Web Development Using Python: Top Frameworks With Best Practices
Risper Bevalyn
Posted On: September 16, 2025
12 Min
Table of Contents
Python is widely recognized for its simplicity, flexibility, and extensive libraries, making it a top choice for web development using Python. Its beginner-friendly nature allows developers to build robust, scalable web applications efficiently, leveraging frameworks, tools, and examples tailored for web development using Python.
Overview
What Is Python Web Development?
Python web development focuses on building server-side applications that handle backend logic, database interactions, API endpoints, and integrate with frontend technologies to create dynamic, user-friendly web apps.
Why Choose Python for Web Development?
Python simplifies backend development with readable syntax, robust frameworks, and extensive libraries, enabling fast, secure, and scalable web applications.
- Easy to Learn: Python’s clear and intuitive syntax allows developers to quickly start projects and maintain them efficiently.
- Rapid Development: Frameworks like Django and Flask speed up application creation, minimizing repetitive coding and accelerating development cycles.
- Versatile Libraries: Python provides numerous tools for data handling, automation, web development, and analytics, supporting a variety of projects.
- Secure by Design: Frameworks include built-in authentication, session management, input validation, and protection mechanisms to ensure applications remain secure.
Frameworks for Python Web Development
Python web development relies on robust frameworks that simplify coding, streamline workflows, and accelerate application building.
Framworks:
- Django: A full-featured Python framework providing authentication, ORM, admin interface, and security features for building scalable applications efficiently.
- Flask: A lightweight Python microframework offering flexibility and simplicity for small to medium web applications with minimal overhead.
- Pyramid: A modular Python framework allowing developers to build complex applications with scalability, flexibility, and reusable components effectively.
- FastAPI: A modern, high-performance Python framework for building APIs with asynchronous support, type hints, and automatic documentation generation.
What Role Does Python Play in AI and Data-Driven Web Apps?
Python is the leading language for artificial intelligence and data analysis, which makes it perfect for building intelligent web applications. Developers can integrate machine learning models built with TensorFlow, PyTorch, or Scikit-learn directly into Python web frameworks such as Flask or FastAPI. This enables features like recommendation engines, chatbots, fraud detection systems, or predictive analytics. The seamless connection between web development and AI is one of Python’s strongest advantages.
What Is Python Web Development?
Python web development refers to building web applications and services with Python. When working on web development using Python, it is primarily used for backend/server-side logic, database operations, data processing, and API endpoints.
This also integrates with frontend technologies, which manage the visual and interactive elements users engage with. Together, the frontend and backend create dynamic, functional, and user-friendly web applications.
Why Use Python for Web Development?
One of the key decisions in web development is selecting the right programming language. Python is widely chosen for web development using Python due to several advantages:
- Easy to Learn: Python’s simple syntax and dynamic typing make it beginner-friendly. It allows developers to write code quickly and flexibly without unnecessary complexity.
- Fast Development: Python’s frameworks and libraries enable rapid prototyping and development. This helps developers bring projects to life much faster than many other languages.
- Extensive Libraries: Python offers libraries for data analysis, machine learning, web scraping, and more. These libraries provide ready-to-use tools that reduce effort and speed up workflows.
- Security: Python and frameworks like Django include built-in security features such as CSRF protection, input escaping, secure session handling, and authentication modules. Libraries and frameworks are also actively maintained with regular updates and security patches.
To get started with web development using Python, check out a beginner-friendly Python tutorial and start learning Python.
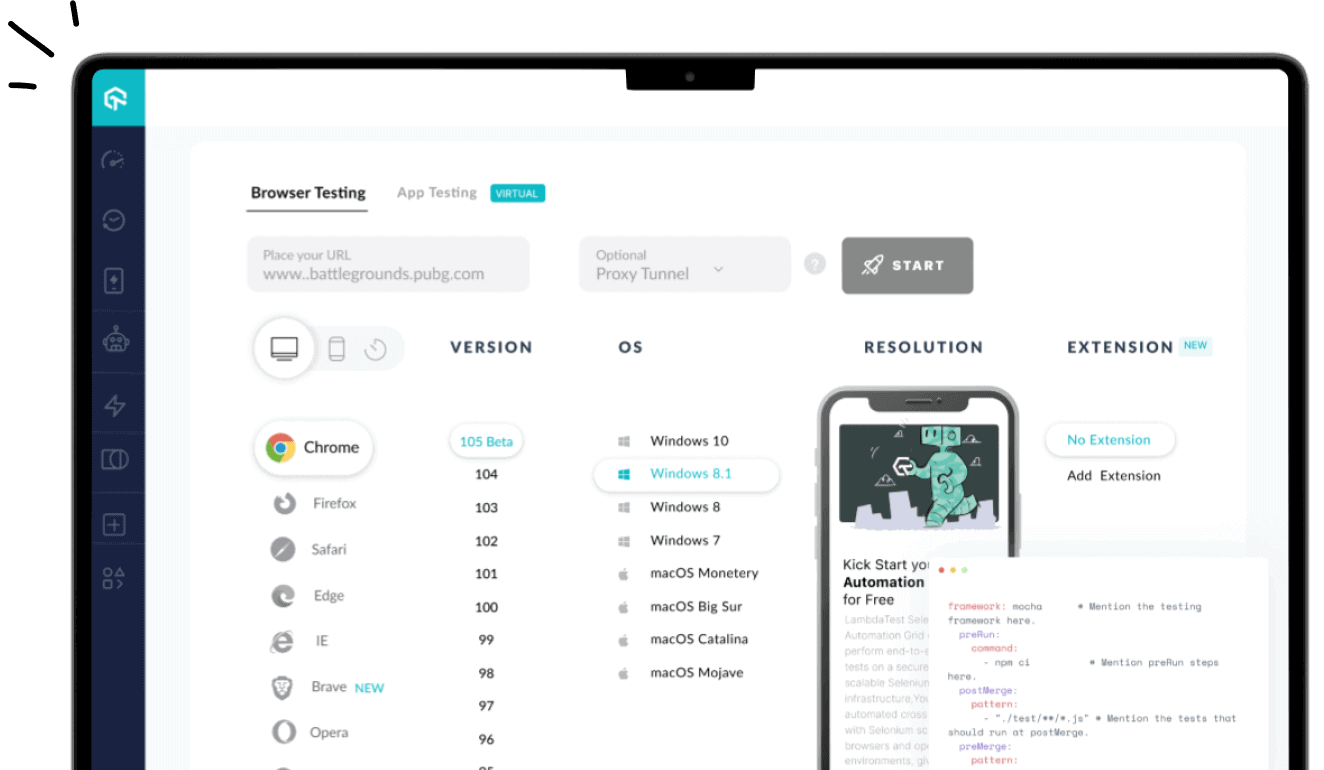
Run your Python tests at scale across 3000+ browsers and OS combinations. Try LambdaTest Now!
Getting Started With Web Development Using Python
Learn the fundamentals of web development using Python, set up your development environment, understand core concepts, and start building interactive web applications efficiently.
To get hands-on experience, we’ll begin by creating a simple To-Do application using Django, covering project setup, app creation, and basic backend logic.
Creating a Simple To-Do Web Application with Django
Creating a simple To-Do web application is a hands-on way to learn web development using Python. Using Django, you can quickly build a functional app that handles tasks like adding, updating, and deleting items while understanding the basics of backend development.
Prerequisites:
- Python: Make sure you have Python installed on your machine. You can download the latest version from the official Python website.
- Code Editor: Use a preferred editor like Visual Studio Code, Sublime Text, or Atom (VS Code recommended).
- Web Framework: Choose a framework suitable for your application. Flask and Django are popular for beginners. For demonstration purposes will use Django.
Setting Up a Django Project:
- Virtual Environment: Install virtualenv using pip install virtualenv and create a new environment with virtualenv todo-project.
- Activate Environment: Activate the virtual environment.
- Linux/Mac: source todo-project/bin/activate
- Windows: todo-project\Scripts\activate
- Install Dependencies: Create a requirements.txt file containing Django>=5.0 and run pip install -r requirements.txt to install Django.
- Create Django Project: Initialize your project with django-admin startproject todo_project and navigate into it using cd todo_project.
- Create Django App: Generate a new app using python manage.py startapp todo_app.
- Register App: Add ‘todo_app’ to the INSTALLED_APPS list in todo_project/settings.py.
- Create Views: In todo_app/views.py, define a view (todo_view) to handle adding and displaying tasks.
- Map App URLs: Create todo_app/urls.py with URL patterns for the app and include it in todo_project/urls.py using path(“todo/”, include(“todo_app.urls”)).
- Create Templates: In todo_app/templates/todo_app/todo.html, create the HTML template to display and add to-do tasks.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
INSTALLED_APPS = [ "django.contrib.admin", "django.contrib.auth", "django.contrib.contenttypes", "django.contrib.sessions", "django.contrib.messages", "django.contrib.staticfiles", "todo_app", ] |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 |
# Create your views here. from django.shortcuts import redirect, render # Very basic in-memory storage TASKS = [] def todo_view(request): if request.method == "POST": task = request.POST.get("task") if task: TASKS.append(task) return redirect("/todo") # Avoid form resubmission return render(request, "./todo_app/todo.html", {"tasks": TASKS}) |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
from django.contrib import admin from django.urls import include, path # todo_project/urls.py urlpatterns = [ path("admin/", admin.site.urls), path("todo/", include("todo_app.urls")), ] |
Now that your project is set up, let’s create a simple HTML template for the to-do list.
Code Implementation:
In your todo.html file, add the following HTML code:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 |
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>To-Do List</title> </head> <body> <h1>My To-Do List</h1> <form method="post"> {% csrf_token %} <input type="text" name="task" placeholder="Enter task" required> <button type="submit">Add</button> </form> <ul> {% for task in tasks %} <li>{{ task }}</li> {% empty %} <li>No tasks yet!</li> {% endfor %} </ul> </body> |
Result:
Run this command on your terminal:
|
1 |
Python manage.py runserver |
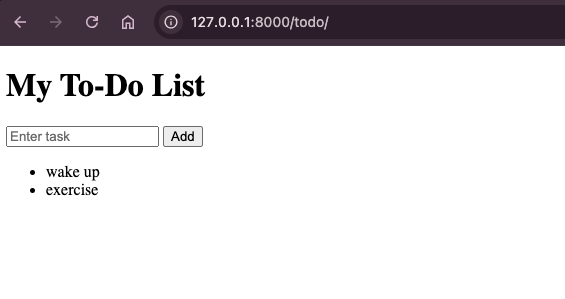
Running your Django To-Do app on your local machine is a crucial step to ensure all features work correctly. It helps identify issues early and guarantees smooth functionality before moving on to deployment or automated testing.
Running Your Web Development Project Using Python
Testing your Python web project locally allows you to confirm that all components operate as intended. This step helps catch errors early, ensures the application runs efficiently, and prepares it for scaling or integration with automated workflows.
Code Implementation:
Add the following test class to your test.py file. This code sets up a Selenium WebDriver, navigates to your To-Do application, adds new tasks, and then verifies they appear in the list.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 |
import time from django.contrib.staticfiles.testing import StaticLiveServerTestCase from selenium import webdriver from selenium.webdriver.chrome.service import Service from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By from selenium.webdriver.common.keys import Keys from selenium.webdriver.support import expected_conditions as EC from selenium.webdriver.support.ui import WebDriverWait from webdriver_manager.chrome import ChromeDriverManager class ToDoAppTest(StaticLiveServerTestCase): """Functional tests for the To-Do List app using Selenium""" def setUp(self): options = webdriver.ChromeOptions() # Comment this line out if you want to SEE the browser # options.add_argument("--headless=new") options.add_argument("--disable-gpu") options.add_argument("--no-sandbox") self.browser = webdriver.Chrome( service=Service(ChromeDriverManager().install()), options=options, ) def tearDown(self): # Keep the browser open for 5 seconds before closing (for demo) time.sleep(5) self.browser.quit() def test_add_multiple_tasks(self): # 1. Open homepage (adjust URL if your form is not at "/todo/") self.browser.get(self.live_server_url + "/todo/") tasks_to_add = ["Buy milk", "Walk the dog"] for task in tasks_to_add: # Wait for the input box fresh on every loop iteration input_box = WebDriverWait(self.browser, 5).until( EC.presence_of_element_located((By.NAME, "task")) ) input_box.clear() # not strictly necessary, but safe input_box.send_keys(task) input_box.send_keys(Keys.RETURN) # Wait until the new task appears in the list WebDriverWait(self.browser, 5).until( EC.text_to_be_present_in_element((By.ID, "task-list"), task) ) # Collect all tasks in the list task_list = self.browser.find_element(By.ID, "task-list") tasks = task_list.find_elements(By.TAG_NAME, "li") task_texts = [t.text for t in tasks] # Assert all tasks are present for task in tasks_to_add: self.assertIn(task, task_texts) # Pause so you can see the final state in the browser import time time.sleep(5) |
Code Walkthrough:
- Class Inheritance: ToDoAppTest inherits from StaticLiveServerTestCase → runs a local Django test server at self.live_server_url.
- setUp (before each test): Configures Chrome browser options (–disable-gpu, –no-sandbox, optional headless), initializes Chrome browser with self.browser = webdriver.Chrome(…), and manages ChromeDriver automatically via ChromeDriverManager().install().
- tearDown (after each test): Closes the browser using self.browser.quit().
- Test_add_multiple_tasks: Opens the To-Do application in Chrome, adds tasks from a list by typing and submitting each, waits for tasks to appear and verifies all tasks are displayed, and pauses briefly for visual inspection.
Output:
To execute the tests, run the following command:
|
1 |
$python manage.py test |
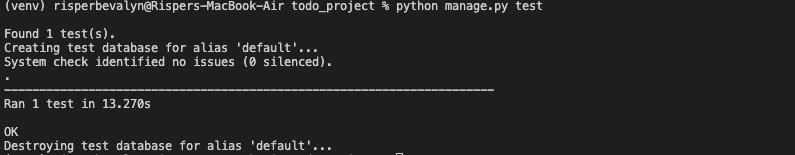
Result:
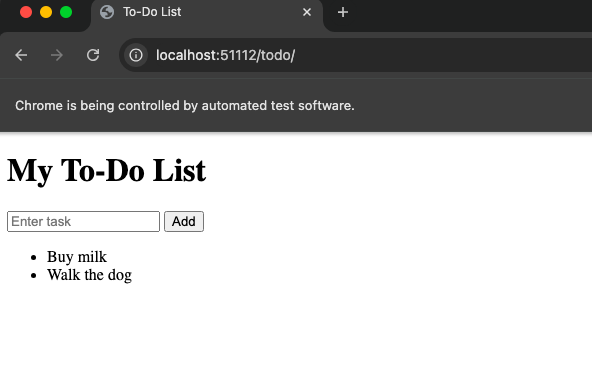
After confirming the app works locally, the next step is scaling it for a larger user base or production environment. This involves configuring the app for performance, security, and stability.
Running Web Development Project at Scale
Scaling your Django To-Do application ensures it can handle increased traffic and multiple users while maintaining performance and reliability.
Testing across multiple devices and browsers is essential to ensure a consistent user experience.
Cloud-based platforms like LambdaTest enable Python automation testing to run parallel tests without managing local setups, making scaling and cross-browser validation more efficient.
LambdaTest is a GenAI-native test execution platform that allows you to perform manual and automated tests at scale across 3000+ browsers and OS combinations.
To get started with running your test at scale on LambdaTest, please follow the steps.
- Download LambdaTest Tunnel (LT): Visit the LambdaTest tunnel downloads page and download the binary compatible with your operating system (Mac, Linux, or Windows).
- Make the Binary Executable (Mac/Linux): Open a terminal and navigate to the directory containing the binary using cd /path/to/directory and make the file executable using chmod +x LT.
- LambdaTest Credentials: Set your LambdaTest Username and Access Key as environment variables. To get your credentials, go to Accounts Settings > Password Security tab and copy your Username and Access Key.
- Run the Tunnel: Start the LambdaTest tunnel using your credentials.
- Get Capabilities: Use the Automation Capabilities Generator to generate the required LambdaTest capabilities for your test configuration, such as OS, browser, and browser version.
|
1 |
$ ./LT --user <your-username> --key <your-access-key> --tunnelName django-tunnel |
Code Implementation:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 |
from django.contrib.staticfiles.testing import StaticLiveServerTestCase from selenium import webdriver from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By from selenium.webdriver.common.keys import Keys from selenium.webdriver.support import expected_conditions as EC from selenium.webdriver.support.ui import WebDriverWait class ToDoAppLambdaTestDevices(StaticLiveServerTestCase): """Run Django Selenium tests on LambdaTest across devices""" def run_test_on_device(self, lt_options): username = "YOUR_USERNAME" # Replace with your LambdaTest username access_key = "YOUR_ACCESS_KEY" # Replace with your LambdaTest access key options = webdriver.ChromeOptions() options.set_capability("LT:Options", lt_options) browser = webdriver.Remote( command_executor=f"https://{username}:{access_key}@hub.lambdatest.com/wd/hub", options=options, ) try: # Open ToDo app browser.get(self.live_server_url + "/todo/") # Update path if different tasks_to_add = ["Buy milk", "Walk the dog"] for task in tasks_to_add: # Wait for the input box and add task input_box = WebDriverWait(browser, 10).until( EC.presence_of_element_located((By.NAME, "task")) ) input_box.clear() input_box.send_keys(task) input_box.send_keys(Keys.RETURN) # Verify task appears in the task-list WebDriverWait(browser, 10).until( EC.text_to_be_present_in_element((By.ID, "task-list"), task) ) # Collect all tasks and assert they exist task_list = browser.find_element(By.ID, "task-list") tasks = task_list.find_elements(By.TAG_NAME, "li") task_texts = [t.text for t in tasks] for task in tasks_to_add: assert task in task_texts finally: browser.quit() def test_desktop_chrome(self): lt_options = { "build": "Django ToDo Cross-Device Tests", "name": "Desktop Chrome Test", "platformName": "Windows 11", "browserName": "Chrome", "browserVersion": "latest", "selenium_version": "4.19.0", "tunnel": True, "tunnelName": "django-tunnel", } self.run_test_on_device(lt_options) def test_mac_safari(self): lt_options = { "build": "Django ToDo Cross-Device Tests", "name": "Mac Safari Test", "platformName": "macOS Ventura", "browserName": "Safari", "browserVersion": "latest", "selenium_version": "4.19.0", "tunnel": True, "tunnelName": "django-tunnel", } self.run_test_on_device(lt_options) |
Code Walkthrough:
- Class Inheritance: ToDoAppLambdaTestDevices inherits from StaticLiveServerTestCase and runs a local Django test server at self.live_server_url. Purpose: Runs Selenium tests on LambdaTest across multiple devices and browsers.
- run_test_on_device(self, lt_options): Connects to LambdaTest using username and access_key, configures Chrome options, sets capabilities via lt_options, opens the To-Do application, adds tasks, verifies tasks appear in <li> elements, and closes the browser.
- test_desktop_chrome(self): Runs the To-Do application on Windows 11 using Chrome, sets lt_options for platform, browser, version, and tunnel, then calls run_test_on_device(lt_options).
- test_mac_safari(self): Runs the To-Do application on macOS Ventura using Safari, sets lt_options for platform and browser, then calls run_test_on_device(lt_options).
Test Execution:
Run the following command given below:
|
1 |
$python manage.py test |
View results on LambdaTest by navigating to Automation > Web Automation.
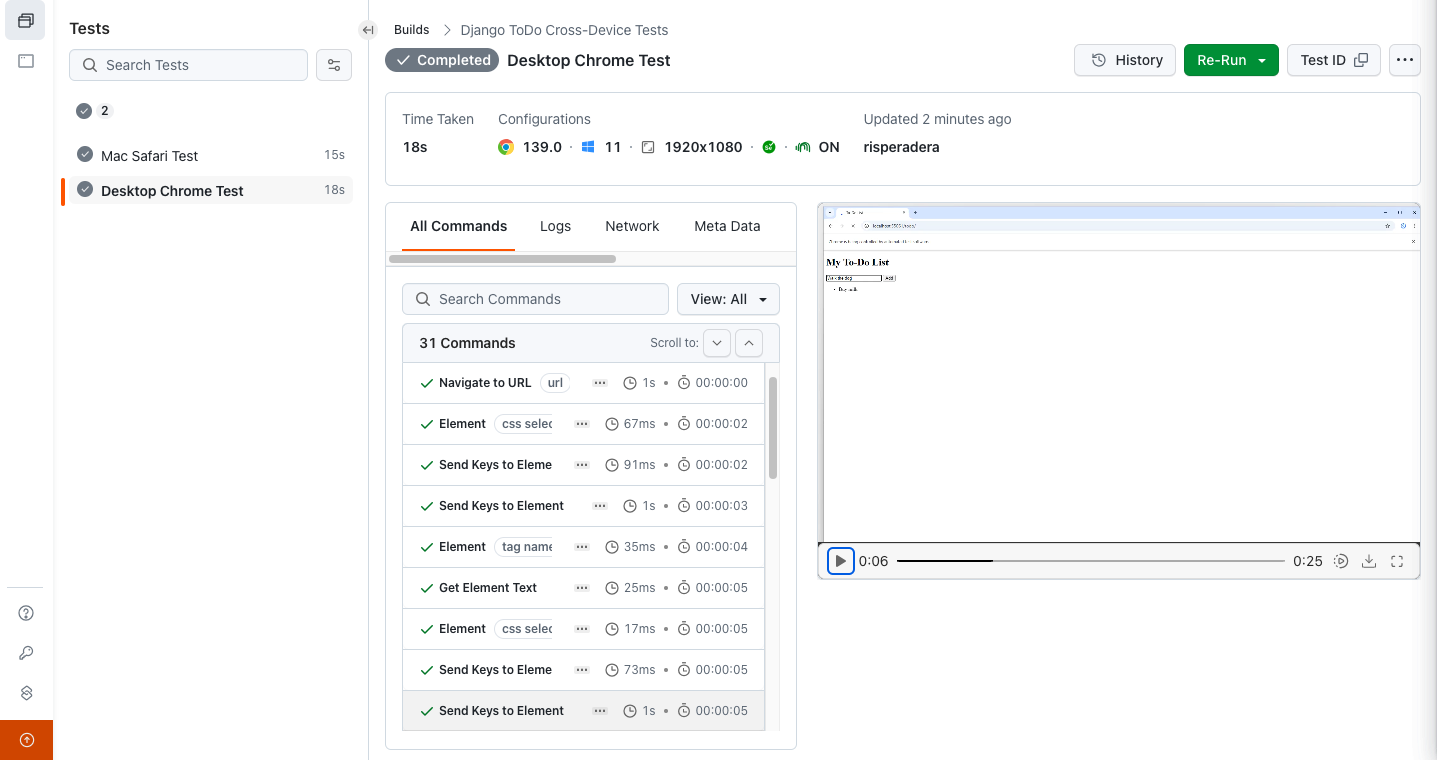
To get started, follow this support documentation on Python testing using Selenium.
Web Development Frameworks and Tools for Python
When working on web development using Python, choosing the right tools and web development frameworks is crucial. These frameworks simplify development, streamline workflows, and provide built-in functionalities to help you build robust applications efficiently. Below is a summary of popular frameworks and essential tools.
Frameworks
Deciding on the correct framework is essential when using Python for web development. A summary of the most widely used frameworks, together with their advantages and disadvantages, is provided below:
- Flask: Flask is a lightweight and flexible web framework, well-suited for developing small to medium-sized web applications. Its simplicity makes it ideal for quick prototyping, microservices, and projects where minimal structure and fast iteration are priorities.
- Django: Django is a full-featured framework that comes with built-in functionalities such as authentication, authorization, and an ORM. Its robust architecture allows it to handle large amounts of data and heavy traffic, making it ideal for developing scalable, production-ready web applications.
- Pyramid: Pyramid’s modular architecture makes it well-suited for developing and maintaining complex applications, offering the flexibility needed for enterprise-grade projects.
- FastAPI: FastAPI is designed to help developers build scalable and efficient web applications. With built-in support for asynchronous programming, it is ideal for developing high-performance APIs.
Tools
A variety of tools are available to make Python web development more efficient and manageable. These tools help with coding, debugging, database interactions, and handling HTTP requests effectively.
- Requests: Requests is designed to make HTTP requests easier to understand and more user-friendly. It supports all standard HTTP methods, including GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, and more.
- ORM (Object-Relational Mapping): An ORM makes it easier to interact with databases in Python, though it is not strictly necessary. It is essential for building web applications that require data storage. For example, Django includes a built-in ORM for managing database models, queries, and relationships. SQLAlchemy, on the other hand, is a widely used ORM for other frameworks or standalone Python applications, providing flexible and powerful database interactions.
- IDE (Integrated Development Environment): An IDE is where we write the code. It provides code editing, debugging, and extensions to ease the development process. One of the commonly used IDEs is Visual Studio Code.
Challenges and Solutions in Python Web Development
The following are some of the challenges that developers usually face when working with Python for web development:
- Challenge 1: Steep Learning Curve: Some Python frameworks, such as Django and Pyramid, are complex frameworks that offer numerous features and tools. New developers usually find it challenging to learn and master Django’s features.
- Challenge 2: Performance Optimisation: As your application grows, performance optimisation becomes critical. Common issues include slow database queries, increased load times, and inefficient rendering of data.
- Challenge 3: Security: Web applications are vulnerable to security threats, such as SQL injection and cross-site scripting (XSS). As a developer, you need to be aware of these threats and use best practices to secure your applications.
Solution: Start by learning the fundamentals of web development using Python with simpler frameworks such as Flask. Once you feel comfortable, you can gradually explore Django by building projects, reading the official Django documentation, and following tutorials.
Solution: Web developers working in web development using Python need to optimise database queries, use caching, and minimise HTTP requests to ensure fast and efficient performance.
Solution: To secure your application, avoid writing raw SQL queries; use Django’s ORM, which uses parameterised queries to prevent SQL injection. Use CSRF tokens in your forms, and make sure to properly authenticate and authorise your REST APIs.
Best Practices for Python Web Development
Following best practices is essential for efficient and secure web development using Python. Adhering to these guidelines helps you write clean, maintainable, and robust code for your web applications.
- Follow the Don’t Repeat Yourself (DRY) Principle: Python web development frameworks, such as Django’s framework, are designed to encourage reusable code, which is essential in web development using Python.
- Variable Names: It is imperative to use descriptive and consistent variable names to make your code easy to read and understand.
- Use Framework’s Built-in Features: For example, when using Django, make use of Django’s built-in authentication and authorisation. Django provides secure and easy-to-use features that simplify web development using Python.
- Test Your Code: Testing is essential to ensure that your code works as expected.
- Input Validation: Validate and sanitise all user inputs to prevent common attacks like SQL injection and cross-site scripting (XSS).
- Password Security: Store passwords securely using techniques like hashing and salting to protect user credentials.
Conclusion
Here you have learned the fundamentals of Python web development, including necessary tools, frameworks, and techniques. By following best practices, you’ll be well on your way to developing reliable and robust Python-powered web applications. Python web development is a broad area with many learning opportunities. Nevertheless, this tutorial will provide you with a solid basis for additional learning.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Why is Python so popular for web development?
Python is popular because of its simplicity, readability, and vast ecosystem of libraries and frameworks. Its clean syntax makes it beginner-friendly and easier to maintain in larger projects. Frameworks like Django, Flask, and FastAPI provide powerful tools that speed up development. In addition, Python integrates well with data science, artificial intelligence, and machine learning, which makes it a strong choice for modern, data-driven applications.
Can Python be used for full-stack development?
Yes, Python can be used as part of full-stack development. On the backend, it manages server logic, authentication, and database interactions with frameworks such as Django and Flask. While Python itself is not used on the frontend, template engines like Django templates or Jinja2 can generate dynamic HTML pages. To create interactive user interfaces, you still need HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, but Python can be combined with frontend frameworks like React or Vue to build complete full-stack applications.
How does Python compare to PHP or Ruby for web development?
Python, PHP, and Ruby each have strong communities and frameworks for web development. PHP has long dominated the web through platforms like WordPress, while Ruby on Rails is admired for its elegant syntax and convention-over-configuration approach. Python stands out for its versatility, as it is widely used beyond web development in areas like data analysis, artificial intelligence, and automation. This broader scope makes Python a more future-ready language, especially for developers who want skills that transfer across different domains.
What advantages does Python offer for startups and rapid prototyping?
Python’s speed of development makes it an excellent choice for startups. With frameworks like Django, developers can quickly access built-in features such as authentication, admin dashboards, and ORM support without spending time building them from scratch. Its large ecosystem of libraries also makes it simple to add functionality like payment systems, data analytics, or third-party integrations. This allows startups to test ideas, release products quickly, and adapt as the business grows.
Is Python scalable enough for large enterprise websites?
Python is very scalable when used with the right architecture. Major companies such as Instagram, Pinterest, and Dropbox rely on Python to serve millions of users daily. Django provides tools that support scalability out of the box, and techniques like caching, load balancing, and asynchronous processing further enhance performance. When deployed with modern solutions such as Docker and Kubernetes, Python applications can meet the demands of enterprise-scale traffic.
Which companies use Python for their web applications?
Several well-known companies use Python to power their web applications. Instagram and Pinterest rely on Django to manage their large platforms. Dropbox uses Python both in its desktop client and server infrastructure. Spotify employs Python for backend services and data processing, and Reddit transitioned from Lisp to Python for better flexibility and maintainability. These examples show that Python is trusted by some of the world’s largest platforms to handle complex and large-scale web systems.
What role does Python play in AI and data-driven web apps?
Python is the leading language for artificial intelligence and data analysis, which makes it perfect for building intelligent web applications. Developers can integrate machine learning models built with TensorFlow, PyTorch, or Scikit-learn directly into Python web frameworks such as Flask or FastAPI. This enables features like recommendation engines, chatbots, fraud detection systems, or predictive analytics. The seamless connection between web development and AI is one of Python’s strongest advantages.
Can I use Python for real-time applications like chat apps?
Yes, Python can be used to create real-time applications such as chat systems or live dashboards. Frameworks like Django Channels extend Django to support WebSockets, which are required for live communication. FastAPI and Sanic also provide asynchronous support that makes building real-time features easier. By combining Python with tools like Redis or RabbitMQ for message handling, developers can build applications that manage real-time interactions efficiently.
What are the drawbacks of using Python for web development?
Despite its strengths, Python does have some drawbacks. Its performance is generally slower compared to languages like Java or C++ because it is interpreted rather than compiled. The Global Interpreter Lock, or GIL, can also limit Python’s efficiency with multi-threading for CPU-intensive tasks, though this is less of a problem for web applications that are primarily I/O bound. Another limitation is that Python does not handle frontend development, so you will always need to combine it with JavaScript for building user interfaces. For projects that demand extremely high performance at scale, Python might not be the first choice.
How can I get started with Python web development as a beginner?
To begin, you should first learn the basics of Python to become comfortable with its syntax and programming style. Understanding HTML, CSS, and JavaScript is also essential because these technologies handle the frontend of web applications. From there, choose a framework to work with—Flask is ideal for lightweight projects while Django is better suited for full-featured applications. Start by building small projects like a blog, a notes app, or a simple to-do list to practice the concepts. As you gain confidence, learn how to connect your application to databases using Django ORM or SQLAlchemy. Finally, explore deployment with services such as Heroku, PythonAnywhere, or Docker so you can bring your projects online and accessible to others.
Citations
- Python’s Role in Accelerating Web Application Development with Django: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/381969758
- Python For Web Development: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/362517489
Author