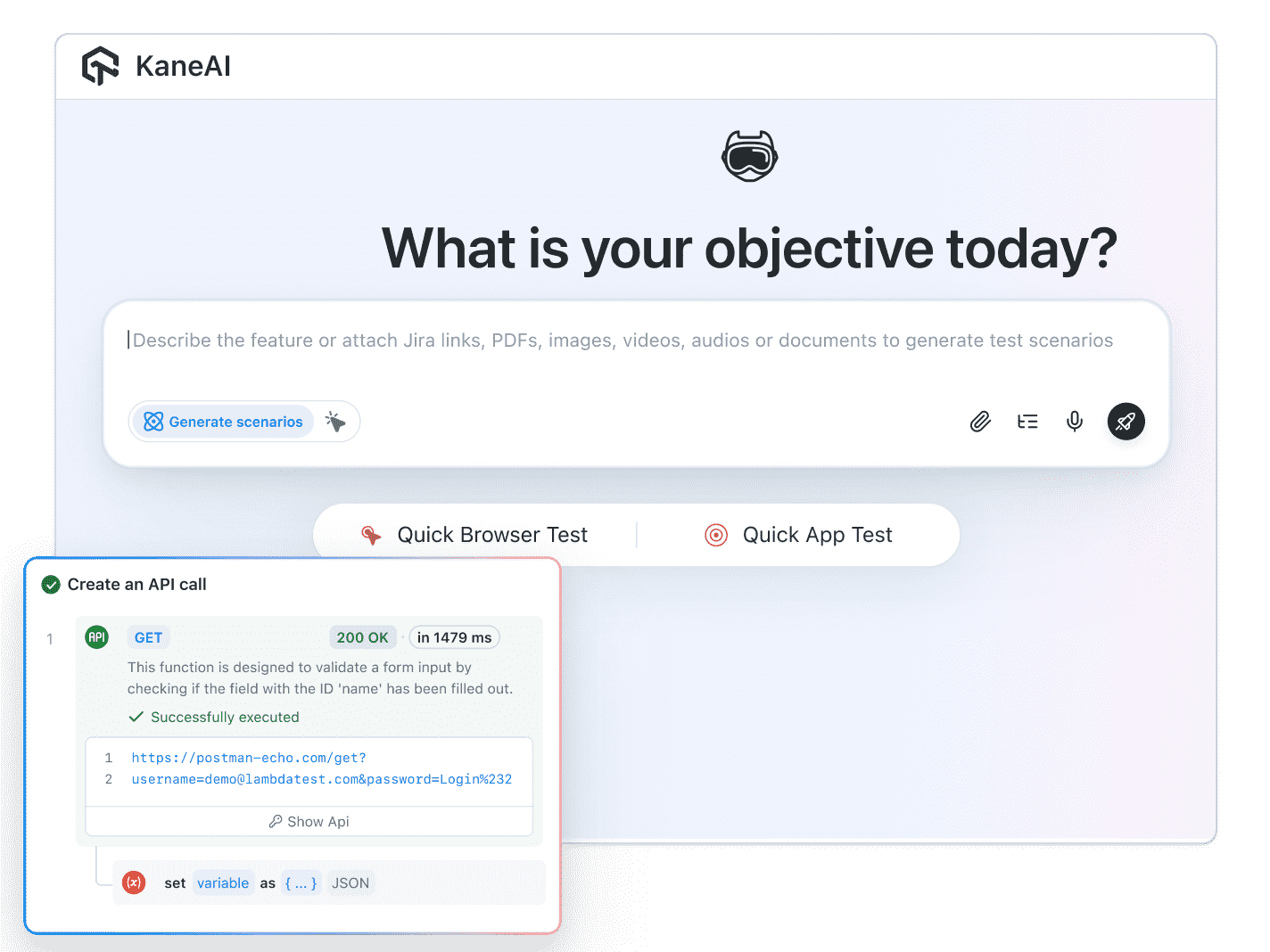
API testing verifies the behavior, performance, security, and reliability of application interfaces. It checks how systems communicate, ensures data flows correctly between services, and confirms that every endpoint behaves as expected without relying on a user interface.
For REST-based API testing, Rest Assured is one of the strongest and most current frameworks because it offers clean syntax, strong JSON validation, powerful request chaining, and seamless integration with CI pipelines and LambdaTest's automation ecosystem.
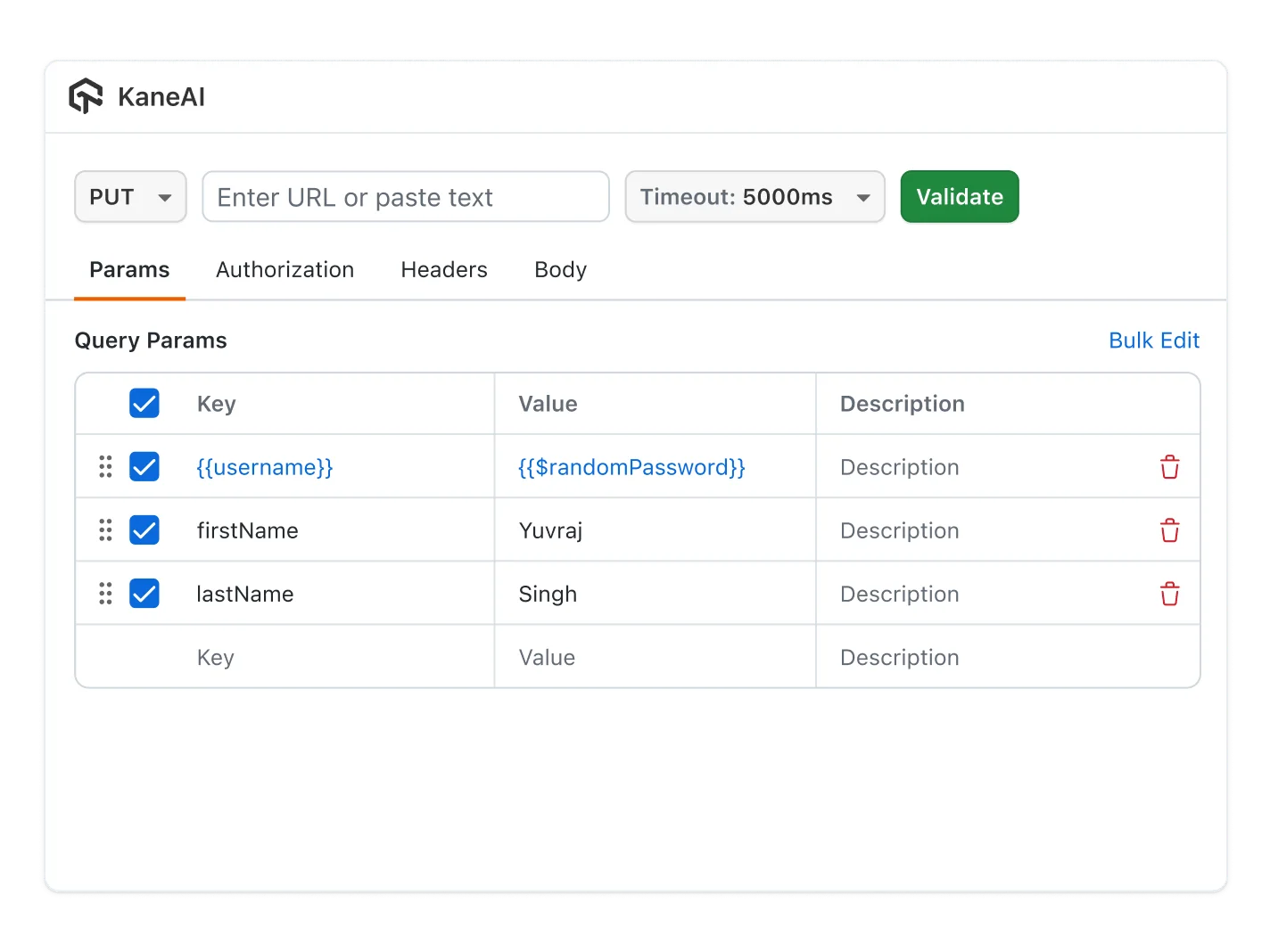
The fundamentals include understanding request methods, request and response structures, headers, authentication, parameter handling, status codes, schema validation, error behavior, performance expectations, and environment management.
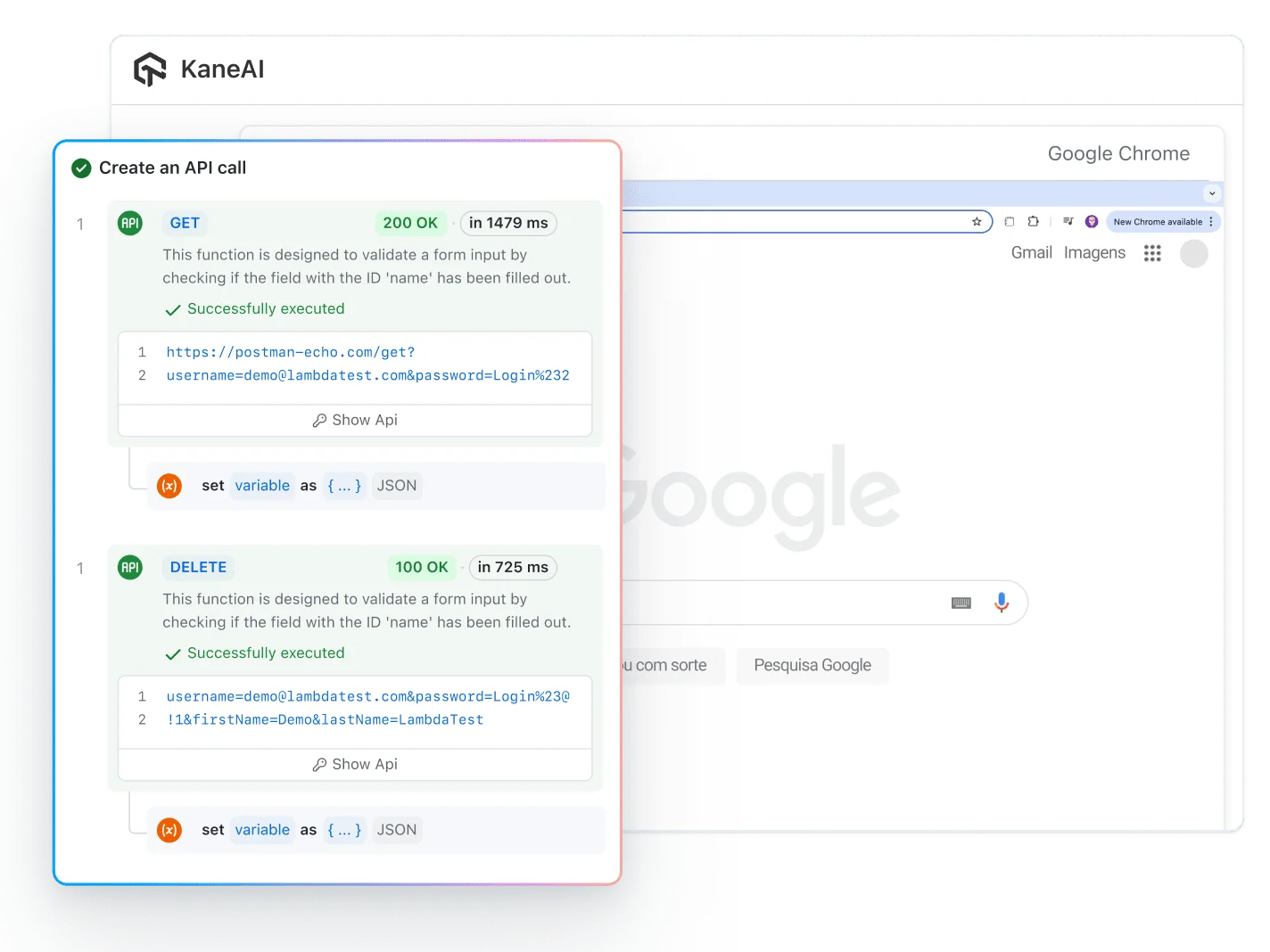
If you mean testing approaches, the four useful methods are functional testing, load testing, security testing, and reliability or recovery testing. If you mean HTTP methods, the four core ones are GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE, which map to read, create, update, and delete operations.
API stands for Application Programming Interface. It defines how different software components communicate, including operations, data formats, and authentication rules.
Start with understanding the API specification, mapping endpoints, methods, and expected responses. Prepare test data, set up the environment, write positive and negative tests, check authentication and error handling, add boundary and schema tests, automate regressions, run load and security checks, and document results with fixes.