Power Your Software Testing with AI and Cloud
Supercharge QA with AI for Faster & Smarter Software Testing

- Automation
- Home
- /
- Learning Hub
- /
- Quality Strategy
How to Create a Quality Strategy That Actually Works
Learn what a quality strategy is, why it matters, its core components, how to implement it, maintain documentation, and apply best practices effectively.
Last Modified on: December 7, 2025
- Share:
Software can fail or cause critical issues when defects are not caught early. A quality strategy identifies and mitigates these risks before they impact users or business operations.
A quality strategy is a structured plan that guides how an organization ensures quality across the entire software life cycle. It is not just about finding bugs; it focuses on preventing them with proactive techniques that align business goals, development priorities, and testing objectives.
Overview
What Is a Software Quality Strategy?
A software quality strategy is a plan aligning QA practices with business goals, defining roles, processes, and metrics to ensure reliable, high-quality software delivery.
How to Implement a Software Quality Strategy?
Implementing a quality strategy ensures software reliability, aligns QA with business objectives, and integrates quality practices across the development lifecycle. Key steps include:
- Align QA With Business Goals: Collaborate with stakeholders to define quality in business terms, translate business metrics into measurable QA objectives, and make a case for automation, test infrastructure, and resources.
- Address Enterprise Challenges: Manage complex architectures, distributed teams, and cross-team dependencies. Provide scalable, reproducible test environments using cloud platforms, containers, and secure test data management.
- Define Governance, Roles, and Ownership: Assign clear roles for QA leads, architects, SDETs, automation engineers, testers, developers, and product managers. Establish decision-making and strategy update processes for transparency and accountability.
- Integrate QA Into SDLC and CI/CD: Apply shift-left practices by embedding testing early, integrate automated quality gates and fail-fast mechanisms, and manage release cycles, regression suites, environments, and rollback strategies effectively.
How to Build and Maintain a Quality Strategy Document?
Maintaining a quality strategy document ensures continuous improvement and alignment with business needs. Key steps include:
- Gather Information: Interview stakeholders, audit QA processes, and define baseline metrics like defect rates, release frequency, production defects, and performance incidents.
- Structure the Document: Include vision, principles, measurable objectives, scope, testing methods, automation tools, workflow, roles, risk prioritization, and continuous improvement practices. Add annexes like KPI dashboards, RACI charts, and environment matrices.
- Review and Update: Set a regular review cadence, assign responsibilities, and incorporate production feedback from defect metrics and user input.
- Promote Cultural and Organizational Alignment: Encourage shared quality ownership, build a transparent, support-focused culture, and provide training on QA best practices and automation frameworks.
- Track Metrics to Measure Success: Monitor defect leakage, post-release defects, mean time to detect/fix, regression failures, test coverage, release stability, production incidents, and user feedback.
- Demonstrate Business Impact: Highlight reductions in support costs, hotfixes, compliance risks, and improvements in customer satisfaction, time-to-market, and release stability.
- Implement Continuous Improvement: Conduct retrospectives, post-release QA reviews, and incident analyses to adjust coverage, automation, resources, and risk prioritization, fostering a learning culture.
What Is a Quality Strategy?
A quality strategy is a structured plan that defines how testing will be carried out for a software. It explains what will be tested, how, under which conditions, and by whom. It ensures testing aligns with project goals and manages risk effectively.
It describes which test types will run. These may include techniques such as functional testing and non-functional testing.
It outlines the testing approach, including choices about manual testing vs automated testing, selection of test tools, setup of test environments, and preparation of test data.
Why Need a Quality Strategy?
A quality strategy catches defects early and reduces rework and costs. It ensures reliable software, enhances user experience, focuses on high-risk areas, and supports maintainable code.
- Catches Defects Early: Planning testing from the start helps detect defects during development or testing phases, preventing issues and unexpected behavior in production.
- Reduces Rework and Cost: Fixing defects during development or testing is far less expensive and faster than addressing them after release.
- Improves User Experience: Software that functions as expected, meets requirements, and performs reliably increases user satisfaction and boosts trust in the product.
- Focuses on High-Risk Areas: Risk-based testing targets critical modules, such as security-sensitive, performance-critical, or complex features, ensuring thorough validation where failures would have a significant impact.
- Supports Maintainable Software: Writing test cases, updating them regularly, and running automated regression tests ensure future changes or updates do not introduce new defects.
What Are the Core Components of Quality Strategy?
Core components of quality strategy include vision, principles, KPIs, and testing coverage. They also cover process integration, automation, risk-based testing, and continuous quality to ensure reliable software delivery.
Here are the core components of a quality strategy that development teams and QA teams can implement:
- Quality Vision & Principles: Define long-term goals like zero critical defects, automated regression coverage, and secure, compliant software. Establish principles such as shift-left testing, prevention over detection, risk-based testing, and customer-first thinking.
- Quality Objectives & Metrics (KPIs): Set measurable objectives tied to business goals. Track defect leakage, test coverage, automation coverage, regression failures, performance benchmarks, compliance metrics, and user-experience quality. Review QA metrics regularly and adjust as priorities evolve.
- Testing Methodologies & Coverage Strategy: Include testing methodologies like unit, functional, integration, performance, security, exploratory, and user acceptance testing. Define in-scope and out-of-scope modules, workflows, and features. Specify triggers like code commits, nightly builds, and pre-release checks.
- Quality Process & Lifecycle Integration: Embed quality assurance across the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) from requirements to production monitoring. Involve QA early in design and requirement reviews. Assign clear roles for QA, developers, product managers, and operations teams.
- Test Automation & Tooling Strategy: Balance automated and manual testing. Automate high-risk, regression, and smoke tests. Use CI/CD, test management, performance and security tools. Maintain modular, maintainable test suites to prevent technical debt.
- Risk-based and Prioritized Testing Strategy: Prioritize tests based on risk and business impact. Focus on high-risk workflows, core functionality, and compliance-critical areas. Maintain a living test backlog and update priorities regularly.
- Continuous Quality: Regularly review QA process, metrics, retrospectives, and lessons learned. Integrate production monitoring, user feedback, and defect trends. Promote a shared quality culture across QA, development, and operations.
Pro-tip: Opt for cloud testing platforms like LambdaTest that let you perform automation testing by integrating easily into automation frameworks and pipelines, helping teams scale parallel execution and reduce test cycles.
It also provides an AI-native Test Manager. With LambdaTest Test Manager, teams organize, create, and manage test cases in one centralized platform. It integrates manual and automated tests, making it easier to track coverage, execution status, and results in real time.
Note: Run manual and automated tests across 3000+ real desktop & mobile environments. Try LambdaTest Now!
How to Implement Quality Strategy?
Implement quality strategy by aligning QA with business goals, addressing enterprise challenges, defining roles and governance. Integrate QA in SDLC and CI/CD, embedding continuous improvement.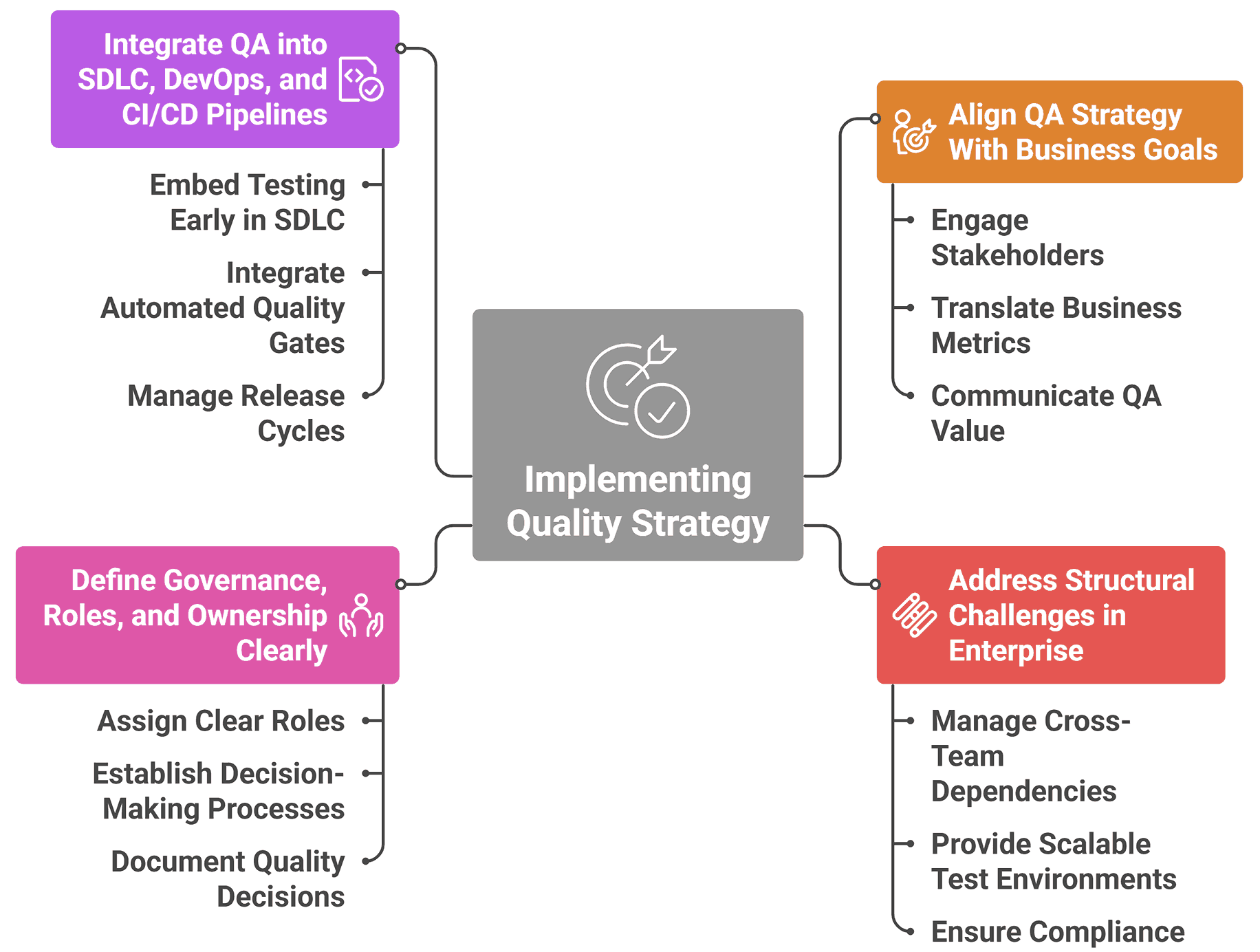
1. Align QA Strategy With Business Goals
Engage stakeholders, including product managers, BAs, compliance, operations, and leadership, to define what software quality means for the business. Translate business metrics into measurable QA objectives.
Communicate QA value clearly. Make a business case for automation, test infrastructure, time, and resource allocation to gain organizational support and align priorities.
2. Address Structural Challenges in Enterprise
Handle large-scale, complex architectures including microservices, legacy systems, and third-party integrations. Manage cross-team dependencies, parallel development streams, and distributed teams while maintaining consistent test coverage.
Provide a scalable, reproducible test environment. Use cloud, containers, and secure test data management. Ensure compliance and infrastructure capabilities support enterprise QA requirements.
Cloud-based testing platforms such as LambdaTest can help teams eliminate environment bottlenecks by offering on-demand access to real browsers, devices, and operating systems. It provides an enterprise execution environment on the cloud without the overhead of maintaining in-house infrastructure.
3. Define Governance, Roles, and Ownership Clearly
Assign clear roles: QA leads, architects, SDETs, automation engineers, testers, developers, DevOps, and product managers. Identify a single owner responsible for the quality strategy document.
Establish decision-making, change management, and strategy evolution processes. Document quality decisions for transparency. Make the strategy visible to all stakeholders to build trust and clarity.
4. Integrate QA into SDLC, DevOps, and CI/CD Pipelines
Embed testing early in the SDLC. Include unit, integration, and regression testing. Apply shift-left practices to catch defects before production deployment.
Integrate automated quality gates in CI/CD pipelines. Implement fail-fast mechanisms. Manage release cycles, regression suites, versioning, test environments, test data, and rollback strategies effectively.
How to Create and Maintain a Quality Strategy Document?
Create and maintain a quality strategy document by gathering stakeholder input and metrics, structuring vision, objectives, testing methods, and roles. Review regularly and update with feedback, and track improvements.
Below are the steps to create and maintain a quality or a test strategy document:
1. Gather Information
Interview stakeholders across product, development, operations, business, and compliance to understand requirements, constraints, and business risk tolerance. Audit current QA processes to identify gaps, technical debt, and flaky tests.
Define baseline metrics, including defect rates, release frequency, production defects, time-to-release, customer complaints, and performance incidents. This establishes a starting point to measure improvements over time.
2. Structure the Strategy Document
Structure the strategy with vision and principles, measurable objectives and metrics, and a defined scope. Document testing methods, automation testing tools, process workflow, roles, risk prioritization, and continuous improvement, including a review cadence to keep it current.
Attach annexes such as environment matrices, compliance checklists, KPI dashboards, RACI charts, release gate criteria, and test data plans to provide practical, ready-to-use reference material.
3. Review and Update Process
Define a review cadence, such as quarterly, semi-annual, or post-major release. Assign responsibility for updates, approval, and communication. Document changes with date, author, and reason.
Incorporate feedback from production through defect metrics and user input. Ensure insights directly inform updates to the strategy to maintain relevance and accuracy.
4. Promote Cultural and Organizational Alignment
Encourage shared quality ownership across QA, development, product, and operations teams. Build a support-focused culture, promote transparency, and discourage blame for defects or failures.
Provide training and mentoring on testing methods, automation frameworks, and QA best practices to strengthen team capability and maintain consistent quality standards.
5. Track Key Metrics to Measure Success
Monitor defect leakage, post-release defects, mean time to detect/fix, regression failures, test and automation coverage. Track execution rates, release frequency, release stability, production incidents, and user feedback.
Track infrastructure usage, automation ROI, maintenance effort, test reliability, and flakiness to ensure QA investments are delivering measurable value to the organization.
6. Demonstrate Business Impact
Show how QA improvements reduce support costs, hotfixes, and compliance risk. Highlight gains in customer satisfaction, brand reputation, time-to-market, and overall software reliability using anonymized case studies.
Illustrate before-and-after scenarios: defect leakage reduction, improved release stability, shorter release cycles, and decreased customer complaints to communicate tangible outcomes.
7. Implement Continuous Improvement and Feedback Loops
Set regular review meetings such as retrospectives, post-release QA reviews, and production incident analyses. Use these insights to adjust coverage, automation, resource allocation, and risk prioritization.
Promote a learning culture where failures become opportunities to improve processes, tools, and skills. Update the strategy continuously to reflect evolving business and technical needs.
Best Practices for an Effective Quality Strategy
Keep the strategy updated, prioritize key automation, and define a clear testing scope. Integrate user feedback, plan resources, and design scalable QA processes for continuous improvement.
You can follow these best practices:
- Keep Your Strategy Updated: Avoid treating the strategy as a static document. Regularly review, update, and share it. Ensure stakeholder buy-in so quality becomes a shared responsibility, not QA’s alone.
- Prioritize and Maintain Automation: Do not automate everything blindly. Focus on high-risk, repeatable workflows. Regularly refactor and maintain test suites to prevent flaky tests and false confidence in results.
- Define Testing Scope Clearly: Set clear boundaries for in-scope and out-of-scope modules, workflows, and features. Adapt the scope as the product evolves to prevent coverage gaps and missed high-risk areas.
- Integrate Real Usage and Feedback: Incorporate post-deployment monitoring, user feedback, and production defect data into QA planning. Use these insights to continuously improve testing strategy and prevent stagnation.
- Plan for Resources and Scalable Infrastructure: Estimate people, time, and infrastructure accurately for testing, automation, and environment provisioning. Design QA processes and tools to scale as the product and user base grow.
Conclusion
A quality strategy is what keeps a business operating efficiently and delivering consistently good results. Understanding why it matters helps everyone see how quality connects to the bigger picture, and focusing on the key components ensures nothing important is missed.
Putting the strategy into action requires planning and teamwork, while keeping a clear, up-to-date document makes it easy to follow and adjust when needed. By following best practices, a company can maintain high standards while continuing to improve and adapt over time.
Citations
- Quality Assurance and Testing Strategies of Quality Engineers in Software Product Development: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/396573375
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Did you find this page helpful?
More Related Hubs

Start your journey with LambdaTest
Get 100 minutes of automation test minutes FREE!!


