Power Your Software Testing with AI and Cloud
Supercharge QA with AI for Faster & Smarter Software Testing

- Automation Testing
- Home
- /
- Learning Hub
- /
- What is Test Harness
What is Test Harness in Software Testing?
A test harness in software testing is a set of tools and scripts that automate execution, simulate dependencies, and provide reliable, repeatable results.
Last Modified on: November 19, 2025
- Share:
Software testing has evolved far beyond manual checks and isolated scripts. Today’s applications are complex, distributed, and integrated with multiple third-party systems. Testing such systems requires a structured way to execute, monitor, and evaluate results consistently.
A test harness provides a controlled environment to run tests, generate results, and even simulate missing or unavailable components. In modern development, this harness is no longer static, it is becoming AI-driven and agentic, capable of making intelligent decisions about test execution.
In this guide, we’ll explore what a test harness is, its components, examples, benefits, and best practices. By the end, you’ll have a complete understanding of why test harnesses are a critical pillar of modern software quality engineering.
Overview
A Test Harness is a structured set of tools, scripts, and processes that helps testers automate the execution of test cases and compare actual outcomes with expected results. It acts as a controlled environment where software can be tested reliably, even when some parts of the application are incomplete or unavailable.
Type of Test Harness:
- Unit Test Harness: Tests individual modules or functions in isolation (e.g., JUnit, NUnit).
- Integration Test Harness: Validates how multiple modules interact using stubs/drivers (e.g., shopping cart with mock payment).
- System Test Harness: Ensures end-to-end validation of the complete application (e.g., flight booking system with UI, DB, and payment).
Why Use a Test Harness?
- Automates repetitive testing for consistency.
- Detects bugs early with stubs/drivers.
- Provides detailed reporting and faster feedback.
- Simulates real-world scenarios like failures/timeouts.
- Scales to enterprise-level test coverage.
- Saves costs by reducing manual effort.
- Supports shift-left testing for quicker releases.
What Is Software Test Harness?
A test harness is a structured toolkit designed to help developers and testers run and manage software tests with ease. It’s like a dedicated test workbench that ensures testing is smooth, repeatable, and efficient. At its core, a test harness includes:
- Execution engine: Runs tests against the software under test.
- Script repository: Stores test scripts and relevant data.
- Stubs and drivers: Simulate parts of a system that aren’t yet available, making testing possible even before everything is fully built.
With the rise of AI agentic systems, harnesses now go further. They can prioritize test cases dynamically, adapt to application changes (self-healing), and optimize execution based on code changes or risk areas.
Core Components of a Test Harness:
A well-designed test harness usually includes:
- Test scripts: Define the actions and conditions for each test.
- Test data: Provide the input values and expected outputs.
- Test execution engine: Runs the scripts and orchestrates the workflow.
- Stubs and drivers: Simulate missing or external modules, allowing tests to run in isolation.
- Result analyzer: Compares actual results against expected outcomes.
- Reporting module: Generates logs, dashboards, or summaries of test execution.
Type of Test Harness
A test harness in software testing can be categorized into three main types: unit test harness, integration test harness, and system test harness. Each serves a different purpose in the testing lifecycle:
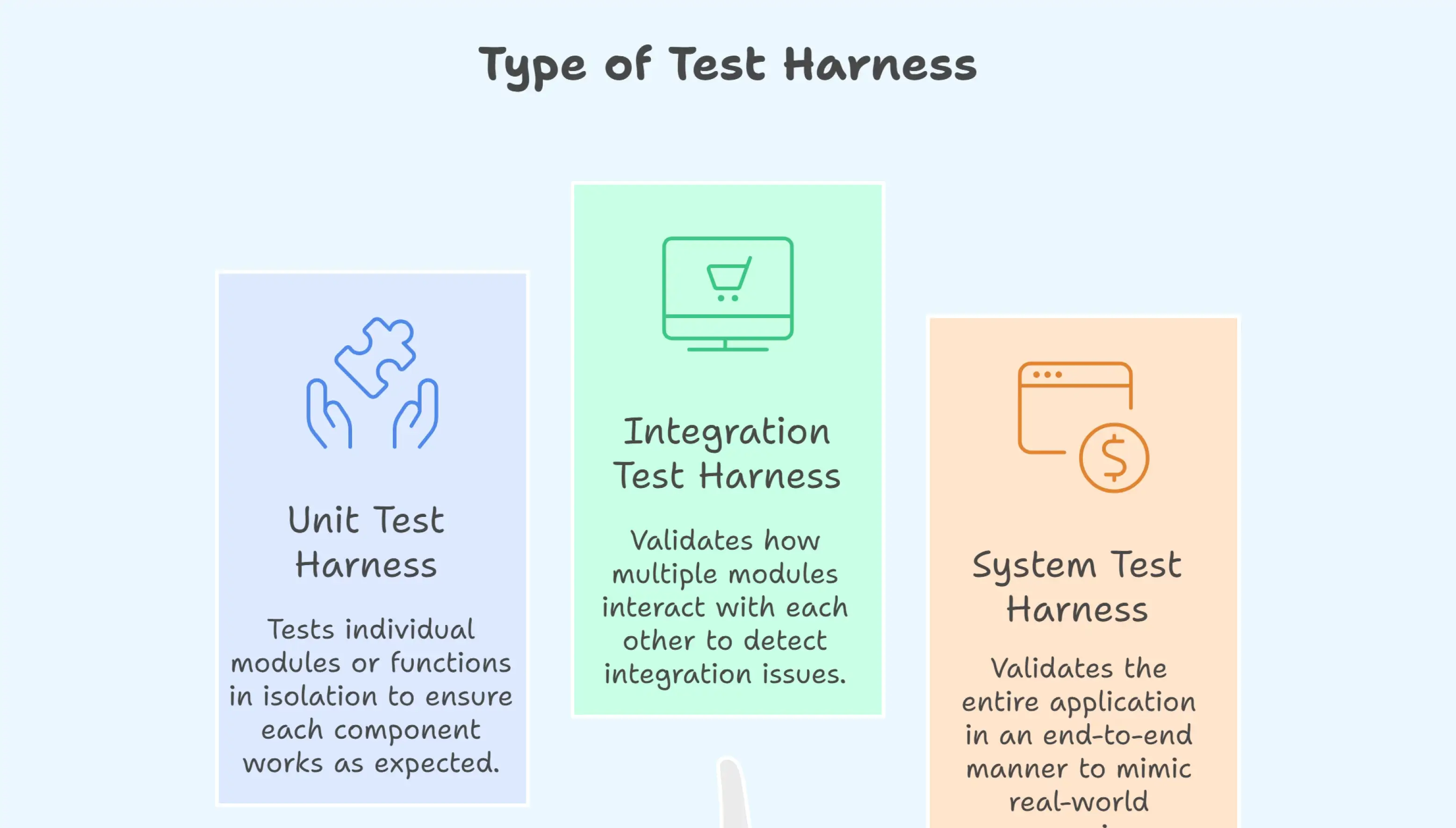
Unit Test Harness
Unit Test Harness is used to test individual modules or functions in isolation. It ensures that each small component of the application works as expected before moving to the next stage. For example, developers often use frameworks like JUnit or NUnit to test a single function such as calculateInterest() in a banking application.
Integration Test Harness
An integration test harness validates how multiple modules interact with each other. It helps detect issues that may occur when different parts of the system interact. Stubs and drivers are commonly used to replace modules that are not yet available. For instance, a shopping cart flow can be tested with a mock payment service before the real gateway is integrated.
System Test Harness
System Test Harness is used to validate the entire application in an end-to-end manner. It includes the user interface, backend systems, and external services to mimic real-world scenarios. A good example is testing a flight booking application where the UI, database, and payment gateway are all connected and validated together.
Why Use a Test Harness?
A test harness in software testing is a strategic advantage for modern development teams. By combining automation, simulation, and reporting, it empowers organizations to deliver high-quality software at speed:
- Automation & Consistency: Automates repetitive testing and ensures reliable, error-free execution every time.
- Isolation of Components: Lets you test parts in isolation using stubs and drivers, even if other modules aren’t complete.
- Early Bug Detection: By using stubs and drivers, teams can test incomplete systems, identifying issues earlier in the development cycle when fixes are cheaper and faster.
- Detailed Reporting: Captures outputs and generates clear test reports for quick issue diagnosis.
- Faster Feedback: Fits well into CI/CD pipelines and supports shift-left testing for early bug detection.
- Simulating Real-world Scenarios: Emulates network failures, service timeouts, or other edge cases that are hard to reproduce manually.
- Enhanced Productivity: By reusing test components and automating runs, teams can focus on innovation rather than repetition.
- Scalability: A test harness easily scales to thousands of test cases, supporting cross-browser, cross-device, and multi-platform validation in enterprise-grade applications.
- Cost Efficiency: Reduced manual testing lowers overall QA costs, freeing testers to focus on exploratory testing, usability validation, and edge case scenarios.
- Comprehensive Coverage: Test harnesses allow simulation of positive, negative, and boundary conditions, ensuring robust application behavior in diverse real-world scenarios.
- Shift-Left Testing: Enables developers to run automated tests early, promoting faster feedback loops, reducing downstream defects, and aligning testing with Agile best practices.
How Does a Test Harness Work?
A test harness works by orchestrating the complete lifecycle of a test, starting from loading scripts and test data to generating actionable reports. The main goal is to provide a repeatable, automated, and reliable testing process that does not depend on manual intervention or the availability of all system components.
Here’s a step-by-step look at how it works:
1. Load Test Scripts and Test Data: The harness begins by pulling in the predefined test scripts (what actions to perform) and test data (inputs and expected results).
Example: A login test might use different sets of credentials as data.
2. Execution Engine Runs the Script: The execution engine is the heart of the harness. It reads the script, executes the actions in sequence, and interacts with the system under test (SUT). This could include UI clicks, API requests, or backend service calls.
3. Use of Stubs and Drivers: If certain modules are missing, unstable, or external (like a payment gateway or third-party API), the harness uses stubs (callee substitutes) and drivers (caller substitutes).
This ensures that testing can proceed even if parts of the system aren’t ready.
4. Generate Actual Results: Once the script runs, the system produces actual outputs.
Example: A login attempt returns either “success” or “invalid password.”
5. Result Analyzer Compares Outcomes: The result analyzer compares the actual outputs with the expected results defined in the test data. Any mismatch is flagged as a failure, and the logs are captured for debugging.
6. Reporting and Logging: The final step is handled by the reporting module, which compiles execution details into structured reports. Reports may include pass/fail counts, screenshots, logs, error traces, and execution time metrics.
Stakeholders; developers, testers, or managers, can quickly review results and take action.
Test Harness Example: Boomi’s Journey with LambdaTest
A test harness in software testing provides the tools and environment to automate execution, simulate dependencies, and analyze results. Boomi’s real-world experience with LambdaTest HyperExecute is a strong example of this in action.
Boomi’s in-house setup required nearly 9.5 hours to run a full suite of tests, creating bottlenecks in its CI/CD pipeline. By adopting HyperExecute as their test harness, they transformed the way testing was executed and reported.
- Execution Engine in Action: HyperExecute served as the central engine, running thousands of tests in parallel across cloud environments. This reduced suite execution time from 9.5 hours to just 2 hours, a 78% improvement.
- Scalability and Coverage: Acting as a harness, it allowed Boomi to run 3x more tests without additional infrastructure, ensuring broader coverage.
- Result Analyzer & Reporting: AI-native analytics worked like an advanced result analyzer, surfacing flaky tests, categorizing errors, and delivering fast, actionable reports.
- CI/CD Integration: Instead of a siloed test setup, the harness plugged directly into Boomi’s pipelines, providing continuous feedback to developers.
Why This Example Fits the Definition:
Boomi’s success illustrates how a modern test harness is not limited to scripts, it can be:
- Execution & Automation: HyperExecute acted as the harness engine, running thousands of tests in parallel.
- Agentic Test Orchestration: Intelligent harnesses will decide which tests to run, in what order, and with what priority based on recent code changes.
- Analytics & Insights: Provided deep analytics on flaky tests, failures, and performance bottlenecks.
- Result Generation: Produced structured reports with clear pass/fail outcomes and execution details.
- CI/CD Integration: Seamlessly fit into pipelines, accelerating Boomi’s release cycles.
In other words, LambdaTest acted as Boomi’s end-to-end test harness, combining execution, analytics, results, and AI. For more read the full Boomi case study.
Test Harness Tools
A variety of test harness tools and frameworks are available to build and run test harnesses, depending on the testing type and scope. Below are some of the most widely used ones:
- JUnit / NUnit / TestNG
These are popular unit testing frameworks for Java and .NET. They allow developers to create automated unit test harnesses to validate individual methods and classes quickly.
- Selenium / Cypress / Playwright
These frameworks are widely used for UI testing harnesses. They automate browser interactions, helping QA teams test end-to-end user flows across different browsers and devices.
- Mockito
Mockito is a powerful mocking and stubbing framework for Java. It’s often used within a test harness to simulate dependencies, allowing modules to be tested in isolation.
- Postman / REST Assured
Both are widely used for API test harnesses. Postman provides a visual interface for building test collections, while REST Assured integrates with code to automate API validation.
- LambdaTest HyperExecute
An AI-native cloud execution platform that functions as an intelligent test harness. It supports the entire testing lifecycle, from planning and authoring to execution and reporting. By adapting test execution dynamically, reducing flakiness, and leveraging advanced analytics, it ensures faster, smarter, and more reliable end-to-end testing.
- Jenkins / GitHub Actions
These CI/CD tools help integrate test harnesses directly into the software delivery pipeline. They ensure that tests are executed automatically after every code commit or build.
Test Harness vs Test Framework vs Test Bed
In software testing, terms like test harness, test framework, and test bed are often used interchangeably, but they serve very different purposes. Understanding the differences helps teams choose the right approach for their testing strategy.
| Aspect | Test Harness | Test Framework | Test Bed |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | A toolkit for executing tests and simulating missing dependencies. | A set of guidelines, libraries, and coding patterns for building structured test cases. | A complete environment that includes hardware, software, and configurations needed to run tests. |
| Components | Stubs, drivers, test scripts, execution engine, reporting module. | APIs, libraries, assertions, utilities, and coding rules. | Servers, operating systems, databases, networks, and applications under test. |
| Focus | Execution, automation, and simulation of incomplete modules. | Structure and design of test cases to ensure reusability and maintainability. | Environment setup and configuration for realistic testing conditions. |
| Example | Mock payment gateway with test runner to validate checkout flow. | Selenium, JUnit, TestNG, or PyTest used to build automated tests. | Cloud-based VM with application, test data, and database preloaded for execution. |
Conclusion
Software delivery today is defined by speed, complexity, and constant change. A test harness is not just a technical utility but a strategic enabler. The future lies in AI-driven, self-healing harnesses that learn, adapt, and optimize in real time. Organizations that embrace this shift will transform testing from a checkpoint into a continuous, intelligent capability and turn it into a competitive advantage.

2M+ Devs and QAs Rely on LambdaTest for Web & App Testing Across 3000 Real Devices
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Did you find this page helpful?
More Related Hubs

Start your journey with LambdaTest
Get 100 minutes of automation test minutes FREE!!