Power Your Software Testing with AI and Cloud
Supercharge QA with AI for Faster & Smarter Software Testing

- Automation Testing
- Home
- /
- Learning Hub
- /
- What is a QA Engineer
What is a QA Engineer: Role, Responsibilities and Skills
Learn what a QA Engineer does, their key responsibilities, and the essential skills needed to succeed in the field. Explore how QA Engineers ensure software quality, improve customer satisfaction, and contribute to the development process.
Last Modified on: November 19, 2025
- Share:
A QA Engineer plays a critical role in the software development lifecycle, ensuring that products are free from defects and meet the required standards of quality.
If you're considering a career in QA or looking to enhance your skills, this guide will provide you with all the essential information.
Overview
QA Engineer stands for Quality Assurance Engineer, a professional dedicated to ensuring that software applications meet specified requirements and are free from defects. In the realm of AI, QA Engineers play a pivotal role in validating and verifying AI models, ensuring their accuracy, fairness, and reliability.
Key Responsibilities of a QA Engineer
- Test Planning & Design: Create detailed test plans and cases to evaluate software functionality.
- Test Execution: Perform manual and automated tests to identify defects and ensure expected software behavior.
- Defect Reporting & Tracking: Document and report issues, collaborating with developers to resolve them.
- Continuous Improvement: Conduct regression and performance testing to ensure the software evolves with changing requirements.
Skills and Qualifications: Career Path
- Technical Expertise: Proficiency in programming languages (e.g., Java, Python) and testing frameworks (e.g., Selenium, JUnit).
- Analytical & Detail-Oriented: Strong problem-solving and attention to detail for identifying and resolving issues.
- Communication: Ability to document findings and collaborate effectively with cross-functional teams.
- Certifications: ISTQB and LambdaTest certifications help validate skills and enhance job prospects in QA engineering.
What is a QA Engineer?
A Quality Assurance (QA) Engineer is a professional responsible for ensuring that software products meet the desired quality standards before being released to end users.
QA Engineers focus on identifying bugs, optimizing performance, and ensuring usability, security, and reliability. Their primary goal is to maintain a high-quality user experience by preventing defects during the software development process.
Roles and Responsibilities of a QA Engineer
The job of a QA Engineer involves a variety of tasks centered around ensuring the functionality and quality of software applications. They are responsible for all aspects of quality assurance, from test planning to execution, to make sure the software is free of defects and performs reliably. Key responsibilities include:
- Design Test Plans: They plan and define what should be tested, how to test it, and the expected results.
- Execute Tests: They run manual and automated tests to detect issues in software behavior.
- Report Defects: QA Engineers document and report any defects or failures, collaborating closely with developers to resolve them.
- Ensure Continuous Improvement: By running regression and performance tests, QA Engineers ensure the software meets evolving business requirements without introducing new issues.
How to Become a QA Engineer?
To become a QA Engineer, you need to follow a clear, structured approach focusing on the necessary skills, tools, and hands-on experience. Here’s a direct and factual breakdown:
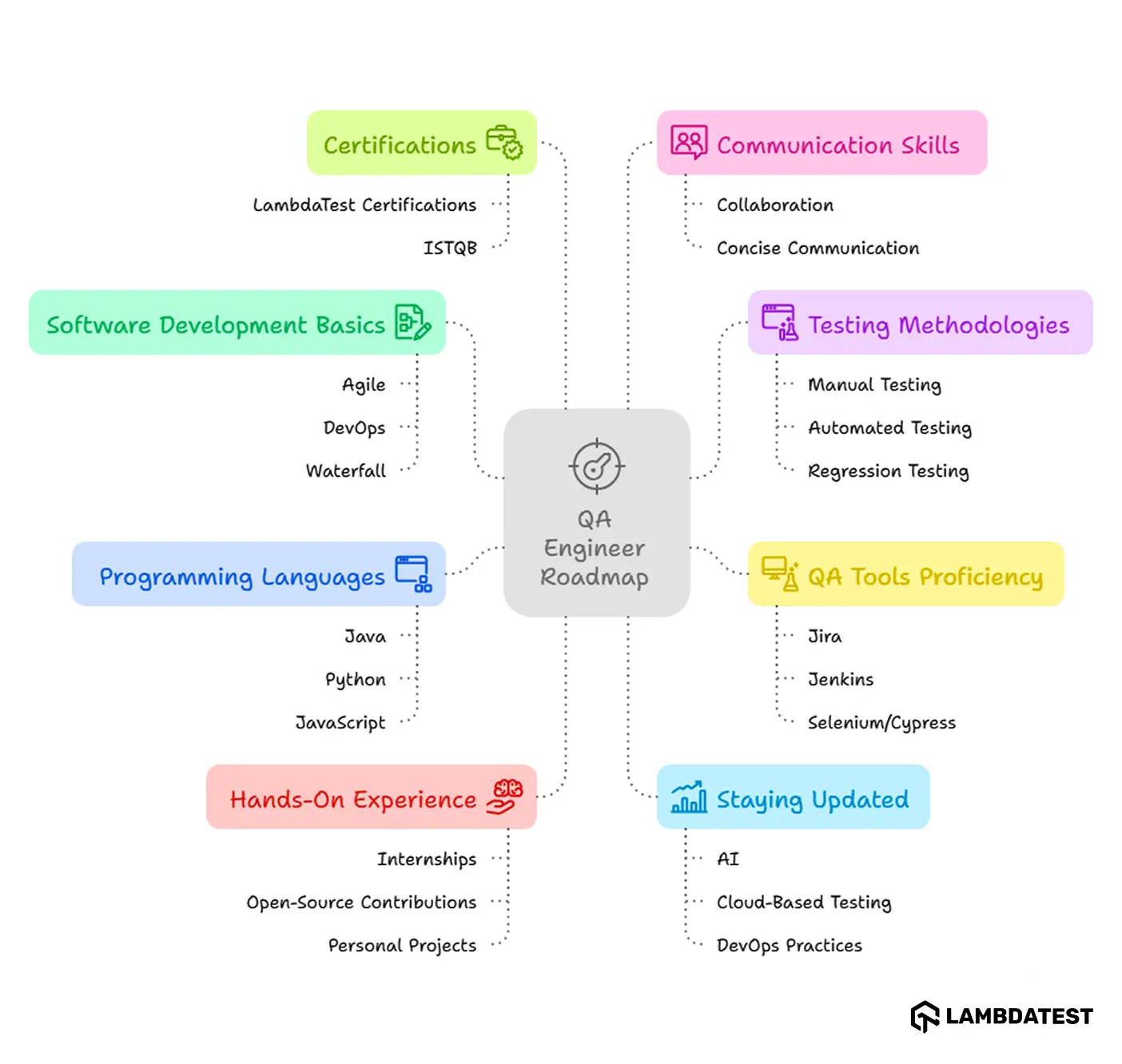
1. Understand Software Development Basics
Learn about software development methodologies like Agile, DevOps, and Waterfall, as QA Engineers work within these frameworks to ensure testing aligns with development processes.
Here's how top companies define the role of a QA Engineer, explore real-world job descriptions:
Amazon- Quality Assurance Engineer I
Microsoft - Software QA Engineer II
Google - Senior Test Engineer
2. Learn Testing Methodologies
Familiarize yourself with:
- Manual Testing: Identifying issues manually.
- Automated Testing: Using tools like Selenium and JUnit to speed up testing.
- Regression Testing: Ensuring that new changes don’t break existing functionality.
3. Gain Proficiency in QA Tools
Learn essential QA tools such as:
- Jira: For bug tracking.
- Jenkins: For continuous testing and continuous delivery
- Selenium/Cypress: For automating tests.
Mastering these tools will enhance your effectiveness as a QA Engineer.
4. Learn Programming Languages
Knowledge of programming languages like Java, Python, and JavaScript is crucial for writing automated tests and understanding the code you're testing.
5. Take Certifications
You can choose from various software testing certifications to validate your skills and enhance your job prospects. LambdaTest Certifications and ISTQB (International Software Testing Qualifications Board) are highly recognized in the industry.
LambdaTest, a GenAI-native platform, allows you to perform manual and automated testing across 5000+ real desktop and mobile environments, providing hands-on experience to boost your expertise.
6. Get Hands-On Experience
Build your skills by developing personal automation frameworks through our internship program. You can also contribute to LambdaTest’s public projects on GitHub and collaborate with a global testing community to sharpen your automation skills in real-world environments.
Or you can also apply for the LambdaTest Open Source Program to take it a step further:
- Access to Unlimited Open-Source Testing: Test across 5,000+ real browsers and devices for free
- Financial Sponsorships: Get support for scaling, infrastructure, and new feature development
- Boost Your Reach: Gain visibility through LambdaTest blog features and social media promotions
- Mentorship and Guidance: Access expert advice to grow your open-source project
- Connect and Collaborate: Join a global community of testers and contributors
7. Develop Communication Skills
QA Engineers must effectively communicate test results and collaborate with developers, product managers, and stakeholders. Clear, concise communication is essential.
8. Stay Updated
Keep up with emerging trends in AI, cloud-based testing, and DevOps practices to remain competitive and adaptable in the evolving field of software testing.
What is the Role of a QA Engineer?
As a QA Engineer, your role is not just about testing; it's about shaping the product from a quality standpoint. You ensure the product is defect-free, secure, and user-friendly. Your day-to-day tasks may include:
- Test Automation: Writing scripts to automate tests, which helps improve efficiency and repeatability.
- Cross-functional Collaboration: Working with developers, project managers, and other stakeholders to ensure smooth communication and timely identification of issues.
- Test Documentation: Creating comprehensive test reports that detail findings, issues, and suggestions for improvement.
- Quality Metrics Monitoring: Tracking the quality of products by monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs) related to defect rates, test coverage, and execution speed.
Essential Skills for QA Engineers in 2025
As a Quality Assurance A Engineer, staying current with the latest skills and technologies is crucial. Here are the essential skills every QA Engineer should focus on in 2025:
- Test Automation: Mastering automated testing tools such as Selenium, Cypress, and Playwright is essential. Automation helps speed up the testing process and improves efficiency.
- Programming Languages: Knowledge of languages like Java, Python, and JavaScript is necessary for writing automated tests and integrating with CI/CD pipelines.
- Performance Testing: Understanding tools like JMeter and LoadRunner to assess the software's performance under stress or high loads.
- Bug Tracking and Management: Familiarity with tools like Jira and Bugzilla to report and track defects efficiently.
- Continuous Integration (CI): Proficiency in CI tools like Jenkins to automate the process of integrating code and running tests.
- Soft Skills: Strong analytical thinking, attention to detail, and effective communication skills are also necessary for a QA Engineer to collaborate with teams and ensure product quality.
Tools and Technologies for QA Engineers
To be an effective QA Engineer, you must be well-versed in the latest tools and technologies that facilitate testing. Here are the most common ones:
- Jenkins: As a QA Engineer, Jenkins is a vital tool for integrating testing within the CI/CD pipeline. By automating the execution of your tests every time there’s a new code push or build, Jenkins helps identify defects early in the development process.
- Jira: Jira is more than just a bug-tracking tool; it’s central to managing your testing workflow. As a QA Engineer, you will use Jira to log defects, track their status, and manage your test cases.
- Postman: As a Quality Assurance Engineer, testing APIs is a major part of your responsibility. Postman allows you to easily send requests to APIs, validate responses, and automate API testing.
- Cucumber: Cucumber is a Behavior-Driven Development (BDD) tool that helps you automate acceptance tests in a way that’s easy to understand for both technical and non-technical stakeholders. As a QA Engineer, Cucumber allows you to write tests in Gherkin, a natural language syntax.
- Docker: Docker is a containerization platform that is becoming increasingly important for QA Engineers. Docker allows you to create isolated environments where you can run your tests in a consistent setup, regardless of the underlying system.
Key Metrics for QA Engineers to Track
Tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) is essential for monitoring the effectiveness of your testing efforts. Some important metrics to focus on include:
- Defect Density: The number of defects found relative to the size of the application. This helps gauge the quality of the software.
- Test Coverage: The percentage of the codebase covered by tests. A higher test coverage indicates thorough testing.
- Defect Resolution Time: The time taken to fix defects after they are reported. Shorter times improve the efficiency of the development process.
- Escaped Defects: Defects that are found by users after the software has been released. This metric helps assess the overall effectiveness of your testing strategy.
Challenges Faced by QA Engineers
QA Engineers face various challenges that impact their work and software quality.
- Time Constraints: Testing often gets compressed into tight timelines, making thorough testing difficult.
- Integration of New Tools: Adapting to the constantly evolving toolset and automation frameworks can be overwhelming.
- Complex Software Systems: Testing modern, complex systems with multiple integrations and dependencies can be resource-intensive.
- Cross-team Collaboration: Miscommunication with development or product teams can lead to misalignment on testing priorities or project goals.
These common challenges are frequently explored in QA engineer interview questions to assess both technical ability and problem-solving mindset in high-pressure scenarios. These issues are often discussed in QA interview questions, as they help evaluate how candidates tackle real-world problems.
How Much Does a QA Engineer Make?
The salary of a QA Engineer depends on several factors, including experience, location, and industry. According to the Careerist, in the United States,the salary breakdown for QA Engineers is as follows:
- Entry-level QA Engineers can expect to earn between $50,000 and $70,000 Engineer/Salary) annually.
- Mid-level QA Engineers can earn between $70,000 and $100,000.
- Senior QA Engineers with experience in automation or leadership roles can make over $100,000 per year.
Future Outlook and Career Planning
The demand for QA Engineers is expected to grow in the coming years, driven by the increasing need for high-quality software and rapid product development cycles. As technology evolves,
- AI-Driven Testing: Tools using AI for test automation, defect prediction, and visual validation (e.g., Testim, Applitools) are becoming mainstream.
- Shift-Left & DevOps Integration: QA is moving earlier into the development cycle, with engineers contributing to CI/CD pipelines and collaborating closely with developers.
- From QA to Quality Engineering: The focus is shifting from finding bugs to preventing them, through strategic test design and continuous feedback loops.
- Performance & Security Focus: Skills in tools like JMeter and OWASP ZAP are increasingly valuable as performance and security become critical quality benchmarks.
- Domain Expertise: Specialized knowledge in fields like fintech, healthcare, or e-commerce helps QA Engineers deliver more relevant and compliant test coverage.
Key Trends to Watch:
Conclusion
As a QA Engineer, you play a vital role in ensuring the quality and reliability of software products. By mastering the right skills, using the latest tools, and adopting best practices, you can excel in this career.
Whether you’re just starting or advancing in your career, the demand for skilled QA Engineers will continue to grow, offering a rewarding and dynamic career path.
On This Page
- What is a QA Engineer?
- Roles and Responsibilities of a QA Engineer
- How to Become a QA Engineer?
- What is the Role of a QA Engineer?
- Essential Skills for QA Engineers in 2025
- Tools and Technologies for QA Engineers
- Key Metrics for QA Engineers to Track
- Challenges Faced by QA Engineers
- How Much Does a QA Engineer Make?
- Future Outlook and Career Planning
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Did you find this page helpful?
More Related Hubs

Start your journey with LambdaTest
Get 100 minutes of automation test minutes FREE!!

