Power Your Software Testing with AI and Cloud
Supercharge QA with AI for Faster & Smarter Software Testing

- Manual Testing
- Home
- /
- Learning Hub
- /
- Manual Testing Tools
Top 15 Must-Have Manual Testing Tools for QA Teams [2026]
Explore the top 15 manual testing tools to boost QA efficiency, track defects, validate UI/UX, and manage test cases across browsers, devices, and workflows.
Last Modified on: November 5, 2025
- Share:
Manual testing remains a vital part of software development. While automation efficiently handles repetitive and regression tasks, human testers are essential for exploratory testing, UI validation, and complex scenarios that require critical judgment.
Choosing the right manual testing tools can be challenging since some focus on bug tracking, others on organizing test cases, and a few specialize in security or usability checks. Different manual testing tools offer distinct features, from lightweight options for small teams to enterprise platforms with dashboards and reporting, and specialized solutions for mobile testing.
Overview
Why Use Manual Testing Tools?
Manual testing tools support human-driven QA, uncovering subtle issues, improving workflow, and enhancing overall software quality beyond automation capabilities.
- Human Skills: Detect issues only a skilled tester can notice, such as subtle UI quirks or unexpected behavior patterns.
- Exploratory Work: Evaluate software freely without pre-written scripts to discover hidden edge cases and workflow problems.
- Interface Validation: Ensure visual layouts, responsiveness, and element interactions perform correctly across devices and screen sizes.
- Test Tracking: Track, organize, and monitor test cases and results efficiently to maintain coverage and clarity.
- Bug Documentation: Generate clear defect documentation with steps, screenshots, and context for developers to reproduce and fix issues.
- Changing Requirements: Adjust testing to evolving features or requirements without rewriting automated test scripts.
- Project Economics: Optimize testing for smaller projects or rapid deadlines where full automation may be unnecessary or impractical.
- Complex Logic: Validate multifaceted business rules and unusual user paths that are difficult for automation scripts.
- Quick Results: Provide on-the-spot insights during development, speeding up issue detection and iterative improvement.
- Standards Checking: Manually check accessibility, security, and regulatory standards that require human judgment for accurate validation.
What Are Some of the Top Manual Testing Tools?
Below is a list of some of the top manual testing tools:
- LambdaTest: A cloud-based platform that enables you to perform live testing for web and mobile apps across multiple desktop and mobile environments.
- Bugzilla: Open-source bug tracker that helps teams log, monitor, and prioritize software defects with customizable workflows and detailed reporting.
- TestLodge: A simple test management tool to organize test cases, plan execution, and link results to requirements and bug trackers.
- ZAP (OWASP): Security-focused tool for manual web testing, inspecting requests, detecting vulnerabilities, and analyzing traffic for safer applications.
- Jira: Flexible issue and project tracker supporting manual testing workflows, bug assignment, progress monitoring, and team collaboration efficiently.
When Should Teams Choose Manual Testing Instead of Automation Testing?
Manual and automation testing both ensure software quality, but the choice depends on the task and context.
- Choose Manual Testing When: Exploring new features, testing complex logic, performing one-off checks, or validating UI/UX and accessibility that need human insight.
- Choose Automation Testing When: Running repetitive regression tests, performing high-volume or performance testing, or validating stable features where scripts save time and reduce errors.
Why Need Manual Testing Tools?
Manual testing tools help you catch bugs that automated scripts miss. Humans spot issues that look fine technically but don't work in practice.
These tools support testing that needs human judgment - checking user experience, exploring edge cases, and validating complex flows. Good tools organize test work, track bugs, and keep teams coordinated. Manual testing remains essential for areas requiring human insight, even as automation grows.
- Human Skills: Testers spot things automated checks miss. Experience helps catch problems that look fine technically but don't work in practice.
- Exploratory Work: Testing without fixed scripts finds unexpected issues. Good testers know where software usually breaks and check those areas.
- Interface Validation: Checking if buttons work, forms submit properly, and screens look right on different devices requires actual use.
- Test Tracking: Tools help manage what needs testing, what passed, and what failed. Prevents losing track of coverage.
- Bug Documentation: Clear reports with steps to recreate problems help developers understand and fix issues efficiently.
- Changing Requirements: When features change during development, manual testing adjusts without rewriting automation code.
- Project Economics: Small projects or tight deadlines often make manual testing more practical than building automated suites.
- Complex Logic: Business rules with multiple conditions and unusual user paths are difficult to automate effectively.
- Quick Results: Manual testing provides immediate feedback during development rather than waiting for automated test runs.
- Standards Checking: Accessibility compliance, security validation, and regulatory requirements need human verification beyond technical scanning.
Manual testing tools support these activities by organizing work, tracking progress, and facilitating team communication throughout development cycles.
What Are Some of the Top Manual Testing Tools?
Manual testing tools enable precise test case creation and execution while integrating with bug tracking and reporting systems. These tools streamline manual testing workflows and improve software quality.
Types of manual testing tools include cloud-based platforms for cross-device testing, open-source test management tools, and enterprise solutions for full test lifecycle management.
Each tool offers features such as simple interfaces, flexible integrations, or detailed analytics, helping QA teams optimize testing processes. Organizations can choose manual testing tools based on requirements like cloud support, budget constraints, or enterprise-level capabilities.
1. LambdaTest
LambdaTest is a cloud testing platform that enables manual and automated testing at scale across 3000+ browser/OS combinations, and 10,000+ real devices.
It offers a real-time, scalable online grid of browsers, operating systems, and devices, allowing QA teams to verify UI behavior, ensure cross-platform functionality, and execute manual test cases without managing physical infrastructure. This helps teams maintain consistency, responsiveness, and reliable UI performance across both desktop and mobile environments.
Key features:
- Browser Testing: Perform manual cross-browser testing on over 3000 browser and operating system combinations to ensure consistent application behavior everywhere.
- Live Device Testing: Execute real-time manual tests on actual Android and iOS devices to verify functionality and appearance.
- Scalable Cloud Grid: Run multiple manual tests simultaneously on cloud infrastructure without needing to manage physical testing devices.
- Visual UI Testing: Check UI layouts, responsiveness, and visual consistency across different screen sizes and devices manually.
- Responsive Testing: Validate application behavior, layout, and interaction on different resolutions and device orientations manually for quality assurance.
- Screenshot and Recording: Capture screenshots and record testing sessions to document manual test results and aid in debugging effectively.
LambdaTest is best for performing real-time, cross-browser and mobile manual testing on virtual devices and browsers, enabling testers to validate apps instantly across multiple platforms without physical devices.
2. Bugzilla
Bugzilla is a widely used open-source bug tracking and manual testing tool that helps teams systematically record, monitor, and resolve software defects. The tool keeps detailed records of each bug, who found it, its severity, what needs fixing, and who’s working on it. It is highly customizable to fit various workflow needs and supports advanced querying and reporting features to help analyze and prioritize issues effectively.
Key features:
- Bug Management: Logs bugs with details like steps to reproduce, severity level, and current status.
- Custom Setup: Changes fields, statuses, and workflows to match how the team actually works.
- Search and Reports: Find specific bugs quickly and create reports showing bug trends and progress.
- Email Updates: Automatically notify team members when bug status changes or new issues get assigned.
- User Access: Controls who can see or edit different bugs based on team roles and project needs.
- Time Records: Tracks how long bugs take to fix for better planning on future projects.
- Review Process: Handles code reviews and approvals connected to specific bug fixes.
- Tool Connections: Works with code repositories and other development tools teams already use.
- Code Review: Views and discusses code changes directly within bug reports.
Bugzilla is ideal for structuring bug tracking and issue management during manual testing, offering customizable workflows and detailed reporting.
Note: Run live-interactive tests across 3000+ browser and OS combinations. Try LambdaTest Now!
3. TestLodge
TestLodge is a manual testing tool that helps that helps QA teams create, organize, and manage manual test cases efficiently. It supports structured manual testing workflows, links test cases to requirements, plans test runs, and tracks execution results. TestLodge also integrates with popular bug tracking tools, making defect management seamless and enabling better collaboration among testers.
Key features:
- Test Case Management: Create, organize, and maintain manual test cases with detailed steps and expected results.
- Test Planning: Plan test runs and schedules to ensure comprehensive manual testing coverage.
- Execution Tracking: Record test results, pass, fail, blocked, and maintain a detailed execution history.
- Requirements Linking: Connect test cases to requirements for traceability and coverage verification.
- Bug Tracker Integration: Sync with Jira, Bugzilla, Mantis, and other defect management tools.
- Collaboration: Share test plans, cases, and results among team members for coordinated manual testing.
- Reporting: Generate progress reports, test coverage summaries, and team performance metrics.
TestLodge is ideal for organizing manual test cases, planning test cycles, and tracking execution progress through a simple, intuitive interface.
4. ZAP
ZAP is a free and open-source manual testing tool from OWASP for security testing web applications. It works between the tester’s browser and the application, capturing and examining web traffic. ZAP enables hands-on inspection of requests, responses, and vulnerabilities, making it practical for manual security testing and helping testers ensure web applications are safe.
Key features:
- Man-in-the-Middle Proxy: Captures and inspects traffic between the tester’s browser and the web app for detailed manual checking.
- Active Scanning: Executes scans to identify known security weaknesses in web applications during manual testing.
- Passive Scanning: Observes traffic without altering it to detect potential security issues safely.
- AJAX Spidering: Explores dynamic website content by simulating user actions for manual vulnerability discovery.
- WebSocket Testing: Enables testers to monitor, inspect, and manipulate WebSocket communications for security verification.
- Fuzzer: Sends various inputs to discover hidden bugs or vulnerabilities in the application manually.
- Custom Scan Profiles: Allows testers to focus scans on specific application areas for targeted manual testing.
- Add-On Support: Let users enhance ZAP with plugins to extend functionality for manual security testing.
- API Testing: Tests web APIs, including JSON and XML, for vulnerabilities during manual testing procedures.
ZAP is best used for manual security testing of web applications, inspecting traffic, identifying vulnerabilities, and analyzing requests and responses.
5. Jira
Jira is a project and issue tracking tool that helps testers manage bugs, tasks, and workflows during manual testing. This manual testing tool helps you capture, prioritize, assign, and monitor issues throughout the software development lifecycle. Its flexible workflow engine allows QA teams to organize bug tracking processes, stay updated on progress, and collaborate effectively to ensure defects are resolved accurately.
Key features:
- Bug Documentation: Records issue details, severity, screenshots, and version numbers to track bugs during manual testing.
- Workflow Setup: Configures how bugs move through team processes from identification to resolution for manual QA tracking.
- Task Assignment: Assigns bugs to team members and sets priorities to organize manual testing work efficiently.
- Progress Tracking: Monitors bug status with notifications to keep testers updated during manual test cycles.
- Code Integration: Links with GitHub, Bitbucket, and build systems to connect manual QA findings with development work.
- Visual Boards: Displays Scrum and Kanban boards for organizing and tracking manual testing tasks clearly.
- Automated Rules: Supports automatic notifications and updates for manual testers to stay informed about bug changes.
- Reporting Tools: Generates charts and reports showing bug trends and manual testing team performance metrics.
- Communication: Enables comments, mentions, and updates to coordinate manual testing and bug resolution effectively.
Jira is useful for managing manual testing workflows, tracking bugs, assigning tasks, and enabling effective collaboration across QA processes.
6. Redmine
Redmine is an open-source project and issue tracking tool that also supports manual testing activities, enabling teams to manage tasks and workflows effectively. QA teams can customize workflows, control access, and plan testing schedules while coordinating communication and linking test results to development changes. Its flexible architecture allows teams to tailor the system to meet the needs of structured manual testing processes, ensuring efficiency and consistency.
Key features:
- Multi-Project Support: Organizes multiple projects and subprojects to manage manual testing efforts across different applications efficiently.
- Issue Customization: Adapts bug tracking with custom statuses and workflows to fit manual QA testing processes.
- Access Management: Controls which team members can view or edit project and testing data based on roles.
- Project Planning: Uses Gantt charts and calendars to schedule, track, and monitor manual testing activities over time.
- Time Recording: Logs hours spent on manual testing tasks for better planning and reporting of QA effort.
- Custom Data Fields: Adds extra fields to capture test-specific information beyond standard bug tracking requirements.
- Team Communication: Provides wikis, forums, and file sharing to coordinate manual testing and QA team activities.
- Version Control Links: Connects with Git, SVN, and other repositories to link manual testing results with code changes.
- Plugin Extensions: Supports add-ons and test management plugins to enhance manual testing workflow management.
Redmine is a free, flexible project management tool that allows for tracking manual testing across multiple projects and workflows.
7. FogBugz
FogBugz is an issue tracking tool designed to help you manage manual testing activities and log bugs efficiently. You can create detailed bug cases with descriptions, screenshots, and priority levels, track testing progress using Kanban or Scrum boards, and organize project backlogs. The tool allows you to assign tasks to team members, and its built-in workflows and tracking features ensure that QA teams can stay focused on testing while maintaining organized bug management.
Key features:
- Case Tracking: Creates cases for bugs with descriptions, screenshots, version details, and priorities for manual testing records.
- Ready-Made Workflows: Provides built-in workflows to reduce setup time, letting testers focus on manual testing activities.
- Backlog Organization: Manages project backlogs, including manually found bugs for better planning and delivery tracking.
- Agile Boards: Use Kanban and Scrum boards for manual testers to visualize, manage, and track testing tasks.
- Issue Collection: Captures bug reports via email or web forms for manual testing teams to review efficiently.
- Work Assignment: Assigns cases to specific team members for clear responsibilities during manual testing and bug resolution.
FogBugz is ideal for combining manual testing management with efficient bug tracking, case assignment, and project backlog organization, helping you organize your testing workflows and ensure timely bug resolution.
8. TESSY
TESSY is a manual testing tool primarily used for embedded C/C++ software. It supports manual test design, execution, and reviews in safety-critical projects. You can create test cases, link them to requirements for traceability, execute tests, analyze results, measure code coverage, and review test data and scenarios. Detailed reporting and documentation help QA teams validate results, maintain compliance with industry standards, and manage structured manual testing workflows.

Key features:
- Manual Testing Tasks and Reviews: Supports manual tests and documentation reviews for safety-critical embedded C/C++ software projects.
- Test Design and Execution: Guides users through the creation, organization, and manual execution of test cases using graphical editors.
- Requirements Management and Traceability: Links requirements to test cases manually, generating coverage analyses and impact reports.
- Test Data and Scenario Editors: Facilitates manual entry, editing, and review of test data and scenarios for testing validation.
- Coverage Measurement: Provides multiple code coverage metrics for testers, displaying results in project structure and reports.
- Documentation and Reporting: Generates detailed reports on manual testing results, scenario coverage, and requirements validation.
TESSY is ideal for safety-critical manual testing of embedded C/C++ software, supporting test execution, coverage measurement, and compliance documentation and validating industry standard adherence.
9. Trac
Trac is an open-source manual testing tool that helps testers organize test cases, track defects, and document results. You can customize workflows, link issues to code changes, and maintain collaborative wiki pages for test plans, requirements, and outcomes. Built-in reporting and plugin support allow QA teams to monitor progress, summarize results, and extend the system to manage structured manual testing workflows efficiently.
Key features:
- Task Tracking: Tracks bugs, issues, and testing tasks through tickets for clear manual testing record-keeping.
- Workflow Setup: Customizes ticket types, workflows, and status fields to match manual QA testing processes.
- Code Integration: Links Git, Subversion, and Mercurial code changes directly to manual testing issues and documentation.
- Wiki Pages: Maintains test plans, requirements, and results collaboratively for documenting manual testing workflows.
- Progress Reports: Generates reports and queries to monitor manual testing progress and summarize QA outcomes.
- Plugin Support: Adds functionality through plugins for test case management, reporting, and enhanced manual testing workflows.
Trac is ideal for teams seeking flexible workflows, integration with code repositories, and efficient progress tracking.
10. SpiraTest
SpiraTest is a test management tool that helps testers manage manual testing activities. Testers can create, organize, and execute test cases, link them to requirements for full traceability, log defects, and monitor progress. The manual testing tool provides reporting and dashboards to track manual testing coverage and team performance, while customizable workflows and collaboration features allow QA teams to efficiently manage structured manual testing processes.
Key features:
- Test Case Management: Create, organize, and maintain manual test cases for structured execution and tracking by QA teams.
- Requirement Traceability: Link manual test cases to requirements to ensure full coverage and traceability during manual testing.
- Test Execution: Allows testers to manually execute test cases, record results, and log defects efficiently.
- Defect Tracking: Log and manage defects discovered during manual testing, including severity, status, and resolution details.
- Reporting and Metrics: Generate reports and dashboards summarizing manual testing progress, coverage, and team performance.
- Workflow Customization: Customize workflows, statuses, and user roles to fit manual QA processes and testing methodologies.
- Collaboration Tools: Facilitate team communication through comments, notifications, and shared test artifacts for manual testing coordination.
- Integration Support: Connects with version control, CI tools, and other systems to provide context for manual test results.
SpiraTest is ideal for managing the full manual testing lifecycle, from test case creation and execution to defect logging and requirement traceability.
11. Mantis
Mantis is an open-source bug tracking tool that helps testers manage manual testing activities effectively. You can log issues with detailed descriptions, track progress, assign tasks, and prioritize bugs throughout the testing lifecycle. This manual testing tool provides a flexible workflow and role-based access, allowing QA teams to organize manual test cases, monitor defect resolution, and collaborate efficiently, making it a practical solution for structured manual testing processes.
Key features:
- Issue Tracking: Logs bugs with descriptions, severity, steps to reproduce, and status for clear manual testing records.
- Workflow Customization: Configures workflows, statuses, and roles to match manual testing processes and team requirements.
- Task Assignment: Assigns issues to testers for accountability and efficient resolution during manual testing cycles.
- Progress Monitoring: Tracks bug resolution progress and sends notifications to keep manual testers updated.
- Reporting Tools: Generates reports and charts summarizing manual testing results, trends, and team performance.
- Collaboration Support: Allows comments, discussions, and attachments to coordinate manual testing and defect management.
- Plugin Extensions: Adds functionality through plugins for enhanced test management, reporting, and workflow customization.
Mantis is best suited for bug tracking and also supports manual testing activities, helping teams log issues, customize workflows, and track resolution progress with clear reporting and collaboration features.
12. TestLink
TestLink is an open-source manual testing tool that helps testers create, organize, and execute manual test cases efficiently. QA teams can track test results, link test cases to requirements, and monitor progress through test cycles. It supports collaboration among multiple testers, integrates with bug trackers like Jira, Bugzilla, and Mantis, and provides detailed reporting for manual testing outcomes.

Key features:
- Test Case Organization: Stores manual test cases with steps, expected results, and priorities for structured execution.
- Test Planning: Plans test cycles and tracks progress throughout manual testing phases for better coordination.
- Execution Records: Records test results, pass, fail, blocked, or not run, with notes for accurate manual testing tracking.
- Requirements Tracking: Links test cases to requirements to ensure all features are manually tested and verified.
- Progress Reports: Generates reports showing test results, coverage levels, and team productivity for manual testing oversight.
- Bug Tracker Links: Integrates with Jira, Bugzilla, and Mantis to associate defects with specific manual test cases.
- Team Access: Allows multiple testers to collaborate with permission levels for organized manual testing workflows.
- Automation Integration: Imports automated tool results alongside manual test data for comprehensive test reporting.
TestLink is ideal for structured manual testing with centralized test management, execution tracking, and reporting to help teams collaborate and monitor progress effectively.
13. Postman
Postman is a widely used manual testing tool for APIs that allows testers to create, send, and validate API requests manually. Testers can inspect responses, verify data formats, log defects, and organize requests into collections for structured manual testing workflows. Postman also supports collaboration, environment management, and documentation, making it easier for QA teams to coordinate and track manual API testing activities effectively.
Key features:
- Request Builder: Create and configure API requests manually with headers, parameters, and authentication.
- Response Inspection: View response status, body, headers, and cookies during manual testing.
- Test Scripts: Write pre-request and post-request scripts to validate API responses manually.
- Environment Management: Use different environments for manual API testing across development stages.
- Collections: Organize manual tests into collections for structured execution.
- Collaboration: Share collections and results with team members for coordinated manual testing.
- Documentation: Generate and maintain API documentation for manual test reference.
Postman is best for manual API testing, enabling testers to validate requests, inspect responses, and organize test collections while managing environments and collaborating efficiently.
14. Testopia
Testopia is an open-source manual testing tool integrated with Bugzilla that helps testers manage test cases, track execution, and log defects. You can create and organize manual test cases, plan test runs, execute tests, and link results to Bugzilla bugs. It provides reporting to monitor manual testing progress, coverage, and team performance, enabling structured workflows and effective collaboration among QA teams for managing manual testing projects efficiently.
Key features:
- Test Case Management: Create, organize, and maintain manual test cases with detailed steps and expected results.
- Test Execution: Execute manual test runs and record results for accurate tracking of testing activities.
- Bug Integration: Link test results to Bugzilla issues for streamlined defect tracking during manual testing.
- Test Planning: Organize test cycles and plan execution to ensure coverage of all features under manual testing.
- Reporting: Generate reports showing manual testing progress, coverage, and team performance metrics.
- Collaboration: Supports multiple testers with roles and permissions for organized manual testing workflows.
- Traceability: Maintains links between test cases, test runs, and defects for full manual testing traceability.
Testopia is best for managing manual test cases integrated with Bugzilla, allowing teams to execute tests, track progress, and generate detailed reports for improved traceability and collaboration.
15. Quality Center / ALM (Micro Focus)
Quality Center / ALM is a manual testing tool and test management platform that helps testers manage manual testing activities across the software lifecycle. You can create, organize, and execute manual test cases, link them to requirements for traceability, log defects, and monitor testing progress. This platform provides dashboards and reports to track status, trends, and team performance.
Key features:
- Test Management: Creates, organizes, and executes manual test cases with detailed steps and expected results for QA tracking.
- Test Lab: Manages manual test execution cycles, records results, and logs defects during manual testing activities.
- Requirements Management: Links requirements to manual test cases to ensure coverage and traceability from design to execution.
- Defect Tracking: Captures and tracks defects found during manual testing, supporting workflows, priority, and resolution tracking.
- Cross-Project Reporting: Provides dashboards and reports summarizing manual testing status, defect trends, and overall QA progress.
- Offline and Mobile Testing Support: Allows manual test execution on mobile or offline environments with later data synchronization.
- Integration: Connects with automation tools to combine manual testing results with automated testing workflows when needed.
- Regulatory Compliance: Supports audit trails, e-signatures, and standards compliance, ensuring structured manual testing in regulated projects.
It is best suited for comprehensive manual testing management across the software lifecycle, offering end-to-end traceability, defect tracking, and detailed reporting to support structured QA processes.
What Are the Differences Between Manual vs Automation Testing?
In the broader context of manual vs automation testing, manual testing is ideal for exploratory, ad-hoc, and usability scenarios, while automation testing excels in regression, performance, and repetitive test workflows.
Below are some of the core aspects that will help you understand the difference between manual vs automation testing, and how both approaches complement each other to deliver faster, more reliable software quality.
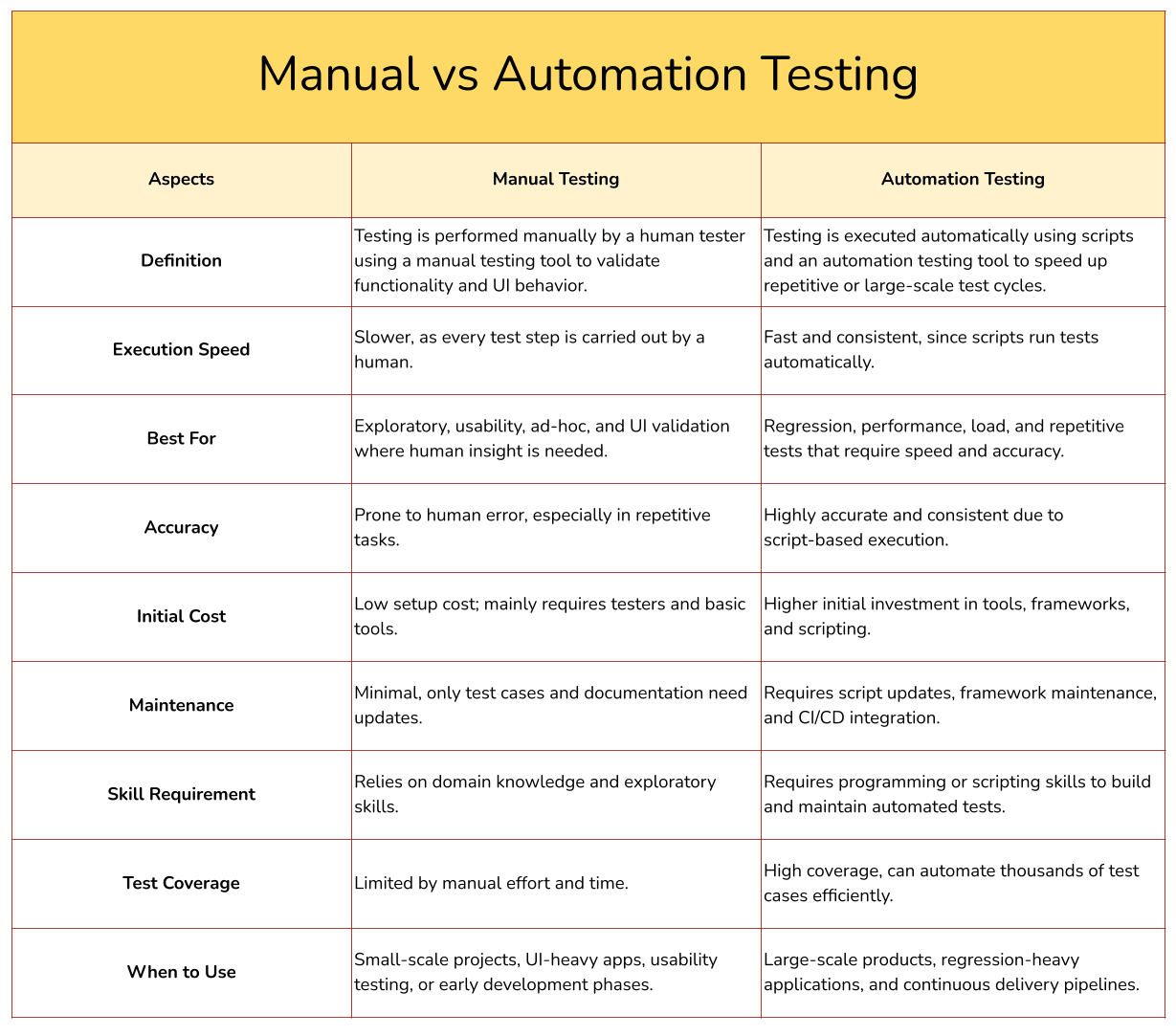
Manual testing relies on human effort to execute test cases, explore the application, and identify usability or visual issues, often using a manual testing tool for tracking, validation, and documentation. Automation testing, on the other hand, uses scripts and frameworks to run tests repeatedly with minimal human intervention, for which you can use automation testing tools.
If you're considering transitioning from manual to automation, there are a few important criteria to evaluate, such as test complexity, repeatability, ROI, and team readiness. To understand this shift in detail, check out our guide on how to move from manual testing to automation.
How to Perform Manual Testing With LambdaTest?
From the above list of manual testing tools, you have already learned about LambdaTest, which is a cloud-based cross-browser testing platform that allows you to perform manual testing on a wide range of browsers, operating systems, and devices without the need for local infrastructure.
Here’s a step-by-step guide to performing manual testing with LambdaTest on web and app:
Manual Testing with Live Web Testing
Manual testing with live web testing allows testers to interact with a real browser environment in real time. It helps identify UI, functional, and compatibility issues across different browsers, operating systems, and devices without setting up local test environments.
Below are the steps on how you can perform manual live testing for browser testing.
- Log In to LambdaTest: Access your LambdaTest account and navigate to the Real Time section.
- Web Browser Testing Option: Select the “Desktop” to start an with web browser live interactive testing session.
- Set the URL: Enter the complete website URL you want to perform manual testing on for accurate validation.
- Choose Environment: From the available options, select the desired operating system, browser, browser version, and screen resolution carefully.
- Launch Browser Session: Click the Start button to initiate your manual testing session and interact with the website directly.

Once the session is open, you can perform various activities such as marking bugs using the “Mark as Bug” option from the left menu.
You can capture screenshots to identify any UI issues related to responsiveness, record sessions, and view console/network logs to detect functional errors.
Additionally, the “Switch” option allows you to change the desired configuration on the go if you want to test the same website on a different browser, operating system, or browser version.
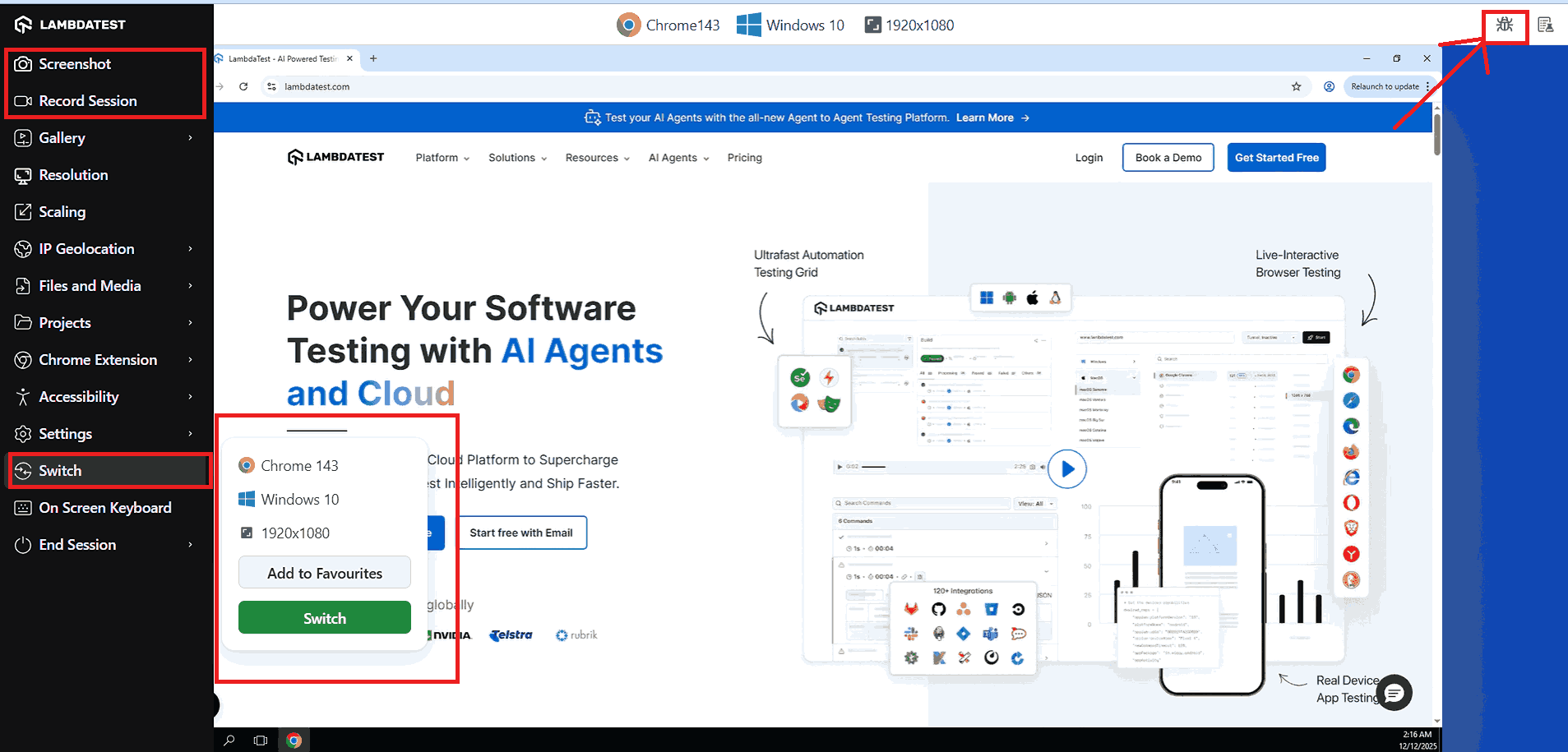
You can also perform Chrome remote debugging using the option in the right menu when testing on the Chrome browser.
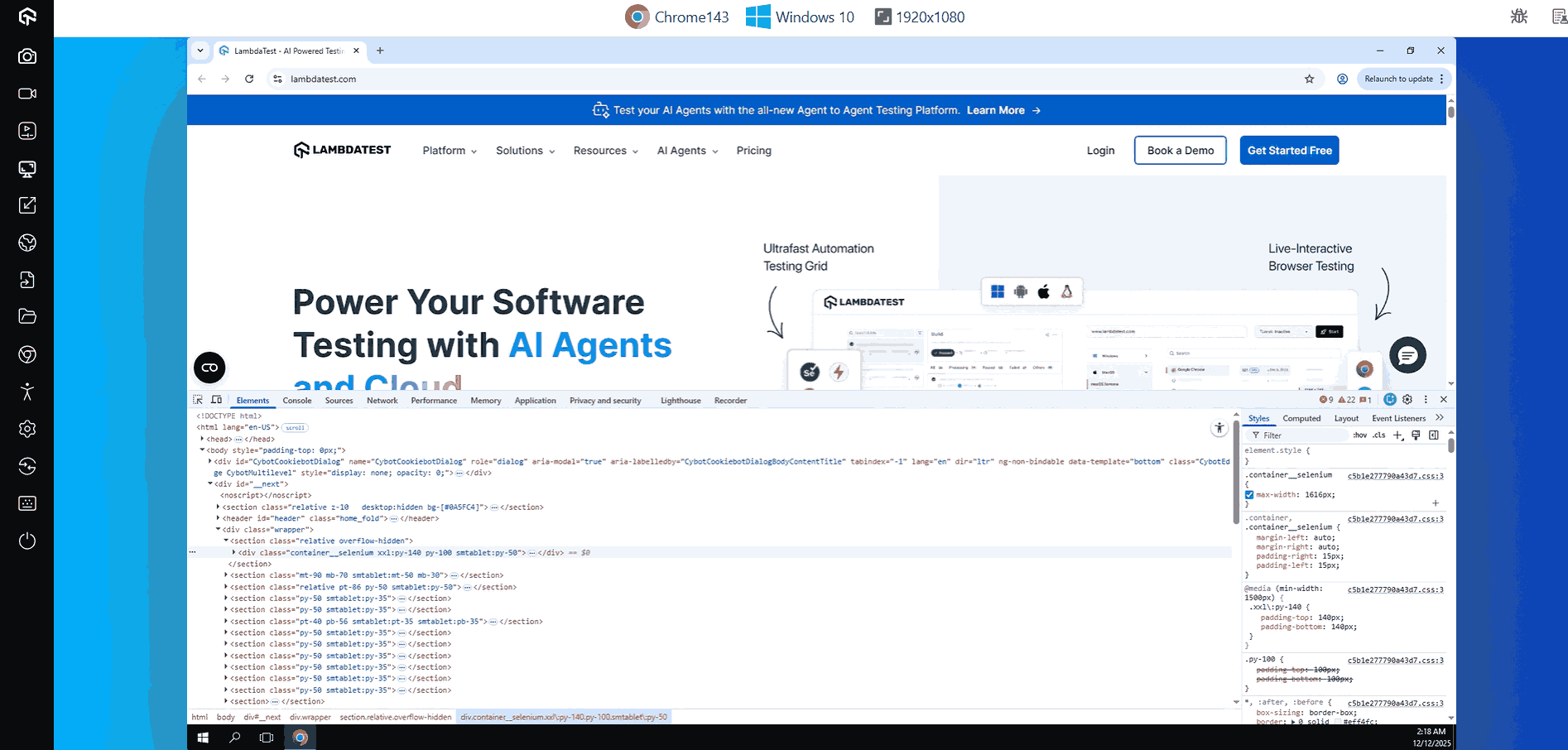
Manual Testing with Live Mobile App Testing
Just like web browser testing, you can perform mobile app testing. Follow these steps to get started with mobile app live testing.
- Select Mobile: From the left menu, select the “Virtual Mobile” option listed under “Web Browser Testing” for mobile testing.
- Set the URL: Enter the complete website URL you want to perform live app testing on for accurate validation results.
- Choose Environment: From the available options, carefully select the desired operating system, device, and device version for testing.
- Launch Browser Session: Click the Start button to begin your manual testing session and interact with your app directly.
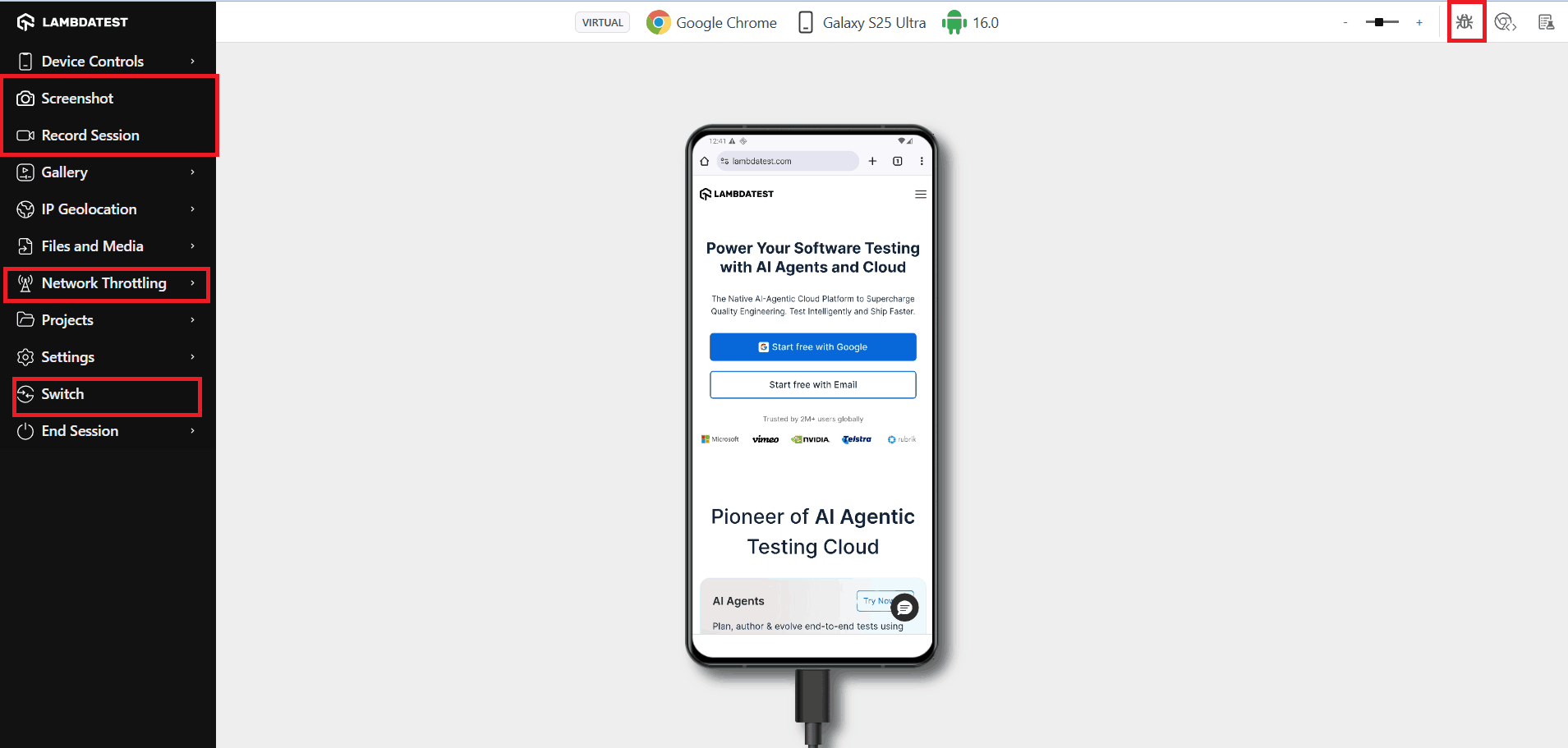
Once the mobile testing session is active, you can ensure flawless app or website performance across devices. Use “Mark as Bug” to report issues directly, capture screenshots for UI or responsiveness problems, record sessions to track interactions, and monitor console/network logs to identify functional errors.
The “Switch” option allows instant testing across different devices, OS versions, and browsers, while device controls enable gesture simulation, screen rotation, screen size changes, and network throttling to test performance under varied connectivity conditions.
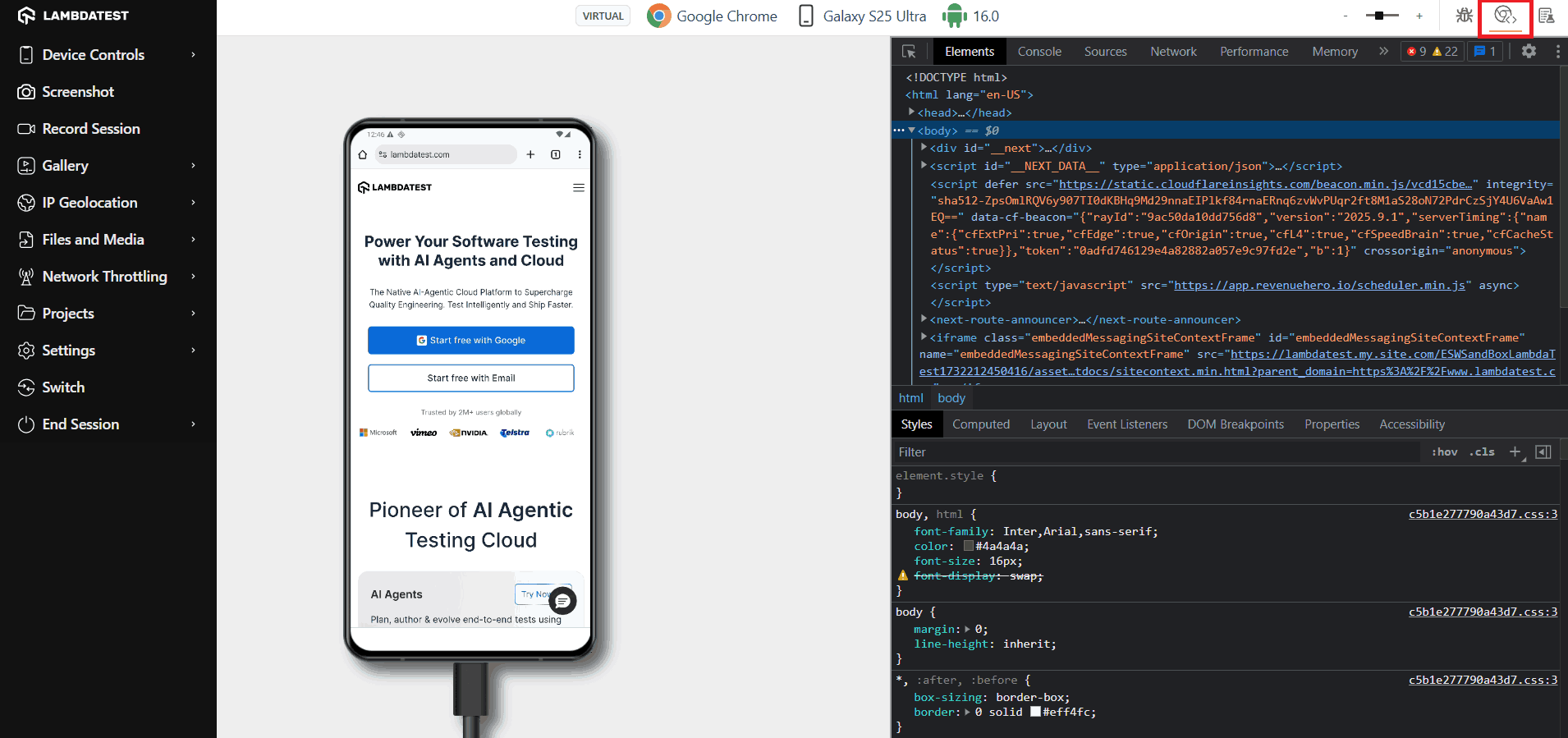
You can easily debug on LambdaTest mobile devices using the option in the top-right menu header when testing on the browser.
How to Choose the Right Manual Testing Tools?
Picking the right manual testing tools affects how well QA teams work together, find bugs, and deliver quality software in their software testing processes.
- Know What Testing Work You Do: Identify which testing activities dominate your projects. Teams may perform exploratory testing, user experience checks, or execute planned test cases.
- Pick Tools That Are Easy to Use: Complex interfaces slow testing. Choose manual testing tools with clear navigation, logical workflows, and simple execution steps.
- Organize Test Cases Properly: Test case management is critical. Effective manual testing tools enable the creation of detailed test steps, conditions, expected results, and priorities. Version control ensures smooth updates for teams performing manual vs automation testing.
- Connect Defects to Testing Work: Clear bug documentation is essential. Manual testing tools should track defects internally or integrate with bug systems like Jira or Bugzilla. This supports efficient defect resolution, whether identified through manual testing or automation testing.
- Track Progress and Measure Quality: Reporting features in manual testing tools show coverage, execution progress, defect trends, and team productivity. Dashboards allow comparison of manual vs automation testing performance and testing effectiveness.
- Support Team Collaboration: Role-based permissions and secure access are important for QA teams performing manual testing. Features like comments, notifications, and task assignments improve coordination alongside automation testing initiatives.
- Work with Other Development Tools: Integration with CI/CD pipelines, automation frameworks, and development environments ensures smoother workflows. Teams can combine manual testing with automation testing for full coverage.
- Support Different Platforms: Manual testing tools should support the platforms used by your applications: web (browser compatibility), mobile (real devices or emulators), and desktop (OS support). Proper integration allows teams to manage manual vs automation testing efficiently.
- Consider Costs and Future Growth: Evaluate licensing, maintenance, user scaling, and feature expansion. Free versions suit small teams, while enterprise manual testing tools support larger projects and integration with automation testing solutions. Consider long-term team growth and testing complexity.
Choosing good manual testing tools means matching capabilities to actual team needs, making sure adoption is easy, providing necessary connections, and supporting effective reporting for continuous improvement in testing quality and efficiency.
Which Tools Are Used in a Manual Testing Toolkit?
A modern manual tester works with more than just defect-tracking or test management tools. To validate data, debug issues, analyze logs, and verify UI behavior, QA teams rely on a set of lightweight utilities that make day-to-day testing faster and more accurate.
LambdaTest also offers a wide range of free online tools that support manual testers with data validation, formatting, debugging, and comparison tasks, making it easier to perform accurate and efficient manual testing without relying on heavy local installations.
Below is a curated manual testing toolkit that includes essential validators, formatters, converters, and comparison utilities widely used during functional, API, and exploratory testing.
Data Validation & Verification Tools
These tools help testers ensure input/output data is accurate, structured correctly, and compliant with expected formats.
- JSON Validator: Check API JSON responses for correct structure and valid syntax.
- XML Validator: Ensure XML feeds, configurations, and integrations are properly formatted and error-free.
- CSV Validator: Verify test data files for accuracy and proper structure during bulk uploads.
Formatters & Beautifiers
Readable data is essential for debugging. These utilities help QA teams prettify logs, API responses, and test data.
- JSON Prettify: Make JSON responses readable or compact for easier debugging.
- XML Prettify: Format XML files for clarity or compression.
Data Comparison Tools
Comparing expected vs actual results is a core part of manual testing. These tools make that process easier:
- JSON Compare: Compare expected and actual JSON data for testing accuracy.
- Excel Compare: Detect differences in spreadsheet or tabular test data.
- Text Compare: Quickly find mismatches in plain text files or logs.
Test Data Generation Tools
Manual testing involves a lot of repetitive data entry. These tools automate the creation of synthetic test data:
- Random Password Generator: Create secure, varied test input quickly.
- Lorem Ipsum Generator: Generate placeholder text for UI or content testing.
Encoding, Decoding & Escaping Tools
Essential for API testers working with encoded or escaped data.
- Base64 Encode: Convert data to/from Base64 format for API testing.
- URL Encode: Safely encode or decode URLs for requests and queries.
- JWT Decoder: Inspect JSON Web Tokens to verify payloads and claims.
Browser, System & Debugging Utilities
Useful for reproducing bugs and logging system-specific issues.
- What Is My Browser: Identify browser type and version for compatibility testing.
- What Is My IP Address: Retrieve device IP for network or environment troubleshooting.
- JavaScript Tester: Execute scripts to validate code snippets and browser behavior.
Conclusion
Manual testing remains a critical component of software quality assurance, even as automation testing becomes more widespread. Manual testing tools streamline workflows by helping teams organize test cases, track defects, and collaborate effectively.
While automation testing excels at repetitive, large-scale test execution, manual testing is essential for exploratory testing, usability checks, and scenarios that require human judgment. Choosing the right manual testing tool depends on project requirements, team expertise, integration capabilities, and the desired reporting and tracking features.
By combining manual testing tools with automation frameworks where appropriate, teams can achieve comprehensive test coverage, improve QA efficiency, and deliver high-quality software. Investing in suitable manual testing tools ensures structured processes, better defect management, and continuous improvement throughout the software development lifecycle.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Did you find this page helpful?
More Related Hubs

Start your journey with LambdaTest
Get 100 minutes of automation test minutes FREE!!



