A Comprehensive Guide to App Localization and Testing
Nishtha Gupta
Posted On: January 12, 2024
![]() 30766 Views
30766 Views
![]() 21 Min Read
21 Min Read
Be it a retail giant expanding its brand to a new country or a small vendor operating in a certain district. App localization is pivotal for any business looking to expand their go-to-market strategy. App localization is a process of transforming an app’s user experience and interface with respect to a certain geography and locale.
According to Forrester, 64% of buyers value content that is localized and as per CSA, 72.1% of internet users opt for shopping on websites in their native language, including those proficient in English who still prefer browsing the Internet in their mother tongue.
As critical as it may sound, some stakeholders may question the relevance of app localization or go live with a half-baked strategy. For instance,
Let’s say you’re developing a fitness app and you want your button to say “workout.” In French, it turns into “entraînement,” which on the first look might seem to resemble “entertainment” or be interpreted around a similar note to someone who isn’t familiar with French.
If you decide to skip the localization process and go with a one-size-fits-all approach, you might end up with unexpected outcomes. However, app localization goes beyond translation. One needs to note various factors i.e. timezone, URL directory, app store listing while planning app localization.
In this blog we’ll discuss why app localization becomes necessary to capture new markets and share some tips and tricks to perform localization testing on your apps and website.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
- What is App Localization?
- Why is App Localization Important?
- Is App Localization the Same as Internationalization?
- App Localization Failures that led to Negative Brand Perception
- What are the Common App Localization Challenges?
- What are the Elements You Should Consider while Localizing your App?
- How to Create an App Localization Strategy?
- How to Localize your Mobile App?
- How to Perform Localization Testing?
- What does the Localization Testing Lifecycle look like?
- How can Localization Testing Make your App Stand Out?
- App Localization is the key to business success!
What is App Localization?
App localization is adapting a mobile application for different languages and regions. It involves translating text, adjusting date formats, and modifying content to suit the cultural preferences of specific target audiences.
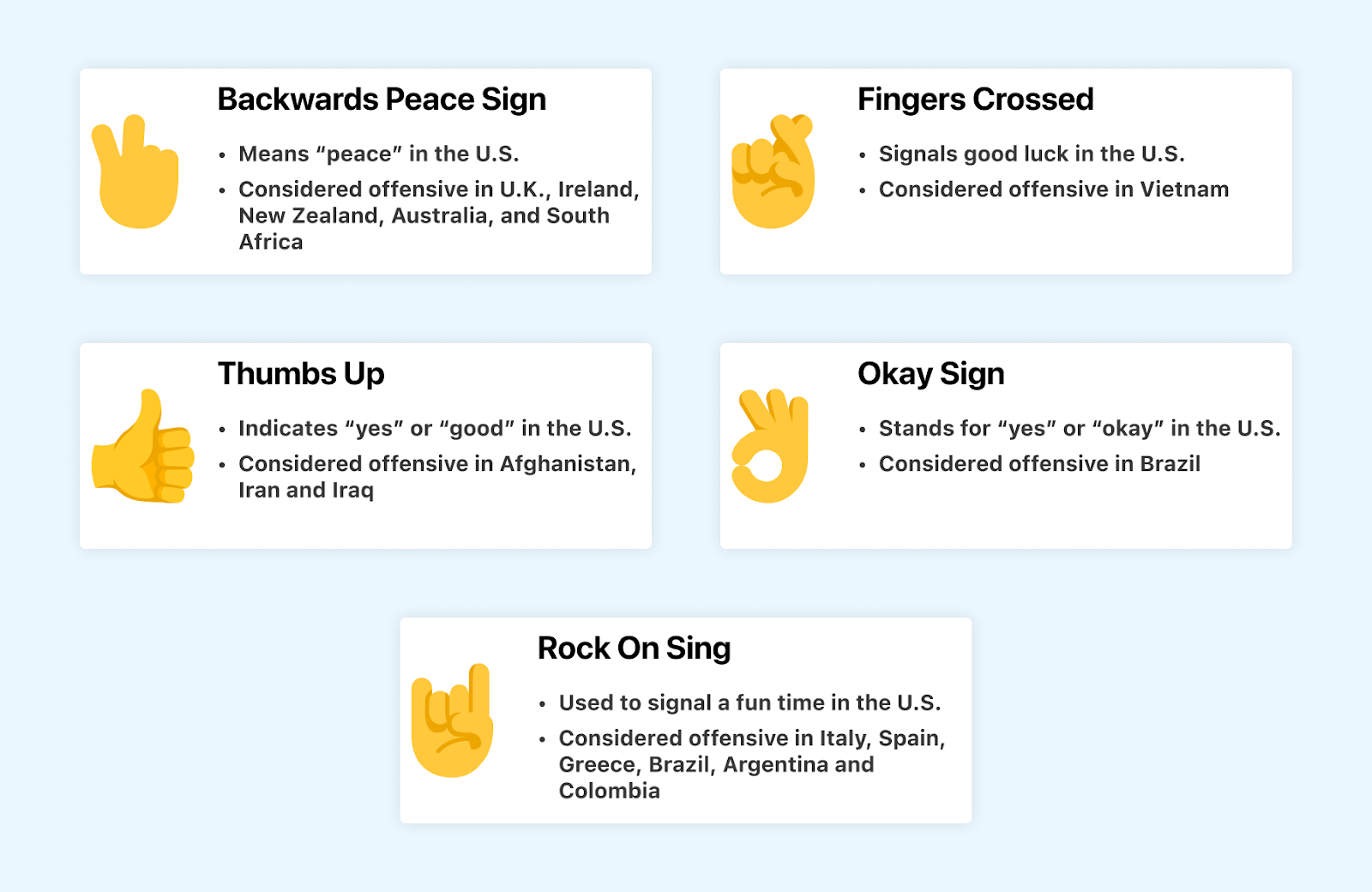
For example if you use emojis to show an action or describe a function- you should keep in mind that while these emojis could be harmless in the U.S, but could actually be very offensive in another country. Regardless, these can be huge factors in the success of your app abroad.
Why is App Localization Important?
Neglecting app localization may lead to missed opportunities, according to the Statista Report showing that 35% of respondents use foreign language documentation daily. Some of the other potential benefits include:
- Unlocking higher growth market with a localized app: App localization serves as a key strategy for expanding into diverse markets. By customizing apps to different languages and cultures, businesses can access high-growth markets effectively.. Beyond market reach, effective localization ensures a consistent and user-friendly experience globally. For example, the language learning app, Duolingo was successfully able to localize their app by tailoring its content to meet the specific language learning needs of users from various regions.
- Boosting app searchability through different search engines: Enhancing your app’s searchability is a key advantage of localization. It increases the likelihood of your app appearing under location filters when users search for similar products on app marketplaces. Users are more inclined to download a localized version of your app when it is presented in their language or tailored to their country, compared to encountering a default English version available worldwide.
- Driving more app downloads in the targeted geography: When you tailor your app to the language, culture, and preferences of a specific target market, you create a more engaging and user-friendly experience. Leading to higher download rates.
- Better app retention and increased engagement: Enhancing the user experience on a global scale is crucial for widespread app engagement and usability. A lack of consistency in user experience can negatively affect your overall performance. Despite initial downloads, users are quick to uninstall apps that provide a subpar user experience or fail to meet their linguistic requirements.
- Positive Impact on the Revenue Improving the Bottom Line: According to a recent study by CSA, 66% of B2B buyers are willing to allocate more resources to an app providing a localized language experience. For B2C buyers, this figure slightly decreases to 34%. This highlights that buyers not only consider purchasing the product but are also willing to invest more for an enhanced experience, leading to higher revenue and customer satisfaction rates.


Moreover, a well-received localized version contributes to higher rankings in app stores. Achieving a high rating is one effective method to boost your app’s visibility, emphasizing the importance of offering a localized experience.
For example- In targeting the Japanese market, a gaming app originally in English undergoes app localization. This involves translating the interface, instructions, and promotional content into Japanese, adding elements that match Japanese gaming preferences. As a result, the app becomes more relatable and enjoyable for Japanese users. This tailored approach significantly boosts downloads in Japan, as users find the app culturally relevant and accessible in their language.
Neglecting globalization puts you at risk of falling behind competitors. As competitors increasingly adopt such technologies in response to growing consumer demand, offering localized options sets you apart from the competition.
Is App Localization the Same as Internationalization?
Though the two terms are often used synonymously, there is actually a difference between app internationalization and localization. In simpler terms, localization involves adapting app content for a specific language or region, including website, app, images, video, and more. Internationalization, on the other hand, focuses on creating a globally adaptable product from the start. The aim of localizing mobile apps is to ensure a natural user experience in their native language, ultimately boosting user affinity, downloads, and revenue.
| Aspect | Localization | Internationalization |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Adapts app for specific culture | Prepares app for global use |
| Timing | After app development | During initial development |
| Content Modification | Adjusts text, images and cultural elements | Focuses on structural changes for language support |
| Target | Specific regions or languages | General language adaptability |
| Dependency | Requires an internationalized app | Can occur independently |
Read more: Localization vs Internationalization Testing
App Localization Failures that led to Negative Brand Perception
As we discussed, when expanding your brand into foreign markets, it’s important to put in the necessary research and effort to truly understand the culture of your target audience. Let’s have a look at some real world examples showcasing how app localization failures impacted these brands:
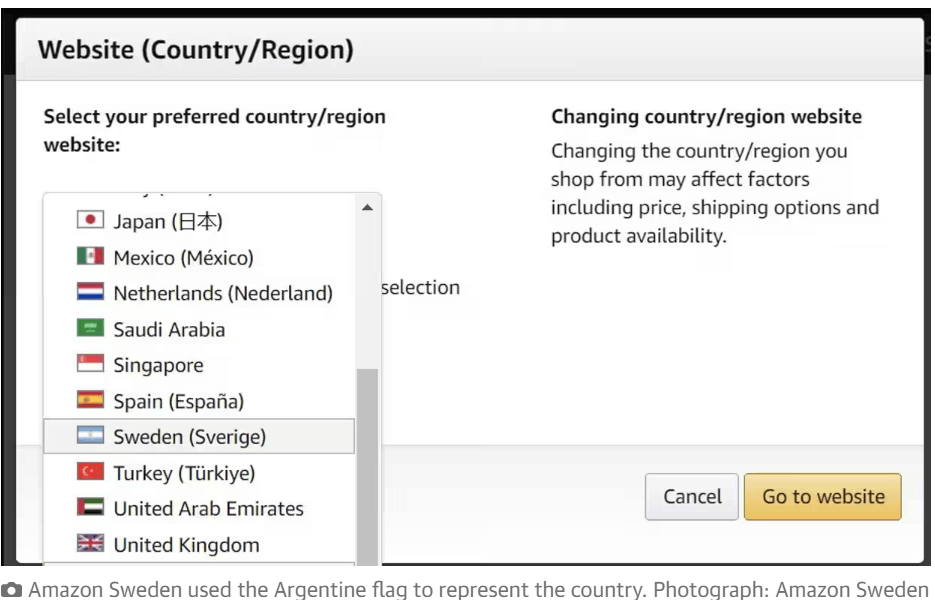
- Amazon’s Hilarious Blunders in the Swedish Launch: In 2020, Amazon faced criticism during the launch of its Swedish website due to translation errors. The company mistakenly used the Argentinian flag instead of the Swedish one and didn’t fix machine translations from English to Swedish. This resulted in product descriptions filled with mistranslations, some even turning amusing or inappropriate, like replacing “rooster” with a Swedish term for private parts and labeling a frying pan as a “product for women.”
- Not Quite Right- Brave’s Spanish UI Translation: Brave, a web browser known for its privacy features, has a somewhat jumbled Spanish translation in its user interface. Various elements display in both English and Spanish, and it seems like many translated parts haven’t been checked for errors. For instance, “Cerca” (meaning “near”) was used instead of “Cerrar” as a caption for closing a tab.
What are the Common App Localization Challenges?
Having discussed the need of app localization, it’s crucial to understand the challenges that you might face before or during the process and how to overcome them:
- Tailored Experience Gaps in Localized Versions: The most common localization challenge involves the inability of localized versions to fully adapt to the specific cultural and user experience expectations of different regions. Technical constraints could limit the app’s ability to dynamically adjust content presentation, resulting in a suboptimal user experience for the new audience.
- Overlooking Global Expansion Impacting Costs and Timelines: Commonly software or app developers overlook the importance of designing and coding apps with future global expansion in mind, neglecting localization until it becomes a last-minute concern. This oversight can lead to complications during app adaptation for new markets, resulting in issues that may be challenging and costly to rectify.
- Localization Bugs Leading to Bad App Reputation at Release: Many localized apps face problems at release due to localization errors, such as mistranslations or incomprehensible app strings, rendering the app unusable. These issues can harm the app’s reputation, drive users away, and lead to negative reviews.
- Localization Falling Behind Development in Fast-paced Workflows: In fast-paced development workflows, if localization operates separately from the agile framework, it may lag behind app development. This delay can increase costs, hinder app release, and impede developers from working on new features while waiting for translation.
- Workflow Inefficiencies due to Limited App Localization Tools: Using the wrong app web or mobile app localization tools can lead to workflow inefficiencies, prolonged email exchanges, difficulties in tracking app strings, and longer release times. Inadequate tools contribute to undetected mistakes and compromised localization quality.
Solution: Implement a robust system that allows for dynamic adjustments in the app’s design and content based on the cultural preferences of each region. This may involve creating modular components that can be easily customized for different markets without compromising the app’s overall functionality. Conduct thorough technical assessments to ensure that the app’s architecture supports these adaptive features for a tailored and immersive user experience across diverse locales.
Solution: To minimize costs and speed up app localization, it’s crucial to integrate internationalization into the early stages of app development. Designing the app to support multiple languages from the beginning allows for more efficient management of localization efforts and costs.
Solution: To prevent localization errors at app release, invest in testing and quality assurance for each language. If testing every single element is not feasible, consider using pseudolocalization tools to identify issues before the translation process. Various pseudolocalization tools on platforms like GitHub can aid in testing usability, readability, and other key aspects.
Solution: To prevent localization from falling behind, establish a localization process within the agile app development framework. Involve localizers in development teams from the start, fostering collaboration, knowledge sharing, and regular feedback loops. Breaking down silos and promoting constant communication ensures an app that’s localized seamlessly.
Solution: Adopting a dedicated app localization platform designed with developers, product teams, and localizers in mind can help in solving this challenge. A reliable platform automates data collection, centralizes localization projects, manages translations efficiently, integrates with development tools, and streamlines communication to enhance overall workflow.
What are the Elements You Should Consider while Localizing your App?
Localizing your app involves adapting various elements to suit the preferences and cultural nuances of specific regions. Here are some essential elements that should be considered for effective app localization:
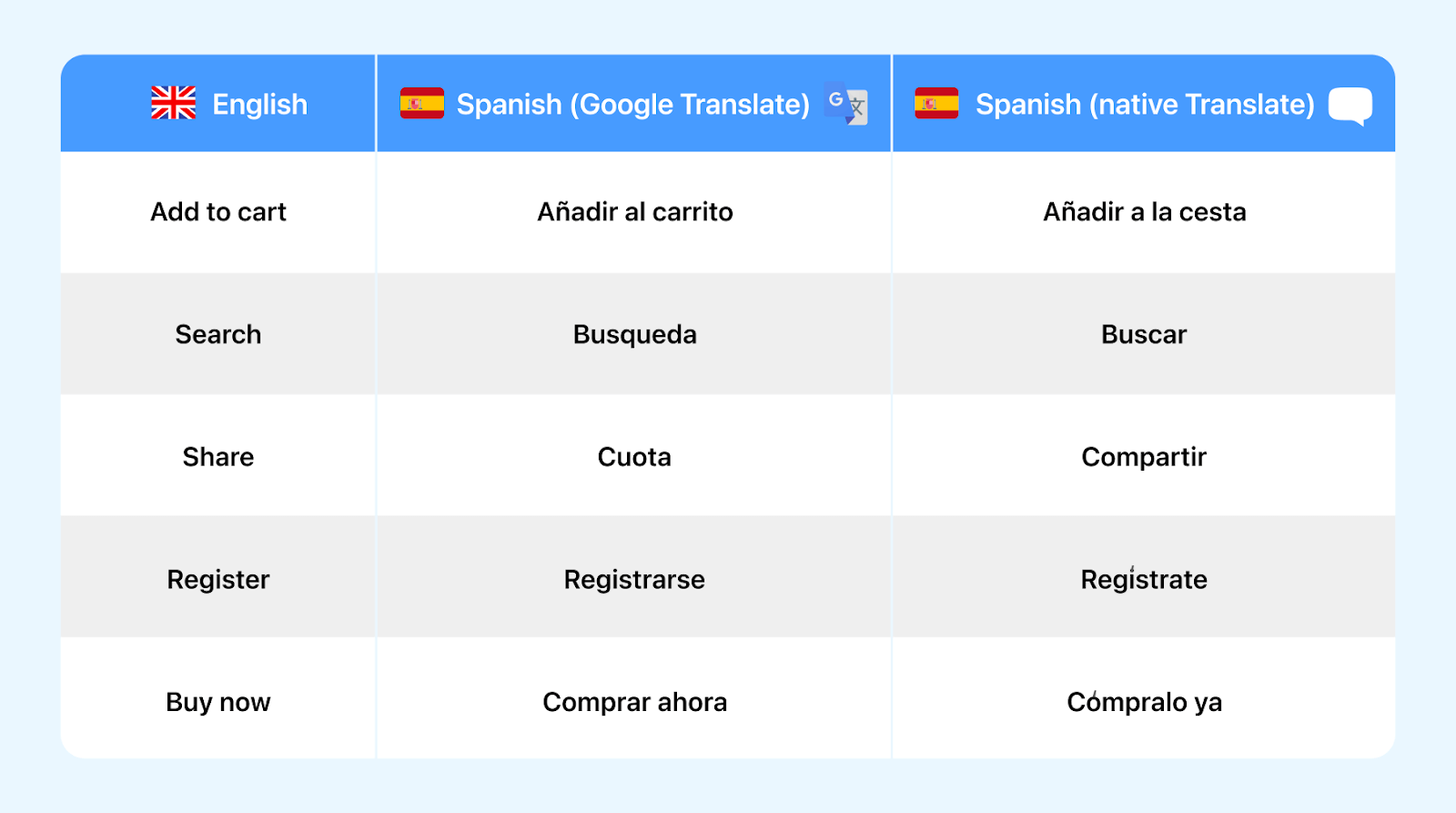
- Language: Often it is observed that sometimes even the best apps can’t adapt to their users’ native language. To get this right, developers solely rely on translation tools like Google Translate but they might not capture the nuances correctly. Instead, an easier way is to involve native speakers to ensure accurate translations.Consider cultural differences and unique phrases, like proverbs, that might not have direct equivalents in other languages.differences and unique phrases, like proverbs, that might not have direct equivalents in other languages. For example:
- Keywords: Keywords play a crucial role when it comes to SEO and ASO and their effectiveness varies by country. Conduct thorough research to identify region-specific keyword volumes and incorporate these relevant keywords into your app listings. If prioritizing localization, focus on adapting app store pages for countries with the highest download volumes. Tailoring unique pages for specific regions not only encourages user engagement but also serves as a valuable indicator for prioritizing more comprehensive localization efforts in those countries.
- Currency: Considering currency localization in mobile apps is crucial, especially for apps that involve transactions, payments, or financial interactions. For example- In USA the currency symbol is denoted by $ while in South Africa it is R or ZAR and in India it is denoted by ₹ or Rs.
- Colors: In different cultures, each color has a different meaning. While as a developer you may think that it’s just a color and how it could offend someone, it’s possible that folks may perceive your app negatively just because of the color scheme you picked. Here are some colors that depict different meanings in every culture or country. Keep in mind that these interpretations can vary within cultures, and individual preferences also play a role. It’s essential to consider cultural nuances and do specific research for the target audience you are catering to.
- Visuals and Language in Imagery: Depending on your imagery, your visuals and text should be culturally more aligned. For instance: For instance, if you’re promoting a travel app, use images of cherry blossoms for Japan but switch to local markets for a Middle Eastern audience. Also, translating any text in images accurately like a discount offer in English may need precise translation for Arabic or Mandarin users. This ensures your visuals connect effectively with diverse audiences.
- Date and Time Format: Adapt your date format – MM/DD/YYYY, DD/MM/YYYY, or YYYY/MM/DD and display a 12 hour or 24 hour time format depending on the country you are localizing for.
- Focus on Device: Concentrate on developing for the preferred OS and devices in each region. For example, if iOS devices are more popular in the United States, allocate more resources and updates for iOS development to cater to the user base there. In contrast, if Android dominates in Southeast Asia, prioritize Android development to better serve the prevalent user devices in that region. This strategy optimizes your app’s compatibility and user experience based on the predominant devices in each targeted market.
- Name and Number Format: While considering localization, small details matter in how numbers and names are written. For example, in the U.S., you might write 2,043.1, while in Brazil it could be written as 2.043,1. Names are also different, like starting with the first name or the last name. Particularly in sectors like banking, it’s important to adjust forms so they match how people do things in each country.
For example: you have a language-learning app, and you’re localizing it for both English-speaking and Spanish-speaking users. In the English version, you might focus on keywords like “language learning,” “vocabulary,” and “English lessons.” However, for the Spanish version, you’d need to research and incorporate keywords like “aprendizaje de idiomas,” “vocabulario,” and “clases de español.” By tailoring your keywords to each language, you enhance the visibility of your app in specific regions, making it more likely for users to find and download it.
| Culture | Western Interpretation | Eastern Interpretation | Other Culture Interpretations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Red | Love, Passion | Good Fortune, Happiness | Warning (South Africa) |
| Blue | Calm, Trust | Wisdom, Immortality | Mourning (Iran) |
| Green | Health, Nature | Infidelity (Some culture) | Color of Islam (Saudi Arabia) |
| Yellow | Happiness, Energy | Sacred, Imperial | Mourning (Egypt) |
| White | Purity, Innocence | Mourning (Some cultures) | Death (China) |
| Black | Mourning, Elegance | Power, Sophistication | Death (Some Middle Eastern Countries) |
| Purple | Royalty, Luxury | Wealth, Prosperity | Mourning (Brazil) |
| Orange | Energy, Enthusiasm | Spirituality | Mourning (Egypt) |
How to Create an App Localization Strategy?
To avoid the common challenges that may arise while localizing your mobile app, you should be ready with a strategy that can include these basic steps:
- Define the Target Market
- Start by choosing the language you want to translate your app into.
- Prioritize based on actual usage data from app analytics, ensuring a targeted approach.
- Study the Feedback
- Analyze feedback from customer support and app reviews to identify potential localization opportunities.
- Look beyond visitor data to understand demographics and usage patterns in selected countries.
- Consider Customer Requests
- While customer requests are important, carefully evaluate them, especially if they involve targeting a new language or region.
- Choose requests that align with your overall strategy and potential user base.
- Do Market and Competitor Research
- Explore competitors’ strategies and market research to identify potential new markets.
- Understand the unique aspects of each market, considering the challenges and benefits of localization.
- Focus on One Language at a Time
- Plan your budget and approach, focusing on one language for localization at a time.
- This staged approach ensures quality and precision in the development and implementation of changes.
- Cover All Available Locales
- If your app is already in English (US), consider easy translations to English (UK) to reach additional markets.
- Evaluate options carefully, considering the benefits of each locale for expansion.
- Find a Great Translation Service
- Opt for professional translation services like OneSky, Wordbee, or PhraseApp to ensure accurate and culturally sensitive translations.
- Native speakers are crucial for quality translations that resonate with users.
How to Localize your Mobile App?
Once you have come up with the right app localization strategy, the next step is to execute the process:
- Prioritize Localization by Geography:
- Create an XML File for Translation:
- Translate Non-String Content:
- Translate App Store Content:
- Implement the Finished Translation:
- Internally Test Your Localized App:
- Make the Translation Available to Users:
Consider prioritizing translations based on target continents or regions. Address the localization needs of specific geographical areas first to optimize the impact of your app in those markets.
Prepare an XML file encompassing all app strings for professional translation. Including comments for context aids in ensuring a smooth translation process, facilitating accurate and meaningful translations.
In addition to strings, extend translation efforts to cover diverse elements such as text, images, video, audio, date format, numbers, and currency. Stay vigilant for potential translation challenges and uphold a professional standard throughout the process.
Localize the content on your Google Play or App Store page to offer users a seamless experience. By presenting app information in their native language, you minimize confusion and enhance user engagement.
Thoroughly review all translations before implementation to prevent errors. Insert the translated XML file into your app, and proceed with testing to validate the effectiveness of the localization.
Conduct smoke testing to assess functionality without language comprehension. Ensure that the localization doesn’t adversely affect app performance, maintaining a positive user experience.
Release the translated app to users who speak the language. Act on gathered feedback and data to promptly address any issues or implement improvements, ensuring a successful localized app launch.
How to Perform Localization Testing?
Since we’ve already discussed how to perform app localization and what elements should be localized, localization testing will ensure that a software or app functions seamlessly in different regions by validating language translations, cultural adaptations, and regional settings. It involves testing elements to guarantee a smooth user experience in diverse locales. This process aims to identify and rectify any issues related to the specific requirements of each target region, ensuring the product aligns with local expectations.
Run Localization Testing on Real Devices and Browsers
Now let’s discuss how can you go ahead with the geolocation testing of your mobile and web apps:
- Start with a Test Plan: Begin by outlining the objectives of the localization testing, specifying goals like ensuring accurate translations and cultural appropriateness. Describe the test environment, including language settings and device types. Define test cases, expected results, and list necessary resources such as translation services or physical devices.
- Simulate the UX: Whether using emulators or physical devices, recreate the user’s experience by testing the website or app in their native language, location, device type, operating system, and browser preference. This ensures a realistic evaluation of the site’s functionality and appearance.
- Initiate High Level Testing: Conduct regional, linguistic, and UI testing, focusing on eliminating translation errors, ensuring cultural appropriateness, and confirming the adapted layout. Verify that the translated content maintains the original message, fits the layout, and upholds the brand personality for the new audience.
- Implement Functionality Testing: Evaluate the website’s or the app’s functionality by checking buttons, hyperlinks, and page loading across supported languages. Ensure a smooth user journey, identifying and addressing any issues that may arise during the website interaction or checkout process.
- Documenting the Findings: Compile all testing observations in a consolidated report to share with translators, developers, and relevant team members. This ensures prompt identification and resolution of issues discovered during testing.
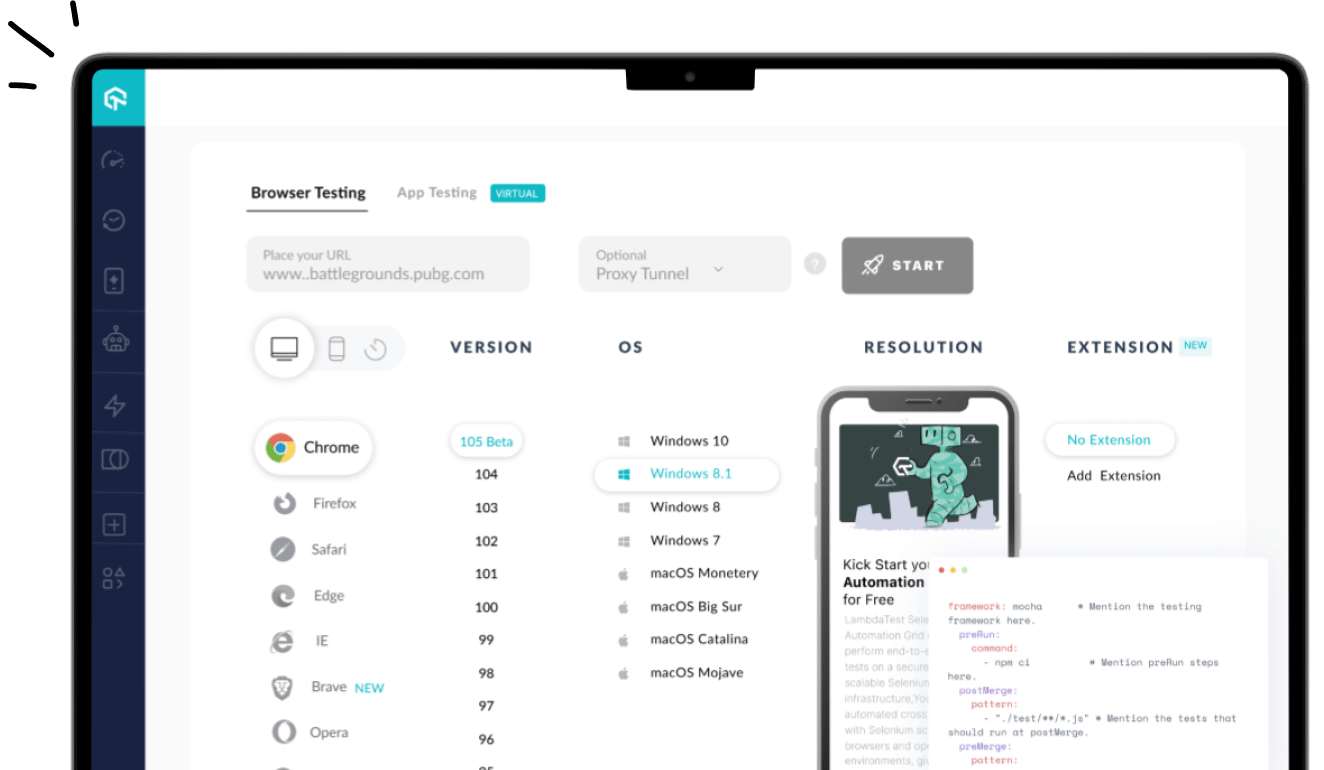
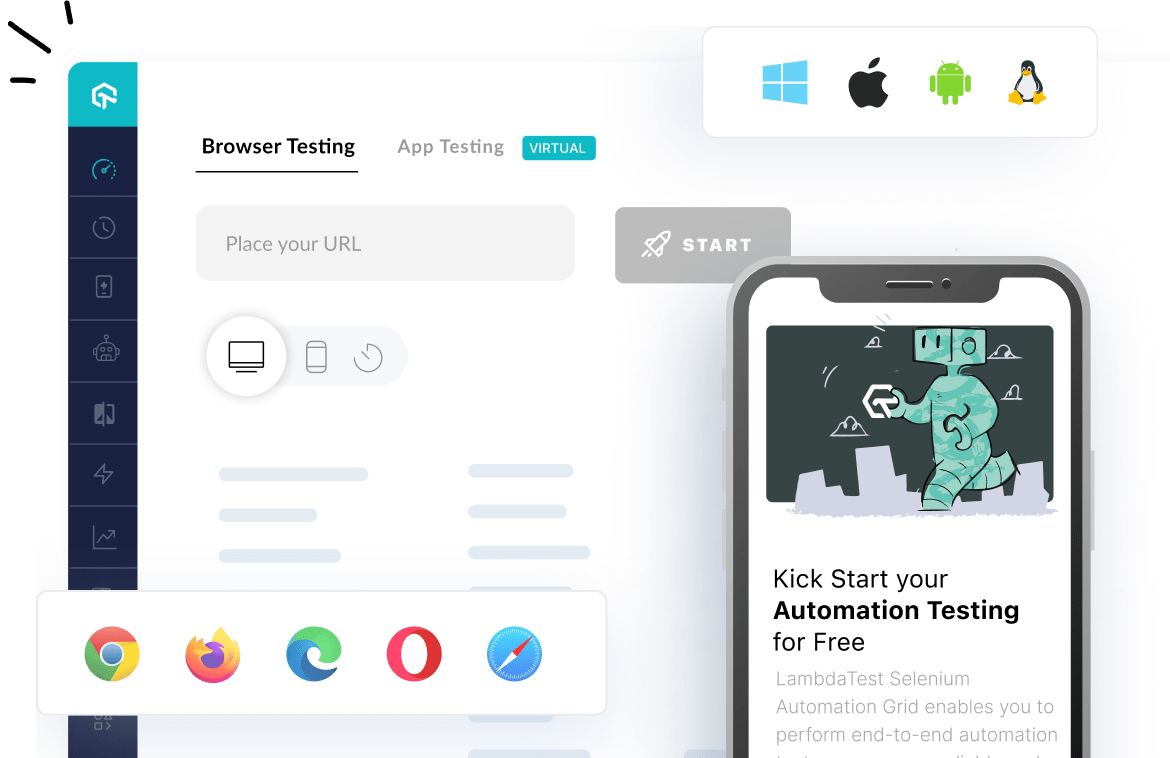
In order to fasttrack your website and app localization testing you can opt for a cloud-based test execution platform like LambdaTest to run localized tests on 3000+ real browsers and devices.
What does the Localization Testing Lifecycle look like?
To make it easier to understand lets breakdown the localized testing into several small steps:
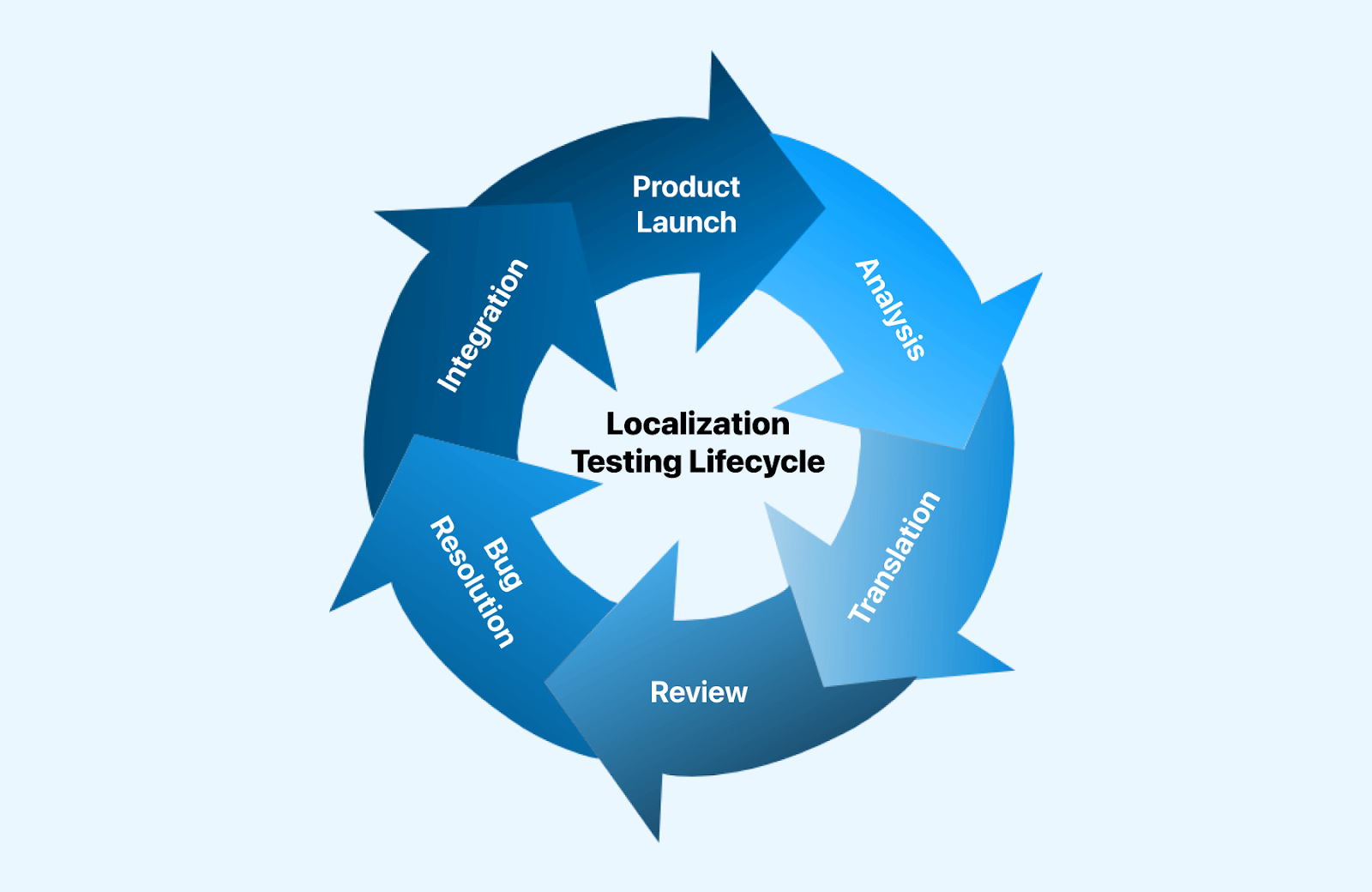
- Analysis: Assess the software’s requirements and determine the extent of localization needed.
- Translation: Accurately translate content into the relevant local language(s).
- Review: Thoroughly examine and evaluate the localized content and user interface.
- Bug Resolution: Address and resolve any issues or bugs identified during the review.
- Integration: Seamlessly integrate the localized components into the software.
- Product Launch: Launch the localized product in the target market.
How can Localization Testing Make your App Stand Out?
Some of the potential benefits of localization testing include:
- Market Expansion: Localizing a product enables its use by diverse regional users, enhancing overall user experience through language and cultural adaptation.
- Global Outreach: Broaden the product’s reach to a wider audience across various regions, thereby expanding its potential market share.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensures product adherence to local laws and regulations in targeted markets, minimizing the risk of legal complications.
- Competitive Edge: Attain a competitive advantage by offering a localized product, distinguishing the company from competitors lacking regional adaptations.
- Enhanced Communication: Mitigates the risk of misunderstandings or cultural insensitivity by localizing the product, safeguarding the company’s reputation.
- Improved Testing: Localization testing improves the entire testing process by streamlining QA operations, saving time and money.
What are the Best Practices for Localization Testing?
Follow some of the best practices to implement the localization testing process of an international or multilingual website:
- Finding the Right Resources: Building a well-localized website or app doesn’t happen overnight. It requires time to gather the needed resources and for marketing teams to research their diverse target audience. Understanding users is key for successful optimization and to achieve this human testers need to step into their shoes to design test cases accordingly.
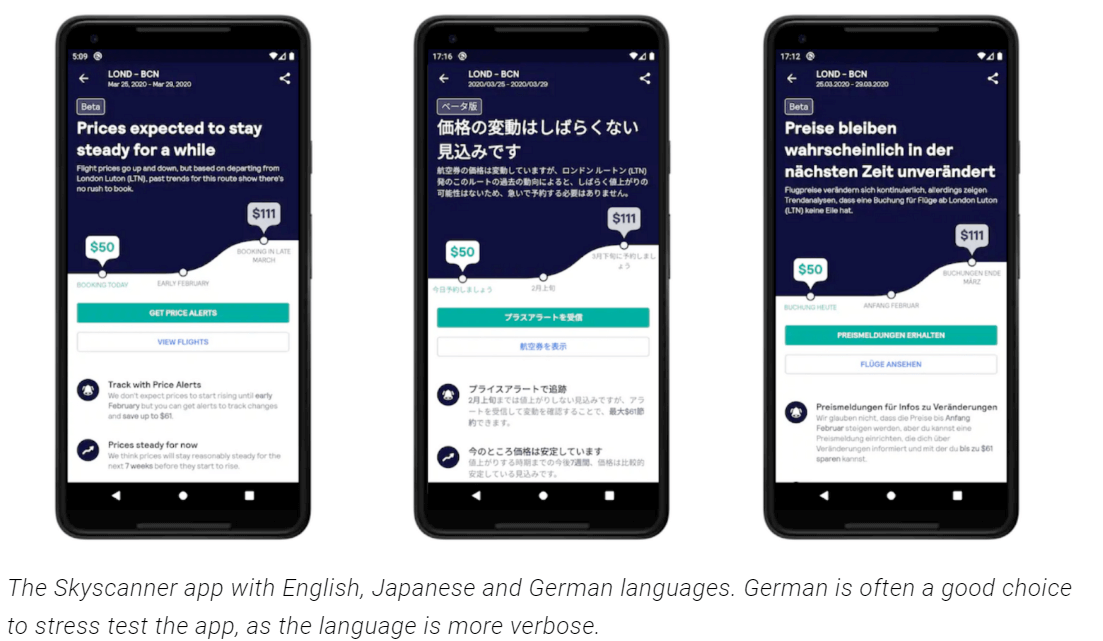
- Early and frequent testing: Don’t leave localization testing until the last minute. It’s not just about translations- factors like text arrangement and product/service inclusions must be considered early in the development process. Expect that developers will need time to make necessary code edits. Combining human testing with automation, using tools like Selenium or Cypress, can help achieve a balance between speed and accuracy.
- Real devices and browser testing: Test your website or app on real devices and browsers. Device fragmentation is a concern, with thousands of devices globally accessing the internet. To ensure seamless performance, optimization for various configurations, viewports, and screen resolutions is essential.
App Localization is the key to business success!
Expanding globally enables companies to reach foreign markets and foster customer loyalty through localized mobile apps that speak to users in their language. With a fully localized app, you create a seamless experience for customers, allowing them to interact with your brand in a way that feels natural and comfortable. This further adds substantial value throughout the entire buyer’s journey, enhancing customer satisfaction and connection.
Ultimately, how you approach localization can make testing faster and easier. One way of doing this is utilizing automated testing tools like LambdaTest. With the Geolocation Testing Tool, test your website and native mobile apps across more than 50 countries across the globe and see if your app or website provides a perfect experience from all locations.
Got Questions? Drop them on LambdaTest Community. Visit now