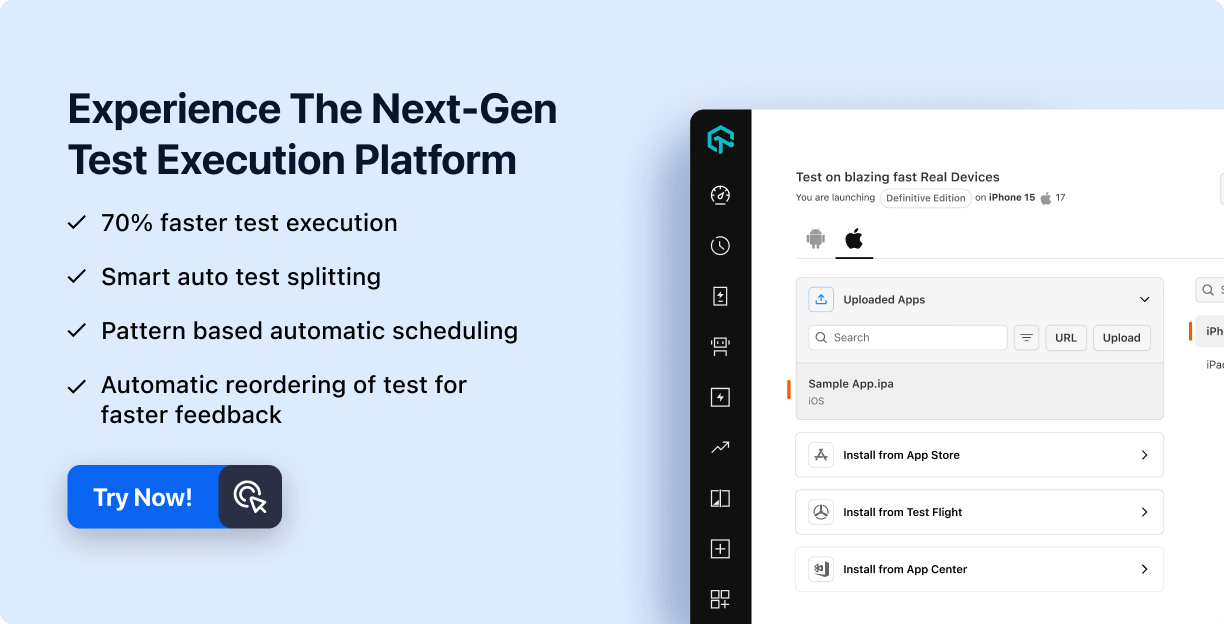
Scale Your Automation Testing with AI
Run end-to-end parallel tests & reduce test execution time by 5x
Generate tests scripts using natural language with KaneAI
Accelerate your testing process with Autoheal, SmartWait & RCA
Jenkins Tutorial for Beginners: A Comprehensive Guide With Examples
- Learning Hub
- Jenkins Tutorial for Beginners: A Comprehensive Guide With Examples
OVERVIEW
We all know that Continuous Integration & Continuous Delivery are integral parts of DevOps, as they are used for integrating multiple stages of the methodology. There are many CI/CD tools in the market, but do you know that Jenkins, the Java-based open-source CI/CD tool, tops the popularity list? Jenkins for test automation is a popular choice among developers because of its ability to easily integrate with a variety of testing tools. It has always been the go-to option for DevOps professionals and beginners.
Jenkins is the oldest player in the CI/CD market, and it has more than 16,000 stars and 6,500 forks on GitHub. It also has huge community support with more than 1500 plugins to help professionals ship faster through their Jenkins Pipelines. Let’s look how we can use Jenkins test automation as it allows developers to quickly and easily run tests on their code to ensure it is working properly.
Why and How to Use Jenkins
Before we dive into how Jenkins works, we must understand what makes Jenkins so popular & why to use it. Jenkins helps organizations automate parts of their software development process, such as building, testing, and deploying applications. It is beneficial for automating repetitive tasks and for integrating different tools and processes in the software development workflow. Jenkins automation testing can be configured to run tests automatically every time new code is pushed to the repository.
Some key benefits of using Jenkins include:
- Automation: Jenkins can automate many tasks in the software development process, such as building, testing, and deploying code. This helps to reduce the risk of errors and improve the speed and efficiency of the development process.
- Customization: Jenkins is highly customizable, with a wide range of plugins available that allow users to tailor Jenkins to their specific needs. This makes it possible to integrate Jenkins with a wide range of tools and processes.
- Collaboration: Jenkins can be configured to send notifications to team members and stakeholders when certain events occur, such as the completion of a build or the detection of an error. This helps to facilitate collaboration and improve communication within the development team.
- Scalability: Jenkins is designed to be scalable and can handle a large number of builds and deployments. This makes it suitable for use in organizations of all sizes, from small startups to large enterprises.
This was just a brief answer in our Jenkins tutorial for beginners, about why it is used. You can read further in our blog about what is Jenkins & its setup.
Also, Jenkins testing automation can help reduce the time and effort required to manually run tests by automating the process.
Create Jenkins Pipeline
Jenkins for automation testing is a great tool for teams who want to ensure the quality and reliability of their code. In this Jenkins tutorial for beginners, lets understand whats a Jenkins pipeline first. A Jenkins pipeline is a set of plugins that enables the implementation and integration of continuous delivery pipelines within Jenkins. The Jenkinsfile is a text file that contains the definition of a Jenkins pipeline and is checked into source control.
A Jenkins pipeline has a specific structure and consists of at least two types of elements: stages and steps. Stages represent phases in the pipeline, such as build, test, and deploy, while steps are specific tasks that are executed in a stage. For example, a build stage may contain steps to compile the code, run tests, and create a package.
Jenkins pipelines are a powerful and flexible way to automate the build, test, and deployment of software. They allow you to define the entire delivery process in a single Jenkinsfile, making it easy to track changes and roll back if necessary.
So a well-defined Jenkins pipeline can help shorten production times and improve the quality of applications. You can learn in detail through our blog on how to create Jenkins pipeline.
Jenkins Integration with Selenium Webdriver
Through this Jenkins tutorial for beginners, lets understand how Jenkins integration with Selenium makes the entire process of Selenium test automation so much easier.
With the Jenkins integration, you can automate the execution of Selenium Webdriver tests as part of the continuous delivery process. This allows you to catch and fix issues early in the development cycle and ensure that the application is high quality.
This can save time and effort by automating repetitive tasks and catching any issues early on in the development process. It not only ensures quality in your deployments but also makes your entire process of Selenium test automation so much easier.
Automated testing with Jenkins can help teams identify and fix defects in their code more quickly and efficiently. Read our detailed blog on Jenkins integration with Selenium Webdriver to understand two different methods of integration.
Selenium Maven Jenkins Integrations
Through this Jenkins tutorial for beginners, we have understood Jenkins & Selenium integration, but now we will learn the integration of Maven with both Jenkins & Selenium.
Maven is a build automation tool used for managing Java-based projects. It can be used to manage project dependencies, build the project, and run tests. Jenkins is a continuous integration and delivery platform that can automate the build and testing process.
To use Maven and Jenkins with Selenium, you will need to install and configure both tools. You will also need to install the Selenium Plugin for Jenkins, which allows Jenkins to run Selenium tests as part of the build process.
Overall, the use of Maven, Jenkins, and Selenium can greatly improve the efficiency, accuracy, and coverage of automated testing, making it an invaluable tool for ensuring the quality and reliability of web applications.
This is a part of Jenkins tutorial for beginners for a complete guide hop onto our blog on Selenium Maven Jenkins integrations.
Jenkins Best Practices
Here are the best practices of jenkins which are to be followed.
- Keep Jenkins Secure At All Times
- Always Backup The “JENKINS_HOME” Directory
- Setup A Different Job/Project For Each Maintenance Or Development Branch Created
- Prevent Resource Collisions In Jobs That Are Running In Parallel
- Use “File Fingerprinting” To Manage Dependencies
- Avoid Complicated Groovy Codesode In Pipelines
- Build A Scalable Jenkins Pipeline
- Manage Declarative Syntax/Declarative Pipelines
- Maintain Higher Test Code Coverage & Run Unit Tests As Part Of Your Pipeline
- Monitor Your CI/CD Pipeline
By following these best practices, you can ensure that your Jenkins instance is running smoothly and efficiently, and that your team is able to effectively collaborate and deliver high-quality software.
In this Jenkins tutorial for beginners we have enlisted the best practices of Jenkins you can read about its importance & how to put it to practice in our blog on Jenkins best practices.
Jenkins Multibranch Pipeline
Jenkins multibranch pipeline is a Jenkins feature that allows you to automatically create a pipeline for each branch in your source code repository. This means that whenever you push a new branch to your repository, Jenkins will create a new pipeline specifically for that branch, and run all the steps defined in the pipeline.
One of the benefits of using a multibranch pipeline is that it allows you to build and test your code in a separate environment for each branch. This is especially useful if you have multiple developers working on different features in separate branches, as it allows you to test and validate each feature individually before merging it into the main branch.
Jenkins automated testing is a powerful tool that can help teams improve the quality and reliability of their software. Overall, the Jenkins multibranch pipeline is a powerful tool that can help teams automate the build and release process for their software projects, and ensure that each branch is thoroughly tested and validated before it is merged into the main branch.
We have explained in brief about Jenkins multibranch pipeline, you can learn about its steps, periodic trigger & its use cases in detail through our blog on Jenkins multibranch pipeline.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is Jenkins tool used for?
Jenkins is written in Java & is an open-source automation tool that is used to automate parts of the software development process. It is a continuous integration tool, which means it is designed to automate the process of building, testing, and deploying software updates.
Is Jenkins CI or CD or both?
Jenkins is a platform that helps automate the software development process through continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD). It provides a range of tools and features for creating pipelines to build, test, and deploy updates, and supports various languages and automation tasks.
What are the 3 types of pipelines in Jenkins?
In Jenkins, there are three main types of pipelines: Declarative, Scripted, and Shared Libraries. Declarative pipelines use a simplified syntax and are easier to read and understand, while Scripted pipelines allow more flexibility and control using Groovy scripts. Shared Libraries are reusable pipelines that can be shared across multiple projects in an organization.

Start your journey with LambdaTest
Get 100 minutes of automation test minutes FREE!!
Did you find this page helpful?