Power Your Software Testing with AI and Cloud
Supercharge QA with AI for Faster & Smarter Software Testing

- Automation
- Home
- /
- Learning Hub
- /
- DevOps Testing: Strategies and Best Practices
DevOps Testing: Strategies and Best Practices
In this guide, explore DevOps testing to boost software quality. Learn how automation, CI/CD, and validation speed up secure, reliable releases.
Last Modified on: September 26, 2025
- Share:
DevOps testing is a modern approach that ensures software remains in a releasable state by embedding continuous, automated testing throughout the development pipeline. It promotes shared quality ownership across cross-functional teams and follows a “shift-left” strategy to catch defects early.
Overview
DevOps testing integrates testing throughout the software development lifecycle, ensuring continuous delivery, faster releases, and high-quality software with minimal risks.
Characteristics of DevOps Testing
- Automated and Continuous Testing: Automated scripts run end-to-end, ensuring faster feedback, wider coverage, and early defect detection.
- Testing Across the SDLC: DevOps shifts testing left, embedding it from coding through deployment for higher stability.
- Faster Feedback and Rollbacks: CI/CD enables real-time results, quick fixes, and safe rollbacks to cut downtime.
- Shared Ownership of Quality: Quality is a shared responsibility across developers, testers, and operations.
DevOps Testing Strategies
- Automate Tests: Use CI/CD tools like Jenkins, GitLab, or CircleCI for faster execution.
- Shift-Left Approach: Test early in the development cycle to reduce downstream defects.
- Continuous Monitoring: Track performance and errors in real-time to react quickly.
- Collaborative Culture: Encourage cross-team communication to resolve issues faster.
What Is DevOps Testing?
DevOps testing is a technique to detect and fix defects in a proactive way so that the software is always in a releasable state and the quality is not compromised. This approach of quality being owned by a single QA team is now completely changed and requires collective responsibility from every member of the cross-functional DevOps team.
The core principle of DevOps software testing is outlined in shift left testing which means going down the testing route as soon as possible in the SDLC. This allows the issues to be found and fixed at an earlier stage. The value of software quality is not seen as a reactive cost center but as a proactive driver of great business outcomes due to this strategic reorientation of testing.
New to DevOps? Check out this guide on what is DevOps.
Characteristics of DevOps Testing
As organizations adopt DevOps to supplement Agile, the testing becomes from a standalone late phase to a more continuous, integrated, and shared responsibility along the software delivery pipeline.
Some of the main characteristics of DevOps testing are:
- Automated and Continuous Testing: Testing is not manual anymore, and it is also not isolated. Automated test scripts are run continuously at every stage, from code commit to deployment, thus providing faster feedback, wider coverage, and early defect detection.
- Testing at Every Stage of the SDLC: DevOps is the best proponent of the “shift-left” mindset, where testing happens during coding and is continuous all the way through integration, staging, and post-deployment. This leads to issue identification at the early stages of product development, hence product stability is better.
- Faster Feedback and Quick Rollbacks: Integration with CI/CD tools allows test results to be there in real-time. The teams get to respond quickly with the issue fix implementation or rolling back of the deployment that is not correct, thus downtime is reduced while risks are minimized.
- Shared Ownership of Quality: Quality assurance is definitely not a separate QA team's job. Developers, testers, and operations teams collaborate on writing, executing, and maintaining tests. This collaborative responsibility is what brings forth an overall quality enhancement in the lifecycle.
- Risk-Based and Business-Aligned Testing: One of the principles of DevOps is the stressing of business impact and risk in the planning phase and then prioritizing tests based on these factors. Teams often make use of domain experts and actual usage patterns to zero in on the critical workflows, thereby eliminating redundant and low-value testing.
- Toolchain Integration: Modern DevOps software testing environments connect with Continuous Integration tools such as Jenkins or GitHub Actions and also make use of DevOps testing tools or cloud testing platforms like LambdaTest for running tests across various environments.
Note: Run automated tests across 3000+ desktop & mobile browsers. Try LambdaTest Now!
DevOps Testing Strategies
Implementing a robust DevOps testing strategy ensures that quality is built into every stage of software delivery. It emphasizes collaboration, automation, monitoring, and continuous feedback, reducing defects, accelerating releases, and aligning technical practices with business objectives.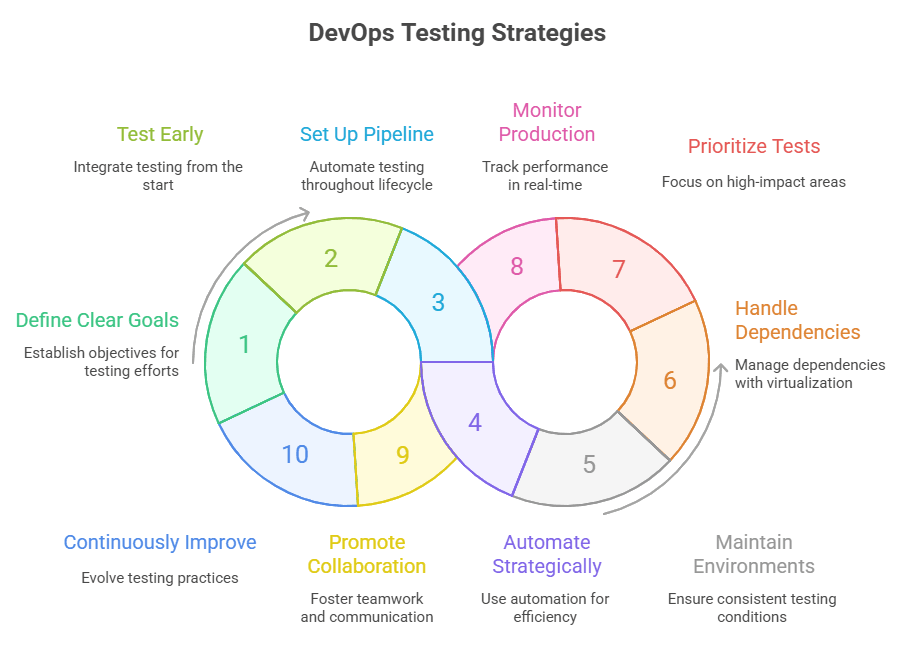
1. Define Clear Testing Goals
Establishing clear testing goals ensures the team focuses on results that truly impact product quality, release velocity, and operational reliability. Goals serve as a reference to prioritize tests, measure success, and prevent wasted effort on low-value checks.
- Quality Assurance: Ensure critical functionalities are tested to prevent defects from reaching production.
- Release Confidence: Enable faster deployments while maintaining high levels of reliability.
- Risk Prioritization: Focus testing on components with the highest potential impact on users and operations.
- Efficiency Measurement: Track defect detection rates and testing coverage to assess value delivered by testing efforts.
2. Test Early in the Process
Integrating testing from requirements and design phases allows issues to be detected before they propagate. Early testing ensures that features are implemented correctly, reduces rework, and builds a culture of shared responsibility for quality across the team.
- Requirement Validation: Ensure that specifications are complete and testable to prevent ambiguous implementations.
- Unit Testing: Catch logic errors within individual modules immediately as code is written.
- Continuous Integration Testing: Execute automated tests on every commit to detect defects early.
- Design Collaboration: Encourage QA to participate in design reviews to anticipate testing challenges.
3. Set Up a Continuous Testing Pipeline
A continuous testing pipeline embeds quality checks throughout the development lifecycle. It provides automated verification at multiple levels, ensures early defect detection, and enables consistent feedback for developers and operations teams, supporting both speed and reliability.
- Unit Level Checks:Test individual components to catch regressions early.
- Integration Testing: Confirm correct interaction between multiple software modules.
- Functional Verification: Test end-to-end workflows to ensure features meet requirements.
- Regression Tests: Run automated tests on critical paths to detect unintended changes.
- Automated Feedback: Provide real-time insights to developers for quick corrective action.
4. Use Test Automation Strategically
Automation accelerates regression cycles, improves repeatability, and reduces human error. Strategic selection of what to automate ensures maximum impact, prevents maintenance overhead, and focuses resources on high-risk areas where failures are most costly.
- Critical Path Automation: Cover essential workflows such as authentication and payments.
- Repeatable Tasks: Automate routine verification that consumes significant manual effort.
- Maintenance Practices: Update test scripts regularly to avoid outdated coverage and false results.
- Cross-Platform Testing: Ensure features function consistently across devices, browsers, and environments.
5. Maintain Consistent Test Environments
Accurate testing depends on environments that closely mirror production. Consistency eliminates false positives, reduces debugging time, and ensures that test outcomes reflect real user experiences, enabling reliable deployments and meaningful defect detection.
- Scripted Provisioning: Use automation to create identical test environments consistently.
- Production Parity: Match OS, database versions, and network configurations to production.
- Parallel Testing: Run multiple suites simultaneously to accelerate feedback.
- Environment Isolation: Prevent conflicts between test runs for reliable results.
6. Handle Dependencies With Virtualization
Dependencies often delay testing when services are unavailable or incomplete. Virtualization and service simulation allow isolated testing, reduce bottlenecks, and ensure that development progress continues without waiting for all system components to be ready.
- Service Simulation: Replace unavailable services with mocks or stubs.
- Component Isolation: Validate each module independently to prevent blockage.
- Parallel Execution: Run multiple tests simultaneously without dependencies.
- Early Detection: Identify integration issues before full system availability.
7. Prioritize Tests
Not all tests are equal in impact. Prioritizing tests ensures the team focuses on high-risk, high-value areas first. This approach reduces wasted effort, accelerates defect detection, and ensures critical functionality is verified before less significant components.
- High-Risk Modules: Focus on components where failures have the largest user or business impact.
- Recent Changes: Test areas affected by new code to quickly catch regressions.
- Frequent Workflows: Validate core user journeys that are used most often.
- Resource Optimization: Allocate testing effort where it delivers maximum value.
- Periodic Review: Reassess test priorities as features evolve and new risks emerge.
8. Monitor in Production
Testing does not end at deployment. Continuous monitoring in production helps detect issues under real user conditions, identify performance bottlenecks, and provide actionable feedback, ensuring rapid response to failures and maintaining high service reliability.
- Performance Tracking: Monitor response times, throughput, and latency to ensure service quality.
- Error Detection: Capture exceptions, failed transactions, and critical errors in real time.
- User Experience Monitoring: Observe actual workflows to identify unexpected behaviors or bottlenecks.
- Alerting: Implement automated alerts for critical failures to accelerate remediation.
- Usage Analytics: Analyze trends and patterns to anticipate future risks or areas for improvement.
9. Promote Collaboration
Collaboration between development, QA, and operations ensures shared ownership of quality. Open communication, synchronized processes, and knowledge sharing prevent siloed work, accelerate problem-solving, and ensure testing aligns with business priorities and technical requirements.
- Cross-Functional Teams: Include developers, testers, and operations for collective accountability.
- Shared Metrics: Use common dashboards to track progress and defects transparently.
- Knowledge Transfer: Encourage team members to share domain expertise and testing techniques.
- Continuous Feedback: Maintain regular communication loops to resolve blockers efficiently.
- Collaborative Planning: Align on priorities, risks, and resource allocation before development cycles.
10. Continuously Improve
Continuous improvement ensures testing evolves with software and business changes. Reviewing outcomes, metrics, and workflows identifies inefficiencies, enables process refinement, and keeps the team aligned with best practices, emerging technologies, and evolving customer expectations.
- Retrospectives: Review each cycle to identify successes and areas for enhancement.
- Metrics Analysis: Measure coverage, defect detection rate, and test execution efficiency.
- Process Refinement: Update workflows, automation strategies, and documentation based on lessons learned.
- Tool Evaluation: Adopt new tools or frameworks that enhance speed, accuracy, or visibility.
- Knowledge Sharing: Disseminate learnings across teams to improve overall testing maturity.
Types of Testing in DevOps
DevOps includes several types of testing, each with its purpose within the continuous delivery pipeline:
- Unit Testing: Validates a single component or function in isolation. In DevOps, these tests run fast and provide immediate feedback in local development and CI pipelines, helping developers catch issues before code merges.
- Integration Testing: Runs automatically in the Continuous Integration (CI) environment whenever code is pushed to the shared repository. These tests confirm that services, APIs, and modules work correctly together.
- Functional Testing: Functional tests in a DevOps pipeline ensure consistent application behavior across releases, aligning with specifications and user expectations.
- Performance Testing: Integrated into the pipeline to simulate load and stress scenarios. Performance tests detect bottlenecks and regressions early, long before production.
- Acceptance Testing: Executes in staging or production-like environments to validate that the software meets business requirements. In DevOps, this step bridges development output with stakeholder approval.
- Regression Testing: Regression suites safeguard existing functionality by verifying that new changes do not reintroduce old bugs. This enables safe, frequent releases.
- End-to-End Testing: Typically run less frequently due to cost and duration. In a DevOps pipeline, these tests validate critical user workflows across the full stack, providing confidence before major releases.
- Security Testing: Built directly into the CI/CD pipeline, security tests checks for vulnerabilities and misconfigurations. This shifts security left so it becomes part of development rather than an afterthought.
Scale DevOps Testing With LambdaTest HyperExecute
Scaling DevOps testing requires speed, reliability, and the ability to handle complex pipelines without slowing down delivery. LambdaTest HyperExecute helps teams achieve this by providing a cloud-based test execution environment that is both fast and highly scalable. Unlike traditional test runners, HyperExecute intelligently distributes tests across multiple environments, reducing bottlenecks and enabling near real-time feedback.
Features:
- AI-Native, High-Speed Execution: Executes tests up to 70% faster with intelligent orchestration.
- Smart Test Splitting and Multiplexing: Distributes tests efficiently across environments using Auto Split, Matrix, or Hybrid strategies.
- Fail-Fast and Job Prioritization: Halts runs on critical failures and ensures high-priority jobs run first.
- Detailed Logs and Reporting: Delivers real-time logs, detailed reports, metrics, and artifact management.
- Automatic Healing and Root Cause Analysis: Uses AI to recover from failures and classify errors for faster debugging.
- Projects and Workflow Scheduling: Organizes tests into projects, enables scheduling, and integrates smoothly with CI/CD pipelines.
- CLI Integration and Secure Tunnels: Supports command-line execution and secure testing for private apps.
- Broad Framework and Language Support: Compatible with Selenium, Cypress, Playwright, and multiple languages.
- Enterprise-Grade Security: Provides SOC2, GDPR, and CCPA compliance with encryption and secure deployments.
- MCP Server Automation: Automates setup, YAML creation, and test commands with AI-driven MCP Server.
To begin with, head over to this HyperExecute guide.
DevOps Testing Best Practices
Implementing effective DevOps best practices for testing is crucial for ensuring quality and reliability in a DevOps environment. Following established best practices helps teams detect issues early, streamline workflows, and maintain continuous delivery with confidence.
- Automate Early and Often: Automated tests must be integrated at every stage of coding. One must start writing unit and integration tests as soon as something is developed in order to catch defects early and give quick feedback.
- Shift Left Testing: Testing activities should be done early in the development process and promote collaboration among developers and testers on test cases that are run before integration, to avoid surprises later.
- Build a Test Environment that Is Realistic and Consistent: Use container- or cloud-based solutions to simulate production in every way possible, thus minimizing environment-specific bugs and maximizing reliability.
- Fast and Reliable Feedback Is Key: Ensure there is a test suite that is fast yet clear. Initiate tests in parallel where applicable; cut down on flaky, slow, or irrelevant test cases to boost teams' confidence in the results given.
- Build a Collaborative Culture: Break down silos by combining every stakeholder, developers, testers, and ops. Promote shared quality ownership by activities such as pair testing and deep communication across the whole pipeline.
- Maintain Proper Documentation: Proper documentation supports transparency, traceability, and consistency in DevOps software testing. Successful DevOps teams usually maintain Quality Management Plans (QMP), test case specifications, test summary reports, regression test reports, and risk assessment reports.
Conclusion
For many organizations, DevOps is not just a buzzword. To stay competitive in an ever-changing marketplace, it is a must-have. Continuous testing is at the heart of DevOps, ensuring fast delivery of high-quality and reliable software through automated validation at every stage of the CI/CD pipeline.
However, DevOps Testing can only generate value if certain best practices are implemented. Here, automation, collaboration, documentation, and tools are integral elements. When done right, new-age testing breeds innovation and stability.
Citations
- DevOps Capabilities, Practices, and Challenges: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1907.10201
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Did you find this page helpful?
More Related Hubs

Start your journey with LambdaTest
Get 100 minutes of automation test minutes FREE!!


