AI in Software Testing: Benefits & Use Cases
Salman Khan
Posted On: December 1, 2025
21 Min
Artificial intelligence is changing the way software is tested. Traditional testing methods rely heavily on writing test scripts, human effort, and predefined test scenarios. In contrast, AI in software testing introduces intelligent agents that can learn from data, understand patterns, and adapt test strategies in real time.
From generating tests to predicting defects and self-healing broken scripts, AI is helping QA teams move faster without sacrificing quality. As software become more complex and release cycles get shorter, organizations are increasingly turning to AI-driven testing to stay competitive.
Overview
What Is AI Software Testing?
AI in software testing involves automating different aspects of testing lifecycle such as test creation and execution. It predicts defects, optimizes test runs, self-heals scripts, reduces human effort, and improves software quality.
How AI Is Used in Software Testing?
Following are some of the steps to integrate AI into your testing workflow, improving efficiency, accuracy, and continuous software quality assurance.
- Define Objectives: Identify tasks for AI such as generating tests, predicting defects, or exploring critical application workflows efficiently.
- Select AI Tools or Agents: Choose tools to enhance existing automation or deploy autonomous AI agents capable of adapting to software changes seamlessly.
- Integrate With CI/CD Pipelines: Connect AI tools or agents with your testing frameworks, pipelines, and applications, providing necessary inputs like stories, logs, or scripts.
- Execute and Monitor Tests: Run tests using AI, generate cases, prioritize risks, repair broken scripts, detect anomalies, and track results for accuracy and coverage.
- Analyze Results and Iterate: Review AI testing outcomes, expand coverage, adjust configurations, and repeat continuously to maintain reliable, comprehensive, and evolving software quality.
Which AI Tools Are Best for Software Testing?
Here are some of the best AI software testing tools for automating test creation, improving accuracy, and reducing manual QA effort:
- LambdaTest KaneAI: A Generative AI testing agent designed for fast QA, automating test case creation, debugging, management, and accelerating natural language test authoring.
- ACCELQ: Cloud-based AI platform enabling enterprise-level codeless test automation across web, mobile, desktop, and API, ensuring reliable long-term execution and reduced maintenance.
- Testim: Simplifies automated testing with minimal coding, using machine learning to stabilize tests, adapt to changes, and reduce maintenance overhead for frequent software updates.
- TestComplete: Offers dynamic AI-driven testing with checkpoints for tables, images, and settings, enabling functional tests across web, desktop, and mobile platforms efficiently.
What Is AI in Software Testing?
AI in software testing refers to the use of artificial intelligence technologies such as Machine Learning (ML), Natural Language Processing (NLP), and deep learning to improve and automate different stages of the testing life cycle.
Unlike traditional automation that follows predefined rules, AI agents can learn from historical test data, adapt to changes in the application, and detect patterns and anomalies. It can also predict high-risk areas and automatically improve test coverage over time.
What Are the Benefits of AI in Software Testing?
AI improves test accuracy, speeds execution, and expands coverage. It reduces flakiness, provides automated maintenance, faster feedback, earlier detection, and more reliable software delivery.
Here are some of the benefits of AI testing:
- Improved Test Accuracy: AI uses predictive analytics in software testing to detect potential issues early and analyze historical test data to identify high-risk areas. This reduces human error and lowers the chance of releasing bugs.
- Faster Test Execution: Machine learning in software testing automates repetitive tasks and optimizes test processes, speeding up execution across different environments. AI also enables continuous testing for quicker feedback.
- Enhanced Test Coverage: AI automates test creation and maintenance, allowing tests to run more frequently and detect issues earlier. QA teams can focus on creating new tests and covering more scenarios instead of repeating manual steps.
- Reduced Test Flakiness: AI stabilizes tests by using dynamic locator strategies and real-time diagnostics to identify and fix flaky behavior.
- Better Test Maintenance and Stability: AI adapts to changes in the application, updating test scripts automatically when UI elements change, reducing maintenance effort and improving reliability.
 Note
NoteAddress flaky test issues with AI-native test intelligence. Try LambdaTest Today!
How to Use AI in Software Testing?
Define goals, choose AI tools or agents, integrate with CI/CD, run tests to detect issues and fix test scripts, then analyze results, expand coverage, and iterate continuously.
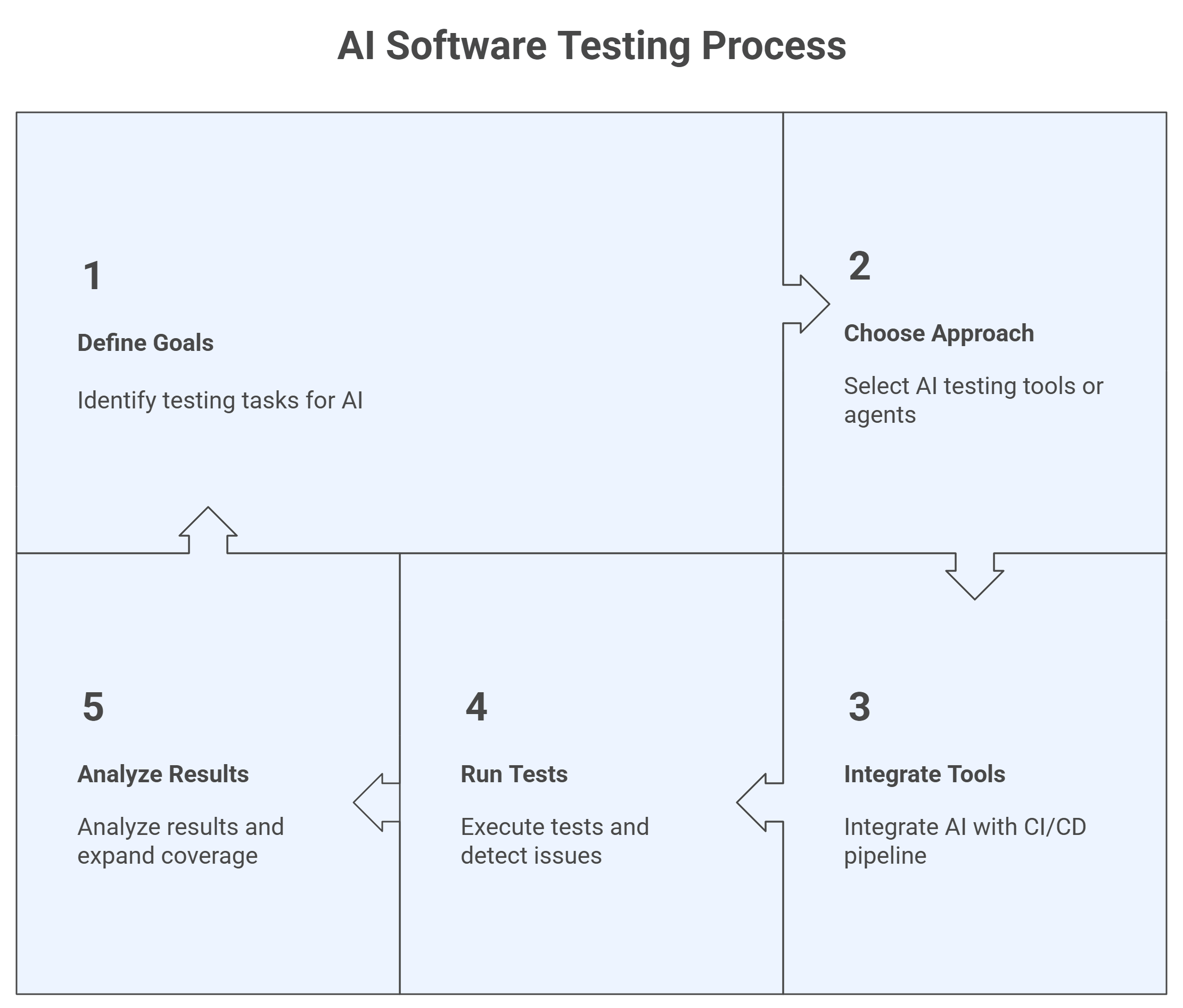
Let’s take a look how to use AI for software testing:
- Define Goals: Identify the testing tasks for AI, including generating tests, predicting defects, or exploring new application flows.
- Choose Approach: Select AI testing tools to enhance existing automated tests or deploy AI agents to run tests autonomously and adapt to changes in the application.
- Integrate with Tools or Agents: Integrate with AI testing tools or AI agents to your CI/CD pipeline, test framework, and software application. Provide inputs such as requirements, user stories, logs, or existing test scripts.
- Run Tests: Execute tests using the AI tool or agent. Generate new test cases, prioritize high-risk modules, repair broken scripts, and detect anomalies while monitoring results for accuracy.
- Analyze Results: Analyze results from the AI tool or agent, expand test coverage where needed, adjust settings, and iterate continuously to maintain reliable testing as the software application evolves.
What Are the Real-World AI Use Cases in Software Testing?
AI generates test cases, repairs scripts, predicts defects, prioritizes tests. It also checks UI, enables continuous testing, converts requirements to tests, and runs autonomous agents.
Let’s take a look at AI applications in software testing:
- AI for Test Case Generation: AI analyzes requirements, user stories, logs, and UI flows to automatically generate diverse functional, edge, and regression test cases. This automatic test case generation process improves coverage and reduces manual effort.
- AI for Self-Healing Automation: AI monitors element attributes, relationships, and historical behavior to automatically repair broken locators, update scripts, and stabilize flaky tests. Self-healing test automation reduces the need for continuous maintenance.
- AI for Smarter Test Execution: AI evaluates recent code changes, impact areas, and risks to prioritize critical tests, skipping low-value cases. This accelerates pipelines while maintaining strong confidence in quality.
- AI for Defect Prediction: AI in software defect prediction checks historical defects, commit patterns, complexity, and developer activity to predict high-risk modules. It helps prevent critical production failures before they occur.
- AI for Visual and UI Testing: AI understands visual layout, spacing, and design intent to detect UI inconsistencies, broken elements, and responsiveness issues. Visual AI for testing can work across browsers, devices, and screen sizes.
- AI for Continuous Testing: AI integrates with CI/CD pipelines, learning from each build and failure to adapt testing strategies and optimize feedback loops. This supports faster, safer deployments for teams.
- AI for Natural Language Testing: In NLP testing, AI converts plain text requirements into structured test steps and automation test scripts. Non-technical stakeholders can contribute directly to creating reliable tests using natural language prompts with minimal effort.
- AI Agents for Autonomous Testing: In autonomous testing, AI agents explore applications independently, create and execute tests, and detect anomalies. They learn from outcomes and continually improve testing strategies without constant human input or supervision.
What Are the Types of AI Testing?
AI-powered testing includes functional, regression, performance, and security testing. It also covers bias/fairness, explainability, data, model drift, ethical/compliance, and autonomous testing.
Let’s take a look at the types of AI software testing:
- Functional Testing: AI can simulate realistic user interactions and test whether the system behaves correctly in everyday scenarios. For example, it can check if a chatbot provides helpful answers or if a recommendation engine suggests relevant content.
- Regression Testing: When software or models are updated, AI can identify which features are most at risk of breaking. It helps maintain stability and prevents new changes from unintentionally causing failures.
- Performance Testing: Instead of running fixed tests, AI can monitor how software performs under different conditions and adapt test scenarios in real time. It can reveal bottlenecks and stress points, ensuring systems handle heavy traffic or complex operations smoothly.
- Security Testing: AI can proactively search for vulnerabilities and attempt to exploit them, just like a hacker would. This helps identify weaknesses in both the software and AI models before attackers can take advantage.
- Bias and Fairness Testing: AI can analyze decisions and the data behind them to spot unfair patterns. This ensures that systems like hiring platforms, loan approvals, or recommendation engines treat all users equitably.
- Explainability Testing: AI can break down complex predictions to show why a certain decision was made. Techniques like SHAP or LIME can provide clarity, which is especially important when outcomes affect health, finance, or legal matters.
- Data Testing: AI can automatically check datasets for errors, gaps, or inconsistencies that might compromise model accuracy. This ensures that training and operational data remain trustworthy and reliable.
- Adversarial Testing: AI can challenge models with tricky or deceptive inputs to test their resilience. For instance, it might feed distorted images or ambiguous text to see if the system still makes correct predictions.
- Model Drift Testing: AI can track performance over time and alert teams when models start losing accuracy due to shifting data trends. This allows timely retraining or adjustments, keeping predictions reliable.
- Ethical and Compliance Testing: AI can automatically verify that systems follow laws and ethical standards. This includes data privacy regulations like GDPR and HIPAA, reducing risks in sensitive applications.
- Autonomous Testing: AI can take the lead in testing itself and other systems, generating and running test cases without human intervention. This speeds up QA cycles and improves coverage across web, mobile, desktop, and API platforms.
Pro-tip: You can also use platforms like LambdaTest Agent to Agent Testing to check how AI agents behave. It simulates real-world interactions, letting you see how agents respond, adapt, and perform in dynamic situations.
You can measure accuracy, reliability, bias, and safety. This helps teams spot weak points and improve agent performance.
To get started, check out this LambdaTest Agent to Agent Testing guide.
What Are Some of the Best AI Software Testing Tools?
Some of the best AI testing tools include LambdaTest KaneAI and several other platforms. These tools help automate test creation, improve accuracy, and reduce manual effort.
- LambdaTest KaneAI: It is a Generative AI testing agent designed for high-speed QA teams seeking to automate multiple aspects of testing, including test case authoring, debugging, and management.
- Test Creation: Enables the development and refinement of tests through natural language instructions, making automation approachable for users of all skill levels.
- Intelligent Test Planner: Generates and executes test steps based on high-level objectives, streamlining the test creation process.
- Multi-Language Code Export: Transforms tests into various major programming languages and frameworks, providing flexibility in automation.
- 2-Way Test Editing: Syncs natural language edits with code, allowing modifications from either interface.
- Integrated Collaboration: Supports tagging KaneAI in tools like Slack, Jira, or GitHub to initiate automation, enhancing teamwork and efficiency.
- ACCELQ: It is a popular cloud-based platform to automate and manage AI-powered tests. It provides many enterprise applications with codeless test automation and automates the entire enterprise stack through desktop, API, mobile, and web. It also ensures reliable test execution by providing long-term automation with the help of AI.
- Testim: It simplifies and enhances testing by enabling testers to create automated tests using minimal coding. This AI platform uses ML for adapting and stabilizing testing and reducing maintenance overhead. That’s a consequence of frequent updates.
- TestComplete: It offers dynamic testing features that are AI-driven, including an important one known as checkpoints responsible for testing tables, images, and application settings. It enables testers to create, maintain, and perform various functional tests across web, mobile, and desktop applications.
By leveraging KaneAI in software testing, This smart test assistant allows teams to create complex test cases that are highly evolved with the help of natural languages, which fastens the pace of test automation and makes it more intuitive.
Features:
How Does LambdaTest KaneAI Help With AI Software Testing?
To see the real impact of AI in software testing, Generative AI testing tools like LambdaTest KaneAI can automate test creation, detect issues faster, and improve overall test coverage.
With KaneAI Web Agent, you can enter natural language prompts as test steps, which are then translated into structured, executable test cases. Each step is interpreted as a user action, such as navigation, interaction, or validation, within a browser environment.
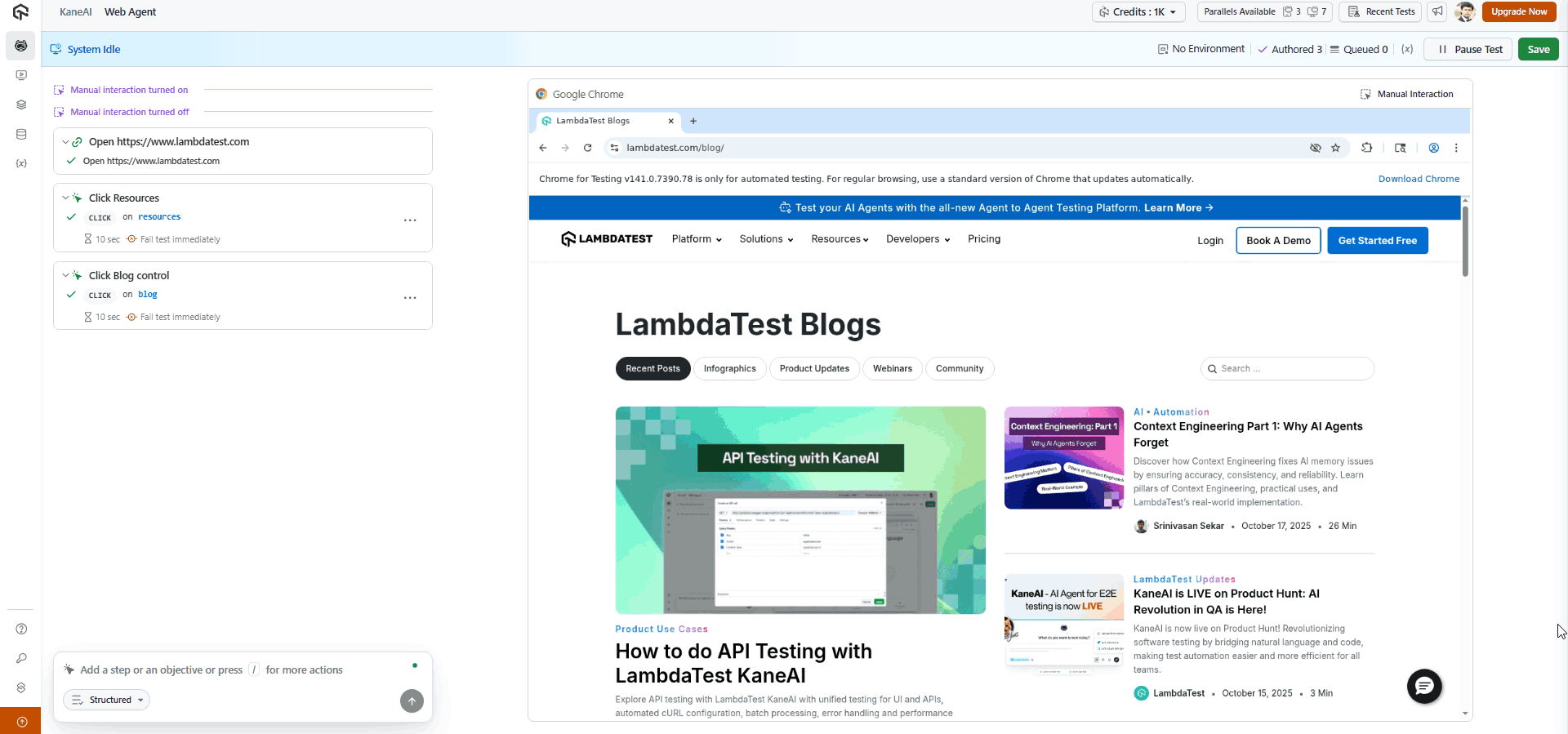
To get started, refer to this guide on LambdaTest KaneAI.
With the rise of using AI in software testing, its crucial to stay competitive by upskilling or polishing your skillsets. The KaneAI Certification proves your hands-on AI testing skills and positions you as a future-ready, high-value QA professional.
AI Software Testing vs Manual Software Testing
Software testing and AI automates checks for correctness, performance, and fairness, and can adapt to changes or new scenarios without constant maintenance where manual testing requires testers to execute predefined steps, while .
| Aspect | AI Software Testing | Manual Software Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Approach | AI-driven automation that analyzes, predicts defects, and optimizes test processes for faster, more reliable outcomes. | Testers execute predefined scripts and exploratory tests. |
| Test Case Generation | Automatically generated using AI insights, historical data, and patterns to improve coverage and effectiveness. | Written and maintained manually by QA engineers. |
| Execution Speed | Fast, parallel execution across multiple environments using AI optimization. | Slower, limited by human pace. |
| Accuracy | High accuracy via predictive analytics and pattern recognition, reducing human error. | Prone to human error and oversight. |
| Test Coverage | Broad and deep; AI identifies and prioritizes high-risk areas efficiently. | Often limited; time-consuming to expand. |
| Maintenance | Self-healing scripts adapt automatically to UI and code changes, reducing manual updates. | Manual updates required for every change. |
| Defect Detection | Proactive; predicts likely failure points before execution using AI insights. | Reactive; defects found during test runs. |
| Feedback Loop | Continuous testing with rapid feedback for faster iterations. | Slower feedback cycles. |
| Flakiness Management | AI stabilizes tests using dynamic locators, diagnostics, and self-healing capabilities. | Troublesome; flaky tests require manual investigation. |
| Resource Utilization | Optimized resource use; focuses human effort on complex scenarios. | High manual effort and staffing. |
| Time to Market | Shorter release cycles with faster, targeted testing enabled by AI. | Longer due to manual cycles. |
Shortcomings of AI in Software Testing
While Generative AI in software testing enhances your testing efficiency in automating repetitive testing tasks, it does have a set of shortcomings.
Here are the ones:
- Testing for Complex Scenarios: AI struggles with complex scenarios involving creativity and domain knowledge, such as multi-module interactions, real-world behaviors, or compliance testing. Human expertise is essential to ensure these scenarios are thoroughly tested and aligned with user expectations.
- UX Testing: While AI can flag usability issues, it cannot evaluate subjective user experiences or emotional responses. Human testers provide insights on design, usability, and workflows to ensure applications meet user needs and uphold brand standards.
- Documentation Review: AI cannot fully grasp business logic or domain-specific nuances, making documentation review reliant on human judgment. Business analysts and QA testers collaborate with stakeholders to clarify priorities and solidify the foundation for effective testing.
- Test Reporting and Analysis: AI generates detailed test reports but lacks the context needed for actionable insights. Human testers interpret results, prioritize fixes, and ensure critical issues are addressed effectively.
What Is the Future of Software Testing With AI?
The future of AI and software testing involves smarter automation, early failure prediction, less manual work, and scalable, self-learning systems guided by human strategy.
- Growing Role of AI: AI will continue shaping software testing, becoming a core part of modern frameworks and automated quality assurance tools for teams.
- Smarter Element Handling: AI in test automation will enhance smarter UI detection, visual validation, and functional testing for web applications and mobile platforms.
- Expanded Automation: AI-driven test automation will handle many testing tasks that once required quick human judgment across multiple testing levels and environments globally.
- Reduced Human Dependency: Human involvement will remain for test strategy, but AI will manage increasing complex testing responsibilities independently as AI agents or models learn over time.
- Quantum Computing Impact: Quantum computing could dramatically boost processing power, making AI driven testing faster, deeper, and more accurate for future software testing.
- Predictive Capabilities: The use of AI for software testing will predict weaknesses and failures before occurrence, allowing proactive fixes and stronger system reliability across critical business applications worldwide.
- Lower Maintenance Effort: Manual test maintenance effort will decrease significantly as intelligent test automation handles repetitive testing and monitoring tasks throughout long term system lifecycles.
Conclusion
AI brings the kinds of technologies and innovations to the table that have the power to completely revolutionize the manner in which we approach testing. Thanks to its integration with next-generation software testing tools, even QA teams with established processes are more than tempted to integrate AI into their systems.
Therefore, it won’t be an overstatement to say that AI is set to continue to bring in more optimizations and sophisticated capabilities to further advance the software testing process.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How does AI improve testing efficiency?
AI improves testing efficiency by automatically prioritizing test cases, detecting unstable tests, predicting defect-prone areas, and reducing repetitive manual tasks. This allows testers to focus on complex scenarios while tests run faster and more accurately with reduced human error.
Can AI replace manual testers?
AI cannot fully replace manual testers. While it automates repetitive and data-driven tasks, human insight is still required for exploratory testing, usability evaluation, business logic understanding, and creative problem solving. AI works best as a powerful assistant, not a replacement.
What types of testing benefit most from AI?
Regression, performance, security, and UI testing benefit most from AI. These testing types involve large volumes of data and repeated actions, which AI can analyze efficiently. It helps detect anomalies, optimize test coverage, and adapt to application changes automatically.
How does AI help in test case generation?
AI analyzes application behavior, user journeys, and previous defects to automatically generate relevant and optimized test cases. It identifies missing coverage and edge cases that may be overlooked by humans, improving the overall quality and reliability of the test suite.
Is AI-based testing expensive to implement?
Initial implementation can be costly due to tool selection, infrastructure, and training. However, in the long run, AI helps reduce testing time, human effort, and bug-related costs. The return on investment improves as automation efficiency increases over time.
What skills are needed to use AI in testing?
Testers should understand basic machine learning concepts, data analysis, scripting languages like Python, and modern automation frameworks. Knowledge of testing fundamentals is still essential. Adaptability and willingness to learn new tools and workflows are equally important.
How does AI detect defects faster?
AI uses pattern recognition and anomaly detection to identify unusual application behavior. It compares expected outcomes with actual results at scale, allowing it to detect hidden patterns and recurring issues much faster than traditional testing approaches and human review.
What are the benefits of AI in software testing for testers in 2026?
Testers gain less repetitive work, smarter test coverage, faster feedback cycles, and better defect prediction. AI helps prioritize high-risk areas, reduces manual effort, and allows testers to focus on complex, creative, and exploratory testing, increasing efficiency and overall software quality.
What are the limitations of AI in testing?
AI depends heavily on data quality. Poor or biased data can lead to inaccurate results. It also struggles with understanding context, emotions, and user experience. Complex business logic and creative testing still require human thinking and judgment.
Citations
- Artificial Intelligence in Software Testing: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Artificial-Intelligence-in-Software-Testing
- Artificial Intelligence in Software Testing: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/
Author