Vibe Testing: The Next Step in Software QA [2026]
Salman Khan
Posted On: December 10, 2025
17 Min
As AI continues to influence the software development process, an important question arises: how to ensure the reliabiity of the software you didn’t code yourself. With the rise in the number of software applications being developed through AI, there is a need to find a smarter way to test them. This is where vibe testing (just like vibe coding) helps in.
Vibe testing provides a structured approach to test code (software), ensuring it meets quality standards from the user standpoint, even when the development process is AI-driven.
Overview
What Is Vibe Testing in Software Testing?
Vibe testing is an AI-augmented, intuition-driven approach to software testing that emphasizes how software feels to a user not just whether it technically meets specifications.
Why Vibe Testing Is Needed?
The purpose of vibe testing is to evaluate how a product behaves and feels during normal user interaction. It focuses on consistency, usability, and flow rather than individual features.
- Focus on User Experience: Tests how the software feels to real users, ensuring it’s intuitive and aligned with expectations.
- Adaptability to Change: AI adapts to UI or workflow changes, reducing test maintenance efforts.
- Reduced Human Effort: Self-healing and predictive detection free up testers to focus on high-value tasks.
- Improved UX Coverage: Captures subtle UX flaws like slow pop-ups or unclear wording that traditional tests miss.
- Test Code: Validates code for logical soundness and user-meaningful behavior.
How AI Revolutionizes Vibe Testing?
AI revolutionizes vibe testing by analyzing user behavior, detecting experience issues at scale, and providing data driven insights. Here are areas where AI plays an essential role in the testing process:
- Natural-Language Test Generation: Create tests using natural language prompts without writing scripts.
- AI-Generated Test Cases: Generate test cases from past bugs, user stories, and requirements for broader coverage.
- Test Data Generation: Automatically generate test data (input values and edge cases) to ensure thorough testing.
- Self-Healing Test Automation: Tests adapt to UI changes without updating the test script manually.
- Smart Test Prioritization: AI ranks tests by risk and history to optimize execution order.
- AI-Powered Debugging: Quickly identify root causes and get suggested fixes when tests fail.
An Overview of Vibe Coding
Vibe coding is an approach where you describe the software requirements to an AI, and it will generate the code for you. The term “vibe coding” was introduced by Andrej Karpathy, founding team member of OpenAI, in early 2025.
It leverages AI techniques like natural language processing to bridge the gap between user requirements and software development, enabling developers to communicate through simple natural language prompts while AI takes care of the technical execution.
What Is Vibe Testing?
Vibe testing refers to the practice of using AI tools or techniques to evaluate the overall sentiment, quality, or consistency of software, especially from a user experience or design alignment perspective.
It uses natural language prompts to test software, focusing on how the software feels to real users. Unlike traditional testing, which checks whether the software works as intended, vibe testing ensures the user experience aligns with expectations.
The vibe testing process involves:
- Describing Expected Behavior: You provide a description of the expected user experience or behavior using natural language prompts.
- Generating Tests With AI: The AI interprets these prompts and automatically creates test cases or automation scripts to run.
- Focusing on User Experience: Vibe testing prioritizes how the software feels (vibe) to the user, not just its functionality.
 Note
NoteCreate, author, and evolve tests using NLP with KaneAI. Book a Demo!
Why Teams Are Rethinking QA With Vibe Testing?
Vibe testing shifts QA toward how software actually feels to users. It adapts to change, needs less upkeep, welcomes non-tech input, catches subtle UX issues, and sanity-checks code logic.
Although a relatively new concept, vibe testing is gaining attention for overcoming the limitations of traditional testing methods.
Here’s how vibe testing helps teams in their Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC):
- Focus on User Experience: It tests software based on real-user experience and ensures the software feels intuitive and aligned with expectations.
- Adaptability to Change: Its AI-driven approach understands the intent behind tests and adapts automatically. It reduces maintenance efforts by adjusting to minor UI or workflow changes.
- Lower Barrier to Entry: Tests are defined in natural language, allowing non-technical stakeholders to get easily started with the testing process.
- Reduced Human Effort: Mechanisms like self-healing and predictive defect detection frees up testers’ bandwidth and increase their efficiency, allowing them to focus on other critical aspects.
- Improved UX Coverage: Vibe tests catch the small yet crucial issues that traditional automated tests often miss.
- Validate Code: Whether generated by AI or written by humans, code can still contain unchecked logic, and that poses a risk. Vibe testing acts as a safety net, not just validating that features work, but ensuring the logic behind them makes sense.
If you’re wondering how to get started, here are some of the best AI/ChatGPT prompts for software testing that can help you shape effective vibe tests.
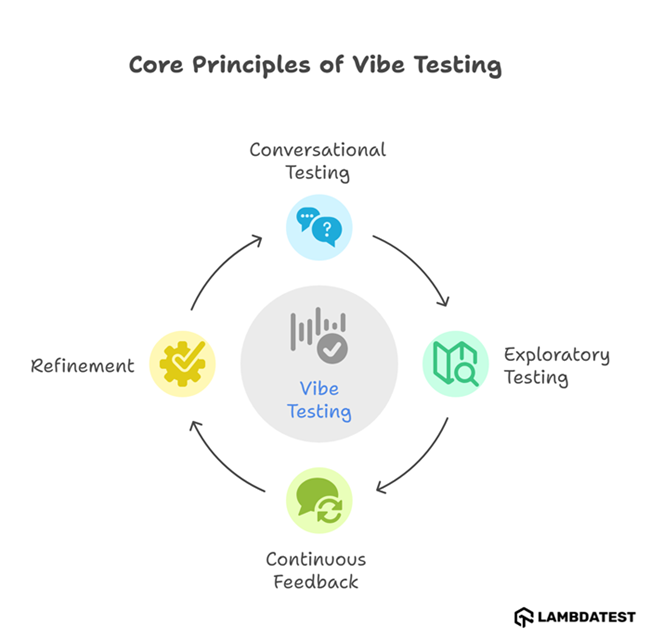
What Are the Core Principles of Vibe Testing
The core principles of vibe testing are intent-driven testing in natural language, adaptive exploration of real user behavior, and continuous learning through feedback to keep tests accurate as software changes.
Vibe testing is based on the following principles:
- Conversational and Intent-Driven Testing: It allows testers to define test scenarios using natural language prompts, enabling AI to generate and execute tests that align with user intent. This approach simplifies the testing process and makes it more accessible to non-technical stakeholders.
- Exploratory and Adaptive Testing: AI-driven vibe testing can simulate real user interactions, exploring edge cases and adapting to dynamic user behaviors. This adaptability ensures that software is tested under a variety of conditions, uncovering potential issues that traditional testing might miss.
- Continuous Feedback and Refinement: It incorporates continuous feedback loops, where AI learns from previous test executions to improve future tests. This iterative process enhances the accuracy and relevance of tests, leading to more reliable software.
How Vibe Testing Differs from Traditional Testing?
Vibe testing focuses on user intent and experience, using AI to adapt as products change, while traditional testing relies on writing test scripts that check functionality and other aspects.
The table below outlines the key differences between the two approaches:
| Aspect | Traditional Testing | Vibe Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Approach | Hand-written test scripts or record-and-playback tools that follow step-by-step instructions. | AI interprets natural language prompts to create and run tests dynamically. |
| Focus | Checks if features work under expected conditions. | Evaluates the feel of the product, uncovering UX issues and emotional friction. |
| Script Maintenance | Test scripts break easily when UI changes; they require manual updates and brittle selectors. | Self-healing AI selectors adapt automatically to UI changes, reducing maintenance. |
| Test Description | Code-based: assert(button.text === “Book a Demo”) | Conversational: “The button should clearly guide the user to request a product demo.” |
| Function vs. Experience | Focuses solely on function: does it work? | Looks beyond functionality: Is the experience smooth, clear, and frustration-free? |
| Adaptability | Must be updated for every small UI or workflow change. | AI evolves tests alongside the product using ML-based understanding. |
| Underlying Technology | Manual effort, hardcoded selectors, often brittle under change. | AI-driven: context-aware, dynamic, and scalable. |
How AI is Revolutionizing Vibe Testing?
AI drives vibe testing with natural-language test creation, auto-generated cases and data, self-healing automation, smart test prioritization, and faster root-cause analysis when tests fail.
According to the survey by Fortune Business Insights, in 2024, the global market for AI-enabled testing was valued at $856.7 million and is expected to reach $3.82 billion by 2032, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 20.9% from 2025 onward.
Let’s look at the areas where AI is actively enhancing the test automation process:
- Natural-Language Test Generation: You can generate tests with AI using natural language prompts, instead of requiring writing test scripts manually. This process is known as NLP testing.
- AI-Generated Test Cases: AI can automatically generate test cases by analyzing past bugs, user stories, and requirements, ensuring more comprehensive test coverage with less manual work.
- Test Data Generation: AI can create and generate test data, such as input values, edge cases, or random data, to ensure tests are thorough and cover various scenarios that might not be considered initially.
- Self-Healing Test Automation: Vibe testing uses AI that can adapt to modified test scripts automatically when there are UI changes, so you don’t need to constantly fix broken test scripts.
- Smart Test Prioritization: AI can determine which tests should be run first, based on factors like risk and past issues, to improve the efficiency of the testing process.
- AI-Powered Debugging: When tests fail, AI helps to quickly identify the root cause of issues and even suggests solutions to resolve them.
What Is the Role of AI Agents in Vibe Testing?
AI QA agents are transforming the landscape of quality assurance by taking on core testing tasks such as writing, running, and maintaining tests. These agents understand natural language prompts, generate tests, and adapt autonomously.
For example, GenAI-native test agents like LambdaTest KaneAI leverage Large Language Models (LLMs) to create, evolve and debug end-to-end tests using natural language.
Features:
- Intelligent Test Generation: Effortlessly create and evolve tests using NLP-based instructions.
- Multi-Language Code Export: Convert your automated tests into all major programming languages and frameworks for broad compatibility.
- API Testing Support: Seamlessly integrate backend testing with your existing UI tests to enhance overall test coverage.
- Leverage Datasets and Parameters: Easily configure, reuse values, and implement flexible parameterized testing using datasets and dynamic parameters.
- Integrated Collaboration: Tag KaneAI in Slack, Jira, or GitHub to kick off automation from various platforms and streamline collaboration.
- Define Reusable Variables: Use dynamic, reusable variables to improve test flexibility, consistency, and readability across scenarios.
- Smart Versioning Support: Track and manage test changes with smart versioning, ensuring a clear history of test updates.
- Resilient Test Cases: Benefit from GenAI-native auto-healing capabilities, which handle unexpected failures and maintain test stability.
To begin with, check out this guide on creating web tests with LambdaTest KaneAI.
Limitations and Key Considerations of Vibe Testing
Below are a few limitations and considerations that every technically grounded QA team should understand before integrating vibe testing into their pipeline.
- Human Review Is Still Required: Human review remains essential because LLMs lack implicit context, requiring testers to clearly define intent, behaviors, validations, and edge cases upfront explicitly.
- Not a Full Replacement: Vibe testing supports end-to-end flows and UX exploration, but cannot replace unit, performance, security, or low-level integration testing disciplines in modern pipelines.
- Prompt Quality Directly Affects Test Reliability: AI test reliability depends on clear prompts, so teams must use structured prompt engineering to achieve accurate, meaningful, and consistent coverage results.
- Review AI Test Results Carefully: AI-generated results require careful review to confirm correct steps, interactions, assertions, and diagnostics truly align with the intended test objectives and outcomes.
- Ethical Implications: Using AI in testing introduces ethical concerns, including bias, transparency, and accountability, which must be addressed to maintain trust and fairness consistently.
Final Thoughts
Vibe testing brings a new dimension to quality assurance, one that aligns with the pace and complexity of modern software development. Vibe testing with KaneAI empowers teams to validate real user flows with natural language prompts, often shaped more effectively through careful phrasing and techniques like prompt engineering, allowing AI to surface issues that often slip through automated tests.
That said, vibe testing works best when integrated thoughtfully. It’s not here to replace traditional testing methods, but to complement them, catching what others miss and speeding up the validation cycle.
By starting small and building confidence through side-by-side comparisons, QA teams can gradually expand their use of vibe testing. The goal isn’t just to pass tests, but to ensure the product delivers the experience it promises.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Does vibe testing replace manual or automated testing?
No. Vibe testing complements existing manual and automated testing efforts. While it excels at finding usability issues and testing broad user flows, traditional automation is still essential for backend validation, performance checks, and low-level functional testing.
What types of bugs does vibe testing catch best?
Vibe testing is highly effective at identifying issues that impact user experience, like confusing flows, inconsistent UI behavior, broken links, or missing error states. It helps spot problems that often go unnoticed in conventional automation because they’re more experiential than technical.
How do you write effective prompts for vibe testing?
To write effective prompts for vibe testing, be clear about the user action, expected outcome, and any edge cases. Use natural, specific language that mirrors real user behavior. Avoid vague commands, but detail matters.
How do I begin incorporating vibe testing into my QA workflow?
Start by selecting one high-impact user flow, like sign-up, search, or checkout. Run a vibe test alongside your existing automated tests and compare results. This side-by-side analysis helps identify where vibe testing adds value and what adjustments are needed to improve prompt quality.
Can vibe testing be added to CI/CD pipelines?
Yes, though support depends on the tool. Some platforms offer CLI tools or APIs for CI/CD integration, allowing vibe tests to be triggered as part of your release pipeline. Teams should start small and validate results before scaling up CI/CD use.
What is vibe coding and vibe testing?
Vibe coding uses natural language to generate code via AI, allowing developers to describe functionality instead of manually writing it. Vibe testing applies the same concept to QA, where testers describe expected user behavior and AI creates and runs the test flow.
Who should use vibe testing?
Vibe testing is ideal for QA engineers, SDETs, product testers, and tech leads working in fast-paced or AI-driven development environments where rapid feedback on user experience is critical.
What skills are needed for effective vibe testing?
Testers should have a strong understanding of user flows, attention to UX details, and the ability to write clear prompts. Familiarity with AI-assisted tools and test validation techniques is also helpful.
Is vibe testing useful for accessibility testing?
While it can flag some usability issues, vibe testing isn’t a substitute for dedicated accessibility audits. However, it may catch broken flows or missing feedback that negatively impact screen reader users or keyboard navigation.
Author