Teams today are shipping features faster than ever, but the pressure to maintain quality keeps rising. Missed bugs, unstable releases, and last-minute fixes still slow down even experienced engineering teams. This is why QA testing tools are especially reliable; automated QA testing tools have become essential for anyone trying to deliver steady, predictable releases.
This guide breaks down the top 15 QA testing tools with their pros, cons, pricing, and best-fit scenarios, helping you pick a tool that matches your team’s actual needs, not just the trend.
Overview
What are QA testing tools, and why are they important?
QA testing tools are used to check whether software is working correctly before it is released. They help teams find bugs, test different features, and make sure the product meets its requirements. These tools matter because they improve software quality, reduce errors, speed up testing, and help deliver a smoother, more reliable experience to users.
Which must-have QA testing tools should teams consider for 2026?
- LambdaTest: AI-native testing cloud with KaneAI for intelligent test creation, HyperExecute for ultra-fast orchestration, real-device coverage, cross-browser automation, geolocation testing, and high-speed parallel runs.
- Selenium: Classic, open-source browser automation with multi-language and grid support for large distributed suites.
- Cypress: Developer-friendly JS/TS end-to-end testing with real-time browser execution and fast debugging.
- Playwright: Unified, multi-browser automation (Chromium/Firefox/WebKit) with auto-waits and cross-platform language bindings.
- Appium: Open-source mobile automation for native, hybrid, and mobile web tests across Android and iOS.
- Apache JMeter: Protocol-level load and performance testing for high-scale traffic simulation and bottleneck analysis.
- Postman: Collaborative API development and automated API tests with collection runners and mock servers.
- Tricentis Tosca: Enterprise, codeless model-based testing with AI-driven self-healing for complex systems.
- SonarQube: Continuous static code analysis for code quality, security flaws, and technical-debt tracking in pipelines.
- Ranorex: All-in-one UI and desktop automation with codeless recording and strong object recognition for desktop apps.
What are the core categories of QA testing tools teams should prioritise?
- Cross-browser & mobile automation: LambdaTest, Selenium, Playwright, Cypress, and Appium help teams run UI tests consistently across browsers, OSs, and real devices.
- API, load & backend testing: LambdaTest, Postman, SoapUI, and JMeter validate APIs, simulate traffic, and catch server-side issues early.
- AI-powered & low-code automation: Platforms like LambdaTest and Tosca add self-healing locators, test generation, and low-code flows to cut test maintenance.
- Test management & collaboration: Tools such as LambdaTest and TestLink organize test cases, track runs, and centralize documentation for distributed teams.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
- Why QA Testing Tools Matter
- Top 15 QA Testing Tools
- LambdaTest
- Selenium
- Cypress
- Appium
- Playwright
- Tricentis Tosca
- TestLodge
- TestLink
- Cucumber
- SoapUI
- Ranorex Studio
- Apache JMeter
- Postman
- SonarQube
- Apiary
- Comparison Metrics Table
- Top Common Selection Mistakes
- Future QA Trends
- Frequently Asked Questions
Why QA Testing Tools Matter?
Quality assurance is no longer just about catching bugs; it’s about enabling continuous delivery, maintaining reliability at scale, and aligning QA with DevOps & engineering workflows.
- With Agile and DevOps practices, QA teams must integrate seamlessly into CI/CD pipelines, test earlier (shift‑left) and measure faster.
- Selecting the right tool impacts critical metrics such as defect leakage, time‑to‑release, test maintenance cost, and team productivity.
- Recent trends (including increased use of AI for test generation, no‑code options, and observability integrations) mean old tools may no longer suffice.
- A tool mismatch can slow release velocity, increase bugs in production, and erode stakeholder confidence. That’s why you must treat tool selection as part of your QA strategy, not an afterthought.
Top 15 QA Testing Tools
1. LambdaTest
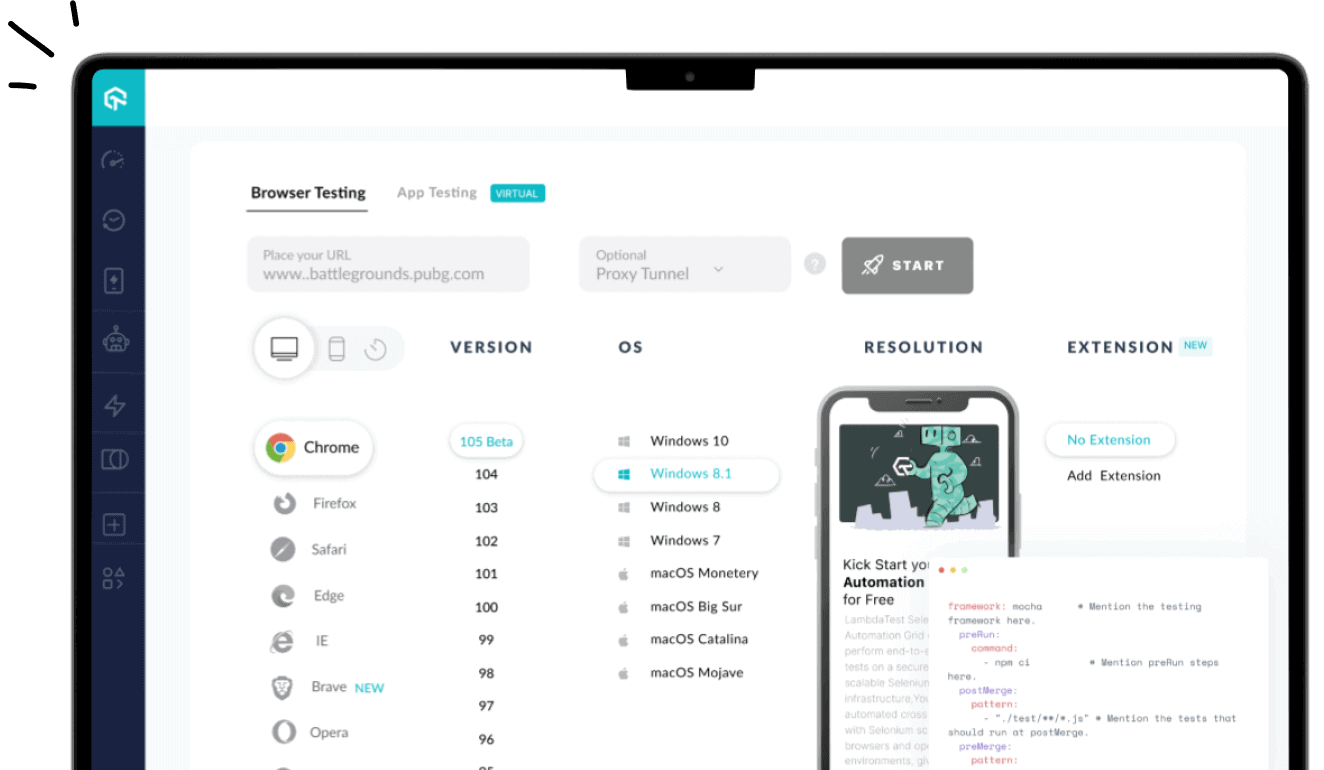
LambdaTest is an AI-native test orchestration and execution platform that helps teams scale manual and automated testing across real browsers, devices, and operating systems. It supports major frameworks like Selenium, Playwright, Cypress, and Appium, making it easy to run reliable tests at pace. With KaneAI for natural-language test creation and HyperExecute for high-speed execution, it streamlines QA workflows and accelerates release cycles.
Best for: AI-native testing with KaneAI, cross-browser & real device cloud coverage, and scalable automation testing.
Key Features:
- Seamless Support for Popular Automation Frameworks: Works effortlessly with Selenium, Playwright, Cypress, Appium, Puppeteer, Espresso, XCUITest, and more, which allows QA teams to run tests using the tools they already trust.
- AI-Powered Visual Regression Testing: Automatically compares UI snapshots across browsers and devices to spot layout issues, broken elements, or unexpected visual changes before they reach production.
- HyperExecute for 70% Faster Test Execution: Delivers lightning-fast automation speed with a high-performance orchestration cloud that cuts execution time by up to 70%, helping teams ship features with confidence and tighter feedback loops.
- Accurate Geolocation Testing Across 50+ Regions: Test web and mobile experiences from multiple countries and cities to verify localization, content variations, compliance, and regional behavior accuracy.
- Strong CI/CD and QA Tool Integrations: Integrates smoothly with major CI/CD pipelines, project management tools, and low-code automation platforms, creating a streamlined and highly efficient QA workflow.
Pros:
- Test in real-time on 3000+ browsers and 10,000+ real devices OS combinations
- Built-in geolocation testing for automation
- Parallel testing cuts down execution time substantially
- Blends with project management, bug tracking, and CI/CD tools
- Quick and helpful technical support team
Cons
- Requires internet for device/cloud access (not ideal for offline teams).
- Some advanced features (AI-driven insights, higher parallelism) are in premium plans.
- Learning curve for beginners unfamiliar with cloud-based automation.
Pricing:
LambdaTest offers a free demo plan, followed by annual paid options, starting with Live Testing at $15/month, Real Device Testing at $39/month, Web Automation at $79/month, Web & Mobile Browser Automation on real devices at $159/month, Native App Automation or HyperExecute Public Cloud at $159/month, and KaneAI for Web & App at $299/month and many more plans, all billed annually.
 Note
NotePerform QA testing across 10,000+ real environments on the cloud. Try LambdaTest Today!
2. Selenium
Selenium is an open-source framework that allows testers to perform web automation. This framework was developed in 2004, and it has three main components: Selenium IDE, Selenium WebDriver and Selenium Grid. It makes the QA test process very easy due to the following features:
Best for: Automated browser testing
Key Features:
- Open-Source With Multi-Language Support: Works with Java, Python, JavaScript, C#, Ruby, and more, allowing full flexibility for diverse QA teams.
- WebDriver for Real Browser Automation: Interacts directly with browsers (Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Edge) to create fast, stable, and reliable automated test scripts.
- Cross-Browser & Cross-Platform Compatibility: Supports testing across all major browsers and operating systems, including Windows, macOS, and Linux.
- Seamless Integration With Testing & CI/CD Tools: Easily integrates with TestNG, JUnit, PyTest, Jenkins, GitHub Actions, and other DevOps tools for continuous testing workflows.
- Parallel & Distributed Test Execution via Selenium Grid: Enables scalable parallel testing across multiple environments to significantly reduce test execution time.
Pros:
- Completely free and open-source
- Supports multiple programming languages, including Java, Python, and JavaScript
- Extensive community support and resources
- Cross-platform compatibility (Windows, Mac, Linux)
- Uninterrupted integration with CI/CD tools
Cons:
- Tests break when UI changes and need maintenance
- Learning curve is steep and demands substantial developer time
- No built-in reporting capabilities
- Resource-intensive and needs substantial server capacity
- Limited to web applications only
Pricing:
Free to use, with no licensing cost. You’ll need to manage the infrastructure (e.g., Selenium Grid) for distributed testing.
3. Cypress
Cypress is a modern JavaScript-based testing framework built to make end-to-end testing fast and reliable for web applications. It runs directly in the browser, giving teams clear visibility into how tests behave in real time. With its intuitive setup and developer-friendly workflow, Cypress has become a popular choice for teams looking to streamline test creation and debugging.
Best for: JavaScript/TypeScript developers
Key Features:
- Built for Modern JavaScript & TypeScript: Optimized for today’s JS/TS frameworks like React, Vue, and Angular, making test creation smooth and developer-friendly.
- Real-Time Browser Execution: Runs tests directly in the browser with live previews, helping teams debug faster and spot issues instantly.
- Native Support for Mocha, Chai & Sinon: Comes with a complete testing ecosystem out of the box, enabling clean assertions, structured tests, and easy mocking.
- Automatic Waiting to Reduce Flaky Tests: Waits for DOM elements, animations, and network calls automatically, eliminating manual delays and stabilizing test runs.
- State Snapshot Debugging: Captures snapshots of every test step, allowing testers to hover and see the exact state of the app during execution.
Pros:
- Developer-friendly with an easy setup.
- Real-time reloading and interactive debugging tools.
- Great for modern web applications and fast test execution.
Cons:
- Limited support for non-web applications (e.g., mobile apps).
- Doesn’t support older browsers (e.g., Internet Explorer).
Pricing:
Cypress offers a free Starter plan (500 test results/month), and its paid Team plan starts at US $ 67/month when billed annually.
4. Appium
Appium is an open-source framework built for testing mobile apps across Android, iOS, and Windows devices. It works with native, hybrid, and mobile web applications while letting teams reuse the same test scripts across platforms. Its flexibility, strong community support, and broad ecosystem make it a reliable option for modern mobile automation workflows.
Best for: Mobile application testing
Key Features:
- Cross-Platform Mobile Automation: Test Android and iOS apps using one framework for native, hybrid, and mobile web apps.
- Real-Device Testing Support: Run tests on real smartphones and tablets for more accurate performance and UI results.
- Wide Language Compatibility: Build tests in your preferred language like Java, Python, C#, Ruby, JavaScript, and more.
- No App Source Code Required: Test apps without modifying or accessing the source code, making it easy to test production builds.
- Gestures + CI/CD Integration: Supports key mobile gestures (tap, swipe, scroll, drag) and integrates smoothly with Jenkins and cloud testing platforms.
Pros:
- Open-source with extensive community support.
- Supports cross-platform testing for both iOS and Android.
- Allows testing of real devices and emulators.
Cons:
- Requires technical knowledge for writing automation scripts.
- It can be slow and resource-intensive compared to other mobile testing tools.
Pricing:
It’s completely free, Appium is an open-source QA automation testing tool with no licensing cost.
5. Playwright
Playwright is an open-source end-to-end testing framework developed by Microsoft that lets QA teams automate browser interactions across Chromium, Firefox, and WebKit using a unified API. It supports multiple programming languages including JavaScript/TypeScript, Python, Java, and .NET and makes test scripts more reliable by automatically waiting for elements, reducing flakiness.
Best for: Cross-browser testing
Key Features
- Cross-browser & Cross-device Testing: Runs reliable tests on Chromium, Firefox, WebKit, and mobile emulators, ensuring consistent behavior across all major environments.
- Auto-wait & Smart Synchronization: Automatically waits for elements to load, animations to complete, and network calls to finish, reducing flaky tests and improving stability.
- Headless & Headed Execution: Offers fast headless test runs for CI pipelines, with a full browser mode available for debugging and visual validation.
- Multi-language Support: Works seamlessly with JavaScript, TypeScript, Python, Java, and C#, making it easy for diverse QA teams to adopt.
- Strong CI/CD Integrations: Fits smoothly into modern DevOps workflows with easy integration into Jenkins, GitHub Actions, GitLab, Azure DevOps, and other automation pipelines.
Pros:
- Supports multiple browsers with a single API.
- Fast and reliable test execution.
- Easy to set up and use with good documentation.
Cons:
- Newer tool with a smaller community compared to Selenium.
- Limited resources for debugging complex issues.
Pricing:
Playwright itself is free and open-source (Apache 2.0 license), but if you use Azure Playwright Testing / Playwright Workspaces, it’s pay-as-you-go based on actual test run time (charged by the second).
6. Tricentis Tosca
Tricentis Tosca is a powerful continuous-testing platform designed for enterprise environments. It uses a model-based, codeless approach to build resilient end-to-end tests across UIs, APIs, mobile, and more. With real-time risk assessment and deep CI/CD integration, Tosca helps teams deliver higher-quality software faster.
Best for: Enterprise teams handling complex testing workflows.
Key Features
- Model-Based Test Automation: Tosca uses a model-based approach that separates test logic, data, and technical layers, allowing teams to reuse components and dramatically cut test maintenance.
- Risk-Based Test Optimization: The platform prioritizes test coverage based on business risk, helping QA teams reduce redundant tests and focus on scenarios that truly impact release quality.
- End-to-End Technology Support: With support for 160+ technologies like web, mobile, API, SAP, Salesforce, mainframe, and more. Tosca enables comprehensive functional testing across complex enterprise environments.
- AI-Driven Codeless Test Creation: Its AI-enabled engine accelerates test design with smart element identification, self-healing, and codeless workflows, making test automation faster and more resilient.
- DevOps & Continuous Testing Integration: Tosca seamlessly connects with modern DevOps toolchains, CI/CD pipelines, and service virtualization tools to support continuous testing at scale.
Pros:
- Test creation without scripts lets non-technical users build tests
- Robust automation engines handle applications of all types
- Smooth integration with Oracle Fusion and other ERP systems
- Model-based framework reduces maintenance work
Cons:
- License costs are too high for smaller teams
- Upgrades can be complex and delay integration
- Large projects may face performance issues
- The platform doesn’t work on Linux and macOS
Pricing:
There’s no public free plan for Tricentis Tosca; its pricing is custom, and you need to contact sales for details.
7. TestLodge
TestLodge is a lightweight, web-based test case management tool that helps QA teams consolidate their test plans, suites, and runs all in one place. It offers a clean, user-friendly interface that’s easy to pick up, and integrates smoothly with many issue-tracking tools so bugs can be reported automatically when tests fail.
Best for: Test case management and execution.
Key Features
- Streamlined Test Case Management: A clean, web-based interface that makes it easy to create, organize, and maintain test cases without unnecessary complexity.
- Effortless Test Execution Tracking: Manage test runs, record results, and track progress in real time for better transparency across QA cycles.
- Smooth Integrations With Dev Tools: Works seamlessly with Jira, GitHub, Trello, and other issue trackers to automatically create and link defects.
- Centralized Team Collaboration: Enables teams to share test suites, assign tasks, and stay aligned throughout the testing process.
- Reusable Test Suites & Templates: Save time by reusing structured test cases and templates across multiple projects and releases.
Pros:
- Lightweight and easy to set up for smaller teams.
- Excellent for managing test cases and defects in one place.
- Great for tracking manual testing efforts.
Cons:
- Lacks some of the advanced features of full automation tools.
- It may not scale as well for larger teams with complex testing needs.
Pricing:
There’s no public free plan for Tricentis Tosca, its pricing is custom and you need to contact sales for details.
8. TestLink
TestLink is an open-source, web-based test management system designed to support QA teams in organizing, planning, and executing test cases. It allows users to define test projects, link test cases to requirements, set up test plans, and track execution over time. With its role-based access model and integration capabilities (e.g., with JIRA, Bugzilla), it provides a central place to manage both manual and automated testing efforts.
Best for: Test case management and integration
Key Features
- Centralized Test Case & Suite Management: A clean, web-based interface helps teams organize, version, and maintain test cases and test suites in one place, ensuring consistent documentation and easy updates.
- Requirement Traceability & Coverage Tracking: Built-in traceability matrices link test cases to requirements, giving QA teams complete visibility into coverage gaps and improving release confidence.
- Seamless Integration With QA Ecosystem: Connects smoothly with Jira, Jenkins, Bugzilla, and other CI/CD tools, enabling streamlined defect tracking and automated test result updates.
- Multi-User Collaboration With Role Controls: Supports multiple users with custom roles, permissions, and access levels, ideal for distributed QA teams managing large test cycles.
- Fast Import/Export & Result Logging: Allows bulk import/export of test cases and provides structured result logging to speed up test execution and reduce repetitive manual work.
Pros:
- Completely free open-source solution
- Excellent user management with permission controls
- Export capabilities to Word format for documentation
- Centralized test repository that prevents redundancy
- Project-wise test cycle tracking with tabular results
Cons:
- A dated user interface that feels hard to use
- Integration challenges with automated test suites
- Complex setup that needs PHP and MySQL knowledge
- Poor optimization for mobile devices
- Limited collaboration features compared to modern alternatives
Pricing:
TestLink is free to use, since it’s open-source under the General Public License(GPL).
9. Cucumber
Cucumber is a behavior-driven testing framework that helps teams write test scenarios in plain, readable language. It bridges the gap between developers, testers, and product owners by turning requirements into executable tests. Widely used in modern automation pipelines, Cucumber keeps collaboration smooth and ensures that product behavior stays aligned with real user expectations.
Best for: Behavior-driven development (BDD)
Key Features:
- Behavior-Driven Testing (BDD) with Gherkin: Uses the Given-When-Then Gherkin syntax to write clear, human-readable scenarios, allowing both technical and non-technical teams to understand test behavior.
- Executable Specifications: Turns plain-text feature files into automated tests, ensuring requirements, scenarios, and system behavior always stay aligned.
- 3. Strong Collaboration Across Teams: Acts as a shared language between developers, QA engineers, and product owners, reducing communication gaps and improving requirement clarity.
- Seamless Integration With Automation Frameworks: Works smoothly with Selenium, Appium, Playwright, and CI/CD pipelines, making it ideal for automated end-to-end testing.
- Multi-Language and Cross-Platform Support: Compatible with popular languages like Java, JavaScript, Ruby, and .NET giving teams flexibility to adopt it within any tech stack.
Pros:
- Closes communication gaps between technical and business teams
- Acts as a living documentation that reflects system changes
- Supports reusable test cases and modular design
- Boosts test automation without code requirements
- Brings teams together using human-readable language
Cons:
- New teams face a learning curve with BDD
- Feature files become hard to maintain as requirements change
- Test scenarios grow too detailed and complex
- Existing projects face integration challenges
- Runs slower compared to lower-level tests
Pricing
Cucumber is a completely free open-source framework without licensing fees or usage restrictions. Cucumber (via CucumberStudio) offers a 14-day free trial, then the Starter plan costs US $36/user/month (billed annually).
10. SoapUI
SoapUI is a widely used open-source tool for testing web services, particularly REST and SOAP APIs. It provides a unified environment to execute functional, regression, and load tests, and even supports service simulation through mock services. Developed by SmartBear, SoapUI is built in Java, making it cross-platform and highly extensible.
Best for: Legacy/SOAP APIs Test
Key Features:
- Comprehensive API Testing (REST, SOAP, GraphQL, JMS): Supports all major API protocols, making it ideal for validating modern and legacy web services.
- Powerful Data-Driven Testing: Enables testers to run the same test with multiple datasets for deeper coverage and reliable results.
- Scripted Automation with Groovy: Allows advanced users to build custom logic, automate complex workflows, and extend test capabilities.
- Asynchronous & Complex Test Case Handling: Efficiently manages real-world scenarios like delayed responses, callbacks, and multi-step API flows.
- Seamless CI/CD Integration: Works smoothly with Jenkins, Azure DevOps, and other pipelines to support continuous testing in fast-moving development environments.
Pros
- Supports SOAP & REST with powerful functional, security, and load testing features.
- Data-driven testing with external files (CSV, Excel, DB) for wider coverage.
- Mock services to simulate APIs when backend isn’t ready.
- Groovy scripting allows deep customization and automation.
Cons
- Complex and outdated UI and a steep learning curve for beginners.
- Heavy on system resources, especially for large test suites.
- Advanced features locked in the paid ReadyAPI version.
- Debugging can be tricky with non-intuitive error messages.
Pricing
SoapUI Open Source is completely free with no licensing fees. For advanced features, ReadyAPI (SoapUI Pro) starts at $990/year per license, with add-ons like Virtualization ($1,310/year) and Load Testing ($6,840/year)
11. Ranorex Studio
Ranorex Studio is a mature, all-in-one QA testing tool designed to automate tests across desktop, web, and mobile applications. It supports both codeless test creation for users who prefer recorder and drag-and-drop workflows, and script-based automation using C# or VB.NET. With its robust object-recognition capabilities and tight integration into CI/CD environments, Ranorex enables teams to build reliable and scalable automated QA suites.
Best for: UI and desktop application testing
Key Features:
- Codeless Test Automation with Smart Recorder: Enables fast test creation through an intuitive record-and-playback interface, allowing both beginners and non-technical testers to build reliable UI tests with ease.
- Powerful Object Recognition with Ranorex Spy: Accurately identifies UI elements across desktop, web, and mobile applications, ensuring stable automation even when UI elements change.
- Cross-Platform and Cross-Device Testing: Supports automated testing on Windows, macOS, Android, and iOS, making it suitable for teams managing multi-environment application releases.
- Parallel and Distributed Test Execution: Allows testers to run multiple test cases simultaneously on virtual or physical machines, reducing execution time and speeding up delivery cycles.
- Seamless Integration with CI/CD and DevOps Tools: Connects smoothly with Jenkins, GitLab, Azure DevOps, Jira, and other pipelines to support continuous testing and modern DevOps workflows.
Pros
- Supports desktop, web, and mobile automation.
- Offers codeless recording + C# coding for hybrid teams.
- Strong UI element recognition with RanorexXPath.
- Integrates easily with CI/CD tools (Jenkins, TeamCity).
Cons
- Expensive licensing, not ideal for small teams.
- Windows-only IDE, limiting for macOS/Linux users.
- Slower test execution for large UI suites.
- Smaller community vs open-source tools.
Pricing
Ranorex Studio offers a 14-day free trial, and its paid plans are available only through contact-sales pricing.
12. Apache JMeter
Apache JMeter is an open-source tool widely used for load and performance testing of web applications, APIs, and server-side services. It helps teams understand how their systems behave under different traffic levels and is known for its flexibility and strong community support. JMeter continues to be a reliable choice for performance engineers who need a scalable and extensible testing solution.
Best for: Performance testing
Key Features:
- High-Scale Load & Performance Testing JMeter can simulate thousands of virtual users simultaneously, helping QA teams measure how applications behave under heavy traffic and real-world stress conditions.
- Wide Protocol Support: It supports testing across multiple protocols, including HTTP/HTTPS, SOAP/REST APIs, JDBC, FTP, LDAP, and JMS making it suitable for web, database, and service-level performance testing.
- Distributed Testing for Large Scenarios: Teams can run tests across multiple machines to generate higher loads, enabling realistic and scalable performance assessments for enterprise applications.
- Flexible Scripting & Extensibility: JMeter’s samplers support Groovy, BeanShell, and other JSR223 languages, allowing testers to customize logic, create dynamic test data, and extend functionality as needed.
- Detailed Reporting & Real-Time Monitoring: The tool provides graphs, logs, listeners, and exportable reports that help QA engineers analyze response times, bottlenecks, throughput, and server behavior during test runs.
Pros:
- No licensing costs at all
- Works on Windows, Linux, and macOS
- Easy-to-use GUI interface helps create test plans
- Rich plugin ecosystem offers 70+ options
- Continuous connection with CI/CD pipelines
Cons:
- Large tests need substantial system resources
- Browser simulation isn’t available (works at protocol level)
- Live monitoring capabilities are limited
- Technical expertise needed for advanced features
Pricing
Apache JMeter Completely free and open-source; there’s no licensing or subscription cost.
13. Postman
Postman is one of the most widely used API testing tools, trusted by QA engineers and developers for building, testing, and documenting APIs. It simplifies API validation with collections, automated test runs, mock servers, and integrated collaboration features.
Best for: API testing, automation of API workflows, contract testing, and collaborative API development.
Key Features
- API Request Builder: Create, test, and document APIs for REST, GraphQL, SOAP, and WebSockets.
- Automated Testing: Write JavaScript scripts for API testing automation and integration with CI/CD pipelines.
- Collection Runner: Execute multiple tests at once, ideal for automating API tests in CI/CD workflows.
- Mock Servers: Simulate API responses for testing without the backend or when APIs are in development.
- API Schema Support: Work with OpenAPI and RAML schemas for enhanced contract testing and validation.
- Version Control: Built-in versioning to track changes and manage API testing workflows.
- Environment Variables: Easily switch between environments (e.g., dev, staging, production) for scalable testing.
- Integrations: Seamless integration with GitHub, GitLab, Jenkins, and Azure DevOps for collaborative API development and testing.
Pros
- Easy-to-use interface for quick request creation
- Strong collaboration and version control features
- Supports automation and CI pipeline execution
- Excellent documentation and learning resources
- Suitable for both beginners and advanced API testers
Cons
- Can become slow with large collections
- Advanced features locked behind paid plans
- Limited load testing capabilities
Pricing
Postman offers a demo plan and a Professional plan at $29/user/month (annual billing).
14. SonarQube
SonarQube helps teams maintain clean, secure, and reliable code by continuously analyzing codebases during development. It highlights issues early in the pipeline, making it easier for teams to improve code quality and reduce long-term technical debt. Its dashboards give a clear view of overall code health across projects.
Best for: Code quality analysis
Key Features
- Deep Static Code Analysis: Identifies bugs, security flaws, and code smells across multiple programming languages before they reach production.
- Quality Gates for Build Validation: Applies strict quality rules that automatically pass or fail builds, ensuring only clean and reliable code moves forward.
- Technical Debt & Maintainability Insights: Highlights risky areas, calculates technical debt, and shows where the codebase needs improvements to stay healthy.
- Seamless CI/CD Integration: Works smoothly with tools like Jenkins, GitHub Actions, GitLab CI, and Azure DevOps to automate continuous code quality checks.
- Developer-Friendly IDE Support: Provides real-time issue detection inside popular IDEs, helping developers fix problems early in the workflow.
Pros:
- Customizable rules to enforce coding standards
- Detailed dashboards that show metrics and trends
- Strong security vulnerability detection
- Continuous integration into developer workflows
Cons:
- Complex configuration and setup process
- Expensive for enterprise features
- Performance issues with large projects
- Occasional software bugs reported
Pricing
SonarQube has a free Community edition, while its commercial Developer Edition starts at around US$ 720 per year. based on lines of code.
15. Apiary
Apiary is a design-first platform for building, documenting, and testing APIs. It uses a human-readable format (API Blueprint) to define endpoints early, and lets teams spin up a mock server so they can prototype before any real code is written. It also offers interactive documentation and a traffic inspector to observe real request/response flows as you develop.
Best for: Design-first API development and early-stage API validation.
Key Features
- API Blueprint–Driven Specification & Validation: Apiary uses the API Blueprint format to clearly define API behavior, helping QA teams validate whether the implementation aligns with the documented specification from day one.
- Instant Mock Server for Early Testing: The platform generates mock servers directly from the API definition, enabling testers and frontend teams to start validating request–response flows long before the backend is built.
- Automated Contract Testing: Apiary automatically checks live API implementations against the defined blueprint, ensuring both remain in sync and reducing defects caused by mismatched contracts.
- Interactive API Console for Hands-On Testing: Its built-in console allows testers to execute real requests, inspect responses, and explore different endpoints without switching tools.
- Centralized, Always-Updated API Documentation: Documentation updates in real time as the API evolves, giving QA teams reliable, up-to-date reference material for test planning and regression testing.
Pros:
- Mock servers make prototyping quick
- Documentation updates happen automatically
- Teams can design together in a shared environment
- You can test without writing code
Cons:
- Advanced testing scenarios have limited flexibility
- You must use API Blueprint language
- Integration works best with Oracle, not other cloud platforms
- Smaller teams might find enterprise features costly
Pricing
Apiary’s Free plan covers basic API design, mock servers, and docs. Their Pro / Enterprise pricing is custom, based on team size.
Metrics Table: What to Evaluate When Choosing QA Testing Tools
This section highlights the core metrics that matter when selecting QA testing tools. Focus on these factors to ensure you’re choosing a tool that meets your team’s testing needs.
| Metric | Why It Matters | Good Benchmark / Example | How You Use It When Evaluating Tools |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automatable Test Case % | Shows how much of your suite can be automated key for ROI | ≥ 70% of regression cases automated | Does the tool support automating your key test types (UI/API/mobile)? |
| Automation Pass Rate | Reflects the reliability of automated tests (low false failures) | ≥ 90%+ passing in stable runs | Does the tool provide stable execution, retry logic or self‑healing? |
| Test Suite Execution Time | Faster feedback = faster releases | Full regression < 30 min (for mid‑sized product) | Can the tool parallelize, run in the cloud, and support CI integration? |
| Defect Leakage % | Shows what slips into production, big risk | < 5% of defects found post‑release | Does the tool integrate with defect tracking, coverage tools, or provide analytics? |
| Test Stability (Flake Rate) | Flaky tests kill trust and waste time | Flake rate < 3% | Does the tool have locator robustness, wait handling, or AI‑driven stability? |
| Coverage % (UI/API/Mobile) | Ensures you’re testing what matters | > 80% of key flows covered | Does the tool support all platforms your product uses (web, mobile, API)? |
| Infrastructure Cost vs ROI | Ensures the tool is cost‑effective | ROI positive within 6–12 months | What’s the licensing/infrastructure cost, and charges for scaling? |
| Integration Depth | QA tools must fit into DevOps/CI/CD | Supports Jenkins/GitHub/Jira/out‑of‑box | Can you use the tool in your existing pipeline with minimal friction? |
| Real‑Device Coverage | Device fragmentation is a huge risk for mobile/web | Access to 1000+ device/browser combos | Does the tool support real devices, device clouds, and parallel runs? |
| Analytics & Reporting | Data drives continuous improvement | Dashboards with trends, root‑cause insights | Does the tool provide robust reporting, logs, and historical tracking? |
Top Mistakes to Avoid When Selecting QA Testing Tools
Choosing the right QA testing tool is critical, but many teams fall into common traps that lead to wasted resources and inefficiency. Here are the key mistakes to avoid when selecting a tool for your testing needs.
- Choosing a tool before defining the test strategy: Without clarity on test types, coverage, skills, you may buy mismatched tools.
- Under‑estimating maintenance & integration cost: Many automation tools require significant investment in infrastructure, flaky test maintenance, and training.
- Ignoring team skills & community support: A tool with little community or training burden can slow adoption.
- Over‑focusing on features rather than fit: Feature‑rich tools may be overkill and heavy for your team. Pick the right scale.
- Neglecting future‑proofing: Choose tools that can evolve as your architecture shifts (micro‑services, cloud‑native, observability).
Future Trends in QA Testing Tools
As technology advances, QA testing is evolving rapidly. Here are the key trends shaping the future of QA tools:
- AI/LLM in test generation and maintenance: Research shows AI‑driven test generation can reduce flaky tests and boost coverage.
- Observability and shift‑left testing: QA tools will integrate more with observability (logs, metrics, dashboards), enabling earlier detection of failures.
- Low‑code/no‑code QA democratization: Citizen testers and business users may create tests, reducing QA backlog and empowering non‑technical roles.
- Cloud‑native, distributed testing: With more micro‑services and containerised apps, tools must support distributed execution, parallel testing, and cloud integration.
- Better analytics and metrics: QA teams will need tools that provide actionable metrics (flakiness rate, test yield, ROI), not just pass/fail counts.
Conclusion
QA automation is the most crucial part of the software development process as it ensures the accurate functioning and performance of the software applications. The QA process requires the choice of the right QA testing tools so that developers and testers can detect bugs in the early stage and expedite the release of the software application. This blog covers the top 15 popular QA testing tools you can choose based on your needs.Explore them individually and consider the factors we have discussed in this blog to make a decision. If your focus is on testing the visual and interactive elements of your application, don’t miss our comprehensive guide on the best UI Testing Tools.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are QA testing tools?
QA testing tools are software applications and platforms that support the quality assurance process by helping testers and QA engineers design, manage, execute and report on test cases. They can automate repetitive tests (UI, API, performance), manage test requirements and traceability, and help ensure that applications meet functional and non-functional requirements before release.
Why should technical QA teams invest in QA testing tools?
Technical QA teams benefit from dedicated tools because they provide efficiency, repeatability, traceability and integration. Proper tools enable scalable automation, align testing with CI/CD pipelines, reduce manual effort, and help detect defects earlier. This improves release velocity, reliability and stakeholder confidence in software quality.
What factors should I consider when choosing a QA testing tool?
Key factors include: your types of testing (UI, API, performance), the technology stack and language support, team skills and training needs, integrations (CI/CD, bug tracking), scalability and maintenance cost, budget and licensing model, community/ vendor support, and future-proofing (no-code, AI capability).
How is a test management tool different from an automation tool?
A test management tool organises test cases, tracks execution results, links tests to requirements and defects, and provides dashboards and traceability. An automation tool executes scripts (UI, API, performance) to validate application behaviour. Both play complementary roles, management ensures control, automation ensures efficiency.
Which QA testing tool categories should I prioritise?
Common categories include: test management/traceability, functional/UI automation, API/back-end testing, performance/load testing, cross-browser/mobile device testing, and emerging no-code/AI platforms. Prioritise based on your project’s dominant testing needs and existing gaps.
Are no-code or AI-driven QA testing tools worth it?
Yes they help reduce dependence on scripting, empower non-technical testers, and accelerate test creation and maintenance. But they must be vetted for integration capability, scalability and actual ROI. They are best used alongside existing automation frameworks in a hybrid strategy.
What are the common mistakes when selecting QA testing tools?
Common mistakes include: picking a tool before defining test strategy, ignoring maintenance and integration costs, neglecting team skills or community support, choosing overly complex tools for small teams, and failing to evaluate future-proofing against evolving QA needs.
How can I compare QA testing tools effectively?
Use a comparison matrix covering: tool category, team size and maturity, budget/licensing, language/stack support, integrations, learning curve, maintenance cost, use-case fit, and vendor community. Use pilot projects, measure key metrics (coverage, flakiness, cycle time) and gather stakeholder feedback before full adoption.
How will QA testing tools evolve in the coming years?
Expect stronger integration of AI/LLM for test generation and maintenance, more low-code/no-code platforms, closer alignment between observability and QA, cloud-native distributed testing, and dashboards offering smarter analytics like defect-prediction and test-health forecasting.
Can QA testing tools integrate with CI/CD and DevOps workflows?
Yes and they should. Modern QA tools support integrations with CI/CD pipelines (Jenkins, GitLab, GitHub Actions), version control, bug-tracking (Jira, Azure DevOps) and test data/observability tools. This enables testing automation to run as part of build/release pipelines and gives faster feedback loops.
What budget should I allocate for QA testing tools?
Budget depends on team size, test type coverage, licensing and infrastructure. For small teams, a mid-tier tool may cost a few thousand USD per year; for enterprise scale expect tens of thousands. Factor in training, setup, maintenance and infrastructure in the total cost of ownership.
How can I measure the ROI of a QA testing tool?
Measure ROI by tracking metrics such as: reduction in manual test effort, percentage of test automation coverage, decrease in defects caught post-release, release cycle time improvement, maintenance cost of test suite, and stakeholder satisfaction. Use pilot projects and baseline prior to tool adoption.
Author