Power Your Software Testing with AI and Cloud
Supercharge QA with AI for Faster & Smarter Software Testing

- Automation
- Home
- /
- Learning Hub
- /
- Python Automation Tutorial: Complete Guide With Examples
Python Automation Tutorial: Complete Guide With Examples
Master Python automation with this complete guide. Learn to automate tasks, streamline workflows, and build practical scripts with real-world examples.
Last Modified on: September 26, 2025
- Share:
Python automation is one of the ways to streamline repetitive tasks, optimize workflow, and enhance productivity. For developers, testers, and analysts, automating routine tasks with Python not only saves time and reduces errors but also frees up resources to focus on more complex, strategic work, driving overall efficiency.
Overview
Python automation is the use of Python scripts and libraries to automate repetitive tasks, workflows, or processes across files, applications, and web platforms.
Python Automation Use Cases
- Data Entry Automation: Automatically input data into spreadsheets, forms, or databases to save time.
- Web Scraping: Extract information from websites for research, analytics, or monitoring purposes.
- Report Generation: Automate creation of Excel, PDF, or CSV reports from raw data.
- Email Handling: Send, organize, and respond to emails automatically using scripts.
- File Management: Rename, move, copy, or clean up files and folders efficiently.
- API and System Integration: Connect applications and APIs to automate workflows across platforms.
How to Perform Python Automation
- Learn Python Basics: Understand variables, loops, functions, and error handling.
- Identify Repetitive Tasks: Choose tasks suitable for automation like file operations, website testing, web scraping, or data entry.
- Select Libraries: Use Selenium, Playwright, PyAutoGUI, pandas, or RPA frameworks based on your task type.
- Write Python Scripts: Start automating simple tasks and test each script thoroughly.
- Combine and Scale: Integrate scripts into full workflows and schedule or trigger them automatically.
What Is Python Automation?
Python automation refers to using automated scripts with Python programming language to handle repetitive tasks with minimal human intervention. It leverages Python libraries to streamline workflows, improve accuracy, and save time across tasks such as web testing, data scraping, file management, and report generation.
Benefits:
- Automates Repetitive Tasks: Python automation reduces time spent on routine tasks, enabling teams to focus on strategic, value-driven activities and innovation.
- Improves Testing Reliability: Python automation testing automates manual testing efforts and ensures your software behaves as expected across environments.
- Accelerates Development Cycles: Python speeds up task execution, enabling parallel test runs and faster feedback, significantly reducing the overall software development cycle.
- Scalable Automation: Python's flexible nature scales with growing complexity, allowing simple scripts to evolve into comprehensive solutions across multiple platforms.
- Real-Time Monitoring and Insights: Python automates real-time data collection, providing actionable insights for quicker decision-making, optimizing system performance, and minimizing downtime.
Learn Python basics and start creating scripts that save time, reduce errors, and make your workflows more efficient.
Real-World Use Cases of Python Automation
Automation with Python powers practical solutions across industries, making everyday tasks faster and more reliable.
Let's explore key real-world use cases, from web testing and data scraping to report generation that showcase how Python streamlines workflows.
- Web Testing: Python can be used with automation testing tools to check that websites behave as expected. This helps developers catch bugs before users do.
- Data Scraping: Using libraries like BeautifulSoup, Python can pull data from websites (also known as Python web scraping). This is useful for gathering prices, news, or job listings.
- Email Automation: Python scripts can read, send, and organize emails. For example, you can send reports or notifications automatically.
- File Management: Python can rename, move, or delete hundreds of files at once. This is useful for cleaning up folders or organizing data.
- Report Generation: Combine Python with Excel or PDF libraries to create automatic daily or weekly reports without opening any files.
- PDF or Image Processing: Python can compare, edit, and extract text from PDF and image files. This is useful for document checks.
- Monitoring Systems: Python scripts can run in the background to watch logs, websites, or apps and alert you if something breaks.
Note: Run Python automation tests in parallel across 3000+ real environments. Try LambdaTest Now!
How to Get Started With Python Automation?
Let's look at the step-by-step process to perform automation with Python, from setup to running your first scripts.
Prerequisites
- Clone this GitHub Python automation repository.
- Download Python and ensure pip is installed by running:
pip --version - Create a virtual environment the below command:
python -m venv env - Activate the virtual environment using the source env/bin/activate command for macOS/Linux and if you are on Windows, use the env\\Scripts\\activate command.
- Run the following command to install required libraries:
pip install -r requirements.txt - Run the following command to install Playwright:
npm init playwright@latest
Automate Web Testing With Python
Let's take a real-world use case of website testing where we will automate the functionality of searching a product on the LambdaTest eCommerce Playground.
To perform Python automation testing, we will use Playwright framework to automate tests. If you are new to Playwright? Check out this Playwright tutorial.
Implementation:
It launches Chrome browser, navigates to the LambdaTest eCommerce Playground, accepts cookies if they appear, performs a product search, verifies the search results, and finally captures a screenshot of the results for reference.
def test_local_ecommerce_search():
"""
Test product search functionality locally in Chrome.
"""
with sync_playwright() as p:
# Launch Chrome (local, visible)
browser = p.chromium.launch(headless=False)
page = browser.new_page()
try:
# Navigate to the e-commerce site
page.goto("https://ecommerce-playground.lambdatest.io/")
# Accept cookies if present
try:
accept_button = page.get_by_role("button", name="Accept")
if accept_button.is_visible():
accept_button.click()
except Exception as e:
logging.warning(f"Cookie banner not found or could not be accepted: {e}")
# Search for product
search_box = page.get_by_role("textbox", name="Search For Products")
expect(search_box).to_be_visible()
search_box.fill(SEARCH_TERM)
search_button = page.get_by_role("button", name="Search")
search_button.click()
# Verify results header
results_header = page.get_by_role("heading", name=f"Search - {SEARCH_TERM}")
expect(results_header).to_be_visible()
# Verify expected terms in page
page_content = page.content().lower()
for term in EXPECTED_RESULTS:
assert term.lower() in page_content, f"Expected '{term}' not found in results"
# Take screenshot
screenshot = page.screenshot()
with open("local_ecommerce_search_results.png", "wb") as f:
f.write(screenshot)
logging.info(f"[Local E-Commerce] Search for '{SEARCH_TERM}' completed successfully")
finally:
browser.close()
if __name__ == "__main__":
test_local_ecommerce_search()
Code Walkthrough:
- Setup and Browser Launch: The function uses the sync_playwright() to start a Chromium browser locally in non-headless mode, opening a new page for interaction.
- Navigate and Handle Cookies: It visits the LambdaTest eCommerce Playground and attempts to click the "Accept" button on the cookie banner, logging a warning if the banner is missing.
- Perform Search: The script locates the search box, ensures it’s visible, fills it with the predefined SEARCH_TERM, and clicks the search button.
- Validate Results: It checks that the search results header displays correctly, then verifies all expected keywords from EXPECTED_RESULTS are present in the page content.
- Capture Evidence and Cleanup: A screenshot of the results page is saved locally for reference, and the browser session is closed safely inside the finally block.
Test Execution:
To run the test, execute the below command:
python web/local_ecommerce_search_test.pyYou can also check out these 13 useful Python automation scripts to streamline your testing workflows.
How to Perform Python Automation With LambdaTest?
LambdaTest is a cloud platform that allows you to perform Python automation testing online that allows you to run your automation scripts with tools like Selenium, Playwright across different browsers and OSes. It handles the infrastructure so you don’t need to manage browsers or devices locally.
To run Playwright automation on LambdaTest, modify your test script to connect via the LambdaTest WebSocket URL. Next, set your LambdaTest Username and Access Key as environment variables and configure the automation capabilities, including browser, browser version, platform, and other relevant settings.
capabilities = {
"browserName": browser_name,
"browserVersion": browser_version,
"LT:Options": {
"platform": platform,
"build": build or "Playwright Python Build",
"name": name or "Playwright Python Test",
"user": LT_USERNAME,
"accessKey": LT_ACCESS_KEY,
"network": True,
"video": True,
"console": True,
"tunnel": False,
},
}
caps_json = json.dumps(capabilities)
return f"wss://cdp.lambdatest.com/playwright?capabilities={caps_json}"You can generate these Playwright capabilities using the LambdaTest Automation Capabilities Generator.
To get started, refer to the documentation on Playwright testing with LambdaTest.
To run the above test scenario on LambdaTest, execute the below command.
python web/ecommerce_search_test.pyYou can now visit the LambdaTest Web Automation dashboard to view your test execution results.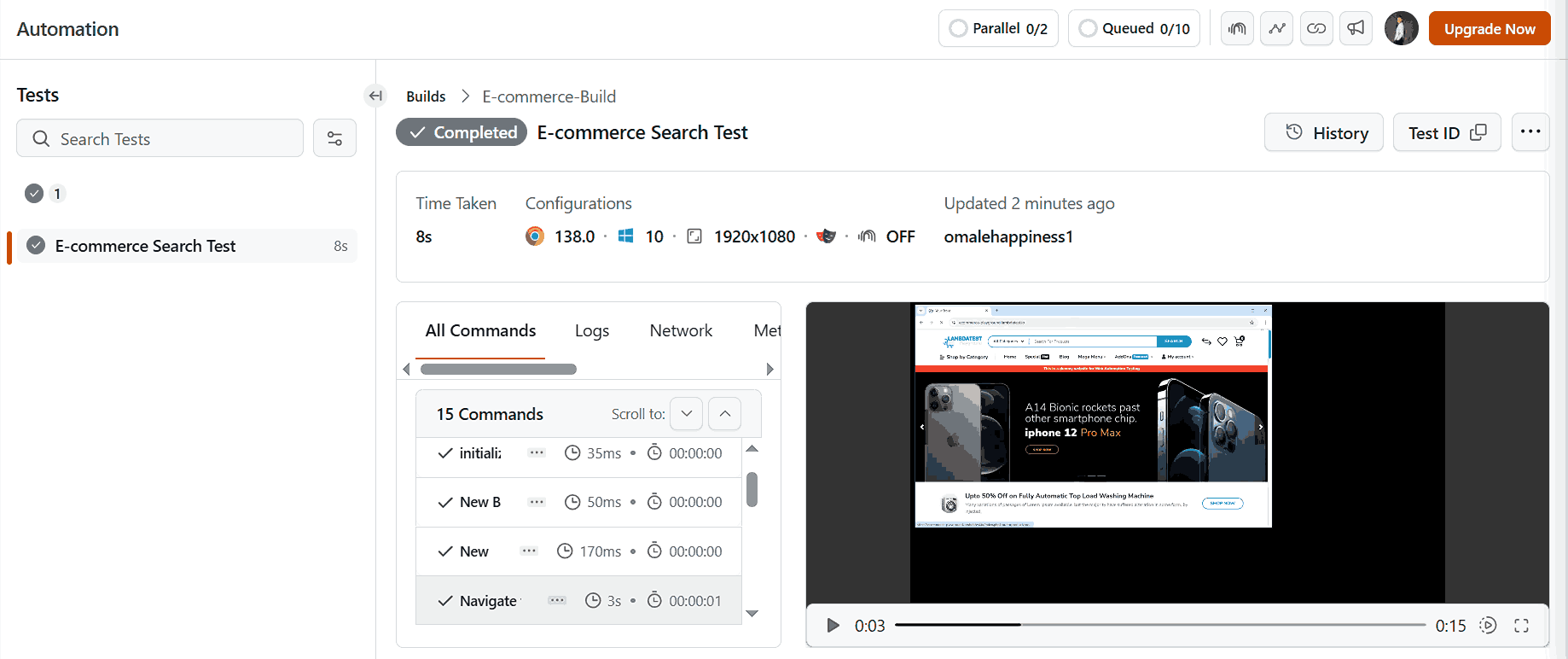
Conclusion
Python makes it simple to automate everyday tasks by providing a readable syntax and a wide range of powerful libraries. In this Python automation tutorial, we explored how to automate search functionality using Playwright, demonstrating how Python can interact with web pages just like a human would.
So, if you're automating browser interactions, managing files, or processing data, Python helps reduce manual effort, minimize errors, and increase efficiency. With the right tools, automation becomes both accessible and scalable.
Other than Playwright framework, you can also use tools like Selenium for Python automation testing. Check out this tutorial on Selenium Python to get started with automated website testing.
Citations
- Python Official Website: https://www.python.org/
- Playwright Official Website: https://playwright.dev/
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Did you find this page helpful?
More Related Hubs

Start your journey with LambdaTest
Get 100 minutes of automation test minutes FREE!!


