Power Your Software Testing with AI and Cloud
Supercharge QA with AI for Faster & Smarter Software Testing

- Automation Testing
- Home
- /
- Learning Hub
- /
- What is Software Delivery
What is Software Delivery: Tools, Key Metrics and Best Practices
Learn what Software Delivery is, key metrics to track, essential tools, and best practices to ensure faster, reliable, and high-quality software releases.
Last Modified on: September 22, 2025
- Share:
Software delivery is more than simply “releasing code to users.” It is the structured process through which software moves from development to end users, balancing speed, reliability, and business impact. Software delivery covers the complete journey of a software artifact, from the initial commit in a repository to production deployment and ongoing improvements.
Overview
Software delivery is the process of planning, building, testing, and maintaining software applications. It ensures that applications are delivered efficiently, securely, and with high quality.
Modern Practices of Software Delivery:
- Automation: Eliminates repetitive manual work by streamlining builds, tests, and deployments. Increases efficiency, reduces human errors, and ensures faster, more reliable delivery of high-quality software.
- Continuous Integration (CI): Developers merge code changes frequently into a shared repository. Automated builds and tests run immediately, detecting integration issues early and improving collaboration, code quality, and release speed.
- Continuous Delivery (CD): Code changes are automatically prepared for release in small, incremental updates, providing faster user feedback, reducing risk, and enabling continuous business value delivery.
Key Technologies:
- DevOps: Integrates development and operations teams to foster collaboration, communication, and shared responsibility. Leverages automation and CI/CD to accelerate software delivery and ensure smoother releases.
- AI-driven Automation: Uses machine learning and predictive analytics to identify issues proactively, optimize workflows, and enhance decision-making for faster, smarter, and more reliable delivery.
- Cloud-Native Architectures: Leverages microservices, containers, and managed cloud services to build scalable, resilient applications. Enables teams to adapt quickly, manage workloads efficiently, and deliver software at global scale.
Benefits of Modern Software Delivery:
- Faster Release Cycles: Streamlined CI/CD, automation, and cloud-native practices shorten release cycles, allowing rapid response to market demands and frequent delivery of value.
- Improved Quality and Bug Fixes: Automated testing and monitoring catch bugs earlier. Continuous updates improve product stability, reduce downtime, and enhance user experience and trust.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Containerization, microservices, and cloud platforms enable seamless scaling, resource optimization, and resilience while reducing operational costs and infrastructure complexity.
What Is Software Delivery?
Software delivery is the end-to-end process of developing, testing, deploying, and maintaining software applications. It involves transforming business requirements into functional products and ensuring continuous improvement and support post-deployment.
What are the Core Components of the Software Delivery Lifecycle?
The Software Development Lifecycle (SDLC) consists of several essential stages that ensure software is developed, tested, deployed, and maintained efficiently.
Here’s a breakdown of each phase:
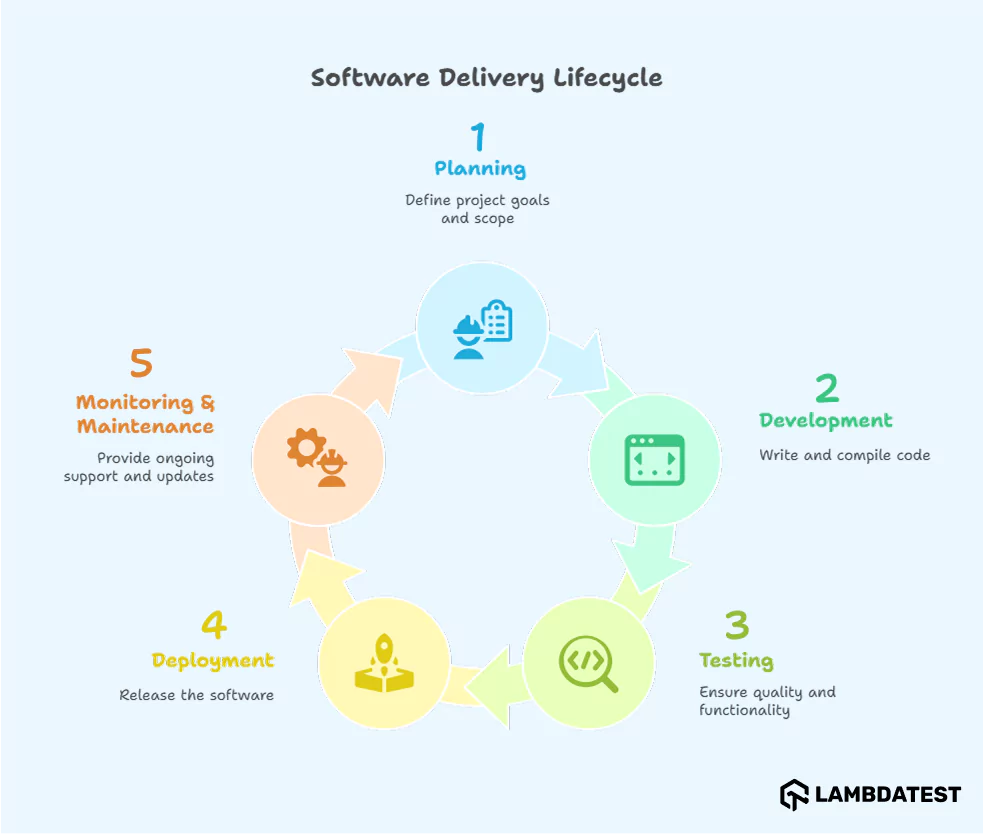
1. Planning: Defining Project Goals, Scope, and Timelines
Planning sets the foundation for the project. This phase involves defining the project’s goals, scope, resources, and timelines. Clear planning ensures alignment with business objectives and sets realistic expectations for the team.
2. Development: Writing and Compiling Code
In the development phase, developers write and compile the code. This stage transforms business requirements into working software, with a focus on functionality and design. Version control systems are used to manage code changes, and unit tests are written to ensure correctness.
3. Testing: Ensuring Quality and Functionality
Testing ensures the software meets the required standards. Various types of testing, such as unit, integration, system, and User Acceptance Testing (UAT), help identify bugs and ensure the software works as expected. Automated tests are often used to speed up the process.
4. Deployment: Releasing the Software
Deployment involves releasing the software to production. This can be done through a full release or staged rollout. Automation tools are used to streamline the deployment process, ensuring consistency and minimizing errors. Monitoring tools track performance post-deployment.
5. Monitoring & Maintenance: Ongoing Support and Updates
Post-deployment, continuous monitoring ensures the software operates smoothly. Maintenance involves fixing bugs, updating features, and addressing user feedback. This phase ensures the software remains secure, scalable, and relevant over time.
Each stage is crucial for delivering reliable and efficient software products.
Modern Methodologies in Software Delivery
Modern software delivery leverages adaptive methodologies to improve speed, collaboration, and reliability. Approaches like Agile, DevOps, and CI/CD empower teams to deliver continuous value while responding quickly to change.
These methodologies enhance every stage of the software development process, ensuring efficient planning, coding, testing, and deployment.
Agile Development
Agile development methodologies, such as Scrum and Kanban, emphasize iterative development, collaboration, and flexibility. Teams work in short cycles (sprints), delivering incremental improvements and adapting to changing requirements.
DevOps
DevOps is a cultural and technical movement that unifies software development and IT operations. It aims to shorten the development lifecycle, increase deployment frequency, and deliver high-quality software through automation and continuous monitoring.
Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD)
CI/CD practices involve automating the integration and deployment processes. Continuous Integration ensures that code changes are automatically tested and integrated into the main codebase, while Continuous Deployment automates the release of these changes to production, facilitating rapid delivery and feedback.
There are also various types of SDLC models available, allowing you to choose the one that best aligns with your project’s requirements and goals.
Tools and Technologies Enabling Modern Software Delivery
Modern software delivery relies on a variety of tools and technologies that streamline processes, increase efficiency, and ensure high-quality, reliable software releases. These tools support automation, collaboration, monitoring, and scalability, helping organizations deliver value faster and maintain consistency across environments.
1. Version Control: Git, SVN
Version control systems are the backbone of modern software development. They track every code change, manage revisions, and enable collaboration among distributed teams.
- Git: A distributed version control system that allows multiple developers to work simultaneously, manage branching and merging, and maintain a complete history of code changes.
- SVN: A centralized version control system that stores code revisions in a single repository, often used in legacy systems and structured enterprise workflows.
Version control ensures that teams can collaborate efficiently, maintain code integrity, and roll back changes when necessary, forming the foundation for CI/CD and modern workflows.
2. CI/CD Platforms: Jenkins, GitLab CI, CircleCI
Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Delivery/Deployment (CD) platforms automate code integration, testing, and release pipelines. They accelerate software delivery while reducing human error.
- Jenkins: An open-source automation server that allows teams to define pipelines, run automated tests, and deploy applications reliably with a vast ecosystem of plugins.
- GitLab CI: Built into GitLab, it provides seamless automation for integration, testing, and deployment workflows, streamlining end-to-end software delivery.
- CircleCI: A cloud-based CI/CD platform that automates building, testing, and deploying applications, enabling fast, repeatable, and consistent software releases.
CI/CD platforms enhance collaboration between developers and operations teams, shorten release cycles, and ensure that high-quality software reaches production consistently.
3. Containerization: Docker, Kubernetes
Containerization allows developers to package applications with all dependencies, ensuring consistent environments across development, testing, and production.
- Docker: Packages applications into lightweight containers, providing portability and eliminating “it works on my machine” issues.
- Kubernetes: Orchestrates containerized applications at scale, automating deployment, scaling, and management while improving resilience and resource utilization.
By using containers, teams achieve faster deployments, predictable environments, and improved scalability, making it easier to adopt microservices and cloud-native architectures.
4. Configuration Management: Ansible, Chef, Puppet
Configuration management tools automate infrastructure provisioning, enforce consistency, and reduce manual administrative tasks.
- Ansible: Agentless automation using YAML playbooks to configure systems, deploy applications, and orchestrate workflows.
- Chef: Uses Ruby-based scripts to automate infrastructure setup and enforce system state across multiple servers.
- Puppet: Provides automated configuration and system administration, helping maintain consistent environments and reduce human errors.
These tools allow teams to treat infrastructure as code, maintain reproducible environments, and scale software delivery efficiently without manual intervention.
5. Monitoring: Prometheus, Grafana, New Relic
Monitoring tools provide visibility into system health, application performance, and user experience, enabling teams to proactively detect and resolve issues.
- Prometheus: Collects and stores metrics with powerful querying capabilities, triggering alerts when issues occur.
- Grafana: Visualizes metrics and logs from various sources, providing dashboards for analysis and insights.
- New Relic: An Application Performance Management (APM) tool offering real-time insights into application performance, bottlenecks, and user experience.
Monitoring ensures reliability, supports quick incident response, and provides data-driven insights to optimize software delivery and operational efficiency.
6. Emerging Technologies
Modern software delivery is increasingly influenced by advanced technologies that further optimize workflows and accelerate delivery:
- AI and Machine Learning: Automate testing, deployment, and monitoring while enabling smarter, predictive, and data-driven decisions.
- Serverless Architectures: Reduce infrastructure management and scale automatically, lowering costs and speeding up deployments.
- Edge Computing: Processes data closer to users, reducing latency and improving performance, especially for IoT and mobile apps.
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC): Automates provisioning and management of infrastructure, ensuring consistency and reducing deployment errors.
- Blockchain: Enhances security and traceability by maintaining immutable records of software changes.
Leveraging these tools and technologies allows organizations to adopt modern practices like DevOps, Agile, and CI/CD effectively, ensuring faster, reliable, and secure software delivery.
Metrics for Measuring Software Delivery Performance
Measuring the performance of software delivery helps identify areas for improvement and ensures faster, reliable, and high-quality releases. The DORA metrics are key indicators in evaluating software delivery effectiveness. Here’s a quick breakdown of the essential metrics:
- Deployment Frequency: Deployment frequency measures how often code changes are released into production. It reflects a team’s agility, ability to deliver value quickly, and responsiveness to customer needs.
Why It Matters: More frequent deployments enable faster feedback, quicker bug fixes, and quicker time-to-market. A high deployment frequency shows an efficient release process.
- Lead Time for Changes: Lead time for changes measures how long it takes for a code change to move from development to production. Shorter lead times indicate efficient workflows and faster delivery of value to users.
Why It Matters: Shorter lead times mean faster feature delivery and quicker responses to user needs, improving overall productivity.
- Change Failure Rate: Change failure rate measures the proportion of code changes that cause failures or incidents in production. A lower rate indicates higher stability, better quality assurance, and effective testing processes.
Why It Matters: A lower failure rate indicates higher code quality and more stable releases. High failure rates can lead to customer dissatisfaction and higher maintenance costs.
- Mean Time to Recovery (MTTR): MTTR measures the average time it takes to recover from a failure or incident in production. Lower MTTR indicates faster issue resolution, improved reliability, and minimal disruption to users.
Why It Matters: Lower MTTR ensures faster incident resolution and minimal downtime, maintaining service availability and user satisfaction.
Challenges in Software Delivery and How to Overcome Them
Software delivery can be challenging, particularly when integrating new methodologies, tools, and technologies into existing processes. Below, we explore these challenges in detail and offer strategies to overcome them.
Legacy Systems: Integrating New Practices with Existing Infrastructure
Legacy infrastructure is often the biggest barrier to digital transformation. These older systems are deeply embedded in business processes, making modernization complex and risky.
- Challenge: Legacy systems often lack compatibility with modern software delivery practices, making integration difficult. They can slow the adoption of CI/CD, automation, and cloud-native approaches.
- Solution: Adopt a phased migration approach to gradually modernize systems without disrupting operations. Use containerization tools like Docker and start with pilot projects to test new methodologies safely.
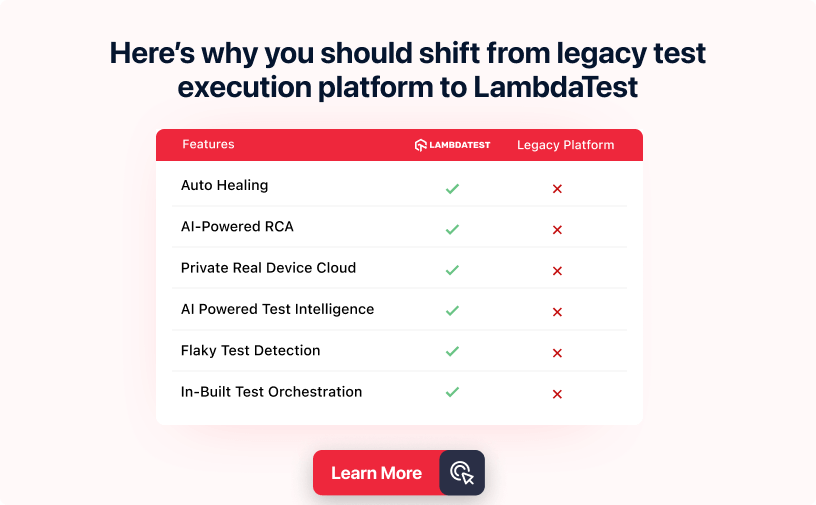
For organizations struggling with legacy system challenges, LambdaTest provides a modern, cloud-based testing platform that integrates seamlessly with CI/CD pipelines. By enabling cross-browser and cross-platform testing without heavy infrastructure changes, LambdaTest helps teams modernize their testing workflows, reduce dependency on outdated systems, and accelerate the shift toward agile delivery practices.
Cultural Resistance: Shifting to New Methodologies
Beyond tools and processes, the mindset of teams plays a crucial role in successful transformation. Resistance to change can quickly stall even the best-planned initiatives.
- Challenge: Teams may resist adopting Agile, DevOps, or CI/CD practices due to fear of change, uncertainty, or comfort with traditional workflows. This can slow transformation.
- Solution: Communicate benefits clearly and provide examples of value. Gain leadership support, involve teams early, and celebrate small, quick wins to encourage adoption and build momentum.
Skill Gaps: Adopting Modern Tools and Practices
Adopting new practices requires more than intention—it demands the right skills. Without adequate expertise, organizations struggle to realize the full potential of modern delivery methods.
- Challenge: Teams often lack the necessary expertise to implement modern tools, automation, and methodologies, which can lead to errors, inefficiencies, and slower delivery.
- Solution: Offer structured training, certification programs, and mentorship. Encourage knowledge sharing and consider bringing in external experts to accelerate learning and support the adoption of modern practices.
Managing Complexity Across Teams and Tools
As organizations scale, multiple teams and tools can create fragmented workflows. Without alignment, efficiency drops and visibility across the delivery pipeline becomes a challenge.
- Challenge: Different teams using diverse tools and processes can create inefficiencies, fragmented workflows, and a lack of visibility, making coordination and delivery more complex.
- Solution: Integrate tools to establish a unified workflow, foster cross-team communication, and implement centralized dashboards for real-time monitoring, improving efficiency and collaborative decision-making.
Managing the Pace of Change
In today’s fast-evolving tech landscape, change happens faster than many teams can comfortably adapt. Balancing innovation with stability is critical to sustaining long-term success.
- Challenge: Rapid technological advancements can overwhelm teams, leading to burnout, errors, and difficulty keeping up with evolving tools and practices.
- Solution: Adopt Agile practices for flexibility, allocate dedicated time for continuous learning, and introduce small, incremental changes to stay updated without disrupting productivity.
The Future of Software Delivery
The future of software delivery is shaped by emerging trends that streamline processes, enhance performance, and improve scalability. Here’s a quick look at the key trends:
1. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and ML will increasingly automate repetitive tasks, predict potential issues before they occur, and support smarter decision-making, accelerating software delivery and improving overall efficiency and reliability.
Impact: AI-driven automation enhances testing, deployment, and monitoring. Leveraging AI testing approaches enables faster delivery cycles and more data-driven decisions, improving software quality and overall operational performance.
2. Serverless Architectures
Serverless computing removes the need to manage infrastructure manually by automatically scaling resources based on demand, allowing teams to focus on development rather than maintenance.
Impact: Reduces operational costs, enhances scalability, and accelerates deployments by removing manual infrastructure management, providing developers with more flexibility and faster time-to-market for applications.
3. Edge Computing
Edge computing processes data closer to the end user rather than relying solely on centralized servers, reducing latency and improving overall application responsiveness and performance.
Impact: Supports real-time data processing, faster responses, and decreased bandwidth usage, making it ideal for IoT, mobile applications, and other latency-sensitive software solutions.
4. Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD) Evolution
CI/CD practices are evolving with AI and advanced automation, enabling more intelligent testing, integration, and deployment pipelines, resulting in faster, more reliable software releases.
Impact: Facilitates continuous delivery with fewer errors, enables efficient rollbacks, and ensures that high-quality software is deployed consistently with improved operational efficiency.
5. Blockchain for Software Integrity and Security
Blockchain provides immutable, tamper-proof records of software changes, enhancing security, traceability, and transparency across the software delivery process.
Impact: Strengthens application security, prevents unauthorized modifications, ensures reliable audit trails, and enables automation through smart contracts to reduce human error in workflows.
6. Automation of Operations with Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
Infrastructure as Code (IaC) automates the provisioning and management of infrastructure, ensuring consistent environments and reducing manual intervention in the software delivery pipeline.
Impact: Speeds up infrastructure setup, maintains consistency across environments, reduces errors, and enables agile, repeatable deployment processes for faster and more reliable software delivery.
Best Practices for Efficient Software Delivery
To optimize software delivery, consider implementing the following best practices. These approaches help teams accelerate releases, improve quality, and ensure software consistently meets evolving business and customer needs.
- Automation: Automate repetitive tasks like building, testing, and deployment to reduce human errors, improve efficiency, and accelerate software delivery.
- Collaboration: Encourage seamless communication between development, operations, and business teams to align objectives, share feedback, and improve delivery outcomes.
- Continuous Testing: Embed automated testing throughout the development lifecycle to detect issues early, reduce risks, and ensure software reliability.
- Version Control: Leverage version control systems to manage code changes, enable collaboration, maintain history, and ensure consistent, trackable development.
- Monitoring: Establish proactive monitoring practices to track system health, identify issues quickly, minimize downtime, and maintain application reliability.
Conclusion
Effective software delivery is critical for organizations aiming to deliver high-quality products swiftly and reliably. By understanding the software delivery lifecycle, adopting modern methodologies, implementing best practices, leveraging appropriate tools, and measuring performance, organizations can enhance their software delivery processes and achieve business objectives.
On This Page
- Overview
- What Is Software Delivery?
- What are the Core Components of the Software Delivery Lifecycle
- Modern Methodologies in Software Delivery
- Tools and Technologies Enabling Modern Software Delivery
- Metrics for Measuring Software Delivery Performance
- Challenges in Software Delivery and How to Overcome Them
- The Future of Software Delivery
- Best Practices for Efficient Software Delivery
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Did you find this page helpful?
More Related Hubs

Start your journey with LambdaTest
Get 100 minutes of automation test minutes FREE!!