Power Your Software Testing with AI and Cloud
Supercharge QA with AI for Faster & Smarter Software Testing

- Automation
- Home
- /
- Learning Hub
- /
- What Is Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
What Is Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
Explore how Robotic Process Automation software bots automate repetitive work, enabling faster execution, fewer errors, and seamless business process optimization.
Last Modified on: September 26, 2025
- Share:
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a technology that uses software bots to automate repetitive, rule-based tasks across digital systems. It helps organizations save time, reduce errors, and free up human teams for more strategic work.
Overview
Robotic Process Automation is a technique that uses software bots to automate repetitive tasks by emulating human interactions with digital systems.
Benefits of Robotic Process Automation
- Increased Efficiency and Speed: RPA accelerates task execution by automating repetitive work and operating around the clock.
- Cost Savings: It reduces labor costs and costly errors by replacing manual processes with automation.
- Improved Customer Service: RPA delivers faster, consistent responses by automating customer interactions.
- Better Compliance: It ensures audit-ready, regulation-compliant processes with minimal human oversight.
- Enhanced Data Accuracy: RPA minimizes errors and improves real-time data insights for smarter decisions.
- Scalability and Flexibility: It scales effortlessly to handle workload spikes without additional staffing.
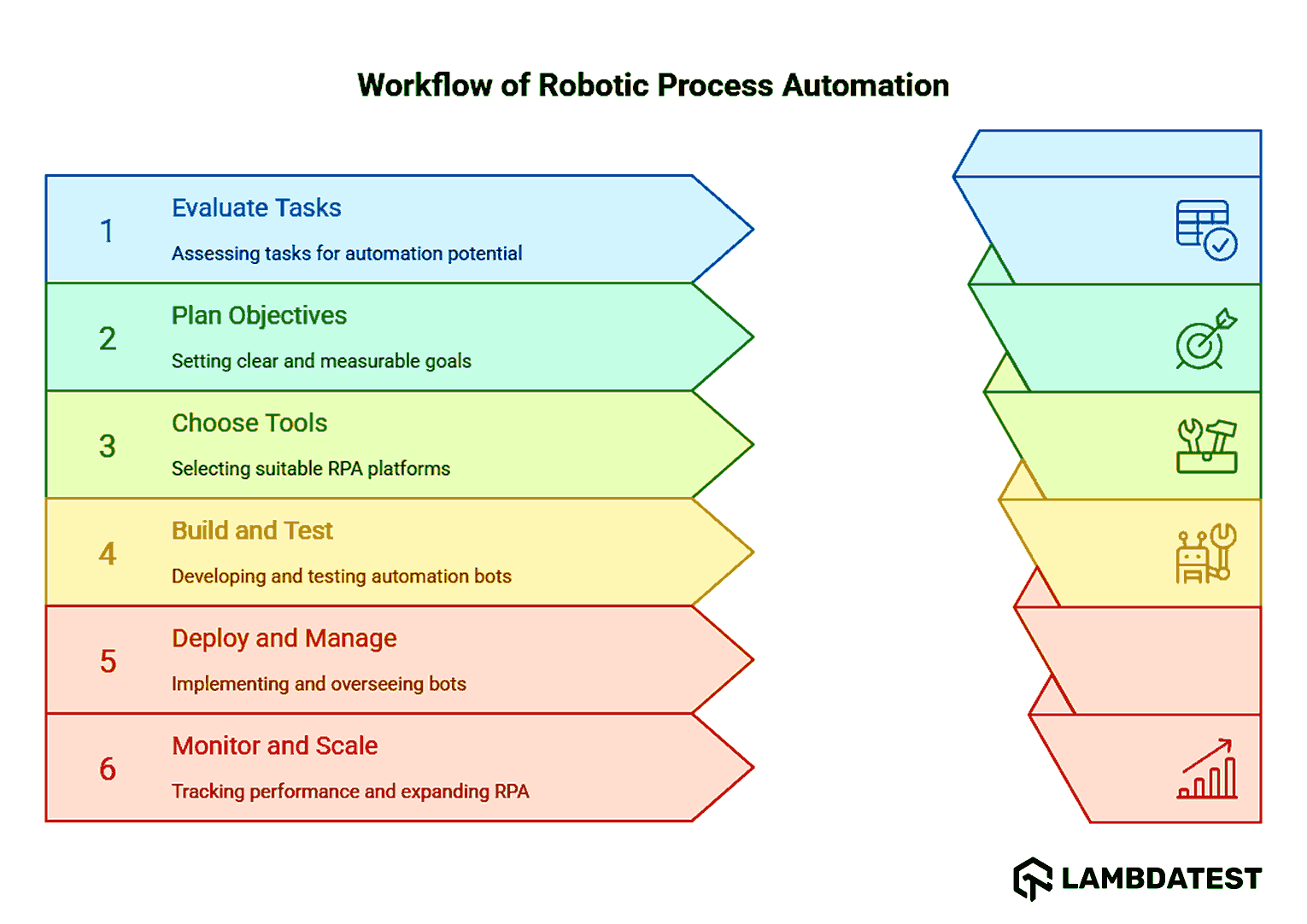
Working of Robotic Process Automation
- Identify and Evaluate: Use process mining to target high-volume, rule-based tasks for automation.
- Plan and Define Objectives: Set measurable goals and KPIs aligned with business outcomes.
- Choose the Right Tools and Vendors: Select RPA platforms that are scalable, secure, and AI-ready.
- Build and Test: Develop bots with clear logic and validate performance through testing.
- Deploy and Manage: Launch bots in production with real-time monitoring and control.
- Monitor, Maintain, and Scale: Continuously optimize bots and expand automation across teams.
What Is Robotic Process Automation?
Robotic Process Automation refers to the use of software robots (bots) that can execute structured, rule-based tasks by interacting with digital systems the same way a human would, at the UI layer.
- Clicking through web and desktop applications.
- Copying data between systems.
- Extracting data from documents or emails.
- Logging into portals.
- Triggering scheduled workflows.
Unlike traditional API-based automation, RPA uses intelligent automation techniques where bots work in environments without requiring system-level access or code changes, which makes them well-suited for legacy systems and siloed tools.
Why Robotic Process Automation?
According to a survey by WifiTalents, 78% of organizations using Robotic Process Automation reported a faster processing time.
Here are some of the benefits that RPA provides:
- Increased Efficiency and Speed: RPA enables businesses to automate repetitive tasks, significantly speeding up processes. Bots work 24/7, ensuring faster completion of tasks and increasing overall throughput.
- Cost Savings: By automating manual tasks, RPA reduces labor costs and eliminates errors that would require costly corrections. It also cuts down on operational expenses, providing an efficient alternative to human-intensive processes.
- Improved Customer Service: RPA enhances customer experience by automating customer interactions, such as query handling and ticket routing. Bots can provide instant responses, ensuring faster and more reliable customer service.
- Better Compliance and Regulation Adherence: RPA ensures processes are executed in full compliance with legal and regulatory standards. It maintains audit trails and helps businesses stay compliant with minimal risk of oversight or non-compliance.
- Enhanced Data Accuracy and Reporting: By digitizing processes, RPA improves the accuracy of data management and reporting. It also provides valuable insights through real-time analytics, helping businesses make data-driven decisions.
- Scalability and Flexibility: RPA allows organizations to scale operations quickly without the need to hire additional staff. It can handle increased volumes of tasks, especially during peak periods, ensuring continuous efficiency.
- Easy Development and Implementation: With the use of low-code tools, RPA can be easily customized and implemented even by non-technical users, reducing the time and effort needed for development.
Note: Generate, author and evolve tests with KaneAI. Book a Demo!
Types of Robotic Process Automation
Let's explore the three primary types of Robotic Process Automation. Each type can address specific business needs and operational requirements.
- Attended RPA: It works on a user's machine and requires human initiation to perform tasks. These bots assist employees by automating repetitive tasks during their workflow.
For example, a customer service representative can trigger an attended bot to retrieve customer information, allowing for quicker and more accurate responses. This type of automation is ideal for front-office operations where human interaction is essential. - Unattended RPA: Its bots operate independently without human intervention. They execute tasks based on predefined rules and schedules, handling back-office processes such as data entry, invoice processing, and report generation. These bots run in the background on servers or virtual machines, ensuring continuous operation and scalability.
- Hybrid RPA: It integrates both attended and unattended bots to automate end-to-end processes that require human judgment and decision-making.
For instance, in loan processing, an attended bot can assist with data entry and document retrieval, while an unattended bot performs background checks and generates reports. This approach ensures seamless collaboration between humans and bots, optimizing both front and back-office operations.
What Tasks RPA Can Automate?
RPA can enhance operations by automating repetitive tasks such as data management, email processing, and system monitoring.
- User Account Management: Managing user access and permissions is essential but can be cumbersome, especially in large businesses with frequent employee changes. RPA automates the creation, modification, and deletion of user accounts across various systems. This ensures that employees always have the appropriate level of access while reducing manual workload and improving security.
- Data Entry and Migration: Handling large volumes of data manually is time-consuming and prone to errors. By automating data entry and migration, RPA ensures data flows seamlessly across systems, minimizing manual intervention. This is particularly useful when transferring data between systems during updates, making the transition smoother and more efficient.
- Email Processing: Email management can quickly become overwhelming, especially in large organizations. RPA steps in by automating the categorization, sorting, and even responding to routine emails. It can handle common queries and route important emails to the right department, saving time and improving overall productivity.
- System Monitoring and Reporting: Many IT issues arise without warning, but RPA can monitor systems continuously for performance or security issues. Instead of waiting for human detection, automated monitoring picks up problems early, generating real-time alerts and reports. This means faster problem resolution and more proactive management of IT systems.
- Report Generation: Generating IT reports is a repetitive task that can eat into valuable time. RPA automates the creation of regular reports, such as system performance or security logs, and ensures they are delivered to the appropriate stakeholders. This saves time and ensures that key decision-makers always have the latest data at their fingertips.
- IT Service Desk Operations: Routine IT support tasks like password resets, basic troubleshooting, and service ticket categorization are time-consuming. RPA can take over these repetitive tasks, allowing IT teams to focus on more complex issues. It can even automatically assign tickets to the right team members, ensuring faster resolution times.
- Compliance Monitoring and Reporting: Compliance is a constant challenge in IT, especially with changing regulations. RPA ensures that systems and processes comply with internal policies and external standards. It can automatically monitor compliance, flag any issues, and generate the necessary documentation for audit trails, reducing manual oversight and the risk of non-compliance.
How Does Robotic Process Automation Work?
To leverage the full potential of Robotic Process Automation, it's crucial to take a structured approach.
- Identify and Evaluate: Identify tasks that are repetitive, rule-based, high in volume, and stable over time, and use process mining tools to gain data-driven insights into current workflows to prioritize the most impactful tasks for automation.
- Plan and Define Objectives: Set clear, measurable goals like ROI and time savings, align all stakeholders, and define KPIs to track and ensure the automation delivers value and meets business objectives.
- Choose the Right Tools and Vendors: Evaluate RPA platforms based on their scalability, security, ease of use, and future potential for AI integration to ensure they support long-term automation needs.
- Build and Test: Develop the automation bots by defining their logic and sequence, followed by thorough testing to ensure they perform as expected without errors before going live.
- Deploy and Manage: Deploy the bots into the production environment and provide continuous monitoring to ensure their smooth operation, making adjustments as needed.
- Monitor, Maintain, and Scale: Regularly track bot performance, update them as systems evolve, and plan for scaling the RPA program across the organization while maintaining efficiency.
Real-World Use Cases of Robotic Process Automation
Let's explore some of the real-world use cases of Robotic Process Automation where RPA is transforming industries by automating repetitive tasks, enhancing efficiency, and improving accuracy.
- Healthcare: In healthcare settings, RPA can automate the patient onboarding process, including data entry, insurance verification, and appointment scheduling. This reduces administrative burdens, minimizes errors, and allows healthcare professionals to focus more on patient care.
- Finance and Accounting: Financial institutions can leverage RPA to automate the processing of invoices, from data extraction to approval workflows. This not only speeds up the process but also ensures compliance with financial regulations and reduces the risk of human error.
- Retail and eCommerce: Retailers can implement RPA to automate order processing, inventory updates, and customer notifications. This leads to faster order fulfillment, improved customer satisfaction, and better resource management.
- Human Resources: HR departments can use RPA to automate tasks such as document verification, account creation, and training schedule coordination for new hires. This streamlines the onboarding process, reduces administrative workload, and enhances the employee experience.
- Customer Service: Customer service teams can deploy RPA to automatically categorize, prioritize, and respond to customer emails. This ensures timely responses, improves customer satisfaction, and allows support agents to focus on more complex inquiries.
How to Leverage AI for Robot Process Automation?
RPA excels at automating repetitive, rule-based processes, whereas AI introduces capabilities such as learning, reasoning, and understanding unstructured data.
A range of AI automation tools, spanning natural language processing, machine learning, and intelligent document processing can be integrated with RPA to build smarter automation systems.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP allows RPA bots to understand and communicate in human language, whether it’s text or speech. This makes it possible to automate customer service tasks like chatbots and process documents. AI-powered RPA bots can read and respond to text just like a human, making it easier to handle things like customer inquiries or feedback.
- Machine Learning: Machine learning helps RPA bots learn from past data, which means they can adapt to new situations without needing to be reprogrammed. With AI, RPA can predict problems before they happen, spot unusual patterns, and even suggest improvements to processes. This makes automation more efficient and flexible in a wide range of industries.
- Intelligent Decision-Making: AI adds the ability for RPA bots to make decisions. Instead of following rigid rules, AI-driven bots can make choices based on the data they get. For example, AI can decide which action to take depending on customer behavior or market trends, making automation more flexible and responsive to changes.
- Cognitive Automation: AI helps RPA bots tackle tasks that need thinking, learning, and decision-making. For example, AI can analyze unstructured data like emails, images, and documents, allowing RPA bots to handle customer service requests or automatically extract information from invoices. This makes RPA smarter and more capable of handling complex tasks.
- Automation of Complex Processes: Traditional RPA is great for repetitive tasks, but AI automation takes it a step further by handling more complex processes. AI allows RPA bots to analyze large amounts of data, make predictions, and even deal with exceptions or surprises, making it useful for more complex jobs in areas like finance, healthcare, and manufacturing.
- Improved Exception Handling: AI helps RPA bots deal with unexpected situations. When things go off track, AI can spot the problem, analyze it, and find a way to fix it. This makes RPA much more reliable, as it can continue running even when things don’t go as planned.
- Enhanced Data Analytics: AI boosts RPA by making it easier to analyze data. It helps bots gather insights, predict trends, and provide useful information that can help improve processes. This way, businesses can use the data from their automation to make better decisions and optimize their operations continuously.
Challenges of Robotic Process Automation
While RPA offers powerful efficiency gains, it also comes with notable challenges:
- Resistance to Change: Introducing RPA can face resistance from employees who are used to traditional ways of working. There can be a reluctance to adopt new technology, especially when it seems complex or unfamiliar. To overcome this, organizations need to offer proper training, clear communication, and gradual implementation to help employees feel more comfortable with the transition.
- Loss of Human Touch: Automation can sometimes make processes feel less personal. For example, in customer service, tasks like answering basic queries can be automated. But there is a risk of losing the human connection that’s often necessary in sensitive or complex situations. Balancing automation with human intervention is crucial to maintaining quality service.
- Over-Reliance on Automation: Over-dependence on RPA can lead to problems when bots encounter unexpected situations. Bots are effective in executing repetitive tasks, but can struggle with exceptions. It’s important to have oversight and be prepared for situations where human intervention is needed to ensure the process runs smoothly.
- Emotional Impact of Repetitive Tasks: While RPA can reduce the burden of repetitive tasks, the initial shift can cause stress for employees, especially those whose roles are directly impacted by automation. Employees may feel uncertain about how their jobs will change, which can affect morale. Addressing these concerns early and showing how RPA will improve job satisfaction is important for smooth adoption.
- Ethical Concerns: RPA, especially when integrated with AI, can raise ethical questions, particularly around data privacy and decision-making. Organizations must ensure that RPA systems follow proper security protocols and comply with regulations. Transparency in how RPA decisions are made and clear accountability for automated actions are critical.
Best Practices for Using Robotic Process Automation
Here are some best practices for implementing RPA effectively, ensuring that organizations can maximize the benefits while minimizing challenges:
- Start with the Right Processes: Identify processes that are repetitive, rule-based, high-volume, and stable over time. These tasks are the best candidates for automation, as they will provide the most significant impact. Use process discovery and task mining tools to get a clear, data-driven view of your current workflows and pinpoint areas that can benefit the most from automation.
- Set Clear Objectives and Metrics: Before implementing RPA, define clear business goals and success metrics. Whether it's improving efficiency, reducing costs, or enhancing accuracy, having measurable objectives will help track progress and evaluate the return on investment (ROI). Align stakeholders on these goals to ensure the automation project meets expectations.
- Involve Key Stakeholders Early: RPA implementations often succeed when all key stakeholders, including business leaders, IT teams, and end-users, are involved from the beginning. Their insights will help identify the right processes to automate and ensure smooth execution. Regular communication keeps everyone aligned and ensures that RPA initiatives meet organizational goals.
- Choose the Right RPA Tool: There are many RPA tools available, each with its strengths. Evaluate tools based on their scalability, security, ease of use, integration capabilities, and support for future technologies like AI and machine learning. Make sure the selected tool fits your organization’s needs and aligns with long-term strategic goals.
- Start Small and Scale Gradually: Begin with a small, manageable automation project to prove the concept. This allows you to learn and refine the process before scaling to more complex or enterprise-wide automation. Starting small reduces the risk and provides tangible results that can build confidence in RPA adoption across the organization.
- Test Rigorously Before Deployment: Thorough testing is crucial to ensure that bots operate as expected under real-world conditions. Test bots in various scenarios to identify and fix bugs or issues before deploying them to production. Use detailed test cases to simulate edge cases and ensure the bots can handle exceptions effectively.
- Provide Continuous Monitoring and Support: Once RPA bots are deployed, continuous monitoring is necessary to ensure their performance remains optimal. Monitor bots for any performance issues, bottlenecks, or failures. Be proactive in identifying problems and updating bots as business processes or underlying systems change.
- Focus on Employee Upskilling: RPA implementation may raise concerns among employees about job displacement. Address these concerns by focusing on upskilling employees to work alongside RPA. Provide training to help them understand the technology and how they can use it to enhance their roles. Employees who see RPA as a tool to increase their productivity will be more likely to embrace it.
- Scale with Governance and Security: As RPA expands, ensure that proper governance and security practices are in place. Implement role-based access control and ensure that bots follow security protocols, especially when handling sensitive data. Governance ensures that automation is aligned with organizational standards and compliance requirements.
- Document and Standardize Processes: Document the processes you automate, including the logic and rules that the bots follow. This helps create a standard for future automation projects and makes it easier to troubleshoot or make improvements later. Standardization also helps with scaling and ensures that automation is consistent across the organization.
Future of Robotic Process Automation
Let’s break down five key shifts that are shaping the future of RPA and what they mean for teams.
- RPA Goes No-Code: Automation is no longer just for developers. No-code tools let business users build bots using drag-and-drop interfaces. This speeds up adoption and puts automation in the hands of everyday teams.
- Bots Get Smarter With AI: RPA is evolving from rule-following bots to AI-powered digital workers. With machine learning, bots can understand documents, adapt to changes, and make decisions based on context.
- Cloud-Native RPA Takes Over: Cloud-based RPA makes deployment faster and scaling easier. It removes infrastructure painpoints and supports distributed teams, becoming the default for modern automation.
- Process Intelligence Fuels Strategy: Techniques like process mining help pinpoint where automation delivers the most value. This shift brings smarter, data-driven decisions instead of guesswork in automation planning.
- RPA Becomes Part of a Bigger Stack: RPA won’t stay standalone, it's merging into broader automation platforms. Expect tighter integration with AI, APIs, and workflows for seamless end-to-end automation.
Conclusion
Robotic Process Automation helps organizations streamline repetitive tasks, cut costs, and boost accuracy without changing existing systems. When applied strategically, RPA becomes more than just automation; it enhances agility, improves compliance, and frees teams to focus on high-value work. The key to success lies in smart implementation, ongoing oversight, and empowering people to work alongside bots, not against them.
Citations
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA) Adoption: A Systematic Literature Review: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/362035572
On This Page
- What Is Robotic Process Automation?
- Why Robotic Process Automation?
- Types of Robotic Process Automation
- What Tasks RPA Can Automate?
- How Does Robotic Process Automation Work?
- Real-World Use Cases of Robotic Process Automation
- How to Leverage AI for Robot Process Automation?
- Challenges of Robotic Process Automation
- Best Practices for Using Robotic Process Automation
- Future of Robotic Process Automation
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Did you find this page helpful?
More Related Hubs

Start your journey with LambdaTest
Get 100 minutes of automation test minutes FREE!!


