Power Your Software Testing with AI and Cloud
Supercharge QA with AI for Faster & Smarter Software Testing

- Automation Testing
- Home
- /
- Learning Hub
- /
- Test Reports Tutorial
What Are Test Reports: With Examples And Best Practices
A complete tutorial that explores test reports, their types and sections, and how to create an effective test report.
Last Modified on: September 26, 2025
- Share:
Test reports are structured documents or dashboards that summarize the outcomes of testing activities. They serve as a record of what was tested, how it was tested, in what configuration, what bugs were found, and what the results were, helping stakeholders understand product quality and make informed release decisions.
Test reports are a critical deliverable. If the team prepares them diligently within the timelines, the resulting test summary report and feedback will remain valuable throughout the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC).
What are Test Reports?
A test report is a comprehensive, in-depth document that contains information on everything that happened during the testing phase, outlining executed test cases, their outcomes, discovered defects, and overall quality observations for the software under evaluation.
After completing testing, the team often prepares a test report (also known as a test execution report), providing details about the testing procedures, results, application quality, and identified defects. This consolidated document is shared with project stakeholders and should include:
- Detailed information: Include all testing details clearly and briefly, enough to give stakeholders a complete picture without turning it into an abstract.
- Clarity: When you include information in this document, you should confirm clarity in all aspects of the testing process.
- Format: You should adhere to a standard template for the test report. When it is in a standard format, the stakeholders can quickly review and understand.
- Specifications: You should include all test result specifications with brevity. These specifications should be to the point.
What are the Types of Test Reports?
Types of Test Reports provide different levels of detail depending on the testing stage and purpose:
- Daily Test Report: Summarizes testing activities, results, and defects identified during a single day’s work.
- Test Cycle Report: Covers the results of a complete testing cycle or sprint, showing progress, pass/fail rates, and defect trends.
- Test Summary Report: High-level overview prepared at the end of a testing phase or project, often used for release decisions.
- Defect Report: Focuses specifically on bugs found, including severity, priority, status, and resolution progress.
- Performance Test Report: Details how the application behaves under various load and stress conditions, highlighting performance bottlenecks.
- Compliance/Regulatory Test Report: Documents testing evidence required to meet industry standards, regulations, or contractual obligations.
What are the Benefits of Software Test Reports?
In many teams, test reports are still treated as an afterthought, something you compile for sign-off at the end of a cycle. In reality, they are strategic quality intelligence tools that influence budgets, engineering priorities, compliance posture, and even brand perception:
- Quality assessment: Evaluates the stability of tests, the team’s ability to detect issues early, and the overall value of testing activities.
- Defect analysis: Identifies defect origins, pinpoints causes like poor implementation or unstable infrastructure, and determines the stage at which issues surfaced.
- Decision support: Provides data to guide release readiness and product launch timing.
- Process improvement: Highlights learnings for better planning, execution, and defect prevention in future cycles.
- Root cause analysis: Identifies defect origins and underlying issues like weak implementation, unstable infrastructure, or faulty automation scripts.
- Continuous improvement: Justifies testing efforts and applies learnings to enhance future testing cycles.
- Quality assurance: Ensures only thoroughly tested, high-quality software is released to customers.
When To Create a Test Report?
A test report should be created at key stages of the testing lifecycle to provide timely insights, with timing based on the development approach, testing type, and release plan.
- End of a Test Cycle or Sprint: Summarizes results at the end of each sprint or cycle in Agile/iterative development to evaluate progress and readiness for the next phase.
- After Major Milestones: Generates a report once a significant feature or module is completed to confirm it meets acceptance criteria.
- Before a Release or Deployment: Prepares a final test summary report to validate release readiness, including go/no-go recommendations.
- Post-Release Monitoring: Creates reports after deployment to track performance, detect early defects, and maintain compliance records.
- Continuous Testing in CI/CD: Automates report generation after every build to quickly detect regressions and maintain code quality.
How to Write a Good Test Summary Report?
A Test Summary Report provides a concise assessment of all testing activities completed in a phase or cycle. It highlights key results, test coverage, product quality, identified defects, and overall release readiness, giving stakeholders a clear snapshot for informed decision-making.
To understand how to create a solid test summary report, consider an example: AB is an online travel agency for which an organization is developing the ABC application. While preparing the report, the testing team documents all activities performed during testing and provides an overview of the application.
The ABC application offers services such as bus and railway ticket bookings, hotel reservations, domestic and international holiday packages, and flight bookings. These functionalities are divided into modules like Registration, Booking, and Payment, all of which are included in the report.
Now, let’s see the steps to create a test summary report for an online travel agency.
Step 1: Create a Testing ScopeThe team mentions those modules or areas that are in scope, out of scope, and untested owing to dependencies or constraints.
- In-scope: We completed the functional testing of the following modules:
- User registration
- Registration confirmation
- Ticket booking
- Hotel package booking
- Payment
- Out of scope:
- Multi-tenant user testing
- Concurrency
- Untested modules:
- The User Registration page that has the field values in mixed cases
Test metrics include the following:
- The count of planned test cases
- The count of executed test cases
- The count of passed test cases
- The count of failed test cases
The usage of test metrics is to analyze test execution results, the status of the cases, and the status of the defects, among others. The testing team can also generate charts or graphs to represent the distribution of defects: function-wise, severity-wise, or module-wise.
Step 3: Implemented Testing Type
The team includes all the types of testing it has implemented on the ABC application. The motive for doing so is to convey to the readers that the team has tested the application properly.
- Smoke testing: When the QA team receives the build, the team implements smoke testing to confirm whether the crucial functionalities are working as expected. The team accepts the build and commences testing. After the software application passes the smoke testing, the testing team gets the confirmation to continue with the next type of testing.
- Regression testing: The team conducts testing not on a particular feature or defect fix but on the entire software application. It consists of defect fixes and new enhancements. This testing confirms that after these defect fixes and new enhancements exist in the software application, the application has rich functionality. The team adds and executes new test cases to the new features.
- System Integration testing: The team performs system integration testing to ensure that the software application is functioning as per the requirements.
The team notes all the details of the test environment used for the testing activities (such as Application URL, Database version, and the tools used).
The team can create tables in the following format.
Step 5: Learnings during the Testing Process
The team includes information such as the critical issues they faced while testing the application and the solutions devised to overcome these issues. The intention of documenting this information is for the team to leverage it in future testing activities.
The team can represent this information in the following format.
Step 6: Suggestions or Recommendations
The team notes suggestions or recommendations while keeping the pertinent stakeholders in mind. These suggestions and recommendations serve as guidance during the next testing cycle.
Step 7: Exit Criteria
When the team defines the exit criteria, it indicates test completion on the fulfillment of specific conditions, such as the following:
- The team has successfully executed all its planned test cases.
- The team has closed all the critical issues.
- The team has planned the actions for all open issues, which it will address in the next release cycle.
Step 8: Sign-off
If the team has fulfilled the exit criteria, the team can provide the go-ahead for the application to ‘go live.’ If the team has not fulfilled the exit criteria, the team should highlight the specific areas of concern. Further, the team should leave the decision about the application going live with the senior management and other top-level stakeholders.
Note: We have provided a free and easy-to-use Test Report Templates. Check it out now.!!
Who Needs Test Reporting?
Test reports serve as a critical communication tool for various stakeholders involved in the software development lifecycle:
- Product Managers & Business Analysts: Evaluate release readiness, track progress, and ensure alignment with business objectives.
- Developers: Gain visibility into defect patterns, root causes, and areas requiring corrective action.
- Testers & QA Leads: Analyze execution outcomes, identify gaps, and refine the overall testing strategy.
- Senior Management: Use clear quality metrics to make informed go/no-go decisions for product releases.
By serving different audiences, test reports bridge the gap between technical execution and business decisions.
AI Dashboards for Smart Test Reporting
Static test reports no longer meet the needs of Agile and DevOps teams. Release cycles are shorter, test data volumes are massive, and stakeholders need instant, actionable insights rather than post-mortem summaries. This is where AI-powered dashboards make a difference.
- Automated analysis: AI scans through massive test data, identifying defect patterns and root causes faster than manual reviews.
- Predictive insights: Machine learning models can forecast areas likely to fail, helping teams focus testing where risk is highest.
- Noise reduction: AI filters out flaky or irrelevant test results, ensuring stakeholders see only actionable data.
- Real-time dashboards: Interactive, visual reports allow stakeholders to track test health continuously and make quicker release decisions.
- Business Impact: AI dashboards align with Agile and DevOps by offering instant, reliable insights. This reduces delays, cuts down defect leakage, and enables faster, higher-quality releases.
Create & Analyze Effective Test Reports with LambdaTest AI Native Analytics
LambdaTest provides two powerful, AI-native solutions to help teams create, analyze, and share test reports effectively:
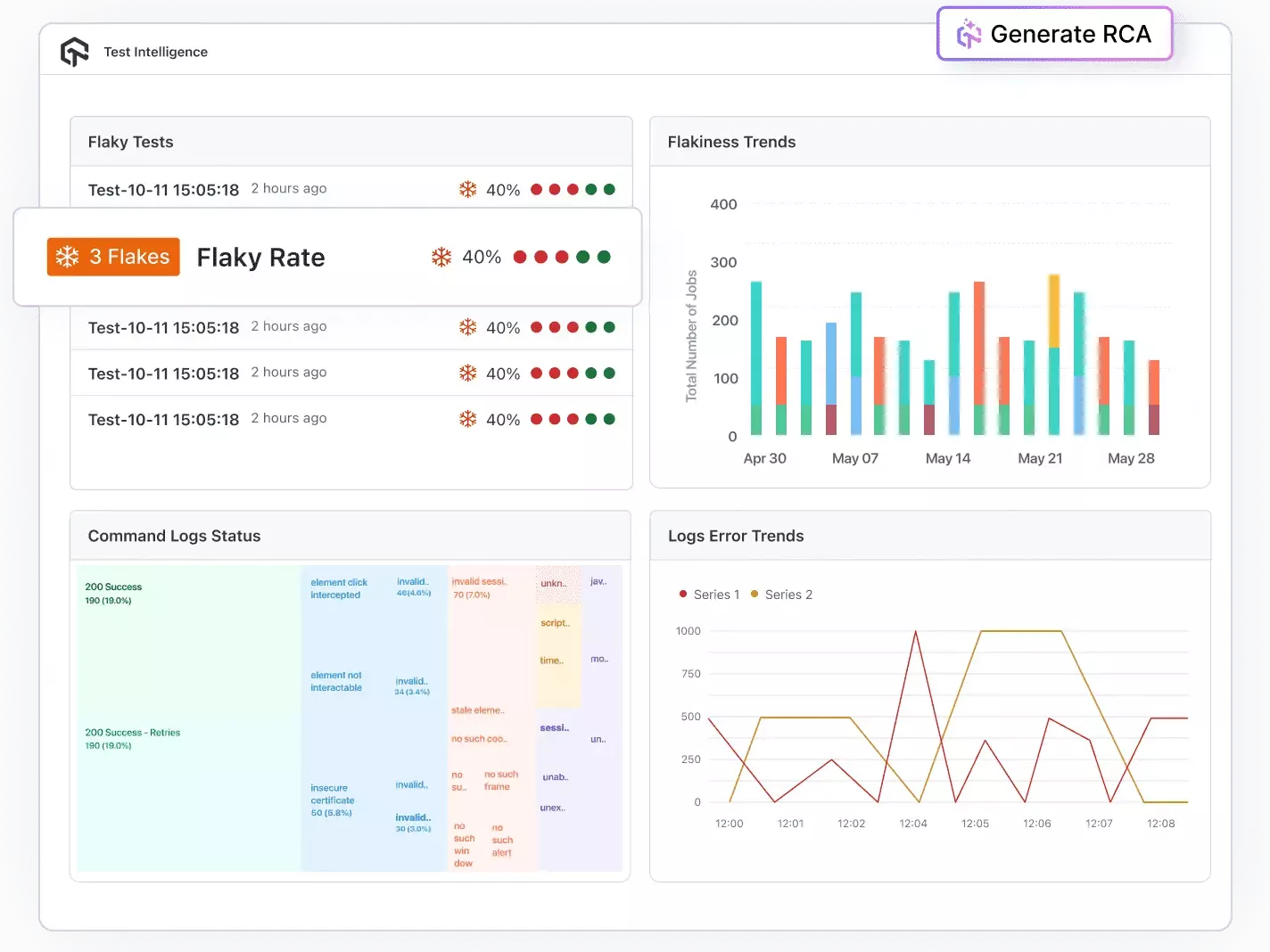
Test Intelligence: Test Intelligence uses data analytics, automation, and AI-driven insights to enhance testing accuracy, speed, and effectiveness. It helps teams detect issues early, identify patterns, optimize test suites, and make informed quality decisions using real-time and historical data.
- Detect Flakiness: Detects flaky tests and anomalies automatically.
- Perform RCA: Perform root cause analysis with AI-driven log and error classification.
- Predict Trends: Forecast error trends based on historical data.
- Customize Insights: Use customizable filters and insights to simplify automation and organize test cases efficiently.
- Spot Irregularities: Identify anomalies across test executions and environments before they impact releases.
- Profile Performance: Analyze CPU, memory, and battery usage during mobile app tests to uncover performance bottlenecks.
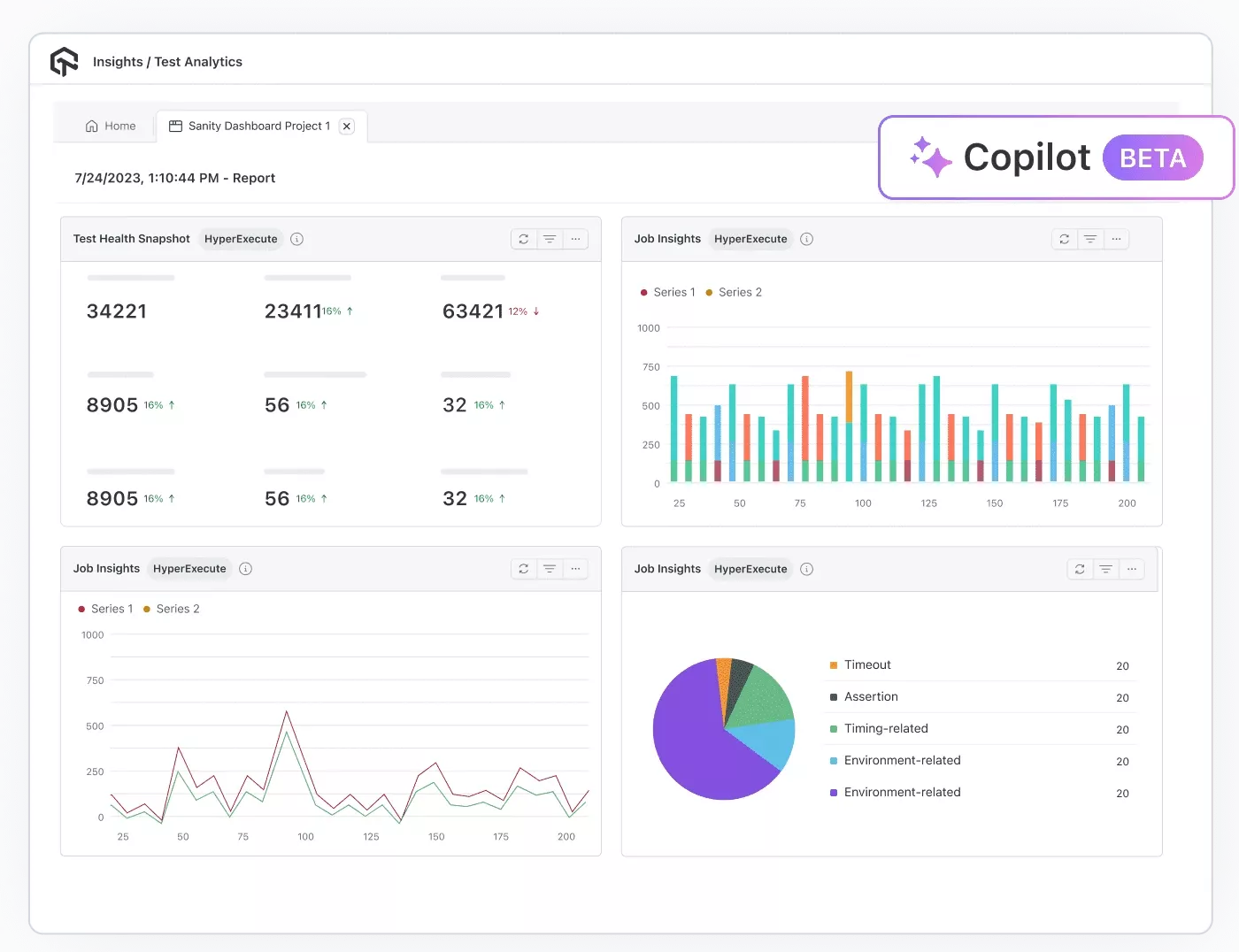
Test Analytics: Test Analytics provides data-driven visibility into testing activities through interactive dashboards and customizable metrics. It helps teams track trends, evaluate performance, optimize resources, and make informed decisions based on real-time and historical test data.
- Access Dashboards: Explore interactive dashboards with customizable widgets tailored to your workflow.
- Track Trends: Monitor historical test execution patterns and performance trends across builds.
- Optimize Parallelism: Track parallel test usage and optimize resource allocation for faster execution.
- Build Dashboards: Create personalized dashboards to follow key team metrics and securely share insights via expiring links or exportable reports.
- Use AI CoPilot: Leverage the AI CoPilot Dashboard for smart recommendations and data-driven decisions.
LambdaTest Test Intelligence vs. Test Analytics - What’s the Difference?
| Aspect | Test Intelligence | Test Analytics |
|---|---|---|
| Primary goal | Explain why tests fail; reduce noise and flakiness | Show what happened; summarize progress & quality |
| Lens | Diagnostic & predictive | Descriptive & observability |
| Best for | SDETs, developers, QE leads | PMs, QA managers, exec stakeholders |
| Key outputs | Failure clusters, flaky test list, probable root causes, anomaly signals | Execution summary, trends, coverage views, environment matrix, and utilization |
| Time horizon | Near-term risk forecasting; immediate triage | Historical & real-time rollups for releases/sprints |
Challenges Faced in Creating Test Reports
- Quick Release Rhythms: Agile, DevOps, and CI/CD require rapid testing and reporting, often within days or hours instead of months. Delayed feedback can postpone releases or risk shipping low-quality products.
- High-volume, Irrelevant Data: Test automation and device/browser proliferation generate massive data, much of which is “noise” from flaky tests, unstable environments, or false negatives.
- Data from Disparate Sources: Large organizations use multiple tools, frameworks, and teams (e.g., Selenium, Appium), making it hard to aggregate and standardize results.
Solution: Automate report generation, integrate testing tools into CI/CD pipelines, and use real-time dashboards for instant feedback.
Solution: Implement test result filtering, maintain stable test environments, and prioritize high-value metrics for reporting.
Solution: Use centralized reporting tools, create standardized data formats, and unify results across frameworks through APIs or integration platforms.
Best Practices for Writing Effective Test Reports
Here are some best practices to follow while creating test reports.
- Close each test execution cycle and then publish the test report.
- Adhere to the standard test report template.
- Include information about all testing cycles to ensure that the stakeholders get a proper and clear picture of the efforts of the testing team.
- Ensure that the information is to the point and can be easily digested.
- Include evaluation metrics, such as schedule slippage, test efficiency, effort ratio, schedule variance, expenses of defect identification, test case adequacy, test case effectiveness, etc.
- Exclude complex technical jargon as several stakeholders need to understand the report.
- Save the test report in a document repository system to ensure its proper maintenance.
Once you generate the test reports, it’s important to share them with stakeholders, customers, and the team to get them an overview of the entire test execution cycle, enhancing their learning and improving further.
Conclusion
Test reports show what the tester thinks of a product. The test analysis report informs stakeholders about the product's current status and possible risks. It enables teams to identify ways to improve the product through valuable insights and feedback.
Removing irrelevant noisy data is necessary to find bugs quickly and get quality results out of the test report. This will help your team to focus and resolve critical issues that need attention.
On This Page
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Did you find this page helpful?
More Related Hubs

Start your journey with LambdaTest
Get 100 minutes of automation test minutes FREE!!