What is Regression Testing: Definition, Types, Examples
Devansh Bhardwaj
Posted On: December 21, 2023
![]() 59726 Views
59726 Views
![]() 7 Min Read
7 Min Read
Updating a large and complex codebase can be challenging. When adding new features, fixing bugs, or improving what’s already there, there’s a chance of accidentally affecting the application’s working, whether it’s a mobile app, a web application, or a website. Developers often perform automated unit testing to prevent these issues, but these tests don’t always catch everything. That’s where regression tests becomes very important.
Regression testing is a type of software testing that ensures recent code changes have not adversely affected existing features. It involves retesting the software after modifications to confirm that previously developed and tested functionality still performs correctly. This process helps identify bugs that might have been introduced into existing areas of a software application due to new changes or enhancements. Not identifying these issues can negatively impact how users feel about your software and can also affect your profits.
In this blog, we will learn what regression tests are, its types, and how it works.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
- What is Regression Testing?
- Regression Testing example
- Why is Regression Testing important?
- When to perform Regression Testing?
- How to perform Regression Testing?
- Developing Regression Testing strategy
- Regression Testing Tools
- Regression Testing techniques
- How much Regression is required?
- Retesting vs Regression Testing: Difference
- Selecting Test Cases for Regression Testing
- Advantages of Regression Testing
- Challenges of Regression Testing
- Best Practices of Regression Testing
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is Regression Testing?
Regression testing is a software testing process conducted after code changes to ensure new updates don’t negatively impact existing functionalities. It helps identify whether new or reemerging bugs are introduced, maintaining software stability and performance consistency.
Every time a change is made, regression tests are put into practice to make sure that it does not unintentionally cause any functional or performance problems. By performing this kind of testing, developers hope to find and address a persistent issue: the reappearance of old defects brought on by the adoption of fresh code changes. Regression tests essentially serve as a safety net, assisting in maintaining the dependability and stability of the software during its cycle of ongoing development.
Example of Regression Testing in practice
Here is an example of Regression tests needed for the Tesla website. This company generates billions of dollars in annual revenues from its Website. Hence their websites must always be up and running – functionally, reliably, and with good performance.
Example – Tesla
On the front page of Tesla.com, you can see all Tesla’s products.
![]()
When Tesla releases their next product, i.e., the Cyber Truck, the developers at Tesla will add a new entry to the Website, most likely next to Model Y. But a lot of care needs to be taken to ensure that even though new UI flows are added to a new “Cyber Truck” entry on the main page, the rest of the product UI flows continue to work functionally as before. A Regression test suite is executed for this purpose. These Regression test cases can be manually executed or automated using a prevalent test automation framework called Selenium.
Let’s say one of the Regression tests fails; this means that an existing function of the Website broke while adding a new product flow. This bug needs to be immediately logged and fixed. This Regression test suite should be executed every time a minor or a significant UI flow addition/changes are made to the Website.
Similarly, the Regression test suite should also be enhanced to cover more UI flows with the help of newer test cases. This ensures that the Website is always up and running; any time there is a breakage, it is immediately detected and flagged with the help of a Regression test suite.
In the next section, we will talk about different Regression testing tools.
Why is Regression Testing important?
When software developers fix a bug, add new functionality, or modify an existing feature or functionality, they must change the program code. Even a slight change will likely result in a plethora of new bugs. In such a scenario, a test engineer can reveal and pinpoint undesirable side effects through regression tests. A properly executed regression test suite is vital. It is imperative that after a bug fix, the original product does not stop working.
Check out our UI comparison tool to easily capture and compare UI screenshots.
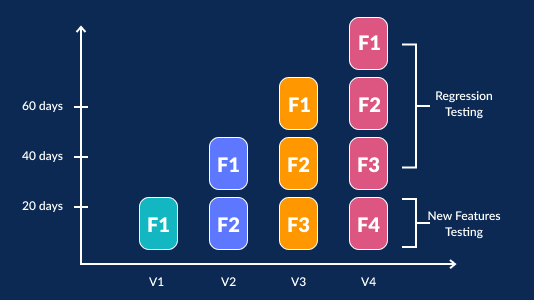
The below graph depicts the importance of the Regression test:
When to perform Regression Testing?
When new features or enhancements are deployed to an existing codebase or application, Regression tests is required. It ensures that any new functionality or update to an existing application works properly without any bugs or defects. Developers and testers often struggle to trace every code thread, with significant chances of code incompatibility issues. As a result, executing regression tests of their codebase (or application) allows them to detect defects earlier and ship applications with fewer risks.
It can be used when a deployment takes longer than expected. In this case, the tester should run Regression tests daily. Also, it is better to run Regression tests after functional testing for weekly releases.
When some functionality is overhauled, Regression test becomes even more critical as it may risk the codebase’s present functionality. Furthermore, repairing one defect can sometimes lead to another. In this case, you can use a blend of best debugging tools and regression tests to ensure that everything works as intended.
Want to make your life of testing easy and fuss-free while debugging? Try LT Debug Chrome extension!
How to perform Regression Testing?
Regression tests can be executed both manually and in an automated manner. Test Engineers primarily use special techniques and methods to perform Regression tests.
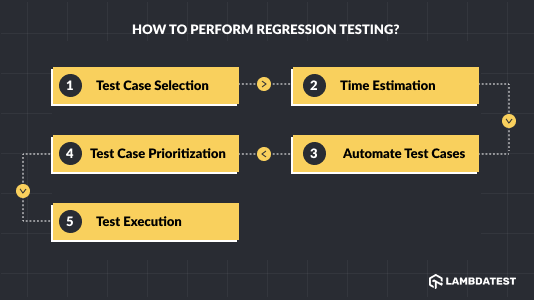
Below are the phases involved in Regression testing –
- Test Case Selection: The selection of test cases is determined by the component, one with a massive number of code modifications. Testers can split the tests into two categories: reusable test cases and obsolete test cases. Reusable test cases will be used in future Regression test cycles, but obsolete test cases will not be considered in further Regression test cycles.
- Time Estimation: Following the selection of test cases, the next step is to estimate the test execution time. Test case generation, test case evaluation, and other factors impact test execution time.
- Automate Test Cases: Testers should select between manual and automated Regression tests based on the number of test cases after time estimation.
- Test Case Prioritization: In this step, testers prioritize test cases based on recent code changes, minimizing Regression time and effort. The test cases with high priority are executed first, followed by medium and low priority.
- Test Execution: Finally, all test cases are run in the order of priority to find flaws and ensure that the application is functioning correctly. Automated regression testing tools like Selenium enable you to reduce test execution time and automate your Regression test suites more quickly.
Developing Regression Testing strategy
If you want to make the most of your Regression test suites, it is essential to plan a proper strategy by keeping certain factors in mind. This section, discusses some ways to help you create a winning Regression tests strategy:
- Execute all existing tests once again: After the product release, Test Engineers must check problem areas again. Many times this can be a challenge, especially when it comes to executing manual testing.
- Run high-priority tests first: About 50% of time spent on regression tests should be devoted to repeating tests that concern the application’s essential functionality.
- Check the complicated features next: Many applications have sophisticated and complicated parts, which can cause problems. Although the functionality is complicated to understand/comprehend, the quality of their functionality must be excellent.
- Execute Exploratory testing: While learning the software version’s new features, design new tests for them and execute them. In the course of this testing, many new bugs will be found.
Boost productivity and reduce time/efforts spent on running tests with the help of automated testing. Using automation scripts, it is possible to perform tests much quicker and in a more effective way.
Finally, it is imperative to perform random testing. A software tester assumes the role of a user and tests randomly. Because there is always some problem or another, it is important to perform random testing.
Regression Testing Tools
Here are some tools that can be useful for creating and executing Regression tests. However, the requirements of each product should be thoroughly studied before deciding which ones to use.
LambdaTest
LambdaTest is an AI-powered test orchestration and execution platform that lets you run manual and automated tests at scale with over 3000+ real devices, browsers, and OS combinations. LambdaTest incorporates screenshots and video recordings, as well as collaborative and responsive testing options. It is extensively used in the DevOps context for complete cross browser compatibility testing.
Selenium
Selenium is an open-source web automation testing tool to test websites and web apps. It is considered one of the top automated Regression tests tools for web application testing. Selenium supports different browsers and platforms for automated browser testing. You can run your automated visual regression tests with Selenium on LambdaTest across 3000+ real browsers and OSes. LambdaTest also allows you to perform Selenium Visual Testing on Cloud that capture and compare screenshots and deliver seamless user experience.
Watir
Watir, short for Web Application Testing in Ruby, is a free tool that uses the Ruby programming language for testing web applications directly. It doesn’t require a separate server, making it straightforward to use. Watir is user-friendly, allowing people to write test code easily without having to go through a lot of instructions.
This tool is compatible with various browsers and operating systems. One of its key features, the Attach Method, keeps the original application window connected even when a new window from a linked domain is opened. Additionally, Watir is versatile in simulating user actions on websites, such as clicking links, filling in forms, and checking if texts are correct.
Serenity
Serenity BDD stands out as an open-source framework designed to enhance the quality of automated regression and acceptance testing. Its flexibility and ease of maintenance are key features that make it a preferred choice for many developers. Beyond just facilitating test creation, Serenity BDD excels in providing detailed test reports. These reports are not only comprehensive but also user-friendly, offering clear insights into the testing process.
One of the standout aspects of Serenity BDD is its ability to give a clear picture of the application coverage. It informs you about which parts of your application have been tested, helping you identify any gaps in your testing strategy. This feature is particularly useful for ensuring that all critical functionalities of your application are thoroughly tested and validated.
Silk Test

Silk Test is a versatile automated testing tool designed for enterprise-level software. It specializes in functional and regression testing, ensuring that applications perform as expected after updates or changes. Silk Test is particularly effective for cross-platform testing, making it suitable for applications that run on multiple devices and operating systems. Additionally, it supports localization testing, which is crucial for verifying that your mobile applications, including web, native, and hybrid apps, are tailored correctly for different languages and regions. This tool streamlines the testing process, making it more efficient and reliable for a wide range of software applications.
QA Wizard

QA Wizard Pro is an automation tool designed for functional and regression testing across web, Windows, and Java applications. It also excels in conducting load testing for web applications, ensuring they can handle high user traffic without compromising performance. This tool streamlines the testing process, making it more efficient and effective in identifying potential issues in various types of applications. Its versatility in handling different testing scenarios makes it a valuable asset for ensuring software quality and reliability.
Apache JMeter
Apache JMeter is a free Java-based tool used for testing the load, performance, and functionality of web applications. It has also been developed to test other aspects, like how efficiently a server handles multiple user requests at the same time.

JMeter has a user-friendly graphical interface, created using the Swing graphical API, making it easy to operate. It works on any system that can run a Java virtual machine, such as Windows, Linux, and Mac. This makes JMeter an excellent choice for conducting functional performance and regression testing across various technologies.
IBM Rational Functional Tester (RFT)
IBM’s Rational Functional Tester (RFT) is a software automation tool designed for various types of testing, including functional, regression, GUI (Graphical User Interface) testing, and data-driven testing. It is versatile and supports a wide range of applications, such as web-based, .NET, Java, Siebel, SAP, applications based on terminal emulators, and PowerBuilder.
RFT is equipped with a script editor that uses natural language, making it easier to visualize and edit tests. It also provides screenshots to help users see exactly what the tests are doing. One of its key features is ScriptAssure technology, which helps create tests that remain effective even when there are frequent changes in the user interface.
Furthermore, RFT includes a feature to record user actions, offering various customization options and capabilities for maintaining scripts. It also facilitates collaboration among team members by allowing them to share functional tests. These tests can be run in hybrid environments, adding to the tool’s flexibility and utility in diverse testing scenarios.
Regression Testing techniques
Depending on your Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) and the new feature or update you aim to deploy, you can implement various types of regression tests. However, it is essential to understand the several regression tests types to choose the right one.
Below are the different types of regression testing –
Corrective Regression Testing
Corrective Regression testing is one of the simpler forms of Regression tests requiring minimal effort. Corrective Regression tests involves no changes to the existing codebase and adding new functionality to the application. You simply need to test the existing functionality and the test cases that go with it rather than creating new ones.
Unit Regression Testing
Unit Regression testing is an integral part of Regression tests in which the code is tested in isolation. All other interactions, integration, and dependencies are disabled while performing unit Regression testing, and the emphasis is on single unit code. Typically, this testing is done during low traffic and off-peak hours.
Selective Regression Testing
Selective Regression testing analyzes the impact of existing code and the effect of both new and existing code. Common elements like variables and functions are incorporated into the application to identify quick results without affecting the process.
Progressive Regression Testing
Test cases are created based on the requirements of a progressive regression test. When there are only minor product improvements, the new test cases are designed without affecting the existing code of a product.
Complete Regression Testing
Some minor or significant changes might have a massive impact on the product. Complete Regression testing is used in this instance when there are significant modifications to the current code. It aids in the repair of any modifications made during the testing process.
Partial Regression Testing
When new code is added to an existing codebase, partial Regression testing is conducted. This aids in the discovery of critical bugs in existing code and allows them to be tested without affecting the system.
Retest-all Regression Testing
Re-test all Regression testing is the process of re-executing all the test cases to ensure that there are no bugs due to code changes in an application. This type of testing needs immense effort from the QA front.
How much Regression is required?
In the previous section, we touched upon selecting the regression test cases. Now let’s look at how much regression is required.
The amount of regression required solely depends on the extent of an application’s new features or updates. If the fix or upgrade is major, extensive Regression tests of all application test cases is required. Since the update is significant, the test cases will also be huge; therefore, you can perform automated testing of all repetitive test cases. For the newly added functionality, the test suites require constant upgrades.
The next step is identifying appropriate Regression test cases in order to cover all of an application’s functionality. However, when the app’s changes are substantial, the most effective approach is to find relevant test cases based on the upgrades and the affected sections of the application. It will help you in cutting costs, time, and effort.
Retesting and Regression Testing: Difference
In this section, we will explore how Retesting is different from Regression testing.
If you are a beginner in the test automation domain, these two-term Retesting, and Regression testing might sound similar. However, both are different from each other.
Retesting is the continuous process of testing specific test cases to ensure that the bugs are fixed and the web product’s functionality works fine in the final execution. The same set of unit tests is repeated in re-testing to verify the code’s functionality. In other words, re-testing is executing the same manual or automated tests to validate that the new build is working flawlessly.
Regression testing is a technique to verify the new build whenever any code commit takes place. In this process, a tester’s job is to verify that no new bugs are included in the code due to software modification and adjustments. Once the Regression test suite is developed, you can automate it using an automation testing tool. However, this does not apply to retesting.
Let’s look at the detailed comparison of Retesting vs. Regression testing
| It is a technique to ensure the test cases are bug-free and run flawlessly in the final execution after the bugs are fixed. | It is a technique to ensure that the code functionality remains unaffected after the application’s adjustment or modifications, |
| It is performed for failed test cases. | It is performed for passed test cases. |
| It ensures the original bug in the build is fixed. | It tests the code for unintended side effects. |
| Automated Retesting of tests is not possible. | Automated Regression testing is possible. |
| It is also known as planned testing. | It is also known as generic testing. |
| It can’t be performed in parallel with Regression tests due to its high priority. | It can be performed in parallel with re-testing due to its lower priority in a few instances and resource availability. |
| It doesn’t include bug verification as a part of testing. | It includes bug verification as a part of testing. |
| It is performed across all software releases. | It is performed across a few latest versions of software. |
| It is less time-consuming. | It is more time-consuming as it involves a detailed analysis of what went wrong in previous software versions. |
Selecting Test Cases for Regression Testing
End-to-end testing is crucial for running your application smoothly across all browsers and operating systems. However, it has been observed that a substantial number of defects leak into an application during the deployment stage. This could be critical from the customer’s standpoint since it could increase turnover and create a terrible customer experience. Therefore, it’s vital to select the test cases wisely based on the customer requirements.
Below are the steps to select regression test cases –
- Select test cases with frequent bugs: A simple code commit can sometimes break an application’s complete functionality. As a result, testers should keep these factors in mind while selecting test cases that involve frequent defects. They can also choose the test cases depending on their prior knowledge and experience with the Regression test cycle.
- Select test cases with critical core features: To ensure that the application runs smoothly across multiple platforms, testers should first focus on choosing test cases that cover the essential key functionalities of an application. For example, an e-commerce application must include multiple payment methods, website navigation, extensive search functionality, etc.
- Select test cases with recent code updates: When new code or features are incorporated into an application, the probability of defects rises, and code must be modified multiple times. As a result, it is critical to prioritize test cases and choose those that involve frequent codebase adjustments and upgrades.
- Select test cases based on the user interface: Testers need to choose test cases based on the areas visible to users. The user interface’s visible elements are the brand logo, images, button text, and so on. However, these issues have low priority, yet they are crucial from the user’s perspective.
- Select integration-based test cases: End-to-end testing ensures an application runs smoothly across different platforms. There may be instances where one component’s functionality is dependent on another. For example, if the function of component C2 is dependent on C1 and C2 is modified, the behavior of C1 may be impacted. Therefore, running regression tests of such bugs is crucial to validate integration-based test scenarios.
- Select complex test cases: Complex test case execution can result in app crashes and poor performance. Testers must use various techniques to test complexity and ensure that all sophisticated test scenarios are addressed.
- Incorporate risk-based testing: In the risk-based testing method, testers prioritize the test cases based on the recent code changes, thereby reducing Regression time and efforts.
The priorities of regression test cases can be classified into three categories –
- High priority: It covers an application’s critical and core functionality, recent code modifications, and components with a significant chance of bugs.
- Medium priority: It involves aspects like field validations and other negative test scenarios.
- Low priority: It includes other functionality like user-interface areas like brand logos, button text, etc.
Advantages of Regression Testing
The software market growth relies heavily on the success of Regression tests. Besides functional tests, Regression tests must be performed at each stage to ensure application stability. DevOps teams can utilize Regression tests in their software development lifecycle and ensure their existing code isn’t affected by the newly added updates and features.
Below are a few advantages of Regression testing:
- It ensures smooth business operations by ensuring the new features are not affecting the existing codebase, dramatically improving the overall product quality.
- Regression tests may be used during the integration testing phase also. In this case, they will help detect bugs across different systems when putting two systems together.
- Manual test cases can be automated, and this automation principle can be applied to Regression checks. Automated Regression testing can help you cut down test execution time by multiple folds.
- A successfully executed Regression test suite ensures that the bugs are detected and fixed early and eventually helps achieve a high Customer Satisfaction Index (CSI).
- It thoroughly validates that the code modifications do not impact the correct functionality of already tested code – detect every side effect of any code change.
Challenges of Regression Testing
It helps uncover bugs while introducing new features or updates in an existing codebase and facilitates mitigation of app crashes and performance bottlenecks. However, while running a Regression test, a tester faces different challenges.
Shown below are a few of the challenges faced by testers –
- Test suite cost and time: A Regression test suite requires continuous improvement when new features are deployed. As a result, the number of test cases varies, and new tests must be re-run with older tests, which require a lot of time to complete. Incorporating parallel testing can be a viable solution as it allows you to run test cases concurrently across multiple browsers and OS combinations, reducing lead time by multiple folds.
- Complex test cases: As the project or application becomes more complex, the number of test cases and their complexity also rise. Thus, consuming a significant amount of time and resources.
- Maintenance: As the application grows in size, the complexity of test cases in Regression test suites increases. Therefore, proper maintenance is vital to handle the complexity and execution time.
Best Practices of Regression Testing
Some challenges were covered in the previous section. Now, let’s look at some of the best Regression testing practices.
- With the introduction of newer upgrades, it is best to keep your Regression test suites up to date. Include tests to see whether the old feature is still functional.
- Check for the features and capabilities of applications used by users, and then include a test case to check whether that specific functionality is working as expected.
- Use Regression testing frameworks in your project to save additional maintenance.
- Update your test designs based on devs and testers requirements.
- Automated Regression testing can help you save time, cost and deliver products faster.
It helps identify bugs ahead of the deployment deadline. However, as your application becomes more complicated, the number of test cases will expand. As a result, you need a cloud-based testing infrastructure that can scale as your testing requirements grow.
AI-powered test orchestration and test execution platforms like LambdaTest help you achieve that. It offers a cloud-scalable infrastructure of 3000+ real browsers, devices, and OS combinations for your test automation needs. With LambdaTest, you can harness the power of the online Selenium Grid to execute thousands of parallel tests in a jiffy, thereby cutting down your test execution time and getting faster feedback on code changes.
Subscribe to the LambdaTest YouTube Channel and stay updated with the latest tutorial around Selenium testing, Cypress E2E testing, Mobile App Testing Tutorial, and more
In addition to web testing, you can perform mobile app testing on an online device farm of 3000+ real Android and iOS devices.
Conclusion
Automated regression testing verifies that recent changes in a software application haven’t adversely affected existing functionalities. This efficient approach uses automation tools to run a comprehensive set of tests repeatedly, ensuring stability and functionality post-updates, and providing detailed insights into any failures.
It can be done in many ways, including Corrective Regression testing, Progressive regression testing, Retest-All Strategy, and Selective Strategies. Some tips for strategies pertaining to Regression tests include Running High priority tests first, executing exploratory testing, etc.
Even though Regression tests consumes vast amounts of resources, it saves your effort and time. It eases the lives of devs and testers in their agile software development lifecycle and yields maximum output.
Don’t forget if you think Regression testing is complex; there are always products like LambdaTest to help you. You can also kick start your visual regression testing journey with LambdaTest for pixel-by-pixel comparison and identify Visual UI mismatches.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is regression testing?
Regression testing is the retesting of modified software to ensure that existing functionalities are not adversely affected.
What is regression testing in Agile?
Regression testing in Agile ensures software stability and high-quality delivery with each product increment. By validating existing functionality against new code modifications, it maintains software integrity and reliability.
What is regression testing and retesting?
Regression testing combines retesting of fixed defects and testing of unchanged functionalities to ensure the overall stability and integrity of the software.
What is visual regression testing?
Visual regression testing is a technique that compares screenshots of the application before and after changes to identify any visual discrepancies.
Why do we do regression testing?
Regression testing is conducted to validate that changes to the software have not introduced new defects or caused any regression in existing functionalities.
Why is regression testing important?
Regression testing is important to ensure that changes or updates to the software do not introduce new defects or cause regression of existing functionalities.
What is a regression test example?
Regression testing is carried out each time a change is made. For example, consider a situation where a tester finds an issue with the login button. After developers fix this issue, the login button is checked to make sure it works as it should. At the same time, tests are also done on other features that are connected to the login button to ensure everything else is still functioning correctly.
What are types of regression testing?
- Regression testing can be categorized into several types, each serving a specific purpose:
- Full Regression Testing: This involves testing the entire application to ensure that new code changes have not affected any existing functionality. It’s comprehensive but can be time-consuming.
- Partial Regression Testing: This type tests a particular subset of the application where changes have been made, along with any areas that might be affected by these changes.
- Unit Regression Testing: This focuses on individual units or components of the software to check if small changes in the code have caused any issues.
- Progressive Regression Testing: Used when there are significant changes in the original code. It focuses on testing the new functionality along with related areas but does not retest the unchanged parts.
What are the 3 techniques of Regression Testing?
The following three techniques can be used for regression testing:
- Re-testing all test cases
- Select test cases for Regression
- Prioritize test cases
What are function regression tests?
Functional testing is usually done at certain times during the development process, like after a new feature is added or just before a big release. On the other hand, regression testing is done regularly throughout the development cycle, especially after any changes are made to the code. This is to make sure that the changes don’t affect the existing features of the software.
What is regression test selection?
Regression test selection techniques involve using existing tests from a test suite to check a program that has been modified. There are many different methods for selecting regression tests, but comparing and evaluating them can be challenging. This is because each technique has its own specific objectives.
What is Regression Testing vs UAT?
In UAT, the question to be answered is: Will the user be able to, or even want to, use the product? UAT has little to do with the actual functionality of the software. Before UAT is performed, all features and functionality are largely completed, tested, and approved by the organization.
How to do regression testing?
Regression testing can be done by creating test cases that cover critical functionalities, executing them after each change, and comparing results with previous test runs.
How to do regression testing manually?
Manual regression testing involves executing test cases and comparing results manually, ensuring that critical functionalities are not impacted by the changes made.
What is the best time to perform regression testing?
The best time to perform regression testing is after making changes to the software, such as implementing new features or fixing bugs, to ensure that existing functionalities remain intact.
Got Questions? Drop them on LambdaTest Community. Visit now