How To Use WebDriverManager In Selenium
Cagri Ataseven
Posted On: February 28, 2024
![]() 433126 Views
433126 Views
![]() 18 Min Read
18 Min Read
Selenium WebDriver is a popular and widely used tool for web automation testing. The latest version of Selenium WebDriver came out with version 4, which is equipped with new features.
With the release of Selenium WebDriver 4.11.0, Selenium Manager has also been released, which takes care of automated browser and driver management. However, with projects or organizations that still use the older version of Selenium (less than 4.11.0), it is necessary to download third-party browser drivers (or WebDrivers) and make various configurations in the framework to use Selenium WebDriver.
Isn’t the manual management (i.e., download, setup, and maintenance) of these drivers in a framework prepared for automated testing annoying? Yes, it is. The good news is that there is an excellent solution to this challenge – WebDriverManager by Bonigarcia.
In this blog on WebDriverManager in Selenium, we demonstrate how WebDriverManager helps in automated driver management and eventually frees the tester’s time to look into other important tasks. If you are preparing for an interview you can learn more through Selenium interview questions.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
- Overview of Selenium WebDriver Architecture
- How to Use Third-Party WebDrivers?
- What is WebDriverManager in Selenium?
- What is Bonigarcia WebDriverManager?
- Resolution Algorithm of WebDriverManager
- How to Set Up WebDriverManager in Selenium?
- Driver Management with WebDriverManager
- Demo: How to Use WebDriverManager in Selenium on the Cloud?
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Overview of Selenium WebDriver Architecture
Before you start using Selenium WebDriver, it will be helpful to understand how it works and solve the challenges that may be encountered in the future. In this section, I will summarize the Selenium WebDriver architecture.
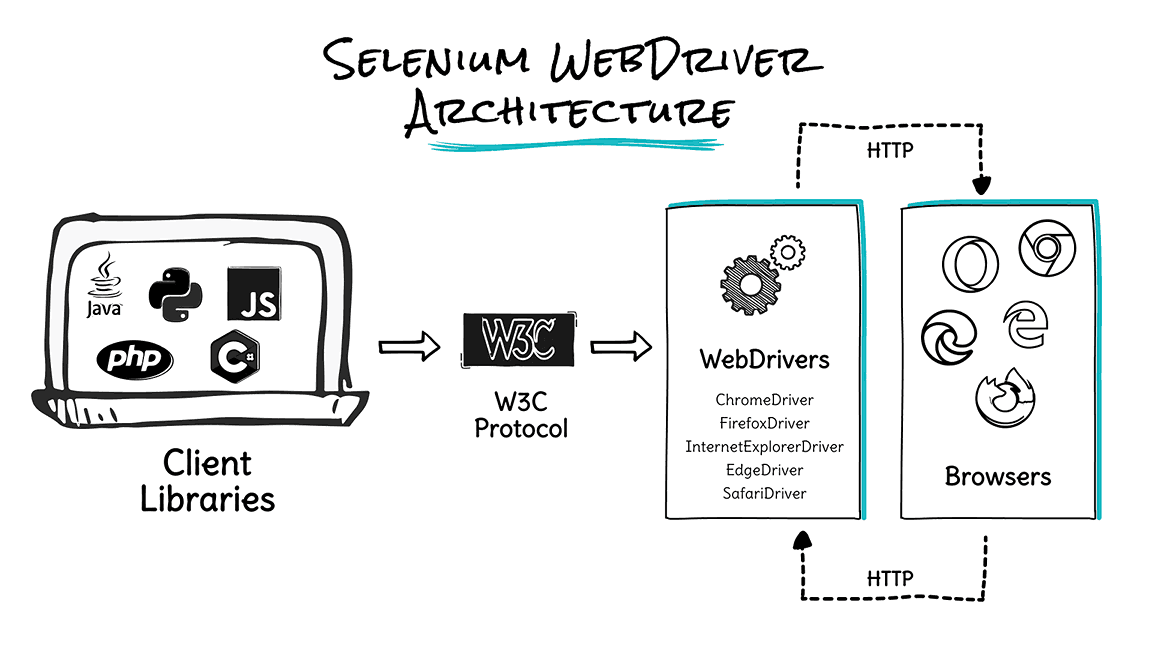
Selenium WebDriver is a library that enables interaction between browsers and browser drivers. It is often used to create automated tests for web applications. This architecture of Selenium WebDriver consists of four components:
- Selenium Client Libraries
- WebDriver W3C Protocol
- Browser Drivers
- Real Web Browsers
- Selenium Client Libraries: One of the most significant advantages of Selenium WebDriver is that it supports multiple programming languages, such as Java, Python, JavaScript, C#, Ruby, etc. Selenium client libraries offer flexibility in programming language selection for test automation.
- W3C WebDriver Protocol: The W3C WebDriver Protocol, which has received the endorsement of W3C Protocol (World Wide Web Consortium), is used with Selenium 4 instead of the JSON Wire Protocol (used in Selenium 3). It means there is direct communication between the browser drivers and Selenium client libraries. It also offers the following advantages:
- Browser Drivers: The browsers supported by Selenium contain a separate browser driver. Browser driver binaries (ChromeDriver for Chrome, GeckoDriver for Firefox, or MSEdgedriver for Edge) communicate with the respective browser by hiding the implementation logic of the browser’s functionality.
- Real Web Browsers: Selenium supports multiple browsers such as Chrome, Firefox, IE, Safari, etc. But remember! You need to install the browser and corresponding browser driver if you are using Selenium version less than 4.11.0 because Selenium can only run tests on the browsers if they are installed.
However, if you are using the Selenium WebDriver version 4.11.0 or greater, you don’t need to worry about the browser and browser driver installation, as Selenium Manager takes care of the installation part internally.
However, this only applies if you run tests on a local Selenium Grid. You would not face similar issues with a cloud grid since the onus of browser and browser driver update is not with us. Cloud-based testing platforms like LambdaTest offer various browsers with multiple versions readily available that can be plugged in and played quickly.
W3C WebDriver Protocol provides international W3C standards. Therefore, it is expected that the UI tests written with Selenium are expected to be much more stable (or less flaky). It provides an updated Actions API that offers new actions like zoom, multi-touch actions, and pressing two keys simultaneously. Also, you can use relative locators in Selenium 4 to locate web elements.
When a browser driver has received any command with the help of W3C WebDriver Protocol, it will trigger the respective browser, and the response will go back as an HTTP response.
How to Use Third-Party WebDrivers?
Since we have basic knowledge about how Selenium WebDriver works, we can talk about how to use third-party WebDrivers. As understood from the architecture I tried to explain above, to perform web browser automation with Selenium, we need to place a binary file called driver between the Selenium client and the web browser on which the Selenium automation tests will be run. So how is it done? Let’s examine the use of third-party drivers in 4 steps:
![]()
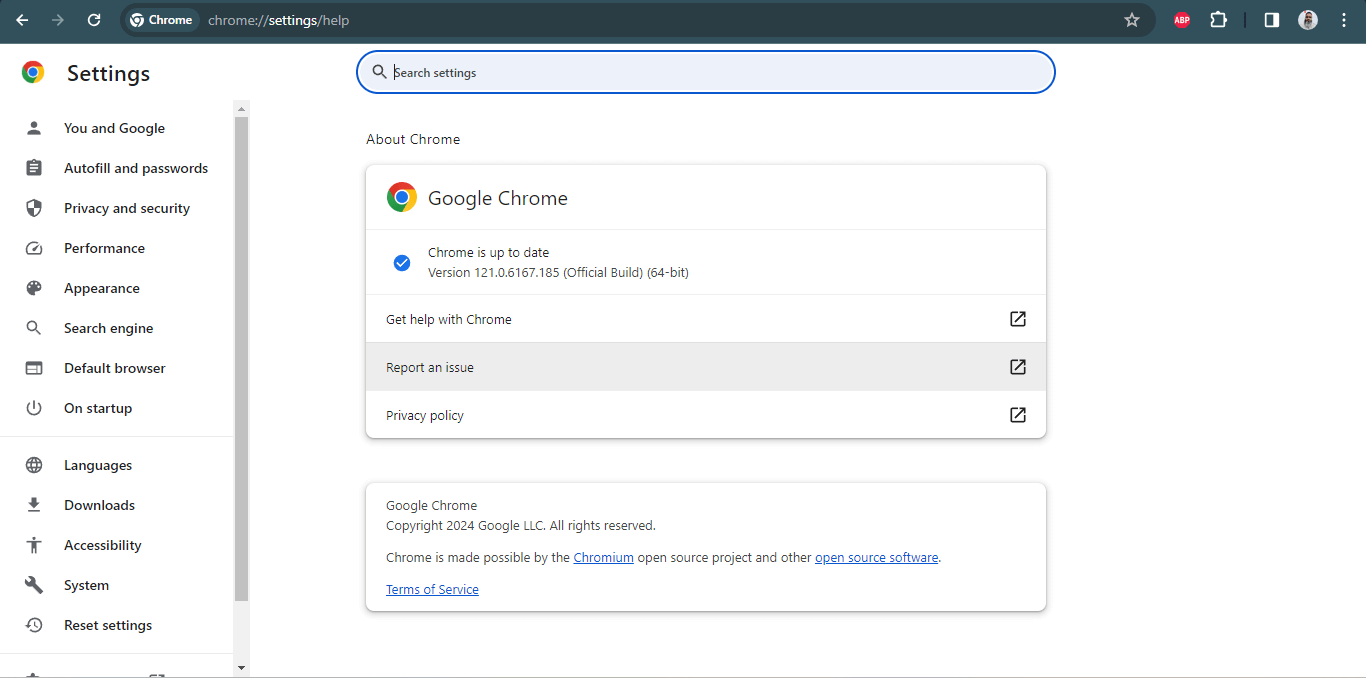
Before downloading the third-party driver, you need to ensure that the browser driver is in sync with the browser version on which the tests would be performed. For instance, you can find the Chrome version on the machine at chrome://settings/help.
Next, you have to download ChromeDriver, which is in sync with the version of the Chrome browser. ChromeDriver with version 115 or below can be downloaded using the ChromeDriver downloads page.
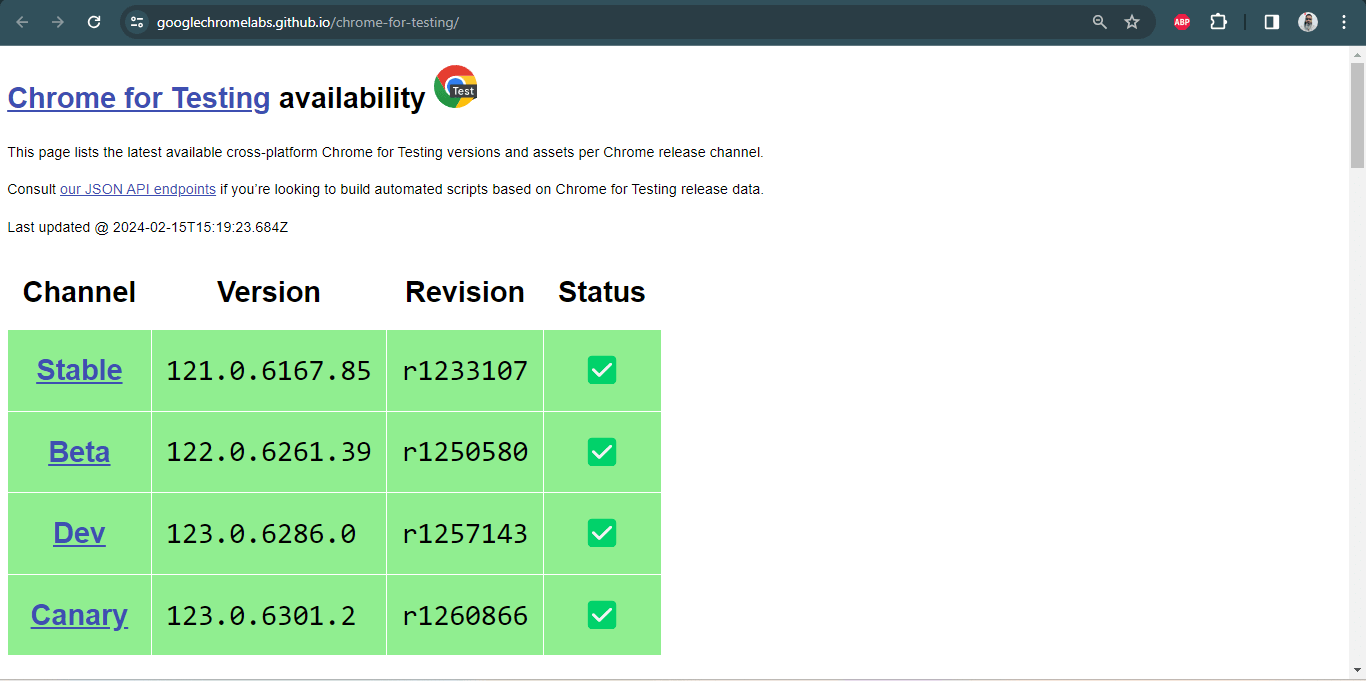
ChromeDriver with the version above 115 can be downloaded using the Chrome for Testing availability dashboard.
If the versions are not in sync, you will encounter a failure message. On the other hand, you would not get such issues when running tests on an online Selenium Grid like LambdaTest.
AI-powered test orchestration and execution platforms like LambdaTest allow you to run Selenium automation tests over an online browser farm of 3000+ browsers and operating systems. You can run tests in parallel, accelerate the release cycle, and cut down test execution by multiple folds.
Also, subscribe to the LambdaTest YouTube Channel and get detailed tutorials around automation testing, Selenium, Appium automation, and more.
The following error message could be encountered if the Chrome browser and ChromeDriver versions are not in sync.
selenium.common.exceptions.SessionNotCreatedException: Message: session not created: This version of ChromeDriver only supports Chrome version 94
Hence, we need to find the correct driver version for a specific browser release.
Drivers are platform-specific binary files. It means we must identify the driver type according to the operating system. For example, if we want to use Chrome, we need to download ChromeDriver by considering the operating system (Windows, Linux, or macOS) and the architecture (typically 32 or 64 bits).
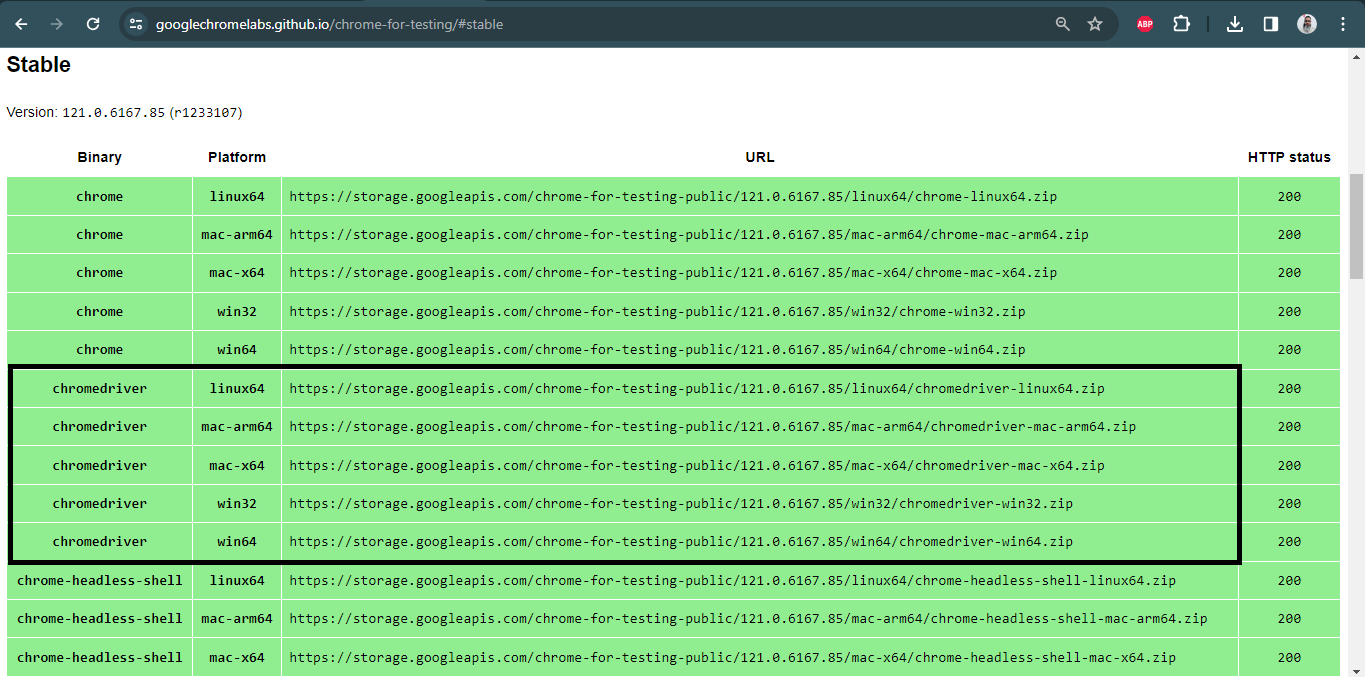
After finding and downloading the proper driver binary file, we can proceed to the setup phase. Here, we should ask a question: How will our Selenium tests find and use this binary driver file? In Java, we use Java system properties to export the driver path as follows:
|
1 2 3 4 |
System.setProperty("webdriver.chrome.driver", System.getProperty("user.dir")+"path of chrome driver"); System.setProperty("webdriver.gecko.driver", System.getProperty("user.dir")+"path of gecko driver"); System.setProperty("webdriver.edge.driver", System.getProperty("user.dir")+"path of msedge driver"); System.setProperty("webdriver.opera.driver", System.getProperty("user.dir")+"path of operadriver"); |
Let’s show the ChromeDriver implementation as an example. Firstly, we need to set the path of the ChromeDriver as follows:
|
1 2 3 |
String pathForChromeDriver= "write here your chromeDriver path"; System.setProperty("webdriver.chrome.driver", System.getProperty("user.dir")+pathForChromeDriver); |
After the path setting, we create an instance of the ChromeDriver.
|
1 |
WebDriver driver = new ChromeDriver(); |
And we are ready to open the website with the get() method:
|
1 |
driver.get("https://ecommerce-playground.lambdatest.io/"); |
So, the binary driver file we downloaded and completed the configuration will open the web page we want by interacting with the Chrome browser on the machine on which we run our tests.
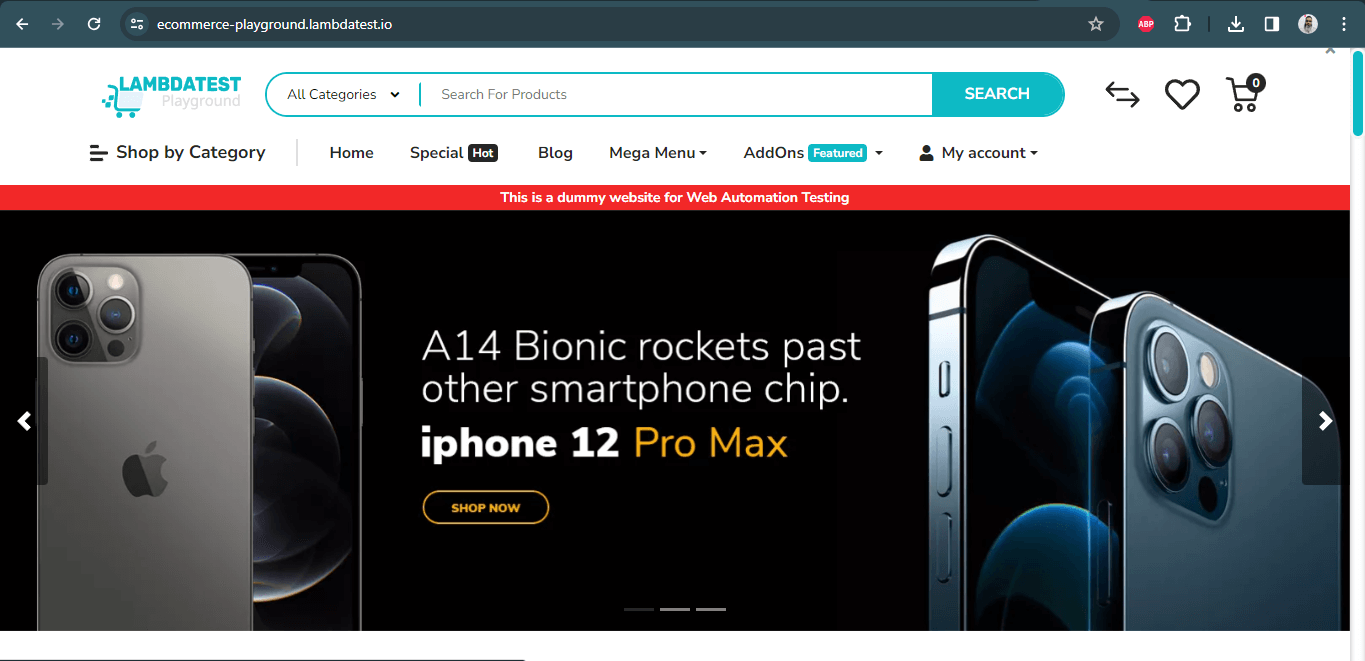
Here, I would like to remind you that the issue you will most likely encounter in the version control (Git, SVN, etc.) is that the driver is not executable if you use the binary driver file for Linux:
|
1 |
java.lang.IllegalStateException: The driver is not executable |
To solve that issue, you need to import the class java.io.File and use the following two lines of code:
|
1 2 |
File file= new File(System.getProperty("user.dir")+"path of driver"); file.setExecutable(true); |
The last step of the third-party driver usage process is maintenance. You’re probably questioning why we need maintenance. The answer is simple but annoying: Modern browsers automatically upgrade themselves. It means the compatibility between driver and browser is not warranted in the long term. That’s why you should do maintenance periodically.
As I mentioned above, our manual maintenance effort for automated tests is laborious. Also, this is an obstacle to universality (Independence from the environment, browser version, operating system, etc.), which is one of the most important test automation principles.
WebDriverManager from Bonigarcia is the solution to the problems mentioned above. Let’s dive deep into the integral aspects of WebDriverManager in Selenium.
What is WebDriverManager in Selenium?
WebDriverManager in Selenium is an open-source Java library automating the management of Selenium WebDriver drivers like chromedriver, geckodriver, msedgedriver. It facilitates automated download, setup, and maintenance, also offering features like browser discovery, WebDriver object building, and seamless Docker container integration.
What is Bonigarcia WebDriverManager?
Dr. Boni Garcia brought a great solution to the problem I mentioned above by creating the first version of the WebDriverManager library in 2015.
Here are some salient benefits of WebDriverManager in Selenium:
- Automates the management of WebDriver binaries, thereby avoiding installing any driver binaries manually.
- Supports all popular browser drivers like Chrome, Firefox, Edge, etc.
- Checks the version of the browser installed on your machine and download the proper driver binaries into the local cache (~/.cache/selenium by default) if not already present.
- Matches the version of the drivers. If unknown, it uses the latest version of the driver.
- Supports the browser options and allows passing on the browser capabilities while setting up the browsers.
- Offers cross browser testing without the hassle of installing and maintaining different browser driver binaries.
- Creates browser sessions in Docker containers.
Resolution Algorithm of WebDriverManager
Before using WebDriverManager in Selenium, let’s look at how it works. How does it find and download the proper versions of browsers? Let’s dive deep into it.
![]()
WebDriverManager executes a resolution algorithm to automate the process given above for the appropriate driver binary.
Here are the brief steps of the resolution algorithm:
Step 1: Find the Proper Driver Version
WebDriverManager tries to find the browser version using the knowledge database called the commands database. This database consists of shell commands used to discover a browser’s version in the different operating systems.
Here are the commands for the Linux environment:
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
google-chrome --version firefox -v microsoft-edge --version opera --version chromium --version |
Also, with the help of another knowledge database called the versions database, WebDriverManager in Selenium maps the browser releases with the known proper driver versions.
Step 2: Download and Set Up the Driver
After the respective driver version is found, WebDriverManager downloads this driver to a local cache (~/.cache/selenium by default). Then, it sets the downloaded driver path using Java system properties corresponding to browsers:
|
1 2 3 4 |
webdriver.chrome.driver webdriver.gecko.driver webdriver.edge.driver webdriver.opera.driver |
Step 3: Maintenance
As mentioned earlier, the most problematic aspect of using third-party driver binaries is maintenance, i.e., finding the appropriate driver version for the browser we use for specific periods and downloading them repeatedly. So, how does WebDriverManager in Selenium handle this process automatically?
WebDriverManager has a resolution cache called resolution.properties. This cache stores the match between the downloaded driver and browser versions. Also, this match is valid for 1 hour for browsers and considered correct for one day for drivers.
Long story short, WebDriverManager does not try to find a new browser and driver version in every test run, so using the current driver and browser in subsequent test runs improves performance.
How to Set Up WebDriverManager in Selenium?
Installing WebDriverManager in Selenium is also very simple. If you are using a Maven project, then you need to go to the Maven Repository website and search for the WebDriverManager dependency.
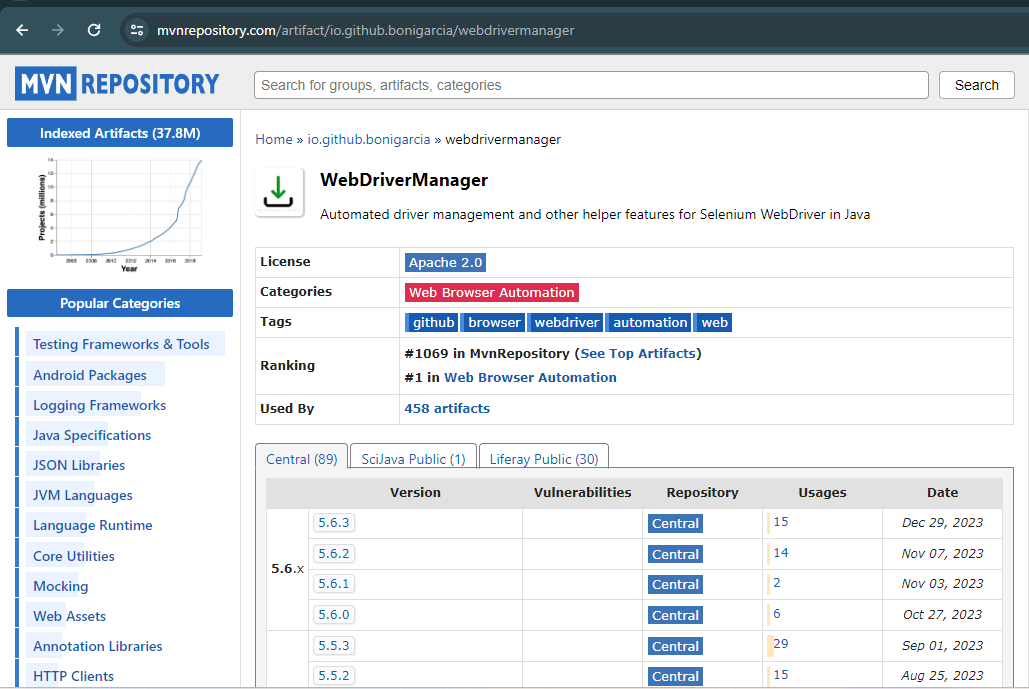
Simply add the following dependency to your pom.xml file. However, it should be noted that the dependency for Selenium WebDriver should also be added in the pom.xml:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/io.github.bonigarcia/webdrivermanager --> <dependency> <groupId>io.github.bonigarcia</groupId> <artifactId>webdrivermanager</artifactId> <version>5.6.4</version> </dependency> |
Don’t forget to include the test scope because WebDriverManager in Selenium is usually used in the testing part of your project.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
<dependency> <groupId>io.github.bonigarcia</groupId> <artifactId>webdrivermanager</artifactId> <version>5.6.4</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> |
If you are using a Gradle project, you can add WebDriverManager to your project as shown below:
|
1 2 3 4 |
dependencies { // https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/io.github.bonigarcia/webdrivermanager implementation group: 'io.github.bonigarcia', name: 'webdrivermanager', version: '5.6.4' } |
Driver Management with WebDriverManager
After the simple setup above, WebDriverManager is ready to manage your browsers. First, let’s examine the components WebDriverManager uses for browser management, then see browser management in practice with an example.
WebDriverManager library provides a class called WebDriverManager:
|
1 |
io.github.bonigarcia.wdm.WebDriverManager |
This class consists of some static methods, as mentioned below, to create managers for driver management. To manage the driver, select a given manager in the WebDriverManager class to manage the driver and invoke the setup() method. Let’s say you want to work with Chrome driver; then you can implement it as shown below:
|
1 |
WebDriverManager.chromedriver().setup(); |
WebDriverManager in Selenium offers a set of managers not only for Chrome but also for various browsers:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
WebDriverManager.chromedriver().setup(); WebDriverManager.firefoxdriver().setup(); WebDriverManager.edgedriver().setup(); WebDriverManager.operadriver().setup(); WebDriverManager.chromiumdriver().setup() WebDriverManager.iedriver().setup(); |
After version 5, WebDriverManager also started providing a Safari manager called safaridriver().
Now, let’s see the practical usage of WebDriverManager in Selenium. The following example shows a test case where the LambdaTest eCommerce Playground website will be loaded, and its URL will be checked to verify that it contains LambdaTest. This test will be run on the Chrome browser using Selenium WebDriver, WebDriverManager, and TestNG.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 |
import io.github.bonigarcia.wdm.WebDriverManager; import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;; import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeDriver; import org.testng.annotations.AfterTest; import org.testng.annotations.BeforeTest; import org.testng.annotations.Test; import static org.testng.Assert.assertTrue; public class ChromeWithWebDriverManagerTest { WebDriver driver; @BeforeTest public void setup() { WebDriverManager.chromedriver().setup(); driver = new ChromeDriver(); } @Test void checkTheUrl() { driver.get("https://ecommerce-playground.lambdatest.io/"); String url = driver.getCurrentUrl(); assertTrue(url.contains("lambdatest")); } @AfterTest void tearDown() { driver.quit(); } } |
Code Walkthrough
If you are going to work on the Chrome browser with Selenium WebDriver, you need to import the WebDriver interface and the ChromeDriver class from Selenium as follows:
To use WebDriverManager in Selenium, the WebDriverManager class must be imported.

Since we want to run WebDriverManager on the Chrome browser, we use the static method chromedriver() by invoking the setup() method, and we also initialize the WebDriver object for the Chrome driver (driver = new ChromeDriver();)

By using @BeforeTest annotation in TestNG, we ensure this setup process happens automatically before each test.
Using driver.get(), the browser is opened to go to any website. Selenium interacts with the browser using the Chrome driver determined by the WebDriverManager resolution algorithm.

Using driver.quit(), we reset the driver object that we initialized and do this after each test with the help of @AfterTest annotation.
 Note
NoteAutomate your tests with Selenium on the Cloud. Try LambdaTest Today!
Demo: How to Use WebDriverManager in Selenium on the Cloud?
In this demonstration, we will open the LambdaTest eCommerce Playground website and verify that the URL contains the word LambdaTest. This test will run on the latest version of the Chrome browser on Windows 10 using the LambdaTest cloud grid.
We would be using the remoteAddress() method from the WebDriverManager library to set the remote URL that will help us execute the test on the LambdaTest platform. The remoteAddress() method specifies the remote URL in the RemoteWebDriver instance, typically when using a Selenium Server or a cloud provider such as LambdaTest.
We need to add the capabilities for running the tests on the LambdaTest cloud grid. These capabilities can easily be set using the LambdaTest Capabilities Generator, which allows the user to set the capabilities using the UI and accordingly generates the configuration code that can be used in the tests directly.
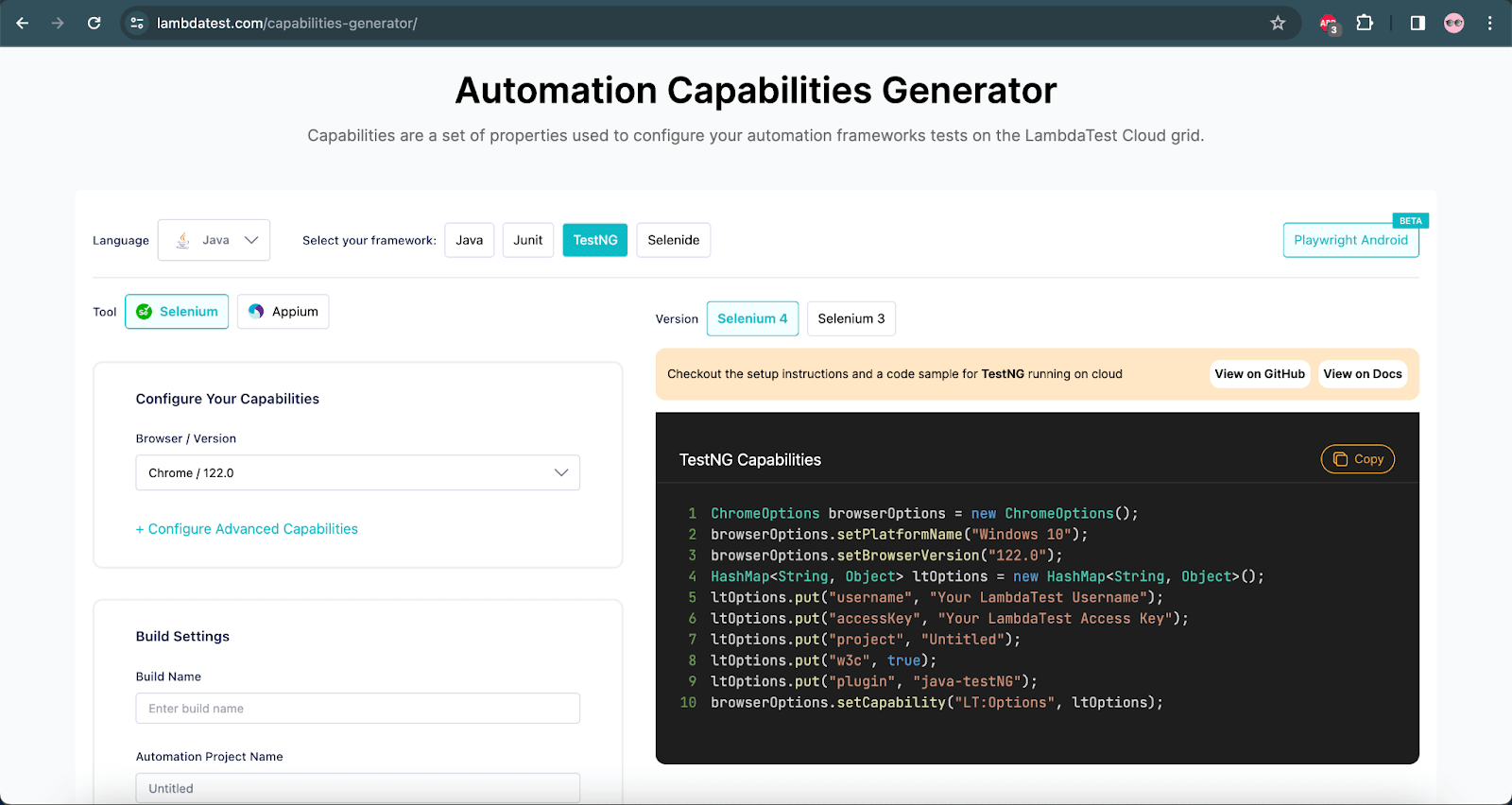
Before running the tests, we should use the terminal to set the environment variables LT_USERNAME and LT_ACCESS_KEY. You can find these credentials by visiting your Profile > Account Settings > Password & Security.
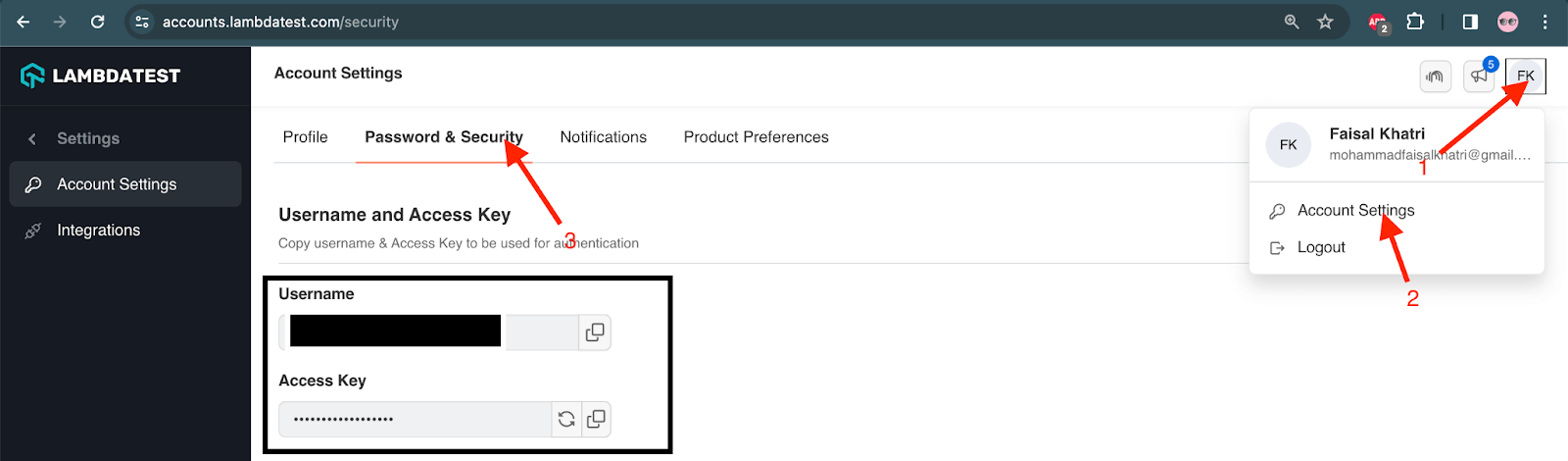
For Windows:
set LT_USERNAME=LT_USERNAME
set LT_ACCESS_KEY=LT_ACCESS_KEY
For macOS:
export LT_USERNAME=LT_USERNAME
export LT_ACCESS_KEY=LT_ACCESS_KEY
For Linux:
export LT_USERNAME=LT_USERNAME
export LT_ACCESS_KEY=LT_ACCESS_KEY
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 |
public class ChromeRemoteWithWebDriverManagerTest { WebDriver driver; String username = System.getenv("LT_USERNAME") == null ? "LT_USERNAME": System.getenv("LT_USERNAME"); String accesskey = System.getenv("LT_ACCESS_KEY") == null ? "LT_ACCESS_KEY": System.getenv("LT_ACCESS_KEY"); String gridURL = "@hub.lambdatest.com/wd/hub"; @BeforeTest public void setup() { ChromeOptions browserOptions = new ChromeOptions(); browserOptions.setPlatformName("Windows 10"); browserOptions.setBrowserVersion("122.0"); HashMap<String, Object> ltOptions = new HashMap<String, Object>(); ltOptions.put("project", "WebDriverManager Demo"); ltOptions.put("w3c", true); ltOptions.put("plugin", "java-testNG"); ltOptions.put("build", "Demonstration: WebDriverManager on LambdaTest"); browserOptions.setCapability("LT:Options", ltOptions); WebDriverManager webDriverManager = WebDriverManager.chromedriver().capabilities(browserOptions); webDriverManager.setup(); driver = webDriverManager.remoteAddress("https://" + username + ":" + accesskey + gridURL).create(); } @Test public void checkTheUrl() { driver.get("https://ecommerce-playground.lambdatest.io/"); String url = driver.getCurrentUrl(); assertTrue(url.contains("lambdatest")); } @AfterTest public void teardown() { driver.quit(); } } |
Test Execution
The following screenshot shows the test execution performed using IntelliJ IDE:
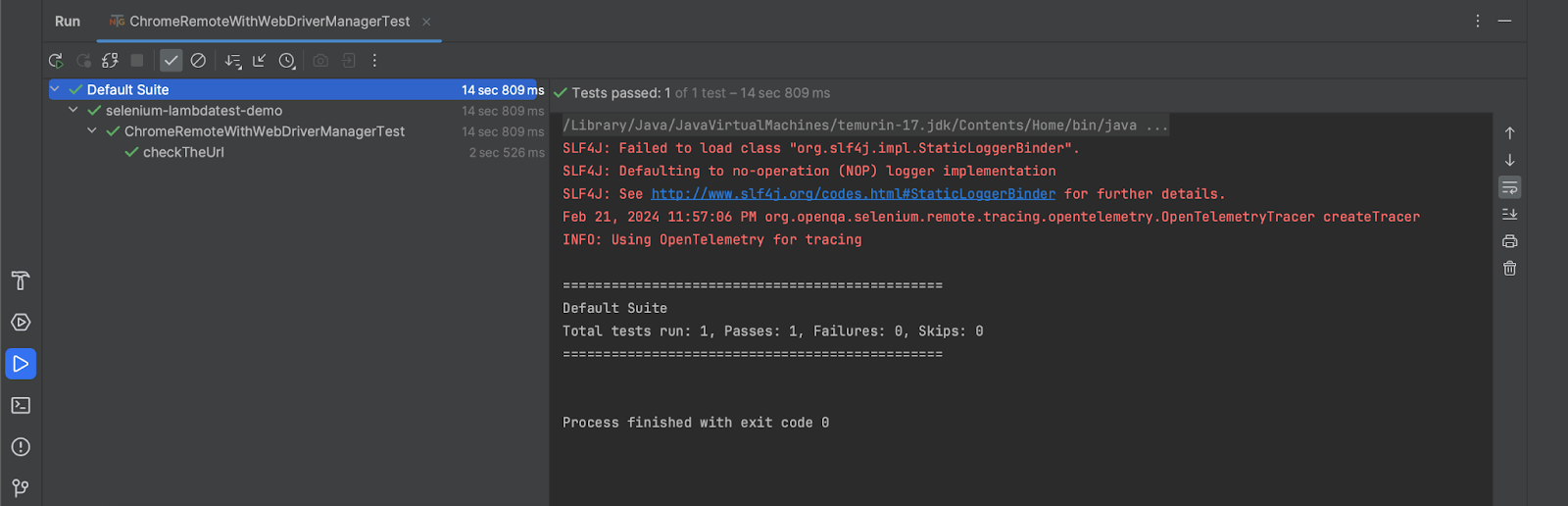
Navigate to the LambdaTest Web Automation Dashboard to look at the execution results.
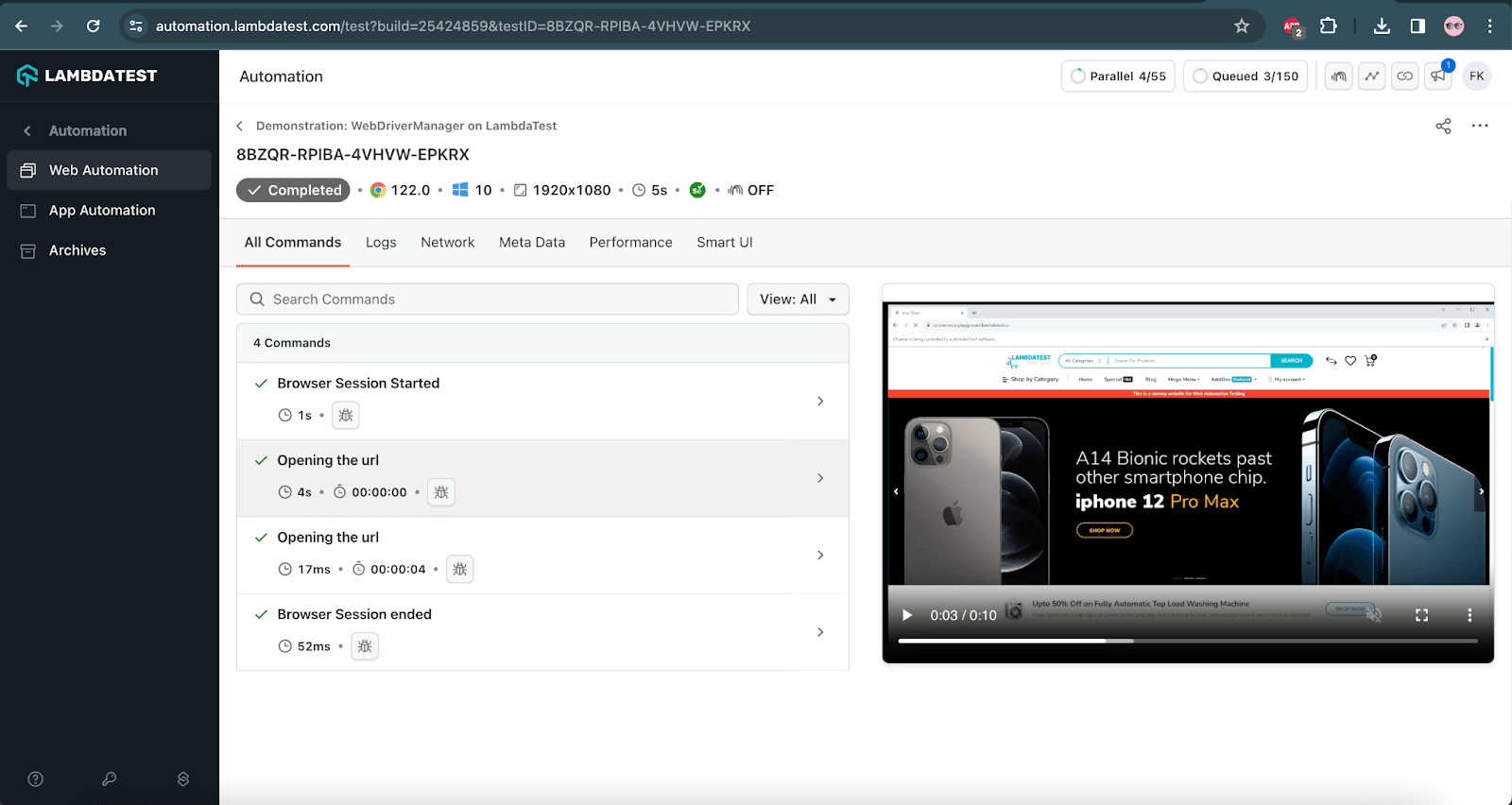
LambdaTest also provides a Test Analytics platform that can be leveraged to view the detailed analytics of the test execution. It also allows the creation of custom dashboards and widget variants for test analytics.
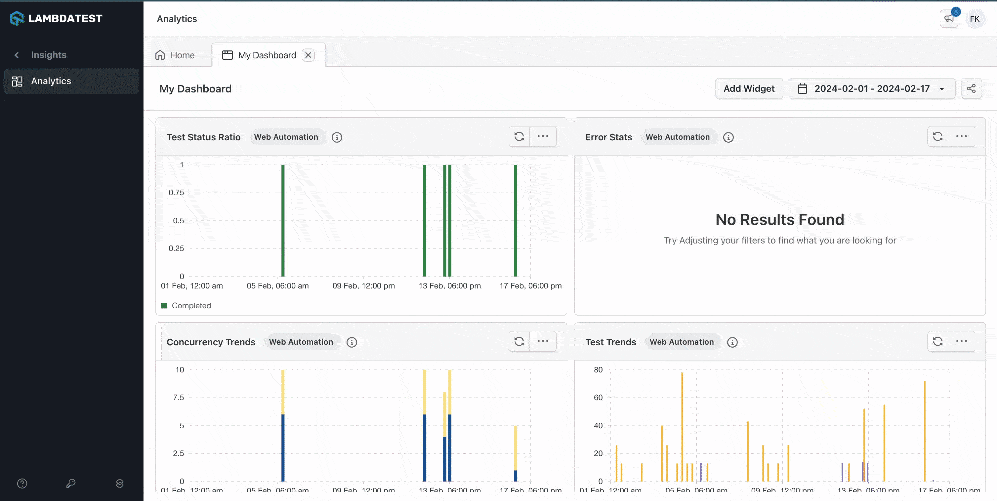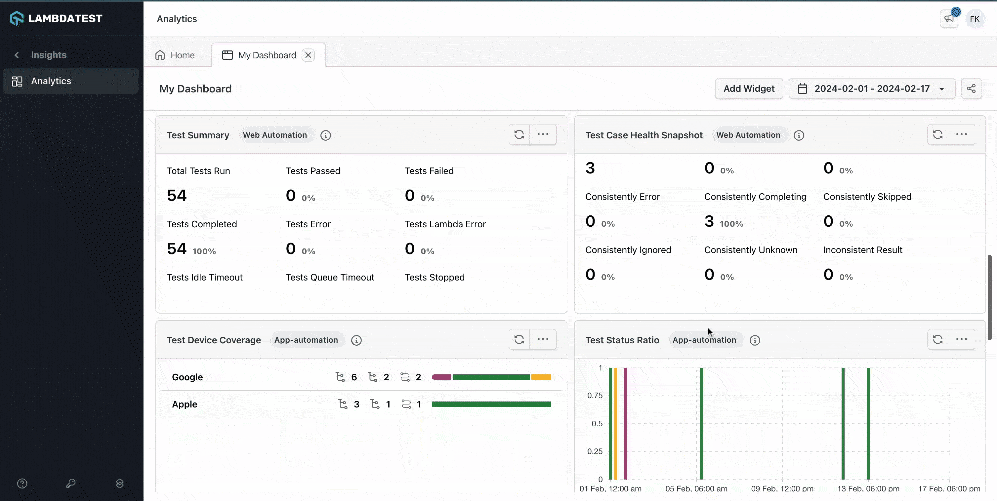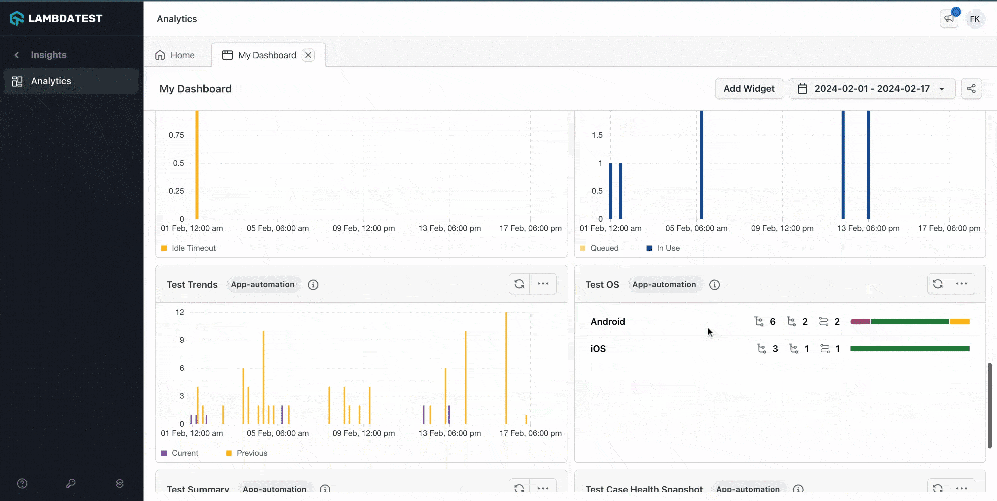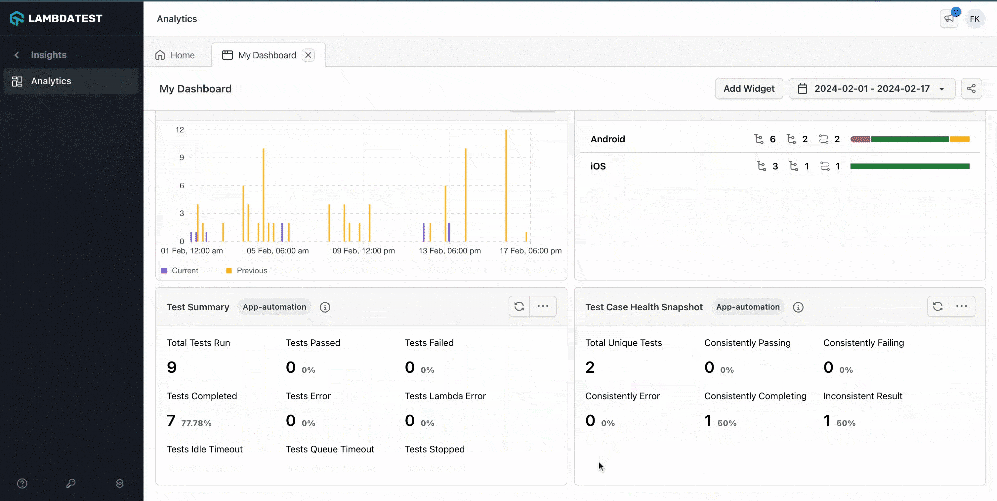
It allows building custom views with various widgets and getting the desired insights quickly by creating dashboards.
Conclusion
In this blog on WebDriverManager in Selenium, we entered the world of WebDriverManager by examining how it solves an important problem in using Selenium WebDriver, how it works with an algorithm in the background, and how it is implemented in practice.
Of course, this is only the beginning of our journey. After version 5, WebDriverManager in Selenium is expected to be enriched with many new great features, such as Browser in Docker and Browser Monitoring.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is WebDriverManager Selenium?
WebDriverManager is a powerful Selenium WebDriver management library that allows you to manage the drivers required by WebDriver automatically and in a fully automated manner.
Why do we use WebDriverManager?
WebDriverManager will enable you to easily automate finding and downloading the correct web driver for your browser, whether Chrome, Firefox, or IE.
What does WebDriverManager do?
WebDriverManager is an open-source Java library that helps automate the browser driver management for running the Selenium WebDriver tests.
What does the driver.manage() do?
driver.manage() returns an instance of the Webdriver.Options interface. When a user types driver.manage(), it returns a list of all the methods available within the WebDriver.Options interface and also the names of other interfaces defined within the Options interface.
Options interface has Timeouts and Window interfaces also defined inside it. Hence, the methods from the respective methods can also be called while using driver.manage().
For example, driver.manage().window().maximize(); and
driver.manage().timeouts.implicitlyWait();
How to launch Chrome browser in Selenium using WebDriverManager?
To launch the Chrome browser in Selenium using WebDriverManager, the following steps must be followed:
- Add the WebDriverManager dependency in pom.xml of the project.
- Add the following lines of code to your test:
WebDriverManager.chromedriver().setup();
WebDriver driver = new ChromeDriver();
Got Questions? Drop them on LambdaTest Community. Visit now