Mimic Real World Scenarios with Real Device Cloud
Test Your Native, Hybrid & Web Apps on 10,000+ real devices.
- Testing Basics
- Home
- /
- Learning Hub
- /
- UX Testing Tutorial
What Is UX Testing: Beginners Guide With Examples
Discover the ins and outs of UX testing with this comprehensive guide. Explore various testing methods, tools, and best practices for measuring success.
Last Modified on: November 28, 2025
- Share:
OVERVIEW
User experience (UX) plays a vital role in the success of any product or service, UX testing has emerged as a crucial aspect of development. UX testing allows businesses to gain insights into user behavior, preferences, and pain points, enabling them to optimize their products for maximum usability and satisfaction. This article explores the significance of UX testing and provides valuable insights into the best practices and methodologies employed in this field.
What is UX Testing?
UX testing serves as a method for evaluating a product's usability and user experience. Real users are recruited to perform specific tasks while researchers observe and collect data. The primary objective is to identify usability issues and areas for improvement, thereby refining the design and enhancing the user experience.
Why UX Testing Important?

UX testing holds immense significance for several reasons.
Firstly, it enables organizations to assess the usability and effectiveness of their products or services from the user's perspective. By observing and analyzing user interactions, organizations gain insights into user behavior, preferences, and pain points, which inform informed design decisions.
Secondly, UX testing helps identify usability issues and bottlenecks early in the development process, saving time and resources in the long run. Moreover, user-friendly and intuitive products foster positive experiences, enhancing user satisfaction. Ultimately, UX testing empowers organizations to create exceptional user experiences, fostering increased customer loyalty and market competitiveness.
How to Perform User Experience Tests
User experience testing is a flexible process that varies based on the product and the type of testing it requires. While complex applications might need extensive user reviews and testing, typically, a substantial number of users can provide statistically significant data and cover most testing objectives.
Now, let's explore some methods of conducting user experience testing:
Laboratory-Based Product Testing
In this case, a large number of people are hired to test the app. They are trained to sit in the middle of a big room while keeping a reasonable distance from the watcher. After a period of time of using the app, the watcher is asked specific questions and the results of this survey are collected.
Guerilla Usability Testing with Random Users
Not all user experience testing requires a large lab setup. An alternative is to approach people in public places like coffee shops or grocery stores and ask them to review your product. Following up with a survey can provide additional valuable feedback. This method is often referred to as Guerilla usability testing.
Remote Web Application Testing
This technique allows participants to test the application at their convenience, without the need to be physically present also known as remote test lab . It offers the flexibility of conducting tests at any time and from any location.
When utilizing a real device cloud like LambdaTest, there's no need for an in-house lab for usability testing. Users can test the application remotely on various device and browser combinations. Tools like real device cloud and real time, facilitates remote testing on a wide range of devices and browsers. This approach enhances the accessibility and convenience of user experience testing.
How to Write User Experience Tests
The user experience is also determined by some other tests, such as responsiveness testing and cross browser compatibility. Lambdatest provides cloud tools to test responsiveness and compatibility in multiple device and browser combinations.
Cross Browser Compatibility Test
Below are the steps on how to perform ux testing of websites.
- If you don't already have an account with LambdaTest you can register for free here.
- From the left menu, select Real Time Testing > Browser Testing.
- Enter the URL, select Desktop, VERSION, OS, and RESOLUTION. Click START.


A new virtual machine will open based on the selected browser-OS combinations where you can test websites or web applications for usability issues.

Testing Responsiveness
The responsiveness of your apps or sites is one of the most important aspects of user experience. You can easily check how responsive your app or site is on various screen sizes and screen resolutions (Portrait and Landscape) using real devices.
- Sign up and login to your LambdaTest account. To get a real device cloud access, contact sales.
- Go to Real Device > App Testing.
- Choose OS type (Android or iOS), upload your app, select BRAND, and DEVICE/OS. Then click START.


It will launch a real device cloud in which you can test the usability of your mobile apps.

Types of UX Testing
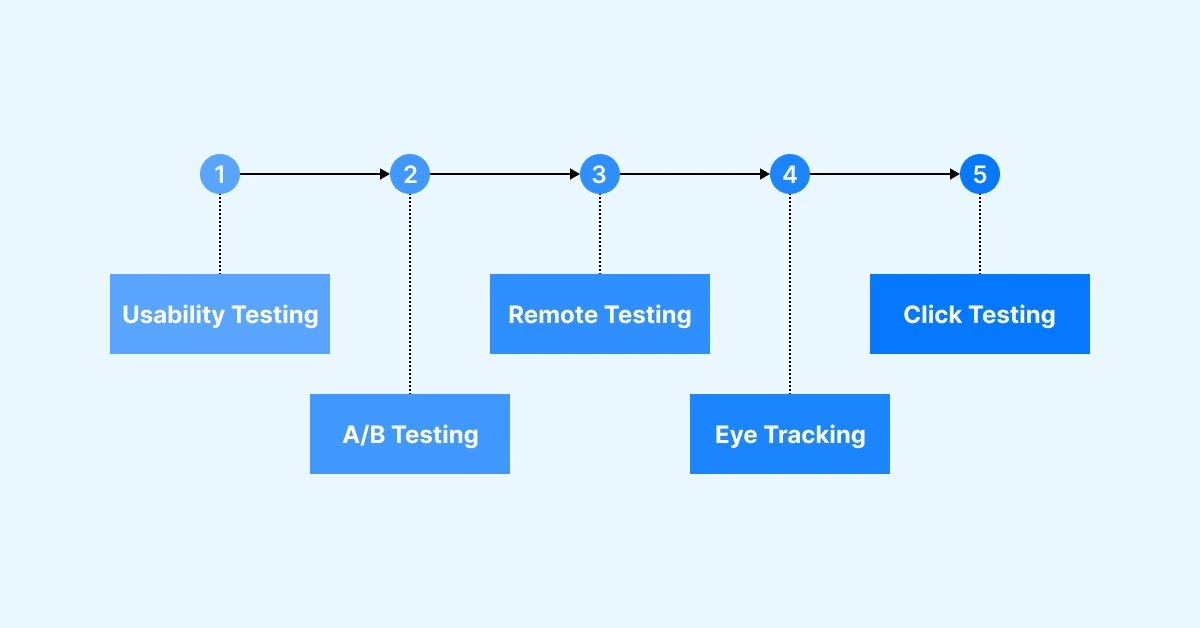
Several UX testing methods aid in evaluating and improving the user experience of a product or interface.
Usability Testing
Usability Testing involves observing individuals as they interact with a product to assess its ease of use, effectiveness, and overall satisfaction. Participants are assigned specific tasks, and their actions and feedback are closely observed. Usability testing helps identify issues related to usability, user dissatisfaction, and areas for enhancement.
A/B Testing
A/B testing also known as split testing, A/B testing compares two versions (A and B) of a webpage or interface to determine the one that performs better in terms of user engagement and conversion. It involves presenting different variants to user groups and comparing their interactions and outcomes. A/B testing facilitates data-driven decision-making and optimization of design elements.
Remote Testing
This form of UX testing takes place at a distance, allowing researchers to engage with a wider range of users and gather feedback from different locations. Participants are equipped with the necessary tools or software to carry out tasks remotely. Remote testing can be accomplished through various approaches, including online surveys, remote usability testing tools, or video conferencing. It offers benefits such as convenience, affordability, and insights from geographically dispersed users.
Eye Tracking
Eye tracking measures and analyzes users' focus and gaze patterns when interacting with a product. Specialized hardware or software tracks the movements of the user's eyes, capturing data on visual attention and fixation points. Eye tracking provides valuable insights into information hierarchy, visual engagement, and the effectiveness of visual design elements. It is commonly used to optimize interfaces, advertisements, and other visual materials.
Click Testing
Click testing, also known as clickstream analysis, evaluates user interactions by analyzing heatmaps, click patterns, and navigation behaviors. It involves tracking and analyzing user clicks, mouse movements, and scrolling actions to understand how users engage with a website or application. Click testing helps identify user preferences, areas of confusion or frustration, and opportunities for improving the user interface. It provides insights into optimizing navigation, content placement, and the overall user experience.
Note: Elevate user experience for seamless and intuitive interactions. Try LambdaTest Now!
Key Steps in Conducting UX Testing
Defining Goals and Metrics
Clearly articulate the objectives of your UX testing. Determine what specific aspects of the user experience you want to evaluate, such as ease of use, efficiency, or user satisfaction. Additionally, identify the key metrics you will use to measure success, such as task completion rates, time on task, or user satisfaction scores.
Creating Test Scenarios
Develop realistic scenarios that mimic user interactions and tasks. These scenarios should cover a range of user journeys and use cases. Ensure that the scenarios are relevant to your product or service. For example, if you are testing an e-commerce website, scenarios could include searching for a product, adding it to the cart, and completing the purchase.
Recruiting Test Participants
Select a diverse group of participants who represent your target audience. The number of participants may vary based on the scope and resources available, but aim for a sample size that allows you to gather meaningful insights without overwhelming your team. Recruiting participants can be done through various methods such as online panels, user research agencies, or even reaching out to your existing user base.
Conducting the Test
Administer the test while observing and recording user interactions. Provide clear instructions to participants about the scenarios they need to complete. Encourage participants to think aloud and share their thoughts, feelings, and experiences during the test. This will help you understand their decision-making process and any challenges they encounter. Record the test sessions through audio, video, or screen capture software.
Analyzing and Acting on the Results
Conduct a comprehensive analysis of the gathered data, encompassing detailed observations, valuable feedback, and precise task completion metrics. Delve into the data to uncover hidden patterns, emerging trends, and recurring usability challenges. Identify the most pivotal issues that profoundly influence the user experience. Prioritize these issues based on their severity and potential impact on user satisfaction, task completion rates, or alignment with business objectives. Harness the knowledge gained from this analysis to drive design enhancements and optimize the overall user experience.
This process may entail modifying elements such as the interface, navigation system, content presentation, or product/service functionality, all with the aim of achieving unparalleled user satisfaction and surpassing organizational goals.
Common UX Testing Tools

There are several common UX testing tools available to evaluate and improve the user experience. Some popular ones include:
UserTesting
UserTesting is a popular UX testing tool that allows you to gather user feedback through remote testing and video recordings. It enables you to create tasks or scenarios for participants to perform on your website or application. Users record their screen and provide real-time audio feedback while completing the tasks. UserTesting provides valuable insights into user behavior, preferences, and pain points. It helps you understand how users interact with your product and identify areas for improvement.
Hotjar
Hotjar is a comprehensive UX testing tool that provides a range of features to understand user behavior. It offers heatmaps, which visually represent where users click, move their cursor, or scroll on your website or app. Heatmaps help you identify popular and underutilized areas of your interface. Hotjar also offers session recordings, which allow you to watch videos of individual users' interactions with your product. This can provide deeper insights into user behavior, frustrations, and areas of confusion. Additionally, Hotjar enables you to gather user feedback through on-site surveys and polls, helping you understand user opinions and preferences.
Optimal Workshop
Optimal Workshop offers a suite of UX testing tools that focus on evaluating and improving information architecture. It includes tree testing, which helps you assess the findability and navigability of your website's structure. Participants are given tasks to find specific items within a hierarchical tree structure, and their success and efficiency are measured. Optimal Workshop also provides card sorting, a method for organizing and categorizing information. Participants group content items into categories, helping you understand how users mentally organize information.
Additionally, Optimal Workshop offers first-click testing, which assesses the usability of your navigation menus by analyzing where users click first when given specific tasks.
Why Should You Run User Experience Tests on Real Devices
When conducting user design testing for a website or web application, the ideal approach involves testing across a diverse range of real devices and browsers. This method helps in uncovering any UX issues that might arise in different environments. However, testing with numerous device and browser combinations can be expensive and resource-intensive. A more practical solution is to utilize cloud-based testing platforms, which allow for testing on multiple devices without the need for physical hardware.
LambdaTest is a cloud-based testing platform that enables users to test their websites across various operating systems and web browsers before launching them to the public. By providing access to a wide array of real devices via cloud services, LambdaTest simplifies the testing process. It also includes additional features crucial for thorough testing, such as Geolocation testing, testing apps with dependencies, Network simulation, and more. These capabilities make LambdaTest an efficient and comprehensive solution for web application and website testing.
UX Testing Best Practices
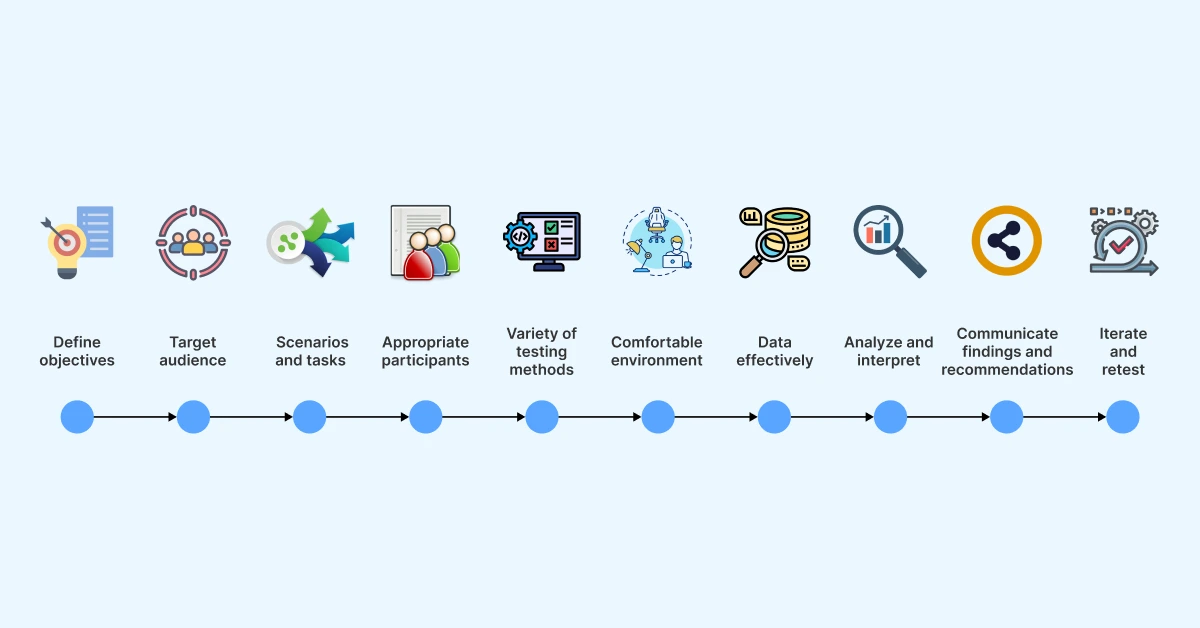
UX testing, or User Experience testing, is a critical process in the field of user-centered design. It involves evaluating a product or system from the perspective of its intended users to ensure that it meets their needs and expectations. To achieve accurate and actionable results, it is essential to follow a set of best practices in UX testing. The following are key principles that professionals should adhere to when conducting UX testing:
- Clearly define objectives: Before initiating UX testing, establish clear and specific objectives. This involves identifying what aspects of the user experience you intend to evaluate and what insights you hope to gain from the testing process. Clearly defined objectives help guide the testing activities and provide focus throughout the evaluation.
- Identify the target audience: Determine the target audience for the product or system being tested. This involves understanding the users' demographics, preferences, goals, and skill levels. By aligning the testing process with the characteristics of the intended users, you can ensure that the insights gathered are representative and relevant.
- Plan test scenarios and tasks: Develop test scenarios and tasks that simulate real-world situations and scenarios that users are likely to encounter. These scenarios should be designed to elicit meaningful interactions with the product, allowing users to provide valuable feedback on their experience. It is important to strike a balance between providing enough structure to guide users and allowing for natural exploration.
- Recruit appropriate participants: Carefully select participants who match the characteristics of the target audience. This includes factors such as age, gender, occupation, and relevant background. Recruiting a diverse set of participants helps capture a broad range of perspectives and ensures that the product is suitable for various user groups.
- Use a variety of testing methods: Employ a combination of qualitative and quantitative testing methods to gain a comprehensive understanding of the user experience. This may include techniques such as usability testing, interviews, surveys, eye-tracking, and A/B testing. By utilizing multiple methods, you can gather different types of data and triangulate findings for more robust insights.
- Create a comfortable testing environment: Establish a comfortable and distraction-free environment for participants during testing sessions. Ensure that the test setup resembles the context in which the product is expected to be used. This helps participants feel at ease and encourages them to provide honest and authentic feedback.
- Capture data effectively: Use appropriate tools and techniques to capture data during testing sessions. This may involve recording audio and video, taking observational notes, collecting survey responses, or analyzing user interactions with the product. Accurate and detailed data capture enables thorough analysis and interpretation of the findings.
- Analyze and interpret results: Once data is collected, analyze and interpret the findings to uncover patterns, trends, and insights. Identify usability issues, pain points, and areas of improvement in the user experience. Use a combination of qualitative and quantitative analysis techniques to ensure a comprehensive evaluation.
- Communicate findings and recommendations: Present the results of the UX testing process in a clear and concise manner. Share actionable recommendations for improving the user experience based on the identified issues. Effective communication ensures that the findings are understood by stakeholders and can be translated into meaningful design decisions.
- Iterate and retest: UX testing should be an iterative process. After implementing design changes based on the initial findings, retest the product to evaluate the impact of the modifications. Repeat the testing process as needed to validate the effectiveness of the design changes and continue improving the user experience.
Measuring Key Success Of UX Metrics
UX metrics refer to quantifiable measurements that assess various aspects of the user experience. These metrics enable businesses to track and evaluate user behaviors, preferences, and attitudes towards their digital products or services. By analyzing these metrics, organizations can identify areas of improvement, make data-driven decisions, and align their strategies with user needs and expectations.
Importance of Measuring UX Metrics
In order to assess and improve the user experience (UX) of a product or service, it is crucial to utilize effective metrics. The following key UX metrics serve as valuable indicators of success:
- Conversion Rate: The conversion rate measures the percentage of users who successfully complete a desired action or goal within a specific interaction or journey. It provides insights into the effectiveness of the user experience in guiding users towards a desired outcome, such as making a purchase, subscribing to a service, or filling out a form.
- Task Success Rate: The task success rate evaluates the percentage of users who are able to accomplish a given task or set of tasks successfully. This metric helps gauge the efficiency and intuitiveness of the user interface and interaction design. A high task success rate indicates that users can easily navigate and complete tasks without confusion or frustration.
- Time on Task: Time on task measures the average duration it takes for users to complete a specific task or set of tasks. This metric provides insights into the efficiency and effectiveness of the user experience. A shorter time on task generally indicates that users can quickly and effortlessly accomplish their objectives, while a longer time may suggest potential usability issues or complexities.
- Error Rate: The error rate quantifies the frequency of user errors or mistakes encountered during interactions with a product or service. It is essential in identifying usability issues and areas of improvement. A low error rate signifies a well-designed user experience with fewer obstacles, while a high error rate indicates potential usability challenges and the need for design adjustments.
These key UX metrics play a significant role in evaluating the success and effectiveness of a product or service's user experience. By regularly monitoring and analyzing these metrics, organizations can make informed decisions to optimize the UX, enhance user satisfaction, and drive desired user behaviors.
The ROI of UX Testing

The Return on Investment (ROI) of User Experience (UX) Testing refers to the financial benefits and value that an organization can derive from investing in the testing of user experiences. UX Testing involves assessing and evaluating how users interact with a product or service, aiming to identify areas of improvement and enhance the overall user experience.
The ROI of UX Testing can be understood in several ways. Firstly, by conducting UX Testing, organizations can identify and address usability issues, ensuring that their product or service meets the needs and expectations of their target audience. This can lead to increased user satisfaction, loyalty, and engagement, which in turn can result in higher customer retention rates and repeat business.
Moreover, UX Testing helps uncover usability problems and friction points that may hinder the conversion process or lead to user frustration. By addressing these issues, organizations can improve the efficiency of their digital platforms, streamline user flows, and optimize conversion rates. This can directly impact the bottom line by increasing sales and revenue generation.
Conclusion
UX testing is a vital component of modern product development, enabling businesses to optimize user experiences and create successful products. By employing various testing methodologies, leveraging essential tools, and following best practices, businesses can enhance user satisfaction, increase conversion rates, and foster brand loyalty. With the continuous evolution of UX testing and the adoption of emerging technologies, the future holds exciting possibilities for further improving user experiences.
On This Page
- Overview
- What is UX Testing?
- Why is UX Testing Important?
- How to Perform User Experience Tests
- How to Write User Experience Tests
- Types of UX Testing
- Key Steps in Conducting UX Testing
- Common UX Testing Tools
- User Experience Tests on Real Devices
- Measuring Success: Key UX Metrics
- The ROI of UX Testing
- Frequently Asked Questions
Frequently asked questions
- General
Did you find this page helpful?
More Related Hubs

Start your journey with LambdaTest
Get 100 minutes of automation test minutes FREE!!



