Power Your Software Testing with AI and Cloud
Supercharge QA with AI for Faster & Smarter Software Testing

- Software Testing
- Home
- /
- Learning Hub
- /
- V-Model in Software Development: Importance, Phases & Differences
V-Model in Software Development: Importance, Phases & Differences
Understand the V-Model in software development, phases, pros, use cases, tools, and how it compares with the Waterfall model. All explained with examples.
Last Modified on: September 26, 2025
- Share:
The V-Model is a structured software development approach where every development phase is paired with a corresponding testing phase. It’s designed to catch bugs early, improve quality, and ensure clear documentation throughout the process. In this detailed guide, we’ll cover what the V-Model is, how it works, when to use it, and why it’s still relevant today.
Overview
The V Model (Verification and Validation Model) is a structured software development approach where every development phase has a matching testing phase. It’s shaped like a “V” to visually represent this parallel structure.
- Development happens on the left side (e.g., requirements, design).
- Testing occurs on the right side (e.g., unit, system, acceptance testing).
- Ensures early bug detection and quality assurance.
Key Features of the V Model
- Clarity, Quality, and Control: The V Model is ideal for projects with minimal changes, emphasizing discipline and precision.
- Verification & Validation at Every Stage: Each phase is reviewed and tested before moving forward, ensuring accuracy.
- Parallel Testing Approach: Testing begins as soon as development starts, reducing the cost and effort of fixing defects later.
- Clear Mapping of Phases: Every development phase (like design) links directly to a test phase (like system testing).
Phases of the V Model
- Requirement Analysis → Acceptance Testing: Ensures software meets business needs and customer expectations.
- System Design → System Testing: Validates the system's complete functionality against the requirements.
- Architecture Design → Integration Testing: Checks interactions between integrated components or modules.
- Module Design → Unit Testing: Tests individual components for functional correctness and logic.
- Coding → Static/Code Reviews: Helps identify logic or syntax errors early in the development cycle.
When to Use the V Model
- Projects with clearly defined requirements from the beginning.
- Systems requiring compliance and traceability, such as aerospace or banking software.
- High-risk industries where failure isn’t an option, like medical devices or embedded systems.
- Small to mid-size applications with a fixed and stable scope.
What is the V-Model?
The V-Model is a linear software development methodology that organizes the process into distinct stages, with testing activities running parallel to each development phase. This model emphasizes the importance of verification vs validation throughout the lifecycle of a project. The "V" shape represents the process: the left side shows the stages of development, while the right side mirrors the corresponding testing activities.
Each phase in the development process corresponds with a testing phase, creating a balanced approach where validation and verification are prioritized early and consistently throughout the process.
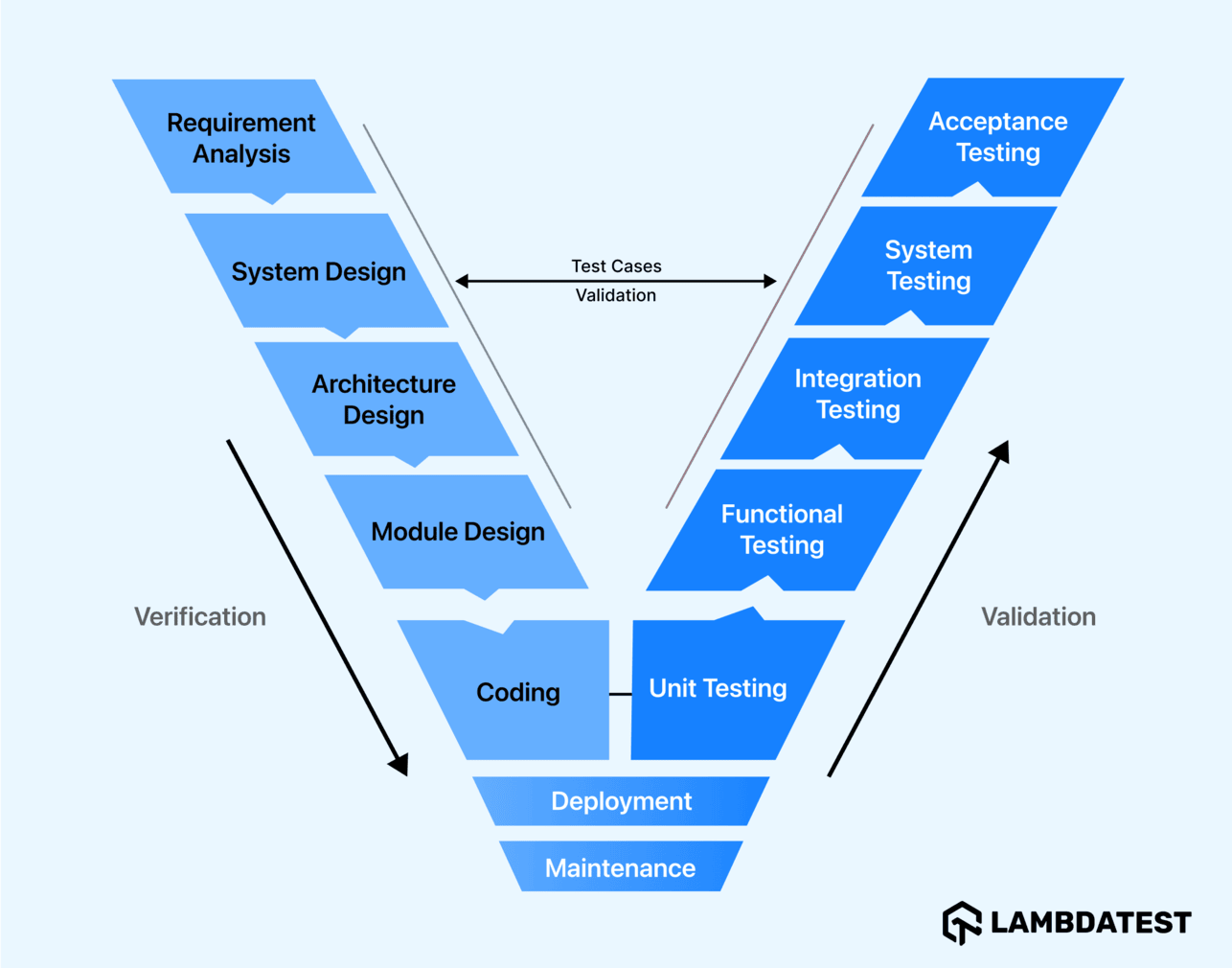
Phases of the V-Model
| Phase | Development Phase | Testing Phase | What It Checks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Requirement Analysis | Gather and define user needs. | Acceptance Testing | Does the system meet user expectations? |
| System Design | Plan system architecture and components. | System Testing | Does the full system work as a whole? |
| Architectural Design | Define tech stack and module interactions. | Integration Testing | Do modules communicate and function together properly? |
| Module Design | Break down into modules; define logic. | Unit Testing | Do individual modules work as expected? |
| Coding | Write the actual code. | Code Reviews / Unit | Are there any coding errors or logic issues? |
| Deployment | Push software to the live/staging environment. | Deployment Testing | Is the setup right for production use? |
| Maintenance | Fix bugs and roll out updates. | Regression Testing | Did new changes break anything? |
Why is V-Model Design Important?
In traditional models, testing often comes after development, making bug fixes time-consuming and costly. But the V-Model flips the script by pairing every development stage with a corresponding testing phase, starting from day one. This means potential issues are spotted early, not after the product is built.
Here’s why the V-Model matters:1. Early Bug Detection = Cost Saving
Detecting defects during the requirement or design phases is 10x cheaper than fixing them post-deployment. V-Model’s parallel testing approach prevents late-stage surprises.
2. Clear Structure & Discipline
The V-Model follows a step-by-step and highly organized approach, making it ideal for regulated industries (like healthcare or finance) that require strict documentation and traceability.
3. Testing is Built-In, Not Bolted-On
With testing planned alongside development, QA teams prepare test cases early, reducing the feedback loop and enabling faster improvements.
4. Better Project Transparency
Each phase has clearly defined deliverables, so stakeholders can track progress easily and make timely decisions.
5. Strong Risk Management
By validating each stage before moving forward, the V-Model reduces technical debt and minimizes project risks like scope creep, mismatched requirements, or missed deadlines.
6. Encourages Developer-Tester Collaboration
The model naturally promotes teamwork, developers and testers work in sync, leading to shared accountability and improved software quality.
7. Ideal for Stable & Well-Defined Projects
If requirements are clear from the start, the V-Model is extremely efficient, it avoids scope shifts and focuses on delivering what’s promised with precision.
Principles of the V-Model
The V-Model is centered on a few core principles that make it distinctive in the world of software development methodologies:
- Early Involvement of Testing: Testing activities are planned in parallel with the development phases. Each stage of development has a corresponding testing phase that begins immediately after the development phase is completed.
- Verification and Validation: The model emphasizes verifying the design and validating the end product to ensure they meet user requirements. Verification ensures the product is being built right, while validation ensures the right product is being built.
- Sequential and Structured Approach: The V-Model follows a step-by-step process where each phase of development flows into the corresponding testing phase. This structured approach ensures that no step is skipped, reducing the risk of errors and missed requirements.
- Clear Documentation: The V-Model requires comprehensive documentation at each stage, making the process transparent and easy to trace. This documentation is crucial for accountability and review in regulated industries.
- Focus on Quality Assurance: Continuous testing and verification ensure that defects are caught early, and the product is of high quality at every stage, which focuses on quality assurance.
V-Model vs Waterfall Model: What’s the Difference?
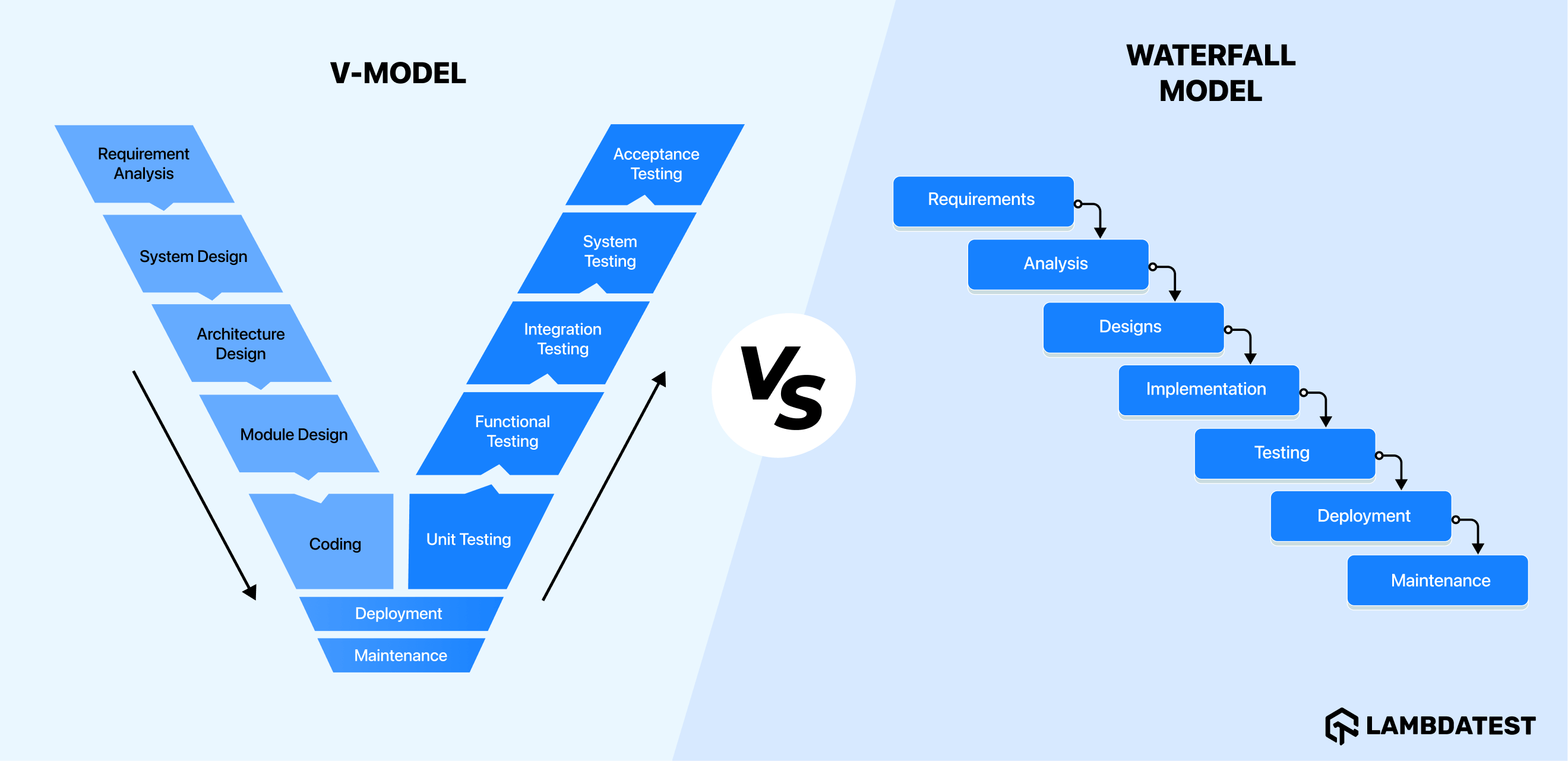
While both the V-Model and Waterfall Model follow a structured approach, they differ in how they handle testing, risk, and project flexibility. Here's a detailed comparison:
| Feature | V-Model | Waterfall Model |
|---|---|---|
| Development Approach | Linear, but testing is planned in parallel with development. | Strictly sequential, with one phase completing before the next begins. |
| Testing Integration | Testing phases are mapped to each development phase (e.g., unit, integration). | Testing happens only after development is fully completed. |
| Bug Detection Timing | Bugs are caught early, reducing the cost of fixing them. | Bugs are detected late, often during final testing, increasing rework. |
| Project Flexibility | Suitable for projects with clear and stable requirements. | Best for small projects with minimal scope changes. |
| Validation & Verification | Strong emphasis on both verification and validation throughout. | Validation occurs at the end, risking missed alignment with user needs. |
| Documentation Needs | Requires detailed documentation at every stage for traceability and compliance. | Documentation is typically produced after each completed phase. |
| Risk Management | Better risk control due to continuous testing and validation. | Higher chance of risks due to late feedback and testing. |
| Use Case Suitability | Ideal for regulated industries (e.g., medical devices, automotive, aerospace). | Often used in academic projects or traditional IT systems with fixed scope. |
| Maintenance Phase | Includes planned regression testing after updates or bug fixes. | Maintenance is done as needed, but not well integrated with initial testing. |
| Example | Developing a medical monitoring system where accuracy and safety are critical. | Creating a college library website with basic features and fixed functionality. |
When to Use the V-Model?
The V-Model is best suited for projects where requirements are well-defined, stable, and unlikely to change during the development process. It works exceptionally well for systems that require high reliability, safety, and documentation, such as in industries like aerospace, automotive, and healthcare. In these sectors, the V-Model’s emphasis on verification and validation ensures that every development stage is rigorously tested and meets strict standards.
Use the V-Model in the following scenarios:
- Clear and Fixed Requirements: Projects with well-understood requirements that are unlikely to change over time.
- Regulatory Compliance: Systems where documentation and traceability are critical to meet regulatory standards.
- Safety-Critical Systems: Projects where failure could lead to significant consequences (e.g., healthcare devices, automotive software).
- Smaller to Medium-Sized Projects: The V-Model’s structured approach makes it ideal for projects that can be completed in a linear fashion.
However, it may not be suitable for projects that need iterative development or constant changes in scope, such as those in fast-paced tech industries.
Pros and Cons of the V-Model
The V-Model offers a structured development process with early testing benefits, but its rigid nature can limit flexibility. Here's a quick look at its pros and cons.
Pros of the V-Model
- Rigidity and Lack of Flexibility: The V-Model is a linear and sequential approach, which makes it difficult to accommodate changes once the development process begins. If requirements change during the project, it can be challenging to adapt.
- Resource-Intensive: The need for extensive documentation and parallel testing increases both the time and cost of the project. This can lead to resource constraints, especially for smaller teams.
- Limited Adaptability for Complex Projects: Projects with complex and evolving requirements may find the V-Model limiting, as it does not lend itself well to iterative or incremental development like Agile or DevOps.
- Slow to Market: Since all development steps must be completed before moving on to the next, the V-Model can be slower than more flexible approaches, making it less suitable for fast-moving industries.
- Overemphasis on Documentation: The heavy focus on documentation can lead to delays and could potentially distract from more critical aspects of development, like feature development or user feedback.
Cons of the V-Model
- Rigidity and Lack of Flexibility: The V-Model is a linear and sequential approach, which makes it difficult to accommodate changes once the development process begins. If requirements change during the project, it can be challenging to adapt.
- Resource-Intensive: The need for extensive documentation and parallel testing increases both the time and cost of the project. This can lead to resource constraints, especially for smaller teams.
- Limited Adaptability for Complex Projects: Projects with complex and evolving requirements may find the V-Model limiting, as it does not lend itself well to iterative or incremental development like Agile or DevOps.
- Slow to Market: Since all development steps must be completed before moving on to the next, the V-Model can be slower than more flexible approaches, making it less suitable for fast-moving industries.
- Overemphasis on Documentation: The heavy focus on documentation can lead to delays and could potentially distract from more critical aspects of development, like feature development or user feedback.
While the V-Model is effective, it does face challenges such as the above. To overcome these limitations, teams can leverage platforms that provide cross-environment testing capabilities, enabling high-volume, complex test execution without the burden of setting up or maintaining test infrastructure. One such platform is LambdaTest.
LambdaTest is a GenAI-native intelligent test orchestration and execution platform that helps you run both manual and automated tests at scale across 3000+ real browsers, 10,000+ devices, and operating systems. It empowers QA teams to:
- Parallel testing across multiple environments for faster feedback.
- Automate unit, integration, and regression tests, even during early phases of the V-Model.
- Eliminate infrastructure setup, making testing more agile within the V-Model’s rigid structure.
- Access detailed logs, screenshots, and video recordings to support traceability and documentation requirements.
By integrating LambdaTest into your V-Model workflow, you bring speed, flexibility, and real-time visibility to an otherwise sequential and rigid process, making the model more adaptable for today’s fast-paced development needs.
Tools and Technologies Used in the V-Model
To ensure the successful implementation of the V-Model, teams often use a combination of tools throughout the development and testing phases:
- Version Control: A system used to manage code and track changes over time (e.g., Git).
- Automation Testing Tools: Tools like Selenium, JUnit, and TestNG are used for automated unit, integration, and system testing.
- Continuous Integration Tools: Tools such as Jenkins and Travis CI help automate testing and integration throughout the development cycle.
- Requirements Management Tools Tools like IBM Rational DOORS help capture and track requirements, ensuring alignment between development and testing phases.
- Bug Tracking Tools: Tools such as JIRA and Bugzilla are used for managing defects identified during testing.
Modern Relevance of the V-Model
While the V-Model was widely used in the past, especially for large, mission-critical systems (like those in aerospace, automotive, and healthcare), its principles continue to influence modern software development, particularly in regulated industries that require extensive documentation, traceability, and structured testing. However, it’s important to note that the V-Model has limitations when it comes to projects that require flexibility and adaptability, such as those in fast-paced, dynamic environments.
- Integration with Agile and DevOps: The V-Model has seen adaptations to better fit modern agile and DevOps environments. In some cases, organizations have incorporated Agile testing principles within the V-Model framework, running tests iteratively while maintaining the V-Model's structured approach.
- Safety-Critical Systems: The V-Model remains an industry standard in sectors like aerospace and automotive, where safety-critical systems must undergo rigorous validation and verification at each stage.
The Future of the V-Model in Software Development
As software development evolves, so too does the V-Model. Although newer methodologies like Agile and DevOps have gained popularity, the V-Model remains relevant for projects that demand strict adherence to regulatory standards and where the cost of failure is high. For industries like aerospace, automotive, and healthcare, where quality, safety, and documentation are critical, the V-Model will continue to be an essential framework.
Furthermore, integrating automation into the V-Model can help reduce the model's inherent inefficiencies, allowing for a more agile-like iteration of testing and development within the strict structure of the V-Model.
On This Page
- What is the V-Model?
- Phases of the V-Model
- Why is V-Model Design Important?
- Principles of the V-Model
- V-Model vs Waterfall Model: What’s the Difference?
- When to Use the V-Model
- Pros and Cons of the V-Model
- Tools and Technologies Used in the V-Model
- Modern Relevance of the V-Model
- The Future of the V-Model in Software Development
- Frequently Asked Questions
Frequently asked questions
- Early Defect Detection: Testing starts early, making it easier to catch errors early in the development process.
- Clear Structure: The V-Model provides a clear and structured approach to both development and testing, ensuring nothing is missed.
- Improved Documentation: With each phase being well-documented, the V-Model enhances traceability, making it easier to meet regulatory requirements.
- Quality Assurance: It focuses on verification and validation, ensuring that the system meets both technical and user requirements.
- Lack of Flexibility: The V-Model does not accommodate changes once the process begins, making it less suitable for projects with evolving requirements.
- Resource Intensive: Extensive documentation and parallel testing increase project costs and timelines.
- Not Ideal for Complex or Agile Projects: The rigid structure makes it difficult to adapt to dynamic or agile project environments, which require flexibility and continuous iteration.
- Version Control (e.g., Git, SVN): For managing code and tracking changes.
- Continuous Integration Tools (e.g., Jenkins, Travis CI): To integrate testing and development seamlessly.
- Test Automation Tools (e.g., Selenium, JUnit): For automating unit, integration, and system testing.
- Requirements Management Tools (e.g., IBM Rational DOORS): For tracking and validating requirements throughout the lifecycle.
- Bug Tracking Tools (e.g., JIRA, Bugzilla): To manage defects and monitor testing progress.
Did you find this page helpful?
More Related Hubs

Start your journey with LambdaTest
Get 100 minutes of automation test minutes FREE!!


