Data Virtualization: Working, Advantages, & Disadvantages Explained
Tanay Kumar Deo
Posted On: November 27, 2023
![]() 38851 Views
38851 Views
![]() 11 Min Read
11 Min Read
Today’s businesses make quick, effective, and strategic decisions using “data.” A data-driven decision-making approach benefits the company regarding implementation, governance, and maintenance. However, these data are unorganized and unstructured across multiple data sources, making it hard to find and retrieve the “right” data.
Hence, to overcome this issue, we need methods and algorithms to organize and handle the data on a large scale and enable logical data management capabilities. Data Virtualization is one solution to overcome this challenge.
This article focuses on how data virtualization can benefit developers and analysts in visualizing, predicting, and analyzing data to make critical and effective business decisions.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
What is Data Virtualization?
Data virtualization is an umbrella term used to represent an approach for data management that allows an application to read and modify data without needing technical details. It includes how the data is stored and where it is physically located and formatted.
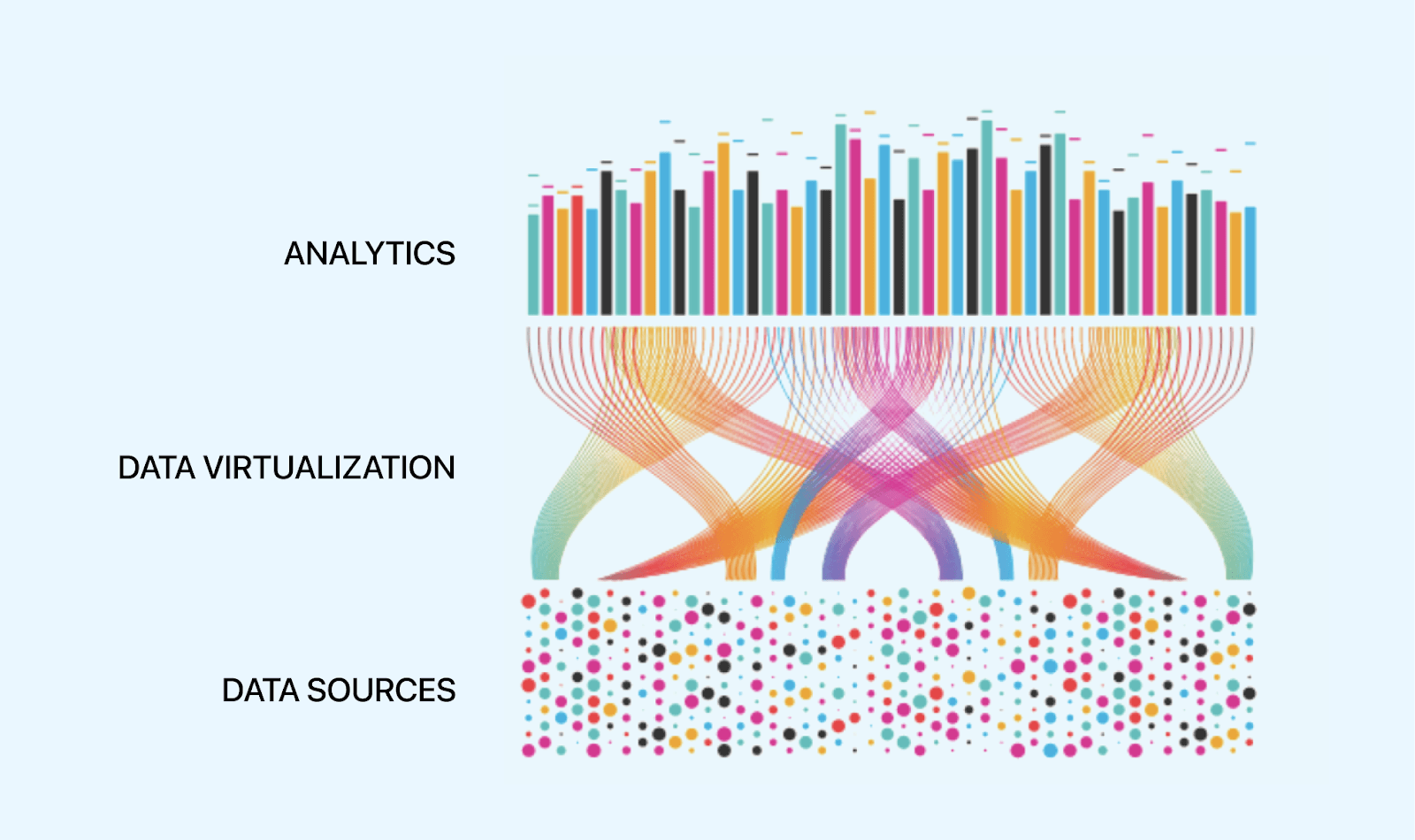
With data virtualization, we can retrieve real-time data from various data sources, like a database, data warehouse, cloud platform, or even an Excel spreadsheet, without physically replicating them. We can create a virtual copy of the data in the form of views.
Retrieving and organizing data from various databases in one place increases productivity and saves time. We can write standard SQL queries to read data from unified real-time sources. We can also modify data and send it back to the source, using transformation techniques(like constructive transformations, destructive transformations, aesthetic transformations, and structural transformations) to resolve differences in the source format.
How Does Data Virtualization Work?
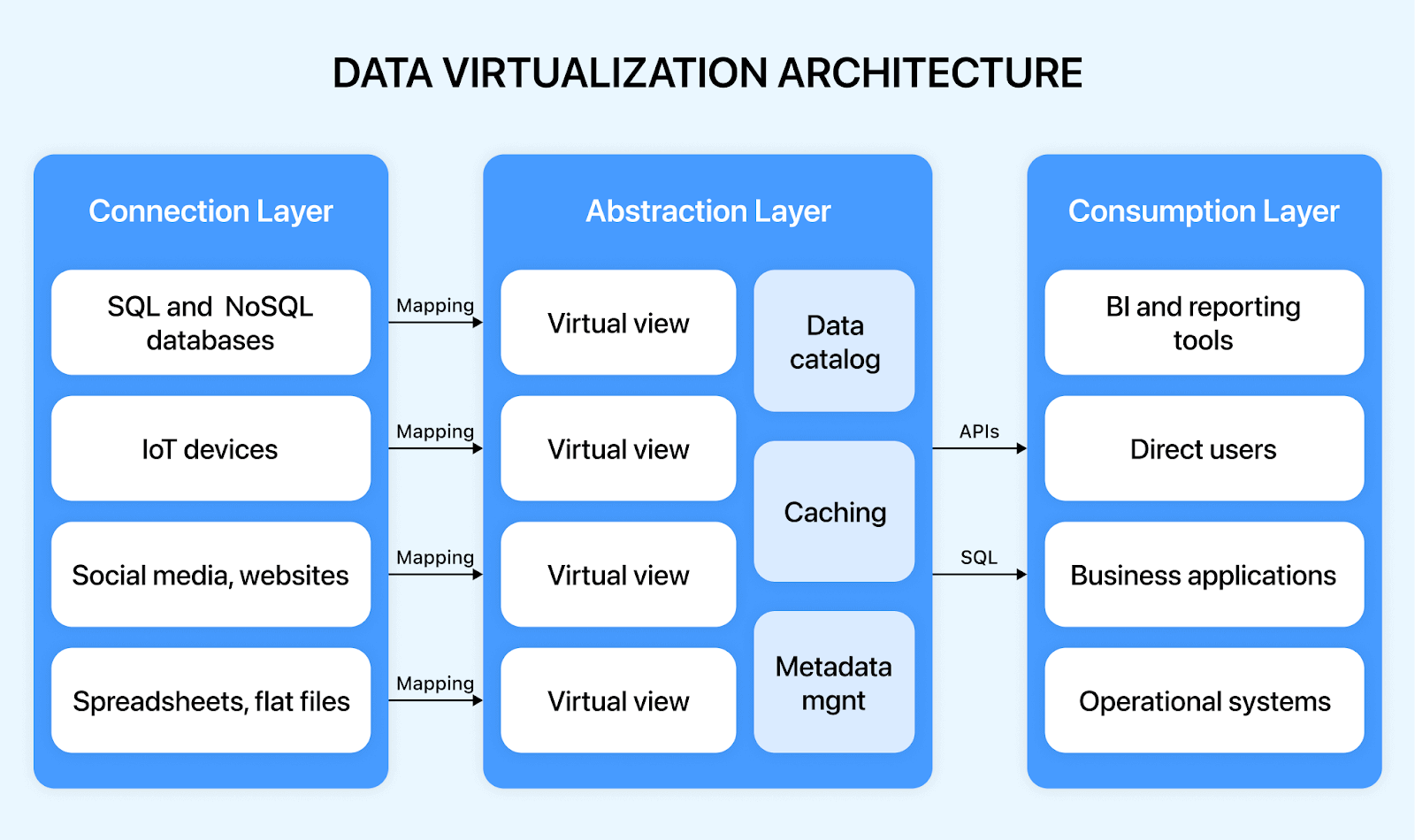
Data virtualization uses a simple three-step method, i.e., Connect, Abstract, and Consume, to generate a holistic view of the required information for the organization’s users. These methods are performed by three layers of the data virtualization architecture:
- Connection Layer
- Abstraction Layer
- Consumption Layer
The Connection layer accesses information from a wide range of data sources – unstructured to structured, including SQL databases, streaming sources, big data systems, cloud repositories, No SQL sources, document files, and the Web. It uses various connectors to access specific data storage or applications. It also carries out normalization and type conversion of data sources so that all base views appear as relational at the upper layers.
The Abstraction layer, also called the semantic or virtual layer, links all business end users and data sources, acting as the backbone of the entire data virtualization system. It allows data transformations with logical operations to seamlessly form abstracted data views using the base views delivered by the connection layer. In this layer, end users can perform metadata modeling, complicated data transformations, and data quality and semantic matching procedures using SQL queries and relational tools.
The consumption layer acts as a single point of interaction and access to the underlying data sources and the abstracted data views in a defined delivery format. The consumption layer offers the widest data delivery choices to suit the business user requirements via RESTful web services (output as JSON, HTML, XML, or RSS), SOAP protocol, ODBC, JDBC, OData, portlets, ADO.NET, and data widgets (JSR-286, JSR-168, or Microsoft Web Parts for SharePoint), JMS message queues, and exports to Microsoft Excel or SQL.
Advantages of Data Virtualization
Data virtualization provides us with a unique data integration and management method that outperforms any other technology. The following are some benefits that data virtualization brings:
- Modernize Data Infrastructure: Data virtualization can abstract underlying data systems, allowing architects to swap traditional systems with modern cloud apps without affecting business.
- Lesser Resources: In data virtualization, data can be abstracted from various non-related sources without needing to have a physical copy of them. Thus, we require fewer hardware resources to process and store data.
- Combine Data from different sources: The virtual data layer simplifies incorporating distributed data from Cloud Solutions, Databases, Data Warehouses, Big Data Platforms, and Data Lakes into user-defined data objects.
- Secure Data: Data virtualization enables organizations to insulate critical data source systems from the end users and web apps, stopping them from unintentionally or intentionally changing the data.
- Faster and Cheaper Information: Data replication costs money and takes time; with its no replication approach, data virtualization helps business users receive faster information without investing in additional storage.
- Flexibility: Data virtualization makes it possible to respond swiftly to new developments in various industries. Data virtualization enables you to react quickly to new demands by providing integrated virtual data objects, eliminating the need to replicate data to other data levels but making it virtually available.
Disadvantages of Data Virtualization
Although data virtualization is versatile and applicable in several industries, the following are some drawbacks of using data virtualization.
- Single point of failure: Because the data virtualization method provides a single point of access to all data sources, it frequently results in a single point of failure. If the server fails, all operational systems will be without a data stream.
- High Initial Cost: The Initial setup of a data virtualization platform can be challenging, and the initial setup costs can be high.
- Not Suitable for Conserving Data: Data virtualization is not suitable for keeping track of historical data; a Data Warehouse is more suitable in such cases.
- No support for batch data: The data virtualization technique does not permit batch or mass data migration, which may be required in some situations. Assume a financial institution handling significant amounts of transactional data that must be processed once a week.
Commonly Used Tools for Data Virtualization
Choosing the right tools and platforms can be a tricky process that demands in-depth research and usually comes down to multiple solutions. To make your quest more comfortable, we have profiled the standard data virtualization tools and platforms all in one place.
- Actifio Virtual Data Pipeline
- Denodo Platform
- IBM Cloud Pak for Data
- Oracle Data Service Integrator
- Data Virtuality Platform
- CData Driver Technologies
Actifio provides a Virtual Data Pipeline (VDP) that automates enterprise workload provisioning and renewal. It integrates with the existing toolchains and provides data scientists with data delivery and reuse via APIs and automation. Users can recover any data from any cloud at any point in time. Actifio is a comprehensive platform providing security and compliance capabilities for protecting, securing, retaining, and governing data regardless of location.
Denodo is a key player in the data management software market and a pioneer in the data virtualization area. It provides a robust capabilities package for data delivery, data integration, and data management, all while enabling self-service business intelligence, data science, hybrid/multi-cloud integration, and enterprise data services. Denodo boasts customers in over 30 industries, including large organizations and mid-market firms.
IBM provides various integration tools for both on-premises and cloud deployments and every organizational use case. Its on-premises data integration package includes solutions for both classic (replication and batch processing) and modern requirements (integration synchronization and data virtualization). IBM also provides many prebuilt functions and interfaces for data virtualization.
Oracle provides comprehensive data integration solutions for classic and new use cases in both on-premises and cloud deployments. The company’s product line includes technologies and services that enable organizations to do full-lifecycle data migration and enrichment. Oracle data integration for customer and product domains enables universal and continuous access to data across heterogeneous systems through bulk data movement, transformation, bidirectional replication, metadata management, data services, and data quality.
The Data Virtuality platform integrates, accesses, and manages any cloud service and database by combining data virtualization and load, extract, and transform (ELT) procedures. It provides data pipeline solutions in two steps (self-service and managed) and Logical Data Warehouse, a semantic later that lets users access and model data from any database and API using analysis tools. Data Virtuality connects to over 200 data sources and provides a variety of data replication functionalities dependent on the use case.
CData Software provides data integration solutions for on-demand or on-premises access to databases, Web APIs, and applications. The provider specializes in giving customers access to data via well-known application platforms and data standards like ODBC, JDBC, ADO.NET, SSIS, BizTalk, and Microsoft Excel. Six categories make up the CData Software product line: OEM and custom drivers, cloud and API connectivity, enterprise connectors, data visualization, and ELT solutions.
 Note
NoteTurn Testing Complexity into Simplicity: Choose LambdaTest for Selenium based cloud grid to run your tests over 3000 real browsers and devices. Try LambdaTest Today!
Practical Use Cases of Data Virtualization
Because of its wide range of advantages, data virtualization is commonly used in the industries. Let’s look at real-world use cases to see how businesses operating in various industries utilize data virtualization technology.
- Business intelligence and analytics
- Data warehousing
- Real-time analytics and reporting
- Identifying Business or Production Issues
- Agile BI (Business Intelligence)
Data virtualization tools can merge databases from various platforms (such as mainframe, UNIX®, and cloud) and kinds (such as VSAM, columnar, and relational databases) into a single view. Standard SQL queries will instruct the system to parse the query, submit it, and return the result set.
Maintaining the most up-to-date information from your organization in your data warehouse while avoiding the impact on underlying systems. You may get all the benefits of cloud data warehouses by using data virtualization techniques. You can duplicate enterprise data to the cloud from nearly any source, capturing changes from various data sources without sacrificing source system availability or performance.
Data virtualization can be used to acquire real-time access to systems and to collect data from several sources to generate complex dashboards and analytics for objectives such as sales reports. These analytics boost company understanding by accessing real-time data, integrating it, and producing user-friendly infographics.
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) can be performed via data virtualization. Changes can also be implemented in virtual copies to check and guarantee that they have no negative consequences before executing changes in the data source.
Data virtualization can be used for self-service BI, regulated procedures, API/system connections, and data science. It enables quick dashboard iterations and smooth connectivity with SaaS cloud services like Salesforce and Google Analytics, making it ideal for agile BI. You may easily centralize your data and guarantee security even in a hybrid environment.
Conclusion
In terms of cost savings and productivity increases, data virtualization is beneficial. Data virtualization allows faster data preparation, date snapshots that demand less disk space, and data from several sources for analytics or other purposes.
Furthermore, data virtualization systems can be highly sophisticated, with capabilities such as data cleansing solutions that assist the system in self-management, integrated governance, security, and the ability to roll back any changes done. Data virtualization has many practical uses, and businesses should investigate the potential solutions it might give for their needs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Why is data virtualization used?
With data virtualization, we can retrieve real-time data from various data sources. Retrieving and organizing data from cloud, relational, legacy, and big data in one place increases productivity and saves time. We can write standard (ANSI) SQL queries to read data from unified real-time data sources. We can also modify data and send it back to the source, using transformation techniques to resolve differences in the source format.
Where is data virtualization used?
Data virtualization is commonly used in Finance, Government, Healthcare, Communication and Technology, and Manufacturing industries.
What is the abstraction layer in data virtualization?
The abstraction layer links all business end users and data sources. It allows data transformations with logical operations to seamlessly form abstracted data views using the base views delivered by the connection layer. In this layer, end users can perform metadata modeling, complicated data transformations, and data quality and semantic matching procedures using SQL queries and relational tools.
Got Questions? Drop them on LambdaTest Community. Visit now