Appium vs Selenium: Choosing the Right Automation Tool for Your Project
Rajas Nawar
Posted On: September 8, 2025
17 Min
In this guide, we will dive deep into Appium vs Selenium, explore their key differences, discuss their pros and cons, showcase real-world use cases, and provide actionable insights to help you choose the right framework for your project.
Overview
Both Selenium and Appium have their unique strengths: Selenium for web, Appium for mobile. Choosing the right tool depends on your application type, testing needs, and team expertise.
What is Selenium?
Selenium is an open-source framework for automating web applications across multiple browsers. It provides tools for writing functional tests in various programming languages like Java, Python, and C#.
What is Appium?
Appium is an open-source automation tool for testing mobile applications across iOS and Android. It supports native, hybrid, and mobile web apps, and allows writing tests in multiple programming languages.
Which Framework Should you Choose Between Selenium and Appium?
Selenium is best suited for web application testing across different browsers, while Appium is designed for mobile automation (native, hybrid, and mobile web apps). Use Selenium for web applications and Appium for mobile apps based on your target platform. In cases where both web and mobile apps need testing, Selenium and Appium can be used simultaneously within the same project, ensuring a comprehensive test strategy across multiple platforms. This enables testing of both web and mobile functionalities in parallel for unified test coverage.
What are the Best Practices for Selenium and Appium Testing?
Best practices include writing maintainable and reusable test scripts, leveraging page object models, and integrating tests into CI/CD pipelines. Additionally, use wait strategies, handle exceptions, and ensure tests are platform-independent.
What is Selenium?
Selenium is an open-source framework designed to automate web browsers. Over the last decade, it has become the standard for web application testing, thanks to its flexibility, robust community support, and compatibility with multiple programming languages.
Selenium Architecture
Selenium follows a client-server architecture that enables automation across multiple browsers and platforms. Here’s how it works:
- Selenium Client Libraries –Test scripts are written in languages like Java, Python, C#, Ruby, etc. The client libraries convert these commands into a standard format that WebDriver can understand.
- JSON Wire Protocol / WebDriver Protocol – Originally, Selenium used the JSON Wire Protocol to communicate between the client libraries and browser drivers. This protocol sends HTTP requests with JSON-formatted commands (e.g., click, type, navigate) from the client to the driver. Modern Selenium follows the W3C WebDriver standard, which is an updated version of this protocol ensuring better browser compatibility.
- Selenium WebDriver – Acts as a bridge. Receives commands from client libraries via the JSON/W3C protocol and passes them to browser-specific drivers. It handles the translation of high-level commands into browser actions.
- Browser Drivers – Examples include ChromeDriver, GeckoDriver (Firefox), EdgeDriver, etc. The driver interprets commands from WebDriver and interacts directly with the browser’s native API to perform actions like clicking, typing, or navigating.
- Browsers – The actual browsers execute the actions sent by the drivers and return the results back up the chain (driver → WebDriver → client library).

Core Features of Selenium:
- Cross-Browser Testing: Chrome, Firefox, Edge, Safari.
- Language Support: Java, Python, C#, Ruby, JavaScript.
- Automation Capabilities: Form submission, button clicks, dynamic content verification.
- Integration: CI/CD pipelines like Jenkins, GitHub Actions, GitLab.
- Parallel Testing: Selenium Grid enables distributed execution across multiple machines.
Example Use Case:
A retail company uses Selenium to validate shopping cart functionality across Chrome, Firefox, and Edge before a global product launch.
What is Appium?
Appium is an open-source automation framework for mobile applications, including native, hybrid, and mobile web apps. It leverages the WebDriver protocol, enabling testers to write scripts in multiple languages and run them across iOS and Android devices.
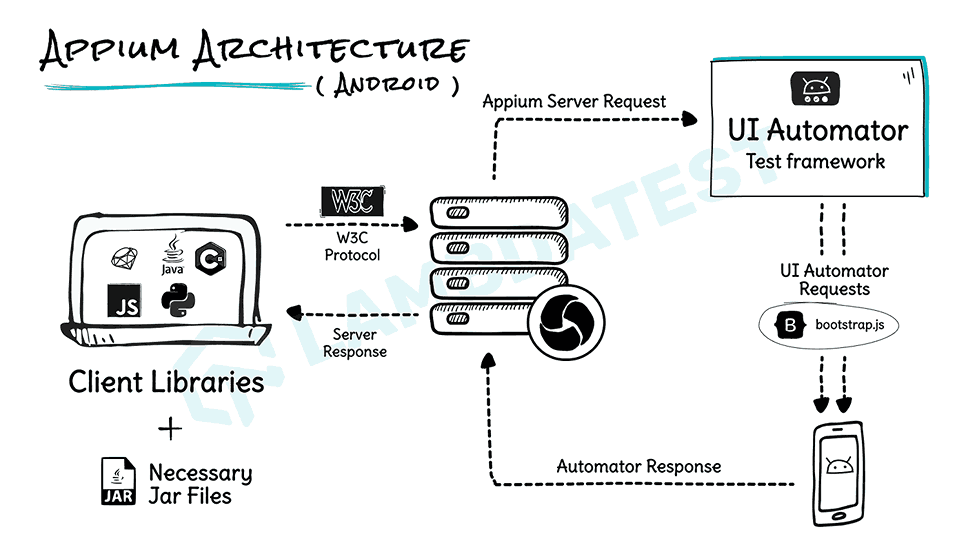
Appium Architecture
Appium follows a similar client-server architecture as Selenium but is designed to handle mobile automation across both Android and iOS. Here’s how it works:
- Appium Client Libraries – Test scripts are written in languages like Java, Python, JavaScript, C#, Ruby, etc., using the Appium client libraries. These libraries convert the test commands into a format that Appium can understand.
- Appium Server – Appium acts as a server between the client libraries and the mobile devices. It listens for HTTP requests sent from the client libraries and handles communication with the mobile device via the Appium Server. The server uses the WebDriver protocol (like Selenium) to interact with the mobile device.
- JSON Wire Protocol / WebDriver Protocol – Appium uses the JSON Wire Protocol (and the newer W3C WebDriver standard) for communication. Test commands from the client libraries are sent over HTTP in JSON format to the Appium server, which converts them into a mobile-specific format that the mobile device can understand. This protocol ensures that the client libraries, Appium server, and mobile devices communicate efficiently.
- Appium Drivers – Appium supports different drivers depending on the mobile platform:
- UIAutomator2 for Android
- XCUITest for iOS – These drivers are responsible for translating the Appium server commands into native commands for interacting with the mobile app or device.
- Mobile Devices (Android/iOS) – The mobile devices (whether Android or iOS) perform the actions (like tapping, swiping, typing, etc.) based on commands from Appium drivers and return results to the Appium server. This is where the actual execution of test actions takes place.
- Results Flow – Once the mobile devices execute the actions, they send the results back up the chain to (Appium Drivers) → (Appium Server) → (Client Libraries). The client libraries then receive the results, such as success or failure, for further analysis.
Core Features of Appium:
- Cross-Platform Support: Run tests on Android, iOS, and Windows devices.
- Gesture Automation: Swipe, pinch, tap, scroll, drag-and-drop.
- Hybrid App Testing: Works for apps combining web and native elements.
- Device & Emulator Support: Real devices, simulators, and emulators.
- Language Flexibility: Java, Python, C#, Ruby, JavaScript.
Example Use Case:
A fintech startup uses Appium to validate mobile banking workflows, ensuring seamless fund transfers and login flows on both iOS and Android devices.
Selenium vs Appium : Feature Comparison
| Feature | Selenium | Appium |
|---|---|---|
| Platform Support | Web browsers only | Mobile (iOS, Android) & Mobile Web |
| Programming Languages | Java, Python, C#, Ruby, JS | Java, Python, C#, Ruby, JS |
| Test Execution | Desktop browsers | Mobile devices & emulators |
| UI Automation | Web elements | Native app elements, gestures, hybrid apps |
| CI/CD Integration | Jenkins, GitHub, GitLab | Jenkins, GitHub, GitLab |
| Parallel Testing | Selenium Grid | Supported on LambdaTest Cloud |
| Mobile Gestures | ❌ Not supported | ✅ Supported |
| Real Device Testing | ❌ Not supported | ✅ Supported |
| Community Support | Mature & large | Growing rapidly |
| Open Source | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes |
Key Takeaway: Selenium is the framework for web automation, while Appium is purpose-built for mobile automation.
Strengths and Limitations
Understanding the strengths and limitations of Selenium vs Appium helps teams make informed decisions about mobile test automation and set realistic expectations for its capabilities.
Selenium Strengths
- Mature ecosystem and large community: Selenium has been around for over a decade, fostering a large, active community of contributors, making it highly reliable and well-supported.
- Extensive documentation and tutorials: It has abundant resources available, such as documentation, tutorials, and forums, ensuring new users can quickly get up to speed.
- Reliable cross-browser automation: Selenium’s ability to automate tests across various browsers like Chrome, Firefox, and Safari is a major advantage for testing web applications on different platforms.
- Integrates seamlessly with modern CI/CD pipelines: Selenium can be easily integrated into CI/CD tools like Jenkins and GitLab, enabling continuous testing throughout the development lifecycle.
Selenium Limitations
- Cannot automate native mobile apps: Selenium is limited to browser-based testing and does not support native or hybrid mobile applications, requiring tools like Appium for mobile automation.
- Limited support for mobile gestures: Selenium lacks native support for gestures like swipe, pinch, and scroll, which are essential for mobile testing.
- Requires additional tools (like Appium) for mobile coverage: While Selenium is robust for web testing, it needs integration with other tools (like Appium) to handle mobile app testing effectively.
Appium Strengths
- Automates native, hybrid, and mobile web apps: Appium provides the flexibility to test mobile apps across iOS and Android, including native, hybrid, and mobile web apps.
- Supports gestures and multi-device testing: Appium supports essential mobile gestures (e.g., swipe, pinch) and allows testing on multiple devices simultaneously, improving testing coverage.
- Unified codebase for iOS and Android tests: With Appium, testers can write one set of tests that run across both iOS and Android, reducing duplication of effort.
- Real device testing for accurate QA validation: Appium allows real device testing (rather than just emulators), providing more accurate results that reflect actual user experiences.
Appium Limitations
- Slower execution for web compared to Selenium: Due to the added complexity of mobile app automation, Appium’s execution speed is generally slower than Selenium when testing web applications.
- Setup for hybrid apps can be complex: Testing hybrid apps (which combine web and native elements) often requires more complex setup and configuration in Appium.
- Requires access to emulators or real devices for full coverage: To achieve the most accurate testing results, Appium requires access to emulators or real devices, which can increase setup time and resource costs.
Choosing Between Selenium and Appium
Selenium and Appium are both powerful test automation tools, but they serve different purposes. Selenium focuses on web automation, while Appium specializes in mobile apps. Comparing them directly can be misleading, as a true comparison works best between tools with similar targets. Here, we highlight their differences to help you choose the right tool for your testing needs.
When to choose Selenium:
- Your application is purely web-based.
- You need cross-browser testing.
- You want a mature framework with strong community support.
When to choose Appium:
- You need mobile automation (iOS, Android).
- Your app uses gestures, hybrid content, or native UI elements.
- Real-device testing is critical for your QA process.
For Both:
If your organization handles both web and mobile apps, it’s practical to combine Selenium for web and Appium for mobile, ideally using a cloud platform like LambdaTest to manage tests at scale.
Best Practices for Selenium and Appium Testing
Following best practices ensures that your automation tests are reliable, maintainable, and efficient. Whether using Selenium for web applications or Appium for mobile apps, adhering to proven strategies helps maximize test coverage, reduce flakiness, and streamline the testing process.
- Use Page Object Model (POM): Keeps scripts organized and maintainable.
- Parallelize Tests: Use Selenium Grid or LambdaTest cloud for faster execution.
- Leverage Real Devices: Test on real devices for accurate results.
- Integrate CI/CD: Ensure automated testing is part of your deployment pipeline.
- Monitor Flaky Tests: Use AI insights (like LambdaTest Test Insights) to detect and mitigate flakiness.
- Use Wait Strategies: Implement wait strategies (like implicit and explicit waits) to handle synchronization issues in tests. This ensures that elements are fully loaded before interaction, preventing errors caused by slow page or element loading.
- Handle Exceptions: Properly handle exceptions in your tests to ensure stability and reliability. By managing errors, you can prevent test failures from halting execution and provide clear insights into issues during the testing process.
- Automate Where It Matters: Focus automation on high-risk or repetitive workflows.
Scaling Selenium and Appium Test with LambdaTest
Selenium is often the go to solution for web application automation, while Appium dominates the mobile automation space. However, teams increasingly need a solution that supports both environments, scales across multiple devices, and integrates with modern CI/CD pipelines.
This is where LambdaTest, an AI-native testing cloud, becomes a powerful ally. LambdaTest is an AI-native testing cloud designed for organizations that require end-to-end automation for web and mobile apps.
LambdaTest allows you to run tests across 3,000+ browser environments and 10,000+ real devices, enabling comprehensive cross-browser and mobile automation. With intelligent dashboards and auto-heal capabilities, it provides seamless monitoring of tests. LambdaTest also integrates easily into CI/CD pipelines, ensuring smooth and continuous testing workflows.
Key Capabilities
- HyperExecute: Accelerate test execution by up to 70%, auto-retries failed tests, and splits test suites efficiently delivering a complete end to end test orchestration platform.
- KaneAI: End to end AI testing agent for creating, managing, and evolving test scripts with natural language.
- AI Test Insights: AI-native test analytics for flaky test detection, error trends, and test optimization.
- MCP Server – Leverage Model Context Protocol (MCP) to create a direct pipeline between AI assistants and your test execution data, eliminating manual transfers and context-switching.
- SmartUI Visual Testing – Detect and highlight key visual differences across browsers and devices, a perfect visual ai testing tool.
- Accessibility Testing – Ensure seamless web and app accessibility through powerful accessibility testing tool that generates detailed reports, identifying issues and offering actionable guidance for effective remediation.
Conclusion
Both Selenium and Appium have their unique strengths: Selenium for web, Appium for mobile. Choosing the right tool depends on your application type, testing needs, and team expertise. For teams looking to scale automation across web and mobile, LambdaTest’s AI-native cloud provides an end-to-end solution, reducing testing.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can Appium replace Selenium?
No, Appium cannot fully replace Selenium, as they are designed for different types of testing. Selenium is primarily for web automation, while Appium is specialized for mobile app testing. However, they can complement each other for web and mobile testing needs.
Can we use Appium without Selenium?
Yes, Appium can be used independently of Selenium for mobile automation. It has its own drivers and does not require Selenium for automation. Appium is designed specifically for mobile testing.
What is the difference between WebDriver and Appium?
WebDriver is the core interface for browser automation, while Appium is a test automation tool that uses WebDriver for mobile apps. WebDriver primarily automates web browsers, while Appium supports web, native, and hybrid mobile apps.
Is Appium used for API testing?
Appium is not designed for API testing. It focuses on automating mobile apps (native, hybrid, and mobile web). For API testing, tools like Postman, Rest Assured, or SoapUI are more suitable.
Is Appium easier than Selenium?
Appium can be seen as more complex than Selenium because it requires additional setup for mobile-specific interactions. However, both tools require a learning curve, and Appium’s complexity comes from managing multiple mobile platforms and device configurations.
What skills are needed for Appium?
To use Appium effectively, one needs skills in programming languages (Java, Python, JavaScript), mobile automation knowledge (Android/iOS), and understanding of mobile application structures. Familiarity with Selenium WebDriver is also beneficial.
Why choose Selenium for web testing?
Selenium is mature, reliable, and supports multiple browsers and languages. It has a large community and a wide range of features for web automation. It’s also scalable, making it ideal for complex web testing environments.
Is Appium better for mobile automation?
Yes, Appium is ideal for mobile automation, including native, hybrid, and mobile web apps. It provides comprehensive support for gestures, device interactions, and cross-platform mobile testing. It’s designed specifically to address mobile testing challenges.
Can Selenium and Appium be used together?
Absolutely. Selenium and Appium can be used together to cover both web and mobile testing needs. LambdaTest enables unified testing across both platforms, ensuring a comprehensive automation strategy.
What languages do Selenium and Appium support?
Both Selenium and Appium support Java, Python, C#, Ruby, and JavaScript. This flexibility allows testers to write test scripts in the language of their choice, integrating easily into different tech stacks.
How does AI accelerate testing?
LambdaTest HyperExecute leverages AI to optimize test execution by predicting flaky tests, retrying failed tests, and providing actionable analytics. It reduces test runtime and increases the overall test coverage.
Can Appium handle hybrid mobile apps?
Yes, Appium supports native, hybrid, and mobile web apps across both Android and iOS platforms. It can automate mobile apps with a variety of functionalities, including gesture support.
Selenium vs Appium which is better for cross-browser testing
Selenium is better suited for cross-browser testing, as it supports multiple web browsers. Appium primarily focuses on mobile platforms and is not optimized for cross-browser automation.
Author