21 Best Accessibility Testing Tools for WCAG and ADA [2025]
Saniya Gazala
Posted On: August 4, 2025
23 Min
Accessibility testing tools play a crucial role in identifying and fixing issues that hinder usability, ensuring compliance with standards like WCAG, ADA, and Section 508. With growing emphasis on digital inclusivity, its crucial to prioritize accessibility. This ensures your websites and mobile applications cater to all users, including those with impairment.
Overview
Accessibility testing tools are software solutions that help identify and fix accessibility issues in websites or applications. They ensure compliance with standards like WCAG, making digital content usable for people with disabilities.
Top Accessibility Testing Tools
- LambdaTest
- WAVE (Web Accessibility Evaluation Tool)
- Accessibility Insights (by Microsoft)
- Axe DevTools (Deque Systems)
- Tenon
- Pa11y
- AChecker (Accessibility Checker)
- IBM Equal Access Accessibility Checker
- SortSite
- aDesigner (from Eclipse Foundation)
- Firefox Accessibility Inspector
- Chrome DevTools – Accessibility Panel
- Dyno Mapper
- NVDA (NonVisual Desktop Access)
- JAWS (Job Access With Speech)
- VoiceOver (macOS/iOS)
- ChromeVox (Chrome OS)
- Functional Accessibility Evaluator (FAE)
- Silktide
- UserWay Accessibility Scanner
- Siteimprove Accessibility Checker
TABLE OF CONTENTS
21 Best Accessibility Testing Tools
Several accessibility testing tools are available that help you assess websites and mobile apps for compliance with accessibility standards, helping developers remove barriers for users with impairments.
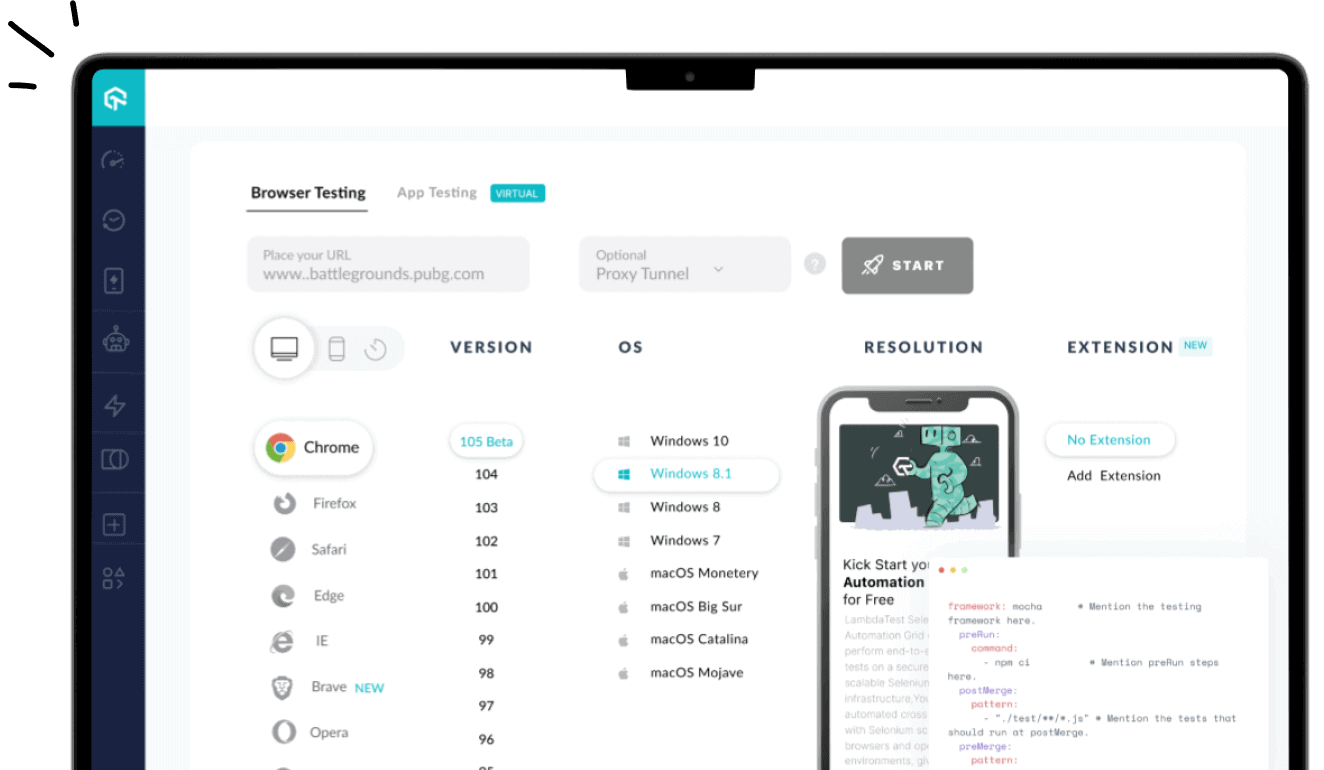
1. LambdaTest
LambdaTest is a cloud-based platform that enables you to perform accessibility testing across a wide range of browsers, devices, and operating systems. It allows you to ensure that web applications comply with accessibility standards such as Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) and are usable by people with disabilities.
It provides automated tools to scan web pages for accessibility issues, highlighting issues like missing alt text, insufficient color contrast, improper ARIA roles, or keyboard navigation issues.
Features:
- LambdaTest Accessibility DevTools: Provides browser-based axe-core powered scanning, detailed issue reporting, full-page checks, and debugging for developers.
- Accessibility Automation: Integrates accessibility testing into CI/CD pipelines using Selenium, Playwright, and Cypress for consistent automated checks.
- Accessibility Test Scheduling: Allows recurring or one-time scans with automatic URL updates to maintain ongoing compliance efficiently.
- Android App Scanner: Scans Android applications for accessibility issues, identifying violations and offering actionable insights to improve app usability and compliance.
- Automated Mobile Accessibility Testing: Runs automated accessibility tests on mobile apps, ensuring continuous compliance without manual intervention across multiple platforms and devices.
- Screen Readers: Tests accessibility on Windows, macOS, and Android using native screen readers and TalkBack, ensuring inclusive experiences for all.
- Accessibility MCP Server: Manages, schedules, and centralizes accessibility testing tasks, providing detailed reporting and ensuring organization-wide compliance efficiently.
You can begin with manual accessibility testing, check out this LambdaTest Accessibility DevTools documentation.
To get started with automated accessibility testing, refer to this Accessibility Automation documentation.
Also, would like to add that our Accessibility Testing Suite was launched in April 2025 and recognized as Product of the Day, securing the top spot on Product Hunt.

2. WAVE (Web Accessibility Evaluation Tool)
WAVE is a browser-based accessibility testing tool developed by WebAIM. It helps developers identify and resolve WCAG violations directly on web pages. The tool visually marks accessibility errors with intuitive indicators. It supports evaluation of semantic structure, alt text, ARIA usage, and contrast.
Features:
- Visual Issue Marking: Highlights elements with accessibility issues using icons and overlays.
- Missing Alt Text Detection: Flags images lacking descriptive alternative text.
- Contrast Analysis: Detects text and background combinations that fail WCAG contrast standards.
- ARIA Validation: Verifies correct usage of ARIA roles, labels, and properties.
- Semantic Structure Review: Assesses heading hierarchy, landmarks, and lists for screen reader compatibility.
3. Accessibility Insights (by Microsoft)
Accessibility Insights is an open-source tool designed to assess web, Windows, and Android applications for accessibility. It combines automated and manual checks based on WCAG guidelines. The tool highlights keyboard traps, poor focus order, and screen reader barriers. It also provides guided audits to walk testers through each accessibility principle.
Features:
- Automated FastPass Test: Detects common accessibility errors such as missing labels or contrast failures.
- Tab Stops and Focus Order Testing: Maps the keyboard navigation path to ensure logical focus flow.
- Landmark and Heading Checks: Validates use of navigational landmarks and heading structure.
- Screen Reader Support Validation: Ensures assistive tech can interpret labels, roles, and states properly.
- Color Contrast Validation: Measures contrast ratios to ensure compliance with WCAG AA/AAA.
4. Axe DevTools (Deque Systems)
Axe DevTools is a powerful browser extension used for in-browser accessibility testing. Built on the Axe-core library, it automates WCAG checks for modern web apps. Developers can inspect elements, visualize problems, and get remediation tips in real time. It integrates easily with developer tools and CI/CD workflows.
Features:
- WCAG-Based Automated Checks: Covers form labeling, contrast, ARIA roles, and heading structure.
- Element-Level Error Highlighting: Marks problematic elements within the DOM.
- Keyboard Accessibility Detection: Verifies focusable elements and interaction via keyboard.
- ARIA Role and Property Verification: Ensures semantic HTML and ARIA are correctly implemented.
- Screen Reader Compatibility Checks: Evaluates whether screen readers can interpret the page content effectively.
5. Tenon
Tenon is a flexible, API-based accessibility testing platform suited for integration into development pipelines. It allows teams to run real-time, automated checks on HTML content against WCAG and Section 508. Tenon also supports deep customization for organization-specific accessibility rules. It’s ideal for scalable, repeatable testing across projects.
Features:
- Custom Rule Sets for WCAG Compliance: Allows tailoring of accessibility standards based on level or locale.
- Alt Text & Label Validation: Detects missing image descriptions and form field associations.
- Keyboard Navigation Testing: Identifies inaccessible interactive components and focus traps.
- ARIA Role & Landmark Review: Verifies roles, states, and landmarks for assistive tech compatibility.
- Real-Time Inline Issue Reporting: Offers actionable guidance directly tied to failing elements.
6. Pa11y
Pa11y is a command-line tool for automated accessibility testing in headless browsers like Puppeteer. It helps developers integrate accessibility checks into CI/CD pipelines. The tool runs audits based on WCAG 2.1, generating clean JSON or HTML reports. It is best suited for automated workflows and quick regression tests.
Features:
- Automated WCAG 2.1 Audits: Identifies violations in structure, ARIA, and contrast levels.
- Keyboard Interaction Checks: Tests whether content is fully operable via keyboard only.
- Focus Management Testing: Flags components with improper or missing focus handling.
- Custom Standard Support: Enables tests against various regulations including WCAG and Section 508.
- Screen Reader Attribute Testing: Validates key attributes used by assistive technologies like aria-hidden, aria-label, etc.
7. AChecker (Accessibility Checker)
AChecker is an open-source tool that evaluates web content for conformance with accessibility standards like WCAG and Section 508. It identifies known, likely, and potential issues based on chosen guidelines. The tool supports uploading HTML or testing via URL. It’s widely used in academic and government settings for detailed audits.
Features:
- Known vs. Likely Issue Detection: Classifies errors based on confidence level and need for manual review.
- Alt Text Verification: Identifies missing or empty alternative text on images.
- Label and Form Element Validation: Ensures accessible labels for input fields and buttons.
- Heading Structure Testing: Evaluates semantic order of headings for assistive technology navigation.
- Accessibility Guideline Configuration: Lets users select which WCAG or Section 508 level to test against.
8. IBM Equal Access Accessibility Checker
Developed by IBM, this tool is available as a browser extension and IDE plugin. It integrates seamlessly into development environments to help developers identify WCAG violations early. The tool is powered by the open-source Equal Access Ruleset and offers detailed reports with links to remediation guidance. It is ideal for Agile and DevOps workflows.
Features:
- Live WCAG Rule Evaluation: Provides real-time analysis as you write code or browse.
- Contrast Ratio Testing: Detects text/background combinations that fail contrast checks.
- ARIA Property Validation: Flags misuse or absence of ARIA roles and labels.
- Keyboard Navigability Checks: Identifies elements that are not accessible via keyboard.
- Screen Reader Role Mapping: Ensures correct role and label associations for assistive technologies.
9. SortSite
SortSite is a comprehensive accessibility checker by PowerMapper that scans entire websites for WCAG and Section 508 compliance. It offers deep-page audits covering both visible content and code-level structure. The tool is ideal for enterprise-level websites requiring compliance across many pages. Reports include categorized accessibility errors with explanations.
Features:
- WCAG 2.1 Compliance Auditing: Automatically scans for structural and semantic violations.
- Image and Form Label Checks: Verifies all visual and interactive elements have descriptive labels.
- Heading Hierarchy Evaluation: Checks for logical nesting and sequence of headings.
- Color Contrast Analysis: Flags text elements that do not meet contrast thresholds.
- ARIA Implementation Review: Detects misuse or missing ARIA roles, labels, and attributes.
10. aDesigner (from Eclipse Foundation)
aDesigner is a visual disability simulator and accessibility testing tool, created by IBM and part of the Eclipse Accessibility Tools Framework. It simulates how a web page appears to users with various visual impairments. In addition to simulation, it evaluates content against WCAG standards with focus on screen reader experience.
Features:
- Visual Impairment Simulation: Emulates how content is perceived with low vision or blindness.
- Screen Reader Compatibility Testing: Analyzes how pages will be interpreted by assistive tech.
- Text Alternative Checks: Flags images and controls missing alt attributes.
- Keyboard Focus Order Evaluation: Reviews tab order and keyboard operability.
- WCAG Rule-Based Reporting: Generates structured issue reports aligned to WCAG success criteria.
11. Firefox Accessibility Inspector
Built into Firefox Developer Tools, the Accessibility Inspector allows developers to analyze a web page’s accessibility tree. It gives insights into roles, names, and states of elements as interpreted by screen readers. This helps developers confirm that assistive technologies will navigate and interpret content correctly.
Features:
- Accessibility Tree View: Displays element roles, states, and names used by assistive tech.
- Focus Management Insights: Shows how keyboard focus is handled across elements.
- Color Contrast Checker: Evaluates text contrast in compliance with WCAG levels.
- ARIA Role Inspection: Verifies that custom widgets use valid ARIA attributes.
- Live Content Accessibility Audit: Highlights real-time WCAG violations as the DOM changes.
12. Chrome DevTools – Accessibility Panel
The Accessibility panel in Chrome DevTools provides developers with insights into how assistive technologies interpret web content. It displays the accessibility tree, computed properties, and node structure. This tool helps developers debug keyboard focus, roles, and ARIA attributes directly in the browser. It’s built into Chrome and works in real time.
Features:
- Accessibility Tree Inspection: Visualizes how screen readers interpret DOM elements.
- ARIA Attribute Analysis: Confirms the presence and correctness of aria-label, aria-hidden, roles, and landmarks.
- Keyboard Focus Debugging: Highlights active focus and identifies traps or broken tab order.
- Color Contrast Testing: Flags insufficient color contrast between foreground and background elements.
- Live DOM Synchronization: Updates accessibility evaluations in real time as elements change.
13. Dyno Mapper
Dyno Mapper is a cloud-based accessibility testing tool that crawls entire websites and provides visual sitemaps with embedded WCAG compliance data. It is particularly useful for large teams and content-heavy sites. It highlights content that may block access for screen reader users or keyboard-only users.
Features:
- WCAG 2.1 Site-Wide Auditing: Scans multiple pages for violations such as missing labels, poor structure, or contrast issues.
- Keyboard Accessibility Testing: Validates tab order and focusability across navigation paths.
- Text Alternative Scanning: Flags missing or inappropriate alternative text on images and media.
- Semantic HTML Structure Checks: Evaluates headings, lists, and ARIA landmarks.
- Interactive Element Accessibility: Identifies inaccessible buttons, links, and form elements.
14. NVDA (NonVisual Desktop Access)
NVDA is a free and open-source screen reader for Windows. It’s used both by end users and accessibility testers to evaluate how screen readers interact with web content. NVDA reads page structure, landmarks, labels, and ARIA roles. It supports keyboard navigation testing and Braille display output.
Features:
- Screen Reader Output Simulation: Reads page content aloud including headings, labels, links, and landmarks.
- ARIA and Role Detection: Highlights how widgets and elements are described by screen reader metadata.
- Keyboard Navigation Evaluation: Allows testing of full interaction via keyboard with spoken feedback.
- Table and Form Accessibility Testing: Verifies that data tables, forms, and inputs are announced correctly.
- Live Region and Focus Handling: Tests dynamic updates and focus shifts for accessibility.
15. JAWS (Job Access With Speech)
JAWS is one of the most advanced screen readers, widely used in enterprise and government environments. It reads content aloud and supports advanced navigation through forms, tables, and ARIA widgets. JAWS also allows for scripting custom interactions to simulate complex accessibility scenarios.
Features:
- Speech and Braille Output: Provides multimodal accessibility testing through audio and tactile feedback.
- Navigation Testing via Keyboard: Tests tab order, logical reading flow, and interaction without mouse use.
- ARIA Role and State Feedback: Announces live updates, control roles, and descriptive labels.
- Labeling and Focus Testing: Confirms whether screen readers can accurately detect labels and focus changes.
- Scripting Support for Custom Testing: Enables simulation of complex user interactions in applications.
16. VoiceOver (macOS/iOS)
VoiceOver is Apple’s built-in screen reader for macOS and iOS, used for testing how web and mobile content is read and navigated by visually impaired users. It provides spoken descriptions, supports rotor-based navigation, and interacts seamlessly with native and web apps.
Features:
- Gesture-Based Screen Reader Simulation: Tests touch navigation and spoken content on mobile and desktop.
- Role and State Announcements: Verifies that buttons, inputs, and controls are described clearly.
- Rotor and Landmark Navigation: Allows testers to jump between headings, links, and ARIA landmarks.
- Form Field and Label Testing: Confirms appropriate association of inputs and visible labels.
- Focus Change Feedback: Announces dynamic focus movements and content updates accurately.
17. ChromeVox (Chrome OS)
ChromeVox is the native screen reader built into Chrome OS, allowing accessibility testers and users to navigate web content using keyboard and spoken feedback. It reads page structure, ARIA attributes, and provides auditory cues for visual changes. This tool is ideal for testing on Chromebooks and Chrome-based environments.
Features:
- Screen Reader Output with Keyboard Navigation: Verifies tab order and interactive element accessibility.
- Live ARIA Role Announcements: Confirms how dynamic content and widgets are communicated.
- Landmark and Heading Navigation: Supports structured exploration by regions, headings, and links.
- Braille Display Integration: Allows tactile testing for users with dual sensory disabilities.
- Focus Indicator Testing: Ensures visually hidden or custom-styled focus states are announced and reachable.
18. Functional Accessibility Evaluator (FAE)
Developed by the University of Illinois, FAE evaluates websites against WCAG 2.1 guidelines. It uses a combination of rule-based analysis and best-practice recommendations. FAE focuses on keyboard accessibility, content structure, and screen-reader-friendliness across entire domains.
Features:
- Domain-Wide WCAG Testing: Scans multiple pages for accessibility violations like missing alt text and headings.
- Keyboard Functionality Review: Verifies if all controls are operable using keyboard alone.
- Image and Link Accessibility: Flags missing alternative text and non-descriptive links.
- Form Label Validation: Ensures labels are programmatically associated with inputs.
- ARIA Landmark and Heading Analysis: Checks page structure for navigational clarity with assistive tech.
19. Silktide
Silktide offers web accessibility testing with a focus on real-world user impact. It presents interactive issue visualizations and teaches users how to fix them. The tool checks for WCAG violations and simulates various disabilities to demonstrate usability challenges for differently-abled users.
Features:
- Screen Reader & Keyboard Simulation: Evaluates how users with no mouse or sight navigate the site.
- Color Contrast Auditing: Highlights foreground–background combinations that fail WCAG AA/AAA.
- ARIA Role and Label Analysis: Detects incorrectly assigned or missing ARIA properties.
- Alt Text & Image Descriptions: Flags non-text content without accessible alternatives.
- Page Structure Review: Analyzes headings, regions, and links for semantic clarity.
20. UserWay Accessibility Scanner
UserWay offers both a widget and a cloud-based scanning engine to test websites for ADA and WCAG compliance. Its platform highlights accessibility issues while allowing teams to generate detailed reports. The tool focuses on barriers for keyboard, screen reader, and low-vision users.
Features:
- Automated WCAG Testing: Scans pages for violations related to contrast, structure, ARIA, and alt text.
- Interactive Element Accessibility Check: Evaluates forms, buttons, and dropdowns for label and keyboard access.
- Screen Reader Compatibility Assessment: Confirms whether content is navigable and understandable.
- Missing Alt Text Detection: Identifies images that lack appropriate descriptive text.
- ARIA Role Evaluation: Flags misuse or absence of semantic roles and properties.
21. Siteimprove Accessibility Checker
Siteimprove is an enterprise-grade solution that provides in-depth accessibility testing, monitoring, and reporting. It aligns audits with WCAG standards and integrates with CMS platforms for remediation. The tool is used by large organizations to track compliance over time.
Features:
- Automated WCAG Rule Testing: Detects errors in alt text, headings, contrast, and keyboard interactions.
- ARIA Usage Monitoring: Validates correct application of roles, labels, and properties.
- Keyboard Operability Verification: Ensures all interactive elements are focusable and usable via keyboard.
- Form & Input Accessibility Review: Tests label-input associations and fieldset usage.
- Screen Reader Preview: Simulates how content is perceived by screen reading tools.
How to Choose the Right Accessibility Testing Tool?
When picking a tool to perform accessibility testing, it’s important to focus on what best fits your needs. Here are some factors to keep in mind:
- Guideline Compliance: Ensure the tool aligns with key standards like WCAG, ADA, and Section 508 to maintain both legal and ethical accessibility.
- Testing Capabilities: Look for tools that support automated and manual testing, screen reader simulation, keyboard navigation, and color contrast checks for a thorough evaluation.
- Ease of Use: The tool should have an intuitive interface so developers and designers can adopt it quickly without extra training or complexity.
- Customization Options: If your organization has specific needs, choose a tool that allows you to tailor test settings and reporting formats accordingly.
- Scalability: Make sure the tool can handle projects of all sizes from small websites to large enterprise applications, without affecting performance.
- CI/CD Integration: A tool that integrates with CI/CD pipelines, Git-based workflows, and issue trackers can streamline testing and team collaboration.
- Support and Resources: Prioritize tools with robust documentation, tutorials, forums, or direct customer support to help troubleshoot efficiently.
- Cost Efficiency: Consider free or budget-friendly tools for basic needs, or invest in premium features if your testing demands are more advanced.
How LambdaTest Simplifies Accessibility Testing?
LambdaTest Accessibility Testing suite allows you to ensure your website and mobile applications are accessible and inclusive.
Features:
- Accessibility DevTools Chrome Extension: It offers Accessibility DevTools Chrome extension that allows you to perform in-depth accessibility checks directly in the browser.
- Manual Accessibility Testing: LambdaTest offers manual accessibility testing tools with assistive tools like screen readers and speech viewers on Windows and macOS.
- Accessibility Automation: You can automate accessibility testing with tools like Selenium, Playwright and Cypress to accelerate your release cycles while ensuring compliance.
- Accessibility Scheduler: It lets you schedule recurring or one-time accessibility scans and minimize the manual effort of running accessibility checks.
Run accessibility tests across 5000+ desktop and mobile browsers. Try LambdaTest Now!
Conclusion
These accessibility testing tools will help developers ensure that their websites and applications are inclusive and accessible to users of all abilities. Using these tools for ADA and WCAG testing, developers can identify and rectify potential issues such as missing alt tags, low-contrast text, or poorly structured HTML. The features and benefits of each tool, along with any limitations, are essential considerations in this process.
In addressing the challenges of accessibility testing, developers should focus on education to overcome awareness gaps, accommodate diverse user needs through comprehensive testing, manage code complexity using analysis tools, and plan for accessibility testing to control time and cost. Staying updated on evolving accessibility standards is crucial for ensuring ongoing compliance.
To conclude, adopting these tools, coupled with a proactive approach to accessibility challenges, empowers developers to create digital experiences that are not only legally compliant but also ethically responsible, fostering inclusivity and improving the overall user experience for everyone.
As the field evolves, exploring how AI and accessibility intersect can further enhance your testing workflows and help scale inclusive design more efficiently.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are accessibility testing tools?
Accessibility testing tools are software solutions used to detect and fix issues that hinder people with disabilities from accessing websites, applications, or digital documents. These tools help ensure compliance with accessibility standards like WCAG, ADA, and Section 508 by identifying problems such as missing alt text, low color contrast, improper navigation, or non-semantic HTML.
What are accessibility testing tools used for?
Accessibility testing tools help developers and testers identify and fix issues that might prevent users with disabilities from accessing digital content. These tools evaluate compliance with accessibility standards like WCAG, Section 508, and ADA.
Which is the best accessibility testing tool?
There’s no single best tool, but popular choices include LambdaTest Accessibility Suite, axe DevTools, WAVE, Lighthouse, Accessibility Insights, and Tenon. Each has unique strengths for different testing needs, such as browser extension scans, automation support, or integration into CI/CD pipelines.
How do accessibility testing tools work?
These tools scan websites or apps for common accessibility violations such as missing alt text, low color contrast, improper heading structure, and non-keyboard-friendly navigation. Some tools offer automated scans, while others support manual testing workflows.
Are accessibility testing tools free?
Many accessibility tools offer free versions or browser extensions. Examples include LambdaTest Accessibility DevTools, axe DevTools, WAVE, and Google Lighthouse. For enterprise-level compliance, paid plans with advanced features like audit reports, team workflows, and integrations are also available.
Can automated tools fully replace manual accessibility testing?
No. While automated tools can catch around 20-50% of accessibility issues, manual testing is essential to detect keyboard traps, screen reader behavior, focus management, and contextual content issues. A combined approach is the most effective.
What are some open-source accessibility testing tools?
Popular open-source options include axe-core, Pa11y, HTML_CodeSniffer, and Google Lighthouse. These tools can be integrated into automated testing workflows and customized for different project needs.
Do accessibility tools support mobile app testing?
Yes, some tools like mbdaTest Android App Scanner, Accessibility Scanner (Android), Xcode Accessibility Inspector (iOS), and Appium with axe-mobile are designed specifically to test native mobile apps for accessibility issues.
What standards do accessibility testing tools check for?
They primarily check against WCAG 2.1/2.2, Section 508, ARIA guidelines, and EN 301 549 depending on the tool and configuration. These standards ensure digital accessibility for users with disabilities across platforms.
How can I integrate accessibility testing into CI/CD?
You can integrate tools like axe-core, Pa11y CI, or Tenon CLI into CI/CD pipelines using tools like Jenkins, GitHub Actions, or GitLab. This helps catch accessibility issues early in the development lifecycle.
Are browser extensions effective for accessibility testing?
Yes, browser extensions like LambdaTest Accessibility DevTools, axe DevTools, WAVE, and Accessibility Insights are great for quick, on-the-spot testing. However, they should be complemented with manual audits and automated scripts for full coverage.
Author