Power Your Software Testing with AI and Cloud
Supercharge QA with AI for Faster & Smarter Software Testing

- Automation
- Home
- /
- Learning Hub
- /
- What Is WCAG Testing
What Is WCAG Testing and Why It Matter for Web Accessibility
Learn WCAG testing essentials such as principles, levels, best practices, and how LambdaTest Accessibility Suite helps ensure full web accessibility compliance.
Last Modified on: December 1, 2025
- Share:
Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) testing is the technique that identifies barriers that prevent people with impairments from using web applications. It highlights issues in structure, navigation, contrast, media, and compatibility with assistive technology.
This testing helps in fixing these issues so that teams create inclusive digital experiences, reduce legal risk, improve usability for everyone, and meet global accessibility standards.
Overview
What Is WCAG Testing?
WCAG testing checks websites for accessibility, ensuring content is perceivable, operable, understandable, and robust for users with impairments, in line with Web Content Accessibility Guidelines.
What Are the 4 WCAG Principles?
Web accessibility ensures that digital content is usable by everyone, including people with disabilities. The WCAG framework defines four key principles to guide accessibility efforts:
- Perceivable: Content must be available through multiple senses. This includes providing alt text for images, captions for videos, and transcripts for audio.
- Operable: Users must be able to interact with the interface using different input methods, including keyboard navigation and assistive devices, while avoiding content that could trigger seizures or motion sensitivity.
- Understandable: Information and interface behavior should be clear and predictable. This involves using simple language, consistent navigation, and helpful error messages.
- Robust: Content should work reliably across browsers, devices, and assistive technologies by using proper markup and following standards.
What Are the WCAG Conformance Levels?
Web accessibility standards help ensure digital content is usable for all individuals, including those with disabilities. WCAG defines three conformance levels to guide implementation and compliance:
- Level A (Basic Accessibility): Covers essential needs such as alt text for images, keyboard access, and basic usability for users with disabilities.
- Level AA (Standard Accessibility): Builds on Level A with requirements like sufficient color contrast, visible focus indicators, and consistent layout. This is the most commonly required level for compliance.
- Level AAA (Highest Accessibility): Represents advanced accessibility, including features such as sign language videos and very high contrast. It is often difficult or costly to implement completely.
How to Perform WCAG Testing?
You can perform WCAG testing using the LambdaTest Accessibility Suite, which supports both manual and automated accessibility testing across real environments.
- LambdaTest Accessibility DevTools: A Chrome extension that runs on-demand scans, highlights accessibility issues, and generates detailed reports with WCAG guidance. It also checks screen reader and keyboard navigation compatibility.
- LambdaTest Accessibility Automation: Enables automated accessibility testing using frameworks such as Selenium, Cypress, and Playwright. It supports CI/CD integration and provides detailed compliance reports.
What Is WCAG Testing?
WCAG testing involves checking whether a website is accessible to people with impairments. It combines automated tools that detect accessibility issues with manual checks to meet accessibility standards.
Running these tests during development catches issues early, saving time and ensuring compliance with WCAG 2.1 and 2.2. The guidelines cover vision, hearing, movement, and cognitive challenges that ensure easier accessibility, making web applications usable for everyone.
Why Perform WCAG Testing?
WCAG testing ensures web applications are accessible to people with disabilities. It reduces legal risk, improves usability, expands market reach, and prevents expensive fixes when issues are caught early.
- Global Market Requirements: Most developed countries require or encourage WCAG compliance. Following universal standards simplifies operations, reduces costs, and ensures web applications serve users across languages, cultures, and assistive technologies consistently.
- Legal and Compliance Requirements: Laws like ADA and Section 508 Compliance require accessibility. Ignoring requirements can lead to lawsuits and financial penalties. Compliance also supports diversity and inclusion within organizational operations.
- Better User Experiences: Accessible design enhances navigation, readability, and interaction. Features like captions, keyboard access, and clear hierarchy improve usability, benefiting all users, not just those with disabilities.
- Business Growth and Market Access: People with disabilities hold significant purchasing power globally. Web accessibility improves reach and engagement. Design improvements often benefit all users and enhance search engine visibility.
- Code Quality and Development: WCAG encourages semantic code, proper labels, and structured forms. Automation testing catches issues early, simplifies debugging, and reduces long-term maintenance costs for development teams.
- Financial Considerations: Addressing accessibility during development costs less than retroactive fixes. Simple issues are inexpensive to resolve early, while ignoring them leads to expensive redesigns and compliance-driven deadlines.
- Brand Trust and Corporate Reputation: Genuine accessibility builds trust. Users recognize superficial compliance. Strong accessibility practices improve reputation, attract inclusion-focused clients, and meet government or B2B contracting expectations effectively.
Note: Run manual and automated WCAG tests online. Try LambdaTest Now!
What Are the Four Principles of WCAG?
Perceivable, Operable, Understandable, and Robust. These ensure content is accessible to the senses, usable with different inputs, easy to follow, and compatible across technologies.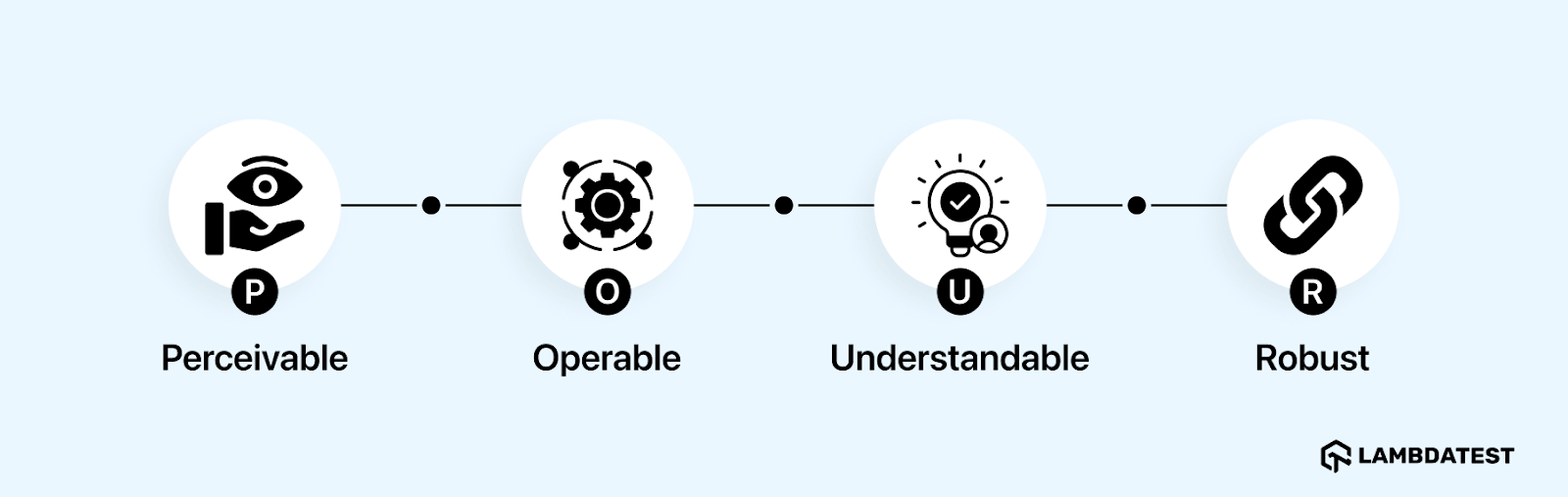
- Perceivable: All content must be available through multiple senses. Images need alternative text, videos require captions, and audio should have transcripts. This ensures users with vision or hearing impairments can access the same information.
- Operable: Users must be able to interact with the interface using different input methods. Keyboard navigation, assistive devices, and adjustable time limits are essential. Avoid features that could trigger seizures or motion-related issues.
- Understandable: Information and interface behavior should be clear and predictable. Use plain language, consistent navigation, and provide guidance for errors to help users interact without confusion.
- Robust: Content should work across different web applications, browsers, and assistive technologies. Proper semantic markup and adherence to standards ensure compatibility now and in the future.
What Are the Conformance Levels of WCAG?
WCAG defines three conformance levels to guide accessibility goals and ensure digital content meets legal and usability standards. Each level builds on the previous one, so higher levels include all requirements from lower levels.
- Level A - Basic Accessibility: Covers the minimum needed to make content usable. Includes essential features like alt text for images and keyboard navigation. Without these, many users with disabilities cannot access the application at all.
- Level AA - Standard Accessibility: Adds usability improvements to Level A. Requires adequate color contrast, visible focus indicators, and consistent layouts. Most organizations aim for this level because it satisfies legal requirements and is practical to implement.
- Level AAA - Highest Accessibility: Represents the highest standard with comprehensive accessibility features. Includes advanced requirements like sign language videos and very high contrast ratios. Achieving full AAA compliance across an entire application is usually impractical due to cost and complexity.
What Are the Different WCAG Testing Approaches?
Accessibility testing often fails when teams rely on a single method. Effective organizations use a mix of automated, manual, or hybrid strategies to ensure digital content meets WCAG standards. Each approach has its own benefits and limitations.
Manual Accessibility Testing
Manual testing involves interacting with the application like a user with disabilities would. Testers navigate with keyboards, check form errors, and ensure dynamic content is announced correctly by screen readers.
This method identifies issues that automated tools miss. For example, a button labeled “Submit” might pass code checks but confuse users if the form context is unclear. Manual testing verifies real-world usability.
Automated Accessibility Testing
Automated accessibility testing involves using automated accessibility testing tools that scan code for accessibility violations such as missing alt text, heading order issues, or low color contrast. They are fast and effective for detecting obvious coding errors.
These tools excel in large web applications or frequent development cycles. They generate reports that show patterns across web pages and can integrate into build processes to catch issues early.
However, automated tools cannot assess context, reading order, or whether alt text is meaningful. They may flag false positives while missing real usability barriers detectable only by humans.
Hybrid (Mixed) Accessibility Testing
Hybrid testing combines automated scans with manual evaluation. Automated checks catch low-hanging technical issues first, while manual testing focuses on complex interactions and user experience.
Some teams include real assistive technology, like screen readers, voice recognition, or magnifiers. This uncovers issues that simulated testing cannot detect, ensuring the web application works for actual users.
Hybrid testing helps prioritize fixes. Automated results show widespread technical issues, while manual testing highlights issues that block task completion. High-impact issues can be addressed first, making the process efficient.
How to Perform WCAG Testing With LambdaTest Accessibility Suite?
To perform WCAG testing, you can leverage platforms such as LambdaTest Accessibility Suite that provides an integrated solution for accessibility testing, helping teams build inclusive digital experiences.
LambdaTest Accessibility DevTools
LambdaTest Accessibility DevTools is a comprehensive solution for evaluating web accessibility in real time. This WCAG accessibility Chrome extension goes beyond basic automated checks by providing deep, contextual insights into how elements behave for users with disabilities.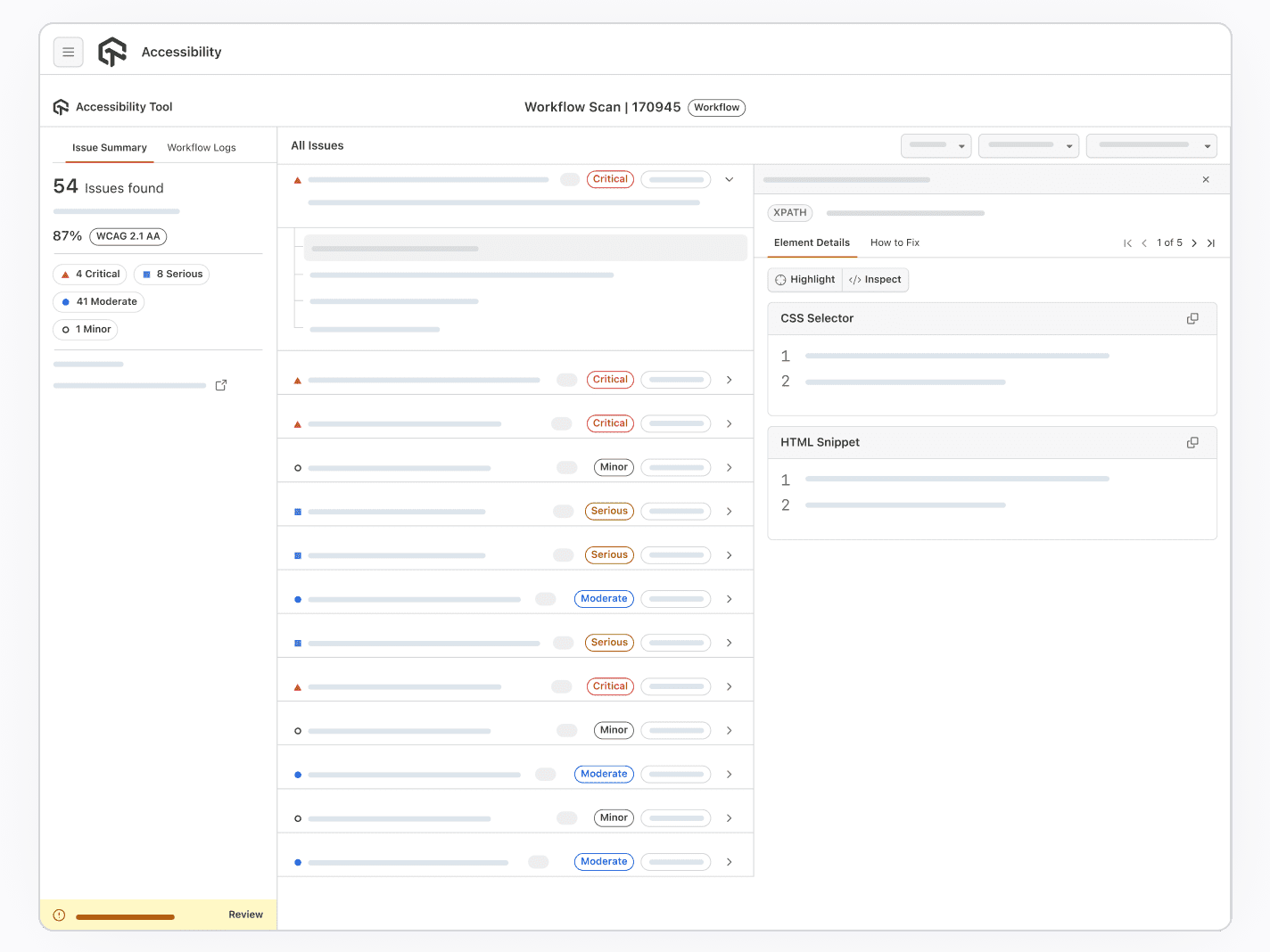
Key Features:
- On-Demand Scans: Run instant accessibility scans on any page within the LambdaTest virtual machine. Violations are identified and presented clearly.
- Visual Highlighting: Problematic elements are highlighted on-screen, showing which WCAG criteria fail, such as missing alt text or improper ARIA attributes.
- Detailed Issue Reporting: Each issue includes a description, WCAG reference, and practical remediation steps to accelerate fixes.
- Screen Reader Testing: Test compatibility with popular screen readers like NVDA and JAWS directly in the cloud environment.
- Keyboard Navigation Testing: Validate that all interactive elements are fully accessible using only a keyboard.
To get started, refer to the LambdaTest Accessibility DevTools documentation.
LambdaTest Accessibility Automation
LambdaTest allows you to perform accessibility automation using frameworks such as Selenium, Cypress, and Playwright.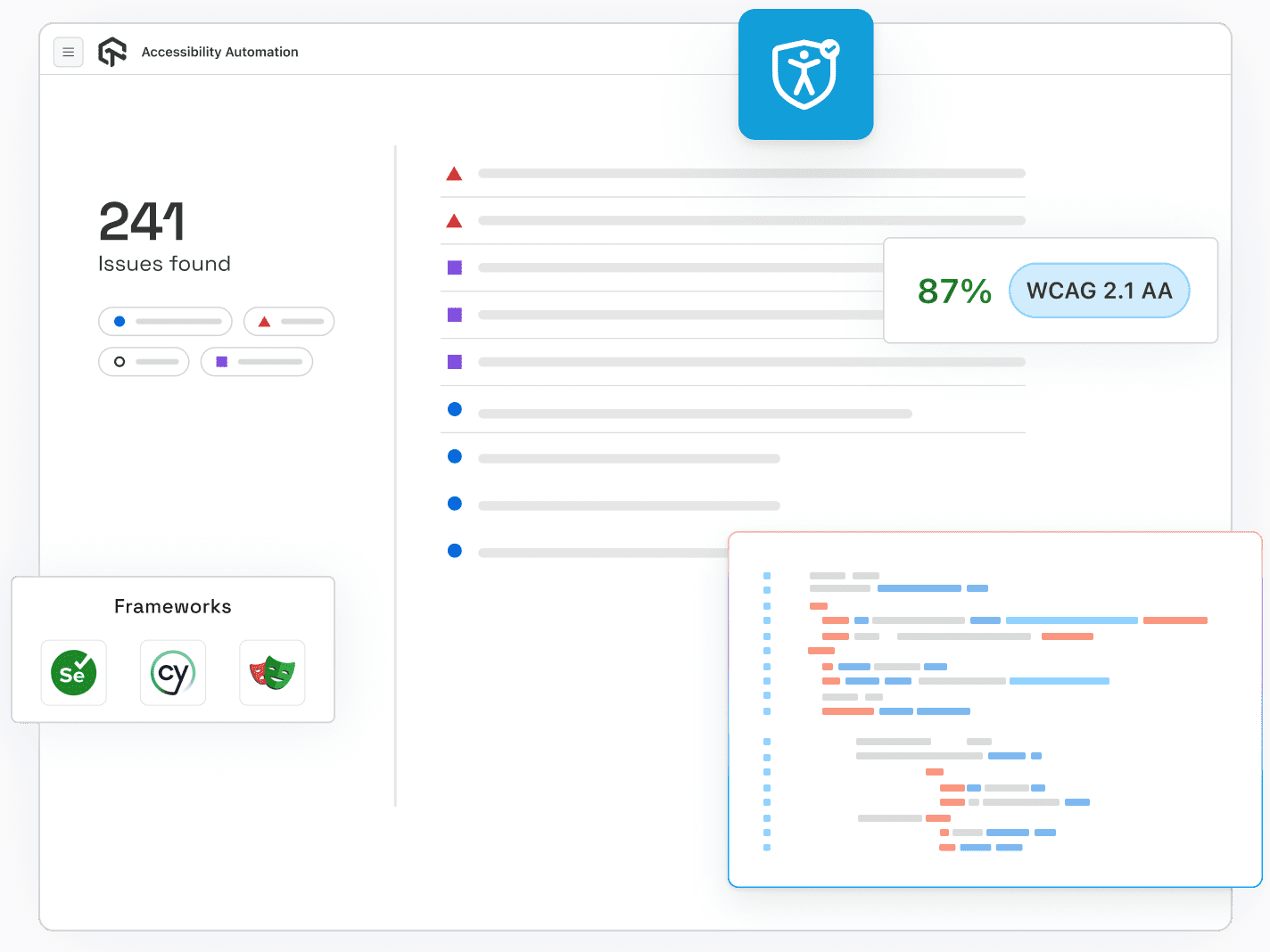
Key Features:
- Accessibility Testing with MCP Server: LambdaTest MCP Server connects AI to your project and instantly finds, explains, and helps fix accessibility issues directly in your editor.
- CI/CD Integration: Run accessibility tests with frameworks like Selenium, Cypress, Playwright, or Puppeteer. Catch issues early in development.
- Automated Scans on Deployments: Trigger tests automatically on each build across hundreds of browser and OS combinations.
- Detailed Automation Reports: Comprehensive execution reports show every passed and failed checkpoint for tracking and stakeholder reporting.
To begin with, visit the LambdaTest Accessibility Automation documentation.
Common WCAG Compliance Challenges
Achieving WCAG compliance is difficult for many organizations due to technical complexities. Frequent issues like low contrast text, missing alt text, and incomplete form labeling continue to block accessibility. Understanding these challenges helps prioritize fixes that make the most impact.
- Color and Visual Design: Low contrast text or information conveyed by color alone makes content unreadable or confusing for users with vision impairments.
You can explore more about color contrast accessibility and how it affects UI design.
- Keyboard Navigation: Interactive elements must support keyboard input, visible focus indicators, and proper focus management; missing these blocks users from completing tasks.
- Alternative Text and Media: Missing or generic alt text, uncaptioned videos, and absent audio descriptions prevent screen reader users from accessing important content.
Learn more about how to perform screen reader accessibility testing.
- Forms: Unlabeled fields, poor error messages, missing required indicators, and illogical grouping confuse users and make form completion difficult or impossible.
- Complex Interactive Components: Custom widgets, dynamic updates, tooltips, or auto-advancing carousels without proper ARIA support or announcements create barriers for assistive technology users.
- Mobile and Responsive Design: Tiny touch targets, broken layouts across devices, and disabled zoom prevent users with motor or vision impairments from interacting effectively.
- Technical Implementation: Non-semantic HTML, broken heading hierarchy, missing skip links, and inaccessible PDFs reduce compatibility with screen readers and other assistive technologies.
- Testing and Organizational Processes: Relying on automated tools alone, late-stage testing, inconsistent procedures, and limited internal expertise creates undetected accessibility issues.
Best Practices for Effective WCAG Testing
Following best practices uncovers hidden barriers and improves usability across devices, browsers, and assistive technologies.
- Define Clear Objectives Early: Set specific goals before testing. Decide which WCAG level(s) to target. Prioritize critical flows, high-traffic pages, and key functionality such as forms, navigation, or media.
- Choose a Representative Sample of Pages: Select a varied set of pages, including different templates, content types, and key workflows such as checkout, search, or interactive elements. Capture both common and edge-case issues.
- Educate and Engage the Entire Team: Train designers, developers, QA, and content creators in accessibility principles. Cross-functional understanding ensures accessibility is integrated consistently and prevents last-minute issues.
- Combine Automated and Manual Testing: Use accessibility testing tools for automation to catch technical issues like missing alt text or poor contrast. Follow up with manual testing for usability, navigation order, and assistive technology compatibility.
- Include Real-User Testing with Disabilities: Engage users with visual, auditory, cognitive, or motor disabilities to test actual workflows. Their feedback reveals real-world issues that automated and expert reviews may miss.
- Test Across Devices, Viewports, and User Agents: Check web applications on desktop, tablet, and mobile using multiple browsers and assistive technologies to detect device- or web accessibility issues.
- Check Keyboard Accessibility and Navigation Order: Ensure all interactive elements are accessible via keyboard, focus indicators are visible, and tab order is logical. These are common points of failure.
- Ensure Clear and Consistent Communication: Use meaningful labels, concise instructions, descriptive links, captions, transcripts, and helpful error messages. Clear communication reduces cognitive load and benefits all users.
- Prioritize by Severity and Impact: Focus first on issues that block user flows or critical functionality. Fixing high-impact issues delivers the greatest benefit to users and overall accessibility.
- Iterate, Retest, and Maintain Documentation: Accessibility is ongoing. Retest after fixes and maintain records of issues, resolutions, and priorities to track progress and guide future improvements.
Also, it is important to keep a web accessibility checklist handy to make sure your content and design work for everyone, including people who rely on assistive technologies.
Future of WCAG Testing
The future of WCAG testing is driven by AI-powered automation, adaptive accessibility standards, and an expanded focus on user-centered and immersive experiences across all digital platforms.
Here are some of the major trends shaping WCAG testing:
- AI and Machine Learning Integration: AI and accessibility are making it easier to spot and anticipate WCAG violations. These tools enable automated, real-time testing and can adapt to new accessibility patterns, covering edge cases missed by manual and static tools.
- Voice, Gesture, and XR Accessibility: Testing will increasingly address voice navigation, gesture-based interactions, and accessibility in AR/VR (extended reality) environments. This ensures inclusivity not just for websites and apps, but for emerging digital platforms.
- Shift-Left and Continuous Testing: Accessibility testing is becoming an intrinsic part of development workflows, integrated from the earliest design stages and maintained throughout every update or release. This minimizes last-minute accessibility risks and increases overall quality.
- Comprehensive Regulatory Coverage: Countries and states are updating laws to mandate stricter, ongoing accessibility checks, the European Accessibility Act and expanded ADA rules, for example, now require active documentation and process transparency, not just initial compliance.
- Focus on Mobile and Neurodiverse Users: Mobile accessibility and designing for neurodiversity are at the forefront, with newer guidelines emphasizing large tap targets, reduced cognitive overload, and age‑friendly navigation features.
- Inclusive Usability and Real User Testing: WCAG testing will rely more on feedback from people with disabilities, ensuring that updates address actual user needs in addition to technical compliance.
Conclusion
WCAG testing is essential for building inclusive digital experiences and meeting global accessibility standards. By understanding its principles, conformance levels, and testing approaches, teams can identify barriers that affect users with disabilities.
Using platforms like the LambdaTest Accessibility Suite simplifies the process through automation, monitoring, and actionable insights. Although challenges exist, following best practices and embracing future advancements in AI and automation will help organizations deliver more accessible, user-friendly, and compliant digital products.
Citations
- WCAG 2 Overview: https://www.w3.org/WAI/standards-guidelines/wcag/
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Did you find this page helpful?
More Related Hubs

Start your journey with LambdaTest
Get 100 minutes of automation test minutes FREE!!