Power Your Software Testing with AI and Cloud
Supercharge QA with AI for Faster & Smarter Software Testing

- Automation
- Home
- /
- Learning Hub
- /
- Website Localization: Step-by-Step Guide
Website Localization: Step-by-Step Guide
Comprehensive guide on website localization covering its definition, importance, examples, key strategies, comparisons, and best practices for global audiences.
Last Modified on: October 4, 2025
- Share:
Website localization ensures a site is tailored to its audience by addressing language, cultural norms, and functional requirements. This involves translation, formatting of regional data like dates and currencies, and modifying visuals, colors, and layouts to match user expectations in each market.
Overview
Website localization is the process that ensures websites resonate with local audiences by adjusting text, visuals, formats, and functions to cultural norms, language preferences, and technical standards in each market.
What Is the Importance of Website Localization?
Website localization involves multiple elements working together to ensure your website feels natural, relevant, and engaging for users in each target market. Some benefits include:
- Translating Content Accurately: Ensure text, idioms, humor, and culturally specific references resonate naturally with local users while preserving meaning and brand voice.
- Adapting Images, Icons, and Graphics: Modify visuals to reflect regional tastes, cultural norms, and expectations, making the website feel familiar, engaging, and relevant.
- Localizing Formats: Align dates, times, addresses, phone numbers, and measurement units with local conventions to maintain consistency and meet user expectations.
- Adjusting Tone of Voice and Messaging Style: Tailor communication style, phrasing, and tone to reflect local preferences, improving clarity, relatability, and audience engagement.
- Ensuring Compatibility: Test and optimize the website across the devices, browsers, and operating systems most commonly used in the target market.
What Are the Key Website Localization Strategies?
Here are some strategies for effective website localization, combining cultural understanding, technical setup, content adaptation, and compliance.
- Identify Your Target Market: Define the target region based on growth potential, demographics, internet access, device usage, demand, competition, and operational capabilities to ensure effective localization.
- Conduct Market Research: Analyze cultural norms, payment methods, device preferences, social media behavior, and local regulations to align content, marketing strategies, and compliance with regional expectations.
- Select a Localization Platform: Choose a platform with automation, API integration, scalability, collaboration, and CMS compatibility to streamline translations, maintain brand consistency, and support multi-language expansion efficiently.
- Implement Technical Infrastructure: Configure URL structures, hreflang tags, CDNs, and geo-targeting to optimize SEO, load times, and regional targeting while maintaining smooth navigation across all markets.
- Translate Content Accurately: Use native-speaking translators, prioritize high-impact pages, review quality professionally, and employ transcreation for marketing copy to preserve tone, intent, and cultural relevance.
- Adapt Visuals and User Interface Design: Adjust images, layouts, colors, symbols, and interactive elements to match local cultural norms, text length, and usability standards, enhancing engagement and conversion rates.
- Integrate Local Features: Implement region-specific payment, shipping, customer support, seasonal promotions, and localized functionality such as measurement units and date formats to improve usability and build trust.
- Ensure Legal and Regulatory Compliance: Follow data protection laws, accessibility standards, eCommerce and tax regulations, and localize legal documentation to protect users, maintain trust, and avoid penalties.
- Test and Launch: Perform functional, linguistic, UI, and cross-browser/device testing, then deploy the localized website while monitoring user interactions to ensure a seamless experience and rapid issue resolution.
What Is Website Localization?
Website localization involves adapting a website to meet the language, cultural, and technical needs of a specific market. Unlike simple translation, it adjusts content, design, and functionality to provide a fully local experience.
Key aspects of website localization include:
- Translating Content Accurately: Adapting text, idioms, humor, and culturally specific references to ensure the website resonates naturally with local users.
- Adapting Images, Icons, and Graphics: Modifying visuals to reflect local tastes, cultural norms, and expectations, ensuring content feels familiar and relevant.
- Modifying Color Schemes: Adjusting colors according to regional interpretations, avoiding cultural missteps and ensuring design conveys the intended meaning accurately.
- Localizing Formats: Formatting dates, times, addresses, phone numbers, and units to align with local conventions and user expectations consistently.
- Adjusting Tone of Voice and Messaging Style: Tailoring communication style, tone, and phrasing to match local preferences and improve audience engagement.
- Using Local Hosting or CDNs: Implementing regional servers to reduce latency, increase speed, and improve the user experience for local visitors.
- Ensuring Compatibility: Performing localization testing and optimizing the website across devices, browsers, and operating systems commonly used in the target market.
- Adapting Layouts: Modifying page structure and navigation to support right-to-left languages like Arabic and Hebrew effectively.
- Implementing Region-Specific SEO Practices: Conducting local keyword research, optimizing metadata, and submitting to regionally popular search engines for better visibility.
- Integrating Local Payment Gateways: Displaying correct currencies, enabling region-specific payment methods, and ensuring secure transactions for local users.
Why Website Localization Is Important?
Website localization is important as it builds trust, enhances engagement, boosts conversions, and improves SEO by adapting content, design, and features to local languages, cultures, and user expectations.
Below are some of the key benefits:
- Expands Global Reach: Localization extends your brand’s presence into new markets by providing language-specific content, adapting cultural nuances, and aligning with local digital infrastructure. Instead of offering a one-size-fits-all website, you deliver experiences that feel native to each region, allowing your business to reach audiences that competitors may overlook.
- Enhances User Engagement and Experience: When a website reflects the local language and cultural expectations, users feel an immediate sense of familiarity. Navigation feels intuitive, messaging resonates naturally, and users are more likely to stay on your site. This alignment reduces friction, improves user satisfaction, and encourages repeat visits, all of which strengthen engagement.
- Builds Loyalty and Trust: Trust is one of the biggest barriers when entering a new market. A localized site builds credibility by using local language, displaying prices in local currency, and adhering to regional compliance norms. These details may seem small, but they strongly influence whether a visitor feels comfortable enough to complete a purchase or share personal information.
- Drives Business Revenue: By eliminating language and cultural barriers, localization improves conversion rates. Customers are far more likely to purchase when product descriptions, payment options, and support channels match their expectations. This creates a direct path to revenue growth, especially in markets with high digital adoption but low availability of website localization services.
- Improves Search Engine Visibility: Localized websites gain stronger visibility in regional search results. This involves using SEO practices tailored to specific markets, such as implementing hreflang tags, researching locally relevant keywords, and hosting content in-region. Together, these steps improve discoverability, helping your website appear in the searches that matter most to your target audience.
Note: Run website localized tests across 3000+ environments. Try LambdaTest Now!
Examples of Localized Websites
Here are a few examples that illustrate that website localization is far more than translating text. It encompasses adapting the interface, content, pricing, and features to align with the expectations and behaviors of local users.
Netflix
On the Netflix France website, Netflix highlights a wide variety of movies, TV shows, and original content tailored to local tastes. The platform is presented in English or French, with subscription prices displayed in EUR, and the sign-up flow emphasizes simple account creation and flexible payment options.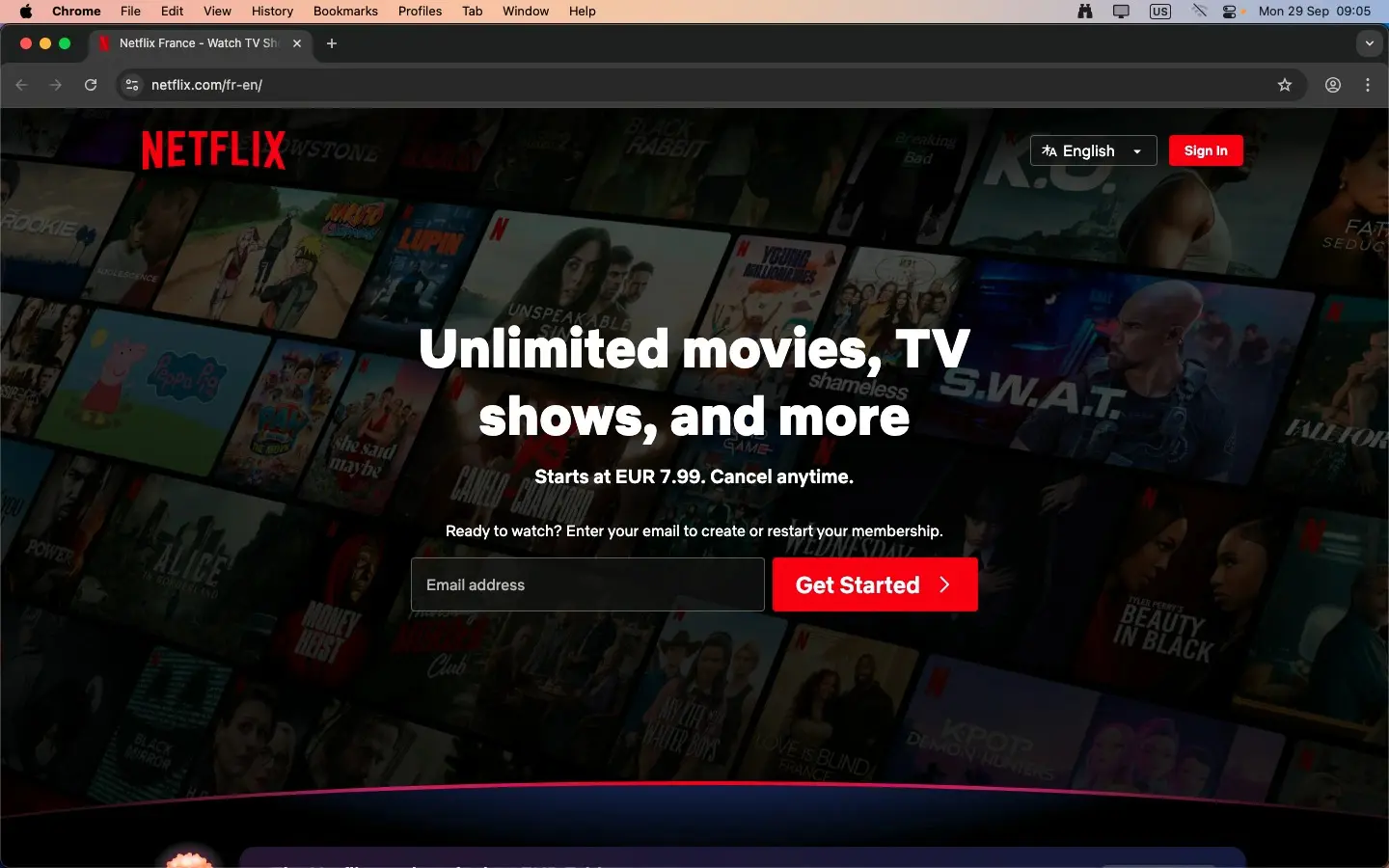
The content often focuses on trending series, popular films, and curated collections, with recommendations based on viewing habits and local preferences. Netflix also emphasizes exclusive originals and international hits, ensuring both global and regional audiences find engaging entertainment options.
Airbnb
The Airbnb French website showcases localization by offering content in French, displaying prices in Canadian dollars (CAD), and highlighting popular accommodations like "Coup de cœur voyageurs" (Traveler's favorites). The properties featured are in various cities such as Alicante and Paris, with details about dates, prices, and user ratings.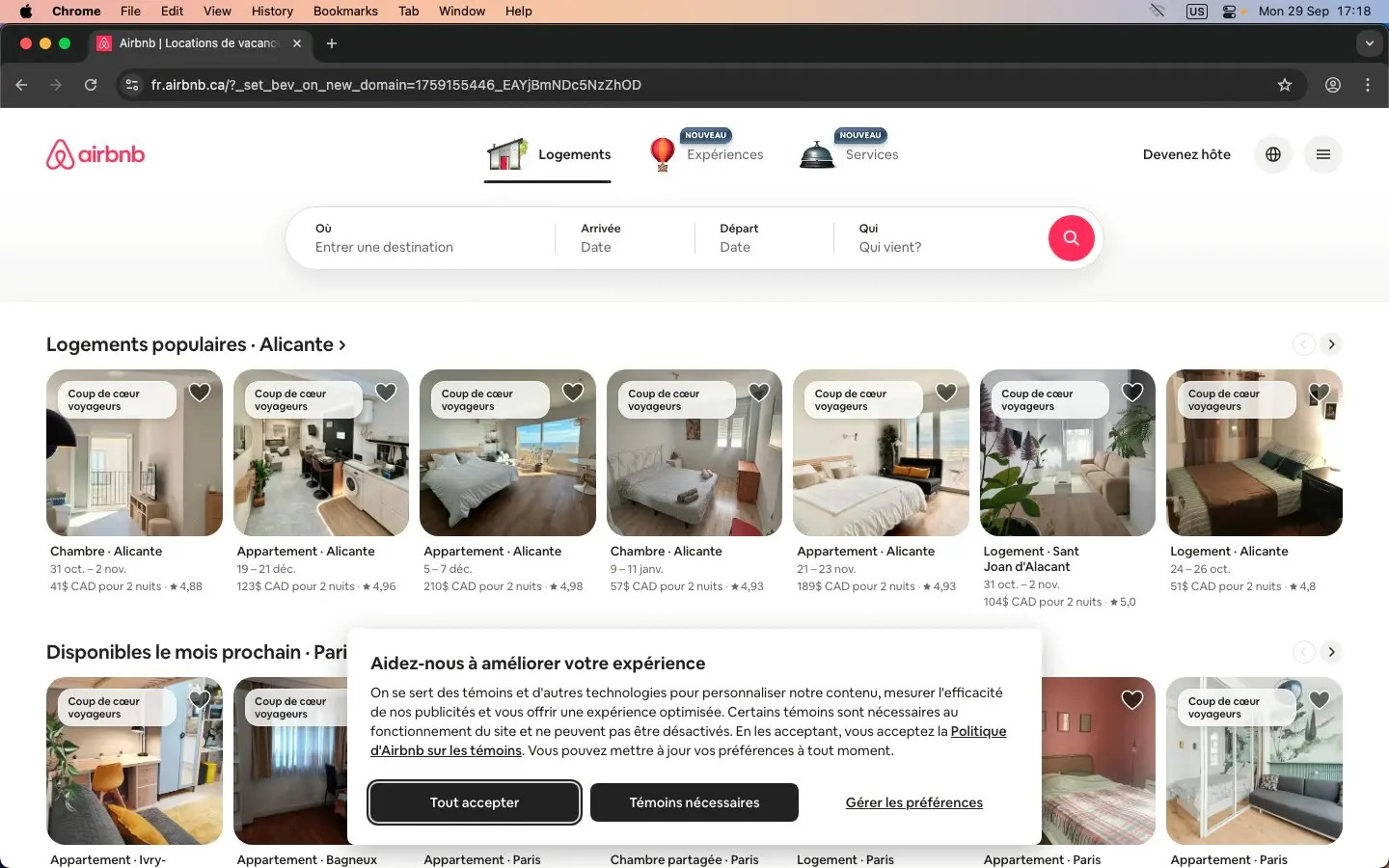
From a testing perspective, this highlights the need to validate multilingual interfaces, ensure accurate date and time formats (DD/MM/YYYY vs. MM/DD/YYYY), confirm payment gateway functionality for regional currencies, and check map integrations for accuracy across different browsers and devices.
9 Key Strategies for Effective Website Localization
Localizing a website involves a structured, multifaceted approach that goes beyond translation. Each step ensures your content resonates with the target audience, meets technical requirements, and adheres to local regulations.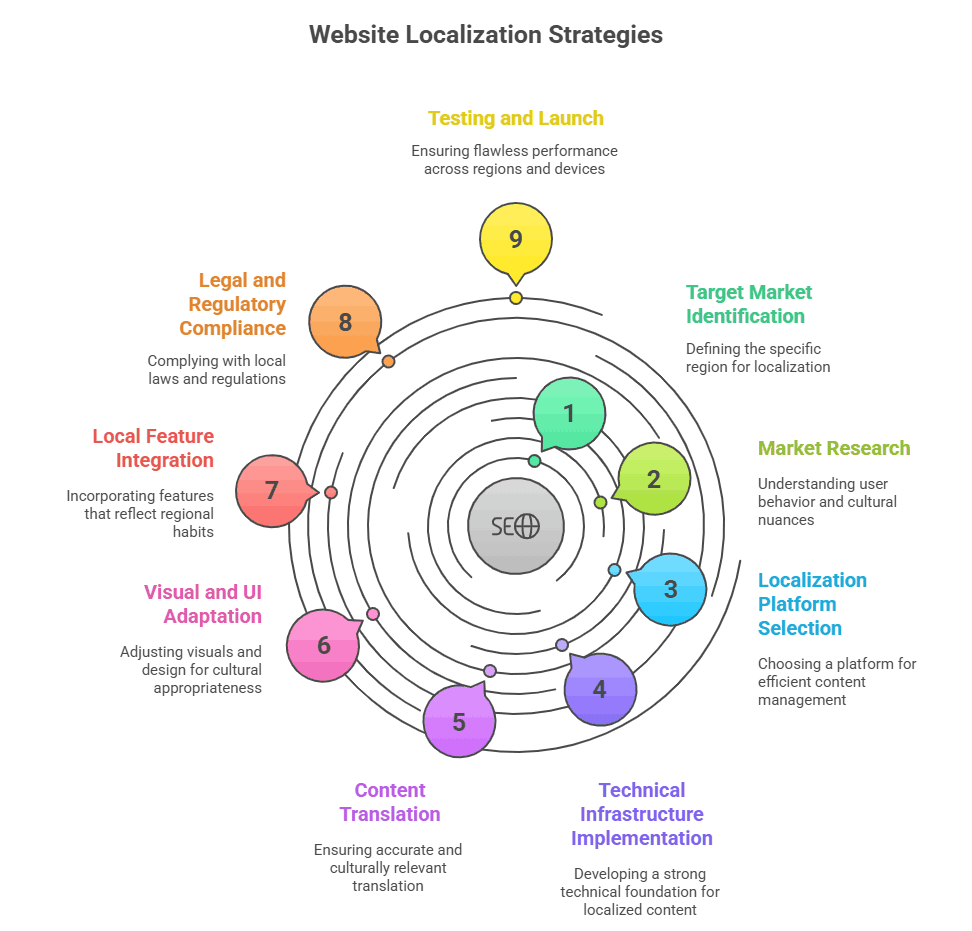
1. Identify Your Target Market
Begin by clearly defining the specific country or region you wish to target for localization, considering growth potential, audience demographics, and existing brand recognition.
- Internet Access and Device Adoption: Evaluate the percentage of people with reliable internet access and assess how widely smartphones, tablets, and desktops are used in the region to ensure content accessibility.
- Customer Demand: Examine existing organic traffic, search behavior, and potential interest in your products or services to determine whether sufficient demand exists to justify full localization efforts.
- Competitive Landscape: Assess the number of competitors, the level of market saturation, and the unique opportunities your brand could leverage to differentiate itself successfully from existing providers.
- Resource Alignment: Confirm whether your organization has operational capabilities, including customer service teams, shipping networks, and logistics infrastructure, to effectively serve customers in the target region without compromising quality.
2. Conduct Market Research
After identifying the target market, conduct detailed research to understand user behavior, cultural nuances, and local purchasing patterns.
- Cultural Analysis: Study local customs, color symbolism, imagery preferences, and communication styles to avoid missteps and ensure content aligns with cultural expectations in the region.
- Payment and Device Preferences: Identify the most widely used payment methods and device types, noting that some regions favor mobile app usage while others predominantly use desktop platforms for shopping. App localization testing adapts mobile apps to local languages, culture, formats, and region-specific features for a smooth user experience.
- Social Media and Digital Behaviors: Identify the most popular social media channels, search engines, and online behaviors, which will guide your marketing, advertising, and user engagement strategies effectively.
- Local Regulations and Policies: Research relevant laws, taxes, and eCommerce rules to ensure that your website complies with legal requirements, including data privacy and customer protection.
3. Select a Localization Platform
Choose a platform that aligns with your content management workflow and technical requirements for scaling localized content efficiently.
- Automation and Integration: Look for platforms that offer API integrations, automated content updates, and collaboration tools to streamline translation and localization across teams and departments.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Ensure the platform can accommodate expansion into multiple languages and regions while maintaining consistency in terminology, formatting, and brand voice across all localized pages.
- Collaboration Features: Opt for tools that enable translators, developers, and marketing professionals to work together seamlessly, reducing bottlenecks and improving overall project efficiency.
- Supported File Types and CMS Compatibility: Check if the platform supports your content types and integrates smoothly with your existing CMS to avoid time-consuming manual adjustments or errors.
4. Implement Technical Infrastructure
Develop a strong technical infrastructure to support localized content, ensuring proper SEO, fast load times, and accurate regional targeting.
- URL Structure: Decide between subdirectories, subdomains, or country-specific domains to clearly indicate language and regional versions, improving both user clarity and search engine indexing.
- Hreflang Tags: Implement hreflang attributes to ensure search engines display the correct language and regional version to users in specific markets, enhancing SEO performance.
- Content Delivery Networks: Use a CDN to reduce page load times globally and ensure a consistent, high-quality browsing experience for users in all target regions.
- Geo-Targeting and Redirects: Configure your site to automatically detect user location and redirect visitors to the appropriate localized version without impacting user experience or navigation.
5. Translate Content Accurately
Translation is only effective when it captures cultural nuance, tone, and intent rather than simply converting words.
- Native-Speaking Translators: Use professional translators who are native speakers and familiar with local idioms, humor, and linguistic subtleties to ensure content resonates authentically.
- Prioritize Critical Pages: Begin with high-impact areas like homepages, product pages, checkout flows, and legal content before moving to secondary informational pages or blog posts.
- Professional Review and Quality Control: Even if automated translation tools are used, a human review ensures accuracy, consistency, and cultural appropriateness, reducing errors that can compromise brand credibility.
- Transcreation for Marketing Copy: Adapt slogans, taglines, and emotional messaging to preserve brand impact rather than relying on literal translation, which can reduce engagement.
6. Adapt Visuals and User Interface Design
Visuals and design must be culturally appropriate, flexible, and responsive to accommodate different languages and preferences.
- Imagery: Use photos, graphics, and illustrations that reflect the culture, lifestyle, and environment familiar to the local audience to improve relatability and engagement.
- Layout and Text Expansion: Ensure your website visual design can accommodate longer text strings, such as German or French translations, without breaking the layout or affecting readability.
- Colors and Symbols: Verify that colors, icons, and symbols convey the intended meaning in the target culture, avoiding unintended negative associations that could confuse or alienate users.
- User Interface Adaptation: Adjust navigation, buttons, forms, and other interactive elements to match regional conventions and user expectations, improving usability and conversion rates.
7. Integrate Local Features
Incorporating features that reflect regional behaviors and expectations demonstrates attention to local needs and builds trust.
- Payment and Shipping Options: Offer region-specific payment methods, currency conversion, and delivery options to remove friction and increase conversions.
- Customer Support: Provide local phone numbers, chat support, and service hours aligned with regional time zones to create a reliable user experience.
- Seasonal and Event-Specific Promotions: Adapt marketing campaigns, banners, and offers to local holidays, cultural events, and seasonal patterns for greater engagement.
- Local Functionality Enhancements: Include regional preferences such as measurement units, date formats, and language-specific search filters to improve overall usability.
8. Ensure Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Complying with local laws protects your brand, prevents penalties, and ensures that users feel secure interacting with your site.
- Data Protection Laws: Follow regulations such as GDPR in Europe or other country-specific privacy legislation to protect user information.
- Accessibility Standards: Implement WCAG guidelines for web accessibility and ensure your site is usable by people with impairments, meeting both legal and ethical requirements.
- eCommerce and Tax Regulations: Adjust your pricing, invoicing, and shipping policies to comply with local tax laws and consumer protection regulations.
- Legal Documentation Localization: Translate and adapt terms of service, privacy policy, and return policy to reflect local requirements and maintain trust with users.
9. Test and Launch
Thorough localization testing ensures your localized website performs flawlessly across regions, devices, and languages.
- Functional Testing: Perform functional testing to ensure that all links, forms, checkout processes, and interactive features work correctly in each localized version.
- Linguistic Testing: Have native speakers review live content for translation accuracy, proper formatting, and cultural appropriateness, correcting any errors before launch.
- UI Testing: Perform UI testing to ensure images, layouts, and text display correctly without truncation, overlapping, or design inconsistencies.
- Cross-Browser and Device Testing: Conduct cross browser testing to verify consistent performance across popular browsers and devices in the target region to simulate user environments. You can leverage platforms like LambdaTest to run cross browser and device tests on a remote test lab of different browsers, real devices and operating systems.
- Final Launch Verification: After successful testing, deploy the localized website and monitor initial user interactions to ensure a seamless experience while addressing any unexpected issues quickly.
Test Websites Across Different Locales With LambdaTest
LambdaTest is a cloud-based testing platform that allows teams to validate their websites and mobile apps across thousands of real browsers, operating systems, and devices without maintaining physical infrastructure. Its online localization testing and geolocation testing capabilities ensure that digital experiences work seamlessly across different regions, languages, and cultural contexts.
It combines manual and automation testing to catch both functional and visual issues, enabling teams to release web products faster while avoiding localization-related errors.
Benefits:
- Enhanced User Experience: LambdaTest ensures websites and apps are culturally, linguistically, and regionally optimized, improving usability, engagement, and satisfaction for every target audience across diverse locales worldwide.
- Expanded Market Reach: By validating functionality and content in multiple languages and geographies, LambdaTest helps businesses access and compete effectively in global markets without localization issues limiting growth.
- Regulatory Compliance: LambdaTest enables testing for local laws, accessibility, and data protection standards, helping companies avoid legal penalties, fines, or operational disruptions while maintaining market credibility.
- Faster Time-to-Market: By addressing locale-specific challenges early through automated and live testing, LambdaTest accelerates product launches in multiple markets while maintaining high quality and user experience.
- Cost Efficiency: Identifying and resolving localization and region-specific issues before release reduces customer support costs, prevents revenue loss, and minimizes rework or patching after deployment.
Website Localization Best Practices
The following best practices provide a structured foundation for approaching website localization, ensuring your efforts are strategic, culturally aligned and consistently effective across global markets.
- Develop a Comprehensive Localization Strategy: A good localization strategy should align with your overall business objectives and your overall international expansion plan. It should outline your target markets, budget allocation, technical infrastructure, project timeline, and success metrics. This provides a clear roadmap that supports smooth execution.
- Invest in Professional Translators: While AI translation tools have advanced significantly, they are not always equipped to capture idioms and cultural nuances. Professional translators ensure accuracy, maintain tone, and adapt the language to resonate with local audiences. This investment strengthens communication and creates long-term value by delivering a polished, reliable experience.
- Optimize for SEO and Speed: Localized content must be discoverable. This means optimizing for search engines that dominate in your target region (e.g., Baidu in China, Yandex in Russia). Using local keywords, meta tags, and search behaviors increases visibility and organic traffic. Implementing a CDN reduces latency, ensuring users worldwide experience fast loading times. Both search visibility and performance enhance customer trust and conversions.
- Maintain Consistent Brand Identity: Your brand should remain recognizable no matter the market. Consistency does not mean uniformity; logos, slogans, and tone can adapt subtly to cultural expectations without losing their essence. For example, a playful tone may work well in the U.S., while a more formal approach may suit Japan. Balancing global identity with local preferences reinforces trust and creates authentic connections.
- Prioritize Cultural Research: Successful localization goes beyond language. It requires an understanding of cultural norms, traditions, humor, colors, and even number symbolism. Detailed research helps you tailor visuals, design, and messaging so your product feels natural in the local context. This makes customers more likely to engage and convert.
- Test Continuously to Refine Quality: Localization is an ongoing process. Regular testing helps confirm accuracy in translation, layout, and functionality across different devices and languages. Usability testing with native speakers ensures content reads naturally and feels intuitive. Continuous improvements strengthen customer satisfaction and support long-term growth.
You can also leverage tools like Selenium to automate your localization testing process. Check out this blog to get started with localization testing with Selenium.
Localization vs Translation vs Internationalization vs Globalization
Expanding into international markets requires understanding several related but distinct processes. While these terms overlap, each plays a unique role in making products and websites effective for global audiences.
| Aspect | Localization (L10n) | Translation | Internationalization (i18n) | Globalization (G11n) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Adapting content, design, and functionality to fit cultural, linguistic, and regional expectations. | Converting written or spoken text from one language into another. | Preparing websites to support multiple languages and regional settings without major rework. | Developing a holistic business strategy for operating effectively across multiple international markets. |
| Primary Focus | Full user experience in a specific market. | Words and meaning. | Technical flexibility for future localization. | Business growth and operational alignment worldwide. |
| Scope | Wide, includes language, visuals, UI, payment systems, and compliance. | Narrow, text-only. | Backend architecture, data models, coding standards, and content separation. | Corporate strategy, logistics, marketing, support, and partnerships. |
| Example | A German retail site offering localized payment methods, VAT pricing, and culturally relevant imagery. | Translating an English product manual into Spanish. | A CMS designed to handle right-to-left languages and multiple currency formats. | Netflix tailors shows, pricing models, and marketing for dozens of regions. |
| Tools / Methods | Translation plus cultural review, design adaptation, and regional QA testing. | CAT tools, machine translation engines. | Unicode support, modular code, and locale-aware libraries. | Market entry frameworks, international marketing campaigns, and global supply chain management. |
| Benefits | Creates trust, usability, and stronger engagement with local users. | Allows basic comprehension across languages. | Reduces the cost and effort of scaling to new markets later. | Enables sustainable global presence and brand consistency across regions. |
Want to see how internalization and localization testing fit into this process? Check out this blog on internalization and localization testing.
Conclusion
Website localization is essential for engaging global audiences by adapting content, design, and functionality to cultural, linguistic, and technical expectations. Following key strategies, testing across locales, and understanding localization versus translation ensures usability, trust, and higher conversions. Best practices such as accurate translation, compliance, and optimized performance enable websites to feel native, strengthen brand credibility, and maintain a competitive advantage internationally.
Citations
- Website Localization Techniques: https://www.ijcaonline.org/archives/volume150/number7/26108-2016911566/
On This Page
- What Is Website Localization?
- Why Website Localization Is Important?
- Examples of Localized Websites
- Key Strategies for Website Localization
- Test Websites Across Locales With LambdaTest
- Localization vs Translation vs Internationalization vs Globalization
- Website Localization Best Practices
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Did you find this page helpful?
More Related Hubs

Start your journey with LambdaTest
Get 100 minutes of automation test minutes FREE!!