Power Your Software Testing with AI and Cloud
Supercharge QA with AI for Faster & Smarter Software Testing

- Automation
- Home
- /
- Learning Hub
- /
- What Is Developer Productivity
What Is Developer Productivity and How to Measure It?
Learn how to measure, track, and boost developer productivity with practical metrics, tools, leadership strategies, best practices, and future-ready approaches.
Last Modified on: November 18, 2025
- Share:
Developer productivity directly affects how quickly software can move from development to production. High productivity relies on clear, detailed technical specifications that prevent misinterpretation and reduce rework.
It also involves effective teamwork. Clear requirements, organized code structure, and tools let developers focus on building features. High software developer productivity means features and fixes are delivered faster, with fewer mistakes, and the team can maintain a steady pace over time.
Overview
Developer productivity measures how efficiently a developer or team delivers high-quality, reliable software that meets requirements, considering both the results and the processes used to achieve them.
What Are the Metrics to Measure Developer Productivity?
Developer productivity is measured using code quality, output, collaboration, and satisfaction metrics. To make productivity measurable and actionable, track these key areas:
- Code Quality Metrics: Monitor code churn, defect density, and change failure rate to maintain reliability, prevent regressions, and improve long-term code stability.
- Output and Delivery Metrics: Track deployment frequency, lead time, sprint velocity, and flow velocity to improve delivery consistency, shorten cycles, and optimize throughput.
- Collaboration and Process Metrics: Measure PR response time, pull request size, cross-team coordination, and meeting load to reduce friction, speed reviews, and strengthen teamwork.
- Satisfaction Metrics: Evaluate developer satisfaction, DevNPS, ease of delivery, build and test time, and onboarding experience to enhance morale, engagement, and retention.
How to Measure Developer Productivity?
Track developer performance using structured metrics frameworks. DORA evaluates delivery, SPACE captures satisfaction and workflow, while DX Core 4 adds speed, quality, and impact.
- DORA Metrics: Measure deployment frequency, lead time for changes, change failure rate, and mean time to recovery to evaluate delivery efficiency and stability.
- SPACE Metrics: Assess developer satisfaction, performance, activity, communication, and efficiency to gain a complete view of team productivity and workflow health.
- DX Core 4 Metrics: Track speed, effectiveness, quality, and impact to ensure development efforts deliver value while maintaining smooth processes and high software reliability.
What Is Developer Productivity?
Developer productivity measures how effectively a developer or engineering team delivers high-quality, reliable software that meets requirements. It is determined by a broader set of performance indicators that evaluate both output and the processes delivering it.
Metrics such as cycle time, time-to-complete, and code coverage provide useful insight. On the other hand, factors like collaboration, developer experience, adaptability, and practices that improve software quality are considered. Evaluating software development productivity this way helps teams optimize workflows, address bottlenecks, and continuously improve software delivery.
Why Measure Developer Productivity?
Measuring developer productivity tracks efficiency, output, processes, and bottlenecks using Agile metrics. It also evaluates collaboration and experience, supporting quality, faster delivery, and continuous workflow improvement.
Here is why you should measure software developer productivity:
- Understanding Efficiency: Measuring developer productivity helps teams assess how effectively tasks are being completed. It highlights areas where processes may slow down delivery and identifies opportunities to improve workflow.
- Tracking Output and Process: Productivity metrics capture both the results of the task, such as developed features, and the processes behind them. This ensures teams can evaluate efficiency without focusing solely on code volume.
- Identifying Bottlenecks: Agile metrics like cycle time, lead time, and velocity reveal stages where progress lags. Identifying these bottlenecks allows teams to streamline the task and reduce delays.
- Improving Quality and Collaboration: Productivity measurements encourage better collaboration, highlight the impact of developer experience, and ensure that code quality is maintained while delivery speed increases.
- Supporting Continuous Improvement: By analyzing trends over time, teams can refine practices, optimize workflows, and adapt to changing requirements, supporting a faster software delivery process.
Note: Enhance developer productivity with AI-native test orchestration.Try HyperExecute Today!
What Are Developer Productivity Metrics?
Developer productivity is measured using code quality, output, collaboration, and developer experience metrics. Agile metrics, PRs, cycle time, build speed, and satisfaction surveys help optimize workflows, quality, and delivery.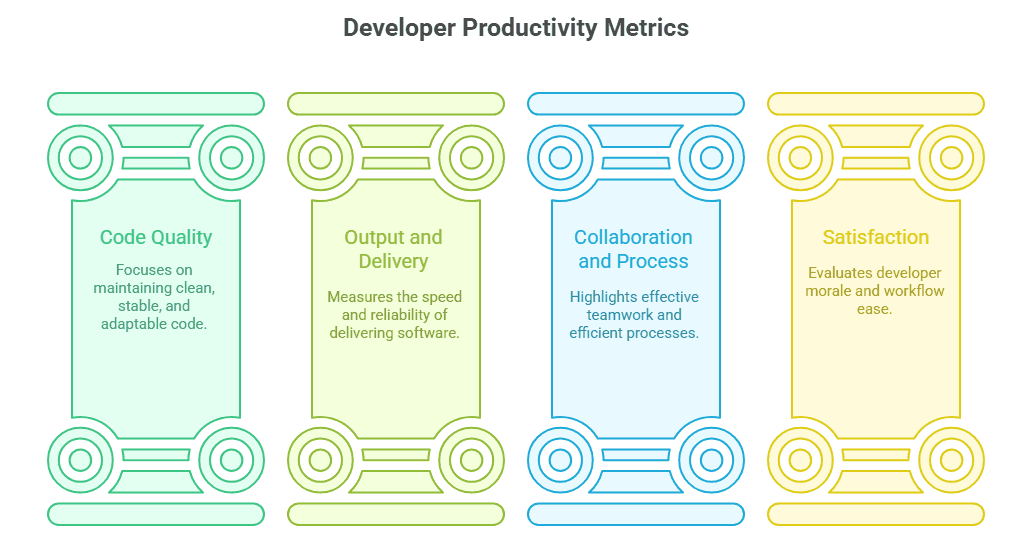
Let’s explore developer productivity metrics:
Code Quality and Maintenance Metrics
Maintaining clean, stable, and adaptable code is essential for long-term software development productivity. These metrics focus on how code changes over time and how effectively developers manage quality and risk.
- Code Churn: Measures how often code is added, modified, or removed. High churn can indicate faster iteration or instability, while low churn may reflect mature, stable code.
- Change Failure Rate: Tracks the percentage of releases that result in issues or rollbacks in production. High rates indicate process or quality gaps, while low rates suggest stable development practices.
- Defect Density / Issues Fixed: Counts issues found per thousand lines of code or per release. Highlights code quality and development effectiveness. High numbers may reflect active review and feedback, while very low numbers could signal missed issues.
Output and Delivery Metrics
Software developer productivity is closely tied to how quickly and reliably work moves from coding to production. These metrics capture efficiency, throughput, and the speed of delivering value to users.
- Deployment Frequency: Highlights how often code is released to production. High frequency reflects streamlined processes and faster delivery, but must be balanced with stability.
- Lead Time / Cycle Time: Measures the time from code commit to production release. Shorter times indicate efficient development processes and help identify bottlenecks in review, integration, or deployment.
- Flow Velocity: Measures how quickly work items (features, improvements) are build. Useful for evaluating sustainable throughput over time. Avoid comparing across teams due to differing estimation practices.
- Sprint Velocity: Tracks story points or work completed per sprint. Useful for planning and assessing team capacity, but not for comparing individual developers.
- Experiment Velocity: Measures how many experiments or prototypes are executed over a period. Reflects a team’s ability to learn, innovate, and validate ideas quickly.
- Pull Request (PR) Count: Tracks the number of PRs merged over time. Provides insight into activity levels, though volume alone does not measure impact.
- Lines of Code (LOC): Counts new or modified lines. More code is not inherently better; focus on maintainability and clarity rather than quantity.
Collaboration and Process Metrics
Productive development relies on effective teamwork and efficient processes. These metrics highlight how developers interact, review work, and manage interruptions.
- Code Review / PR Response Time: Measures how quickly reviews are done. Faster reviews prevent blockers, but rushing can reduce code quality. So, balance speed with review complexity.
- Pull Request Size: Tracks the size of pull requests by lines or files changed. Smaller PRs are easier to review, while very large PRs may need additional review.
- Cross-Team Collaboration: Assesses how well teams work together on shared projects. Combine with qualitative feedback to evaluate knowledge sharing and team collaboration.
- Meeting Load / Context Switching: Measures time spent in meetings or context switching between tasks. Reducing interruptions preserves focus and development flow.
Satisfaction Metrics
A productive team depends on developers being engaged, satisfied, and able to work efficiently. These metrics evaluate morale, workflow ease, and how quickly developers become effective contributors.
- Developer Satisfaction / Happiness: Captured through surveys, reflecting how developers feel about tools, processes, and environment. High satisfaction typically aligns with better performance and retention.
- Developer Net Promoter Score (DevNPS): Asks whether developers would recommend their team or organization. Indicates engagement and team culture, not individual performance.
- Ease of Delivery: Evaluates how smooth developers find workflows, builds, and deployments. Identifies friction points that slow development.
- Local Build / Test Time: Measures the duration of local builds and test runs. Short feedback loops improve software development productivity, while long waits interrupt flow.
- Onboarding Time / Ramp-up: Tracks how quickly new developers contribute meaningful code. Highlights the effectiveness of onboarding, documentation, and mentoring.
How to Measure Developer Productivity?
Measure developer productivity by tracking outcomes, efficiency, and quality. DORA metrics track delivery speed, lead time, failure rate, and recovery, while SPACE metrics track satisfaction, performance, activity, collaboration, and workflow.
Let’s explore how these approaches work in practice:
DORA Metrics
DORA metrics quantify software delivery performance. These metrics capture both throughput and stability of the delivery pipeline. In practice, teams collect data from their version control or version control systems, CI/CD pipelines, and incident trackers to measure productivity.
- Deployment Frequency: Measures how often new code is successfully released to production. Frequent deployments, such as daily or multiple times per day, indicate a high-velocity delivery process. High deployment frequency allows teams to deliver value faster and respond quickly to feedback or market changes.
- Lead Time for Changes: Tracks the time from code commit to running in production. Short lead times, measured in minutes or hours rather than days, reflect an efficient pipeline with minimal delays.
- Change Failure Rate: The percentage of deployments that result in a production failure, such as requiring a hotfix or rollback. Lower rates indicate higher delivery quality and fewer defects slipping through.
- Mean Time to Recovery (MTTR): Measures the average time to restore service after a failure. Faster recovery demonstrates the team’s ability to troubleshoot and resolve issues quickly.
SPACE Metrics
While DORA focuses on delivery outcomes, the SPACE framework provides a broader view of software developer productivity. SPACE stands for Satisfaction & Well-being, Performance, Activity, Communication & Collaboration, and Efficiency & Flow. Each dimension captures a critical aspect of how developers work.
- Satisfaction and Well-being: Measures how engaged, fulfilled, and healthy developers feel. Surveys or one-on-one feedback can reveal job satisfaction, morale, and burnout risk. High satisfaction correlates with productivity, while dips can signal potential slowdowns.
- Performance: Focuses on the outcomes of a developer’s work, including quality and impact rather than raw output. Metrics may include defect rates, service reliability, feature usage, or customer satisfaction. The goal is reliable, valuable software rather than simply counting lines of code or tickets closed.
- Activity: Tracks quantitative developer actions such as commits, pull requests, code reviews, issue resolutions, builds, and releases. Alone, these metrics provide limited insight, but when viewed in context, they help indicate workload, velocity, and overall progress.
- Communication and Collaboration: Evaluates how effectively team members coordinate. Metrics include code review turnaround, documentation quality, cross-team support, and tool-based connectivity. Strong collaboration, including mentoring and design discussions, leads to smoother development and fewer delays.
- Efficiency and Flow: Measures the ability of developers to work without unnecessary interruptions. This includes focused coding time, delays in CI pipelines, or time to set up development environments.
DX Core 4 Metrics
While SPACE provides a broad view of developer productivity, the DX Core 4 framework focuses on balancing speed, effectiveness, quality, and impact across software development teams. Each dimension captures a key aspect of how engineering teams deliver value.
- Speed: Measures how quickly development teams can deliver code changes. Primary metrics include pull request throughput, lead time for changes, and deployment frequency. High speed indicates efficient workflows, but it should be evaluated alongside other dimensions to avoid sacrificing quality.
- Effectiveness: Focuses on the quality of the developer experience and how well teams can perform their tasks. Metrics include the Developer Experience Index (DXI), regrettable attrition, and ease of delivery. High effectiveness reflects low friction in processes, strong morale, and developers’ ability to work efficiently without unnecessary obstacles.
- Quality: Assesses the reliability and stability of software delivery. Metrics include change failure rate, time to restore service, and perceived software quality. Maintaining high quality ensures that speed and effectiveness improvements do not compromise the reliability of the product.
- Impact: Evaluates the business value generated by development efforts. Metrics include the percentage of time spent on new capabilities, initiative progress, and return on investment. High impact shows that engineering efforts are aligned with strategic goals and are creating meaningful outcomes for the organization.
Case Study: Boosting Developer Productivity With LambdaTest HyperExecute
Boomi, an enterprise integration platform, faced long test cycles, slow developer feedback, and intermittent test failures caused by infrastructure issues. These delays slowed developers and QA teams, affecting feature delivery.
To learn more, you can visit this LambdaTest Boomi case study page.
Using the SPACE framework, let’s analyze the impact and improvements.
- Satisfaction and Well-being: Initially, running the full test suite took around 9.5 hours. Developers often waited for results or reran failing tests, creating frustration and slowing momentum.
By adopting HyperExecute with AI-native test orchestration and flakiness detection, test cycles dropped to 2 hours. Developers received faster feedback and could focus on coding.
- Performance: AI-native Test Insights and Test Intelligence helped identify bottlenecks and optimize test reliability. The team ran three times more tests in the same time, caught defects earlier, and maintained more stable CI/CD pipelines. This ensured higher-quality software and faster delivery of features.
- Activity: With faster and more reliable testing, developers completed more pull requests, automated tests, and builds per cycle. Monitoring these activities provided clear visibility into team progress and workflow efficiency.
- Communication and Collaboration: HyperExecute centralized dashboards offered real-time visibility into test results. Teams across locations coordinated efficiently, addressed issues quickly, and reduced duplicated work. HyperExecute ensured everyone had access to consistent data, improving collaboration between development and QA teams.
- Efficiency and Flow: Parallel test execution, automatic retries, and stable infrastructure minimized interruptions. Developers could maintain focus on feature development, relying on predictable test results without spending time troubleshooting test infrastructure issues.
Key Results:
- Test cycles reduced from 9.5 hours to 2 hours.
- Test coverage increased threefold.
- Feedback cycles are shortened to near real-time.
- CI/CD pipelines became more reliable.
To get started, check out this HyperExecute guide.
What Are the Best Developer Productivity Tools?
You can maximize developer efficiency with tools for version control, CI/CD, collaboration, testing, monitoring, analytics, and developer experience, streamlining workflows and boosting productivity.
- Version Control and CI/CD Tools: Tools like Git, GitHub, GitLab, and CI/CD tools such as Jenkins, track code changes, automate builds, and enable reliable, frequent deployments efficiently.
- Collaboration and Communication Tools: Collaboration tools such as Slack, Microsoft Teams, Jira, and Confluence improve team coordination, streamline communication, and ensure alignment across projects and teams.
- Testing Tools: Automation testing tools such as Selenium and Postman automate repetitive testing, accelerate QA, and integrate seamlessly into CI/CD pipelines to reduce development bottlenecks.
- Monitoring and Analytics Tools: Datadog, New Relic, and Grafana provide real-time insights, identify workflow bottlenecks, and support data-driven improvements across development teams.
- Developer Experience Tools: IDEs, linters, code formatters, and documentation platforms streamline coding, reduce context switching, and maintain high-quality, efficient, and consistent software development.
Role of Leadership in Developer Productivity
Effective leadership plays a critical role in shaping software developer productivity. Leaders guide teams, remove obstacles, and create an environment where developers can focus on delivering high-quality software efficiently.
Here are the key ways leadership influences developer productivity:
- Set Clear Objectives: Leaders must define and communicate clear goals and expectations. Well-defined objectives give developers direction, reduce ambiguity, and align individual work with organizational priorities. Clear goals also help teams measure progress and understand success.
- Provide Adequate Resources: Teams require the right tools, technologies, and support to work efficiently. Ensuring access to modern development platforms, frameworks, tools, and documentation reduces friction and empowers developers to focus on high-value tasks.
- Cultivate a Positive Culture: A culture of trust, recognition, and psychological safety enhances engagement and productivity. When developers feel supported, valued, and safe to experiment or ask questions, collaboration improves, and high-quality work follows.
- Monitor and Feedback: Regular check-ins, feedback loops, and performance reviews are critical to sustaining productivity. Continuous monitoring allows leaders to identify obstacles, provide guidance, and adjust priorities, ensuring teams stay focused and efficient without micromanagement.
Challenges of Measuring Developer Productivity
Measuring developer productivity is complex and cannot be captured by a single metric. Developers work on tasks of varying complexity, and output quality matters as much as quantity.
Here are some of the challenges of measuring software developer productivity:
- Productivity Is Multi-Dimensional and Hard to Pin Down: Simple metrics like commits or tickets closed often miss quality work, architecture, or complex problem-solving. High output numbers can reflect busy work rather than real impact. True software development productivity requires metrics that measure outcomes and value, not just raw activity.
- Metrics Can Change Behavior in Unintended Ways: When developers are measured by metrics such as lines of code, pull request count, or velocity, they naturally focus on improving those numbers. This can reduce quality, encourage low-value work, or create unhealthy competition. When metrics become targets, they lose their usefulness.
- Invisible Work and Collaboration Often Go Unnoticed: Mentoring, cross-team coordination, architecture discussions, debugging, and design exploration are essential but rarely tracked. These contributions multiply the team’s impact but often do not appear in dashboards, undervaluing important work.
- Tools and Data Can Be Fragmented: Measuring productivity often requires connecting multiple tools, including version control, CI/CD pipelines, and issue trackers. Data gaps and inconsistent tracking can leave incomplete views. Large organizations may need months to create reliable metric pipelines.
How to Improve Developer Productivity?
To boost developer productivity, focus on outcomes, share knowledge, recognize contributions, maintain transparency, manage technical debt, support inclusion, and streamline collaboration.
The following are the best practices to improve developer productivity:
- Focus on Outcomes Over Outputs: Productivity should be judged by value delivered, not lines of code or tickets closed. Prioritize features that solve real user issues, maintain quality over speed, and foster sustainable workflows. Developers produce better work when they see meaningful impact.
- Encourage Knowledge Sharing: Promote open communication through wikis, showcases, or documentation. Shared understanding reduces duplicated effort, speeds problem-solving, and strengthens team resilience.
- Recognize and Advocate Developer Work: Acknowledge contributions publicly, whether launching features, fixing bugs, or improving tools. Recognition boosts morale, engagement, and reinforces the value of technical work.
- Ensure Transparency: Be clear about priorities, metrics, and decisions. Shared visibility aligns teams, builds trust, and ensures measurement feels meaningful and fair.
- Keep Metrics Consistent: Use standard frameworks like DORA or SPACE across teams. Consistent metrics reduce confusion, improve benchmarking, and support productive discussions.
- Manage Technical Debt: Allocate time for refactoring and infrastructure updates. Reducing technical debt improves maintainability, prevents slowdowns, and signals long-term quality matters.
- Support Inclusion and Diversity: Foster an environment where all developers feel heard and supported. Inclusive teams are more creative, resilient, and productive.
- Streamline Collaboration: Clarify roles, limit unnecessary meetings, and use asynchronous tools. Encourage pair programming, code reviews, and retrospectives to remove blockers and improve workflow.
Future Trends in Developer Productivity
Developer productivity is constantly evolving as technology, work models, and tools change. Understanding emerging trends helps teams adapt, stay efficient, and leverage new opportunities for delivering value.
Here are the key trends shaping developer productivity:
- Integration of AI and Machine Learning: AI and machine learning will increasingly shape developer productivity. These technologies can help identify bottlenecks, predict delays, and suggest workflow improvements. AI-driven code analysis, automation testing, and intelligent task prioritization may allow developers to focus more on high-value work while reducing manual, repetitive tasks.
- Evolution of Remote and Hybrid Work Models: Flexible work arrangements continue to change productivity dynamics. Remote and hybrid models require clear communication, asynchronous collaboration tools, and structured workflows. Teams that successfully balance flexibility with accountability tend to maintain high productivity while improving developer satisfaction.
- Emerging Tools and Technologies: New AI tools for developers and platforms are constantly evolving to support software developer productivity. Advanced CI/CD pipelines, workflow automation, integrated monitoring, and collaboration tools streamline development processes. Early adoption of these technologies can reduce friction, shorten lead times, and help teams deliver reliable software faster.
Conclusion
Improving developer productivity isn’t just about working faster or producing more code; it’s about creating conditions where developers can do their best work. When teams have the right tools, clear goals, and a supportive culture that balances performance with well-being, productivity naturally follows.
Reducing friction with automation, encouraging knowledge sharing, and aligning work with business priorities all contribute to meaningful, lasting impact. True software developer productivity comes from enabling focus, collaboration, and sustainable practices that improve both output and team satisfaction.
Citations
- What Improves Developer Productivity at Google? Code Quality: https://research.google/pubs/what-improves-developer-productivity-at-google-code-quality/
On This Page
- What Is Developer Productivity?
- Why Measure Developer Productivity?
- Developer Productivity Metrics
- Measure Developer Productivity
- Case Study for Developer Productivity
- Developer Productivity Tools
- Role of Leadership
- Developer Productivity Challenges
- How to Improve Developer Productivity?
- Developer Productivity Future Trends
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Did you find this page helpful?
More Related Hubs

Start your journey with LambdaTest
Get 100 minutes of automation test minutes FREE!!


