14 Best GUI Testing Tools [2025]
Nandini Pawar
Posted On: September 1, 2025
19 Min
Table of Contents
- What Are GUI Testing Tools?
- List of Best GUI Testing Tools
- LambdaTest SmartUI
- Selenium
- Cypress
- Playwright
- Puppeteer
- Appium
- UiPath
- WebdriverIO
- Tricentis Tosca
- Ranorex Studio
- Squish GUI Tester
- AutoIt
- QF-Test
- Functionize
- Select Right GUI Testing Tool
- Future of GUI Testing Tools
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Creating a flawless user experience goes beyond writing clean code it requires ensuring that every click, scroll, and interaction works exactly as intended. GUI testing tools make this possible by validating the visual and functional integrity of software applications across platforms. They help teams streamline testing, reduce risks, and deliver interfaces users can truly trust.
Overview
GUI testing tools are software applications that simulate user interactions with an application’s interface to ensure visual elements and workflows function correctly across different devices, browsers, and environments.
Some of the Best GUI Testing Tools
- LambdaTest SmartUI: Cloud-based platform for cross-browser and cross-device GUI testing, supporting real devices and AI-driven automation.
- Selenium: Open-source framework for browser automation with multi-language support and broad integration capabilities.
- Cypress: Fast, developer-friendly tool for real-time GUI testing with automatic waits and time-travel debugging.
- Playwright: Microsoft’s automation framework with strong support for modern UIs, shadow DOM, and mobile emulation.
- Puppeteer: Google’s JavaScript library for Chrome/Chromium automation, offering full browser control and visual validation.
- Appium: Leading open-source framework for mobile GUI testing across Android and iOS with real device and emulator support.
- UiPath: RPA-driven platform that mimics real user actions for GUI testing across web, desktop, and legacy systems.
- WebdriverIO: Node.js-based automation framework designed for modern web GUI testing with strong CI/CD compatibility.
- Tricentis Tosca: Enterprise-grade, model-based automation tool offering risk-based GUI testing and cross-technology coverage.
What Are GUI Testing Tools?
GUI testing tools help teams ensure that applications provide a seamless and intuitive user experience. They validate whether visual elements such as buttons, menus, and forms behave correctly by simulating real user actions across platforms. This way, potential issues that could disrupt usability are caught before release.
Key Capabilities:
- GUI Testing: It allows you to automatically test that UI features work identically on different browsers, mobile devices, and operating systems, helping catch environment-specific bugs before release.
- Visual Testing: It helps you compare UI layouts against expected designs to detect misalignments, broken elements, or rendering inconsistencies.
- Regression Testing: You can reruns existing test scripts on new code changes to ensure updates don’t introduce new bugs or break previous functionality.
- Accessibility Testing: It ensures that users with impairments can fully interact with the interface by testing for screen reader compatibility, keyboard navigation, and color contrast
Test your UI across 3,000+ browser and OS combinations. Try LambdaTest Now!
List of Best GUI Testing Tools
Exploring the best GUI testing tools gives you a clear view of the options available to streamline interface validation. These tools help you compare features, strengths, and use cases so you can choose the one that best supports your UI testing goals.
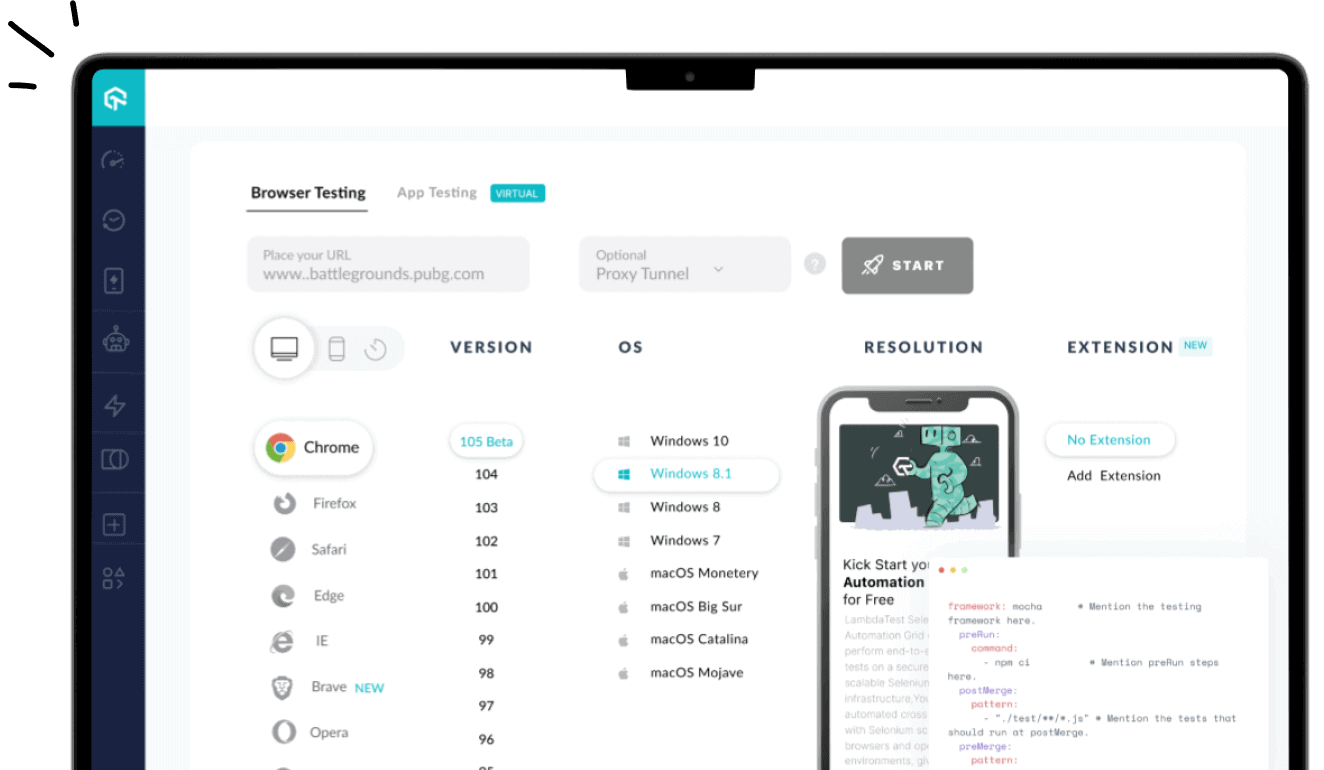
1. LambdaTest SmartUI
LambdaTest SmartUI is an AI-native platform for visual regression testing that automates pixel-level and DOM-aware comparisons of screenshots across browsers, devices, PDFs, Figma designs, and Storybook builds.
It reduces false positives via the Smart Ignore feature, OCR text stabilization, layout analysis, and defined ignore-regions. Integrated into CI/CD pipelines, LambdaTest visual comparison tool offers versioned baselines, and a rich review UI for efficient GUI testing.
Features:
- SmartIgnore via APIs and Annotations: Define ignore or select regions manually, via DOM, or in code; available through SmartUI public APIs.
- Pre-Snapshot JavaScript Execution: Run custom JavaScript on target pages through the CLI before capturing snapshots to stabilize or control dynamic states.
- Multi-Framework CLI and SDK Support: Integrates with Selenium, Playwright, Puppeteer, TestCafe, Storybook, Figma CLI, Appium, Espresso, and XCUITest.
- PDF Baseline Control: Use entire PDFs or individual pages as baselines, allowing more granular visual validation.
- Layout Comparison Mode: Detect layout shifts and element misplacements, especially helpful for responsive and localized testing.
- Coded Region Overlay: Display regions defined in code as overlays on the dashboard alongside manual annotations.
- Smart Crop for Mobile: Automatically crops status and navigation bars in screenshots taken from mobile apps with Appium or Espresso.
To get started, check out this LambdaTest SmartUI guide.
2. Selenium
Selenium is one of the best automated GUI testing tools for automating web browsers. It allows developers and testers to programmatically interact with web applications, simulating user actions like clicking, typing, and navigating.
It supports multiple programming languages and browsers, making it widely used for functional testing, regression testing, and automating repetitive web tasks. Its core component, WebDriver, provides a standardized way to control browsers with precision across different platforms.
Features:
- Cross Browser Testing Support: Supports cross browser testing allowing you to run test across major browsers like Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Edge.
- Multi-Language Support: Supports Java, Python, C#, Ruby, JavaScript, and more.
- Platform Independence: Can run tests on Windows, macOS, Linux, and cloud environments.
- Framework Integration: Easily integrates with testing frameworks like TestNG, JUnit, and pytest.
- Parallel Testing: Supports parallel testing across multiple test environment simultaneously to save time.
- Record and Playback (Selenium IDE): Offers a simple tool for beginners to record tests without coding.
Check out this blog to know how to automate UI testing with Selenium.
3. Cypress
Cypress is a modern end-to-end testing framework designed for fast and developer-friendly GUI testing. It runs directly in the browser, allowing real-time validation of user interactions and easy debugging. With its intuitive interface, automatic reloading, and rich debugging capabilities, Cypress streamlines front-end testing and accelerates development workflows.
Features:
- Real-time Execution: Watch GUI tests execute instantly in the browser for immediate feedback.
- Automatic Waiting: Automatically handles asynchronous UI changes, eliminating manual sleep or wait commands.
- Time-Travel Debugging: Captures snapshots of application state, allowing step-by-step inspection during tests.
- Cross-Browser Support: Compatible with Chrome, Firefox, Edge, and WebKit browsers for thorough testing.
- CI/CD Integration: Integrates easily into pipelines, enabling automation testing within continuous deployment workflows.
4. Playwright
Playwright is a robust automation framework developed by Microsoft, designed for reliable end-to-end GUI testing across multiple browsers. It handles complex web elements, including shadow DOMs and iframes, making it ideal for modern web applications. Playwright supports advanced automation scenarios and offers tools for fast, cross-platform testing.
Features:
- Multi-Browser Support: Automates Chromium, Firefox, and WebKit browsers for comprehensive cross-browser testing.
- Shadow DOM and iFrame Handling: Tests modern UI components, including shadow DOMs and embedded iframes, reliably.
- Cross-Platform Testing: Executes seamlessly on Windows, macOS, and Linux environments for versatility.
- Mobile Emulation: Simulates mobile devices to validate responsive designs across multiple screen sizes.
- Parallel Execution: Runs multiple test sessions concurrently, significantly speeding up GUI test automation.
5. Puppeteer
Puppeteer is a JavaScript library developed by Google that provides a high-level API to control Chrome or Chromium browsers. It is widely used for GUI testing, web scraping, and automation tasks, offering full access to the browser’s rendering engine and developer tools. With headless and full-browser modes, Puppeteer ensures reliable validation of UI behavior across environments.
Features:
- Headless and Full-Browser Modes: Run tests in background headless mode or visible browser mode for debugging.
- Rich Browser Automation: Interact with pages by simulating clicks, typing, navigation, and form submissions.
- Advanced DOM and Network Control: Capture requests, block resources, and manipulate page states for precise testing.
- Screenshot and PDF Generation: Validate visual layouts by exporting page snapshots or full-page PDFs.
- Integration with CI/CD: Easily integrates with pipelines for automated UI regression testing.
6. Appium
Appium is an open-source framework for automating mobile UI testing on Android and iOS. It allows writing a single test script for both platforms, supports multiple programming languages, real devices, and emulators, and integrates seamlessly with CI/CD pipelines, enabling reliable, scalable, and maintainable mobile GUI testing across diverse environments.
Features:
- Multi-Language Support: Allows tests in Java, Python, Ruby, JavaScript, and more.
- Real Device and Emulator Support: Test mobile applications on physical devices or simulators.
- Native, Hybrid, and Web App Testing: Supports testing across all types of mobile applications.
- No App Modification Needed: Tests run without altering the application code.
- CI/CD Integration: Seamlessly automates mobile GUI testing within continuous integration and deployment pipelines.
- Usability Testing: Allows you to the perform usability testing to checks how real users interact with interfaces to ensure UX quality.
- CI/CD Support: Integrates GUI testing into agile pipelines for automated continuous delivery.
7. UiPath
UiPath, known for Robotic Process Automation, extends capabilities to GUI testing by automating workflows. It mimics user interactions, supports multiple technologies including web, desktop, and legacy systems, and enables building visual workflows. Reusable components and enterprise-grade orchestration allow scalable, maintainable, and efficient GUI test automation.
Features:
- RPA-Driven GUI Testing: Automates business processes while validating UI elements accurately and efficiently.
- Cross-Technology Support: Works seamlessly across web, desktop, and legacy system interfaces.
- Visual Workflow Design: Enables creation of GUI tests without extensive coding requirements.
- Reusable Components: Allows storing, sharing, and reusing GUI testing assets across projects.
- Enterprise Scalability: Supports managing and orchestrating large-scale GUI testing operations efficiently.
8. WebdriverIO
WebdriverIO is a Node.js-based automation framework designed for modern web GUI testing. Built on WebDriver and Chrome DevTools, it supports cross-browser testing, integrates with Mocha, Jasmine, and Cucumber, and enables parallel execution. Its cloud compatibility and developer-centric design make it ideal for JavaScript-driven web application testing.
Features:
- Browser Automation: Automates interactions using WebDriver and Chrome DevTools for reliable browser automation.
- Cross-Browser GUI Testing: Validates web applications consistently across multiple browsers.
- Integration Support: Works seamlessly with Mocha, Jasmine, and Cucumber frameworks.
- Parallel Execution: Runs multiple GUI tests simultaneously for faster feedback.
- Cloud Grid Compatibility: Integrates with Selenium Grid and cloud testing services easily.
9. Tricentis Tosca
Tricentis Tosca is an enterprise-grade, model-based GUI testing tool that emphasizes efficiency and risk-based testing. It simplifies creating, maintaining, and executing automated tests across web, mobile, SAP, and desktop applications. By focusing on business-critical areas, it reduces maintenance effort and improves test coverage and reliability at scale.
Features:
- Model-Based Testing: Reduces maintenance by abstracting test logic into reusable models for GUI testing.
- Cross-Technology Support: Supports testing across web, mobile, SAP, and desktop applications efficiently.
- Risk-Based Approach: Prioritizes testing of high-impact GUI components for business-critical validation.
- Reusable Modules: Build flexible, modular GUI test components for efficiency.
- Enterprise Reporting: Provides detailed insights into GUI test coverage, results, and execution.
10. Ranorex Studio
Ranorex Studio specializes in GUI automation with robust object recognition and low-code automation. It supports web, desktop, and mobile platforms, making it suitable for complex interfaces. Data-driven testing, reporting, and debugging tools streamline automation workflows, while its intuitive interface allows testers to build reliable, maintainable tests without deep programming knowledge.
Features:
- GUI Object Recognition: Identifies UI elements reliably across technologies for accurate automation.
- Low-Code Automation: Build tests without extensive programming knowledge efficiently.
- Cross-Platform GUI Testing: Automates web, desktop, and mobile application interfaces.
- Data-Driven Testing: Validates UI behavior using multiple datasets for thorough testing.
- Reporting and Debugging: Built-in logs and video recordings streamline issue resolution.
11. Squish GUI Tester
Squish GUI Tester, by Qt Group, automates GUI testing across platforms and frameworks. It is particularly effective for Qt-based applications but supports Java, .NET, and web. Squish offers robust object recognition, BDD syntax support, and CI/CD integration, enabling reliable, scalable, and maintainable automation of complex GUI workflows across desktop, mobile, and web applications.
Features:
- Cross-Platform Support: Works on Windows, macOS, Linux, and mobile platforms reliably.
- Technology Coverage: Supports Qt, Java, .NET, web, and other UI technologies.
- Robust Object Recognition: Handles dynamic GUI components accurately during automation.
- BDD Support: Enables GUI tests using Gherkin syntax for behavior-driven development.
- CI/CD Integration: Seamlessly integrates automated GUI testing into pipelines.
12. AutoIt
AutoIt is a lightweight Windows automation tool designed for GUI testing of desktop applications. Using a BASIC-like scripting language, it simulates keyboard, mouse, and window operations. Its small footprint, simplicity, and open-source nature make it ideal for automating repetitive tasks and validating Windows GUIs quickly and efficiently.
Features:
- Free and Open-Source: Budget-friendly solution for Windows GUI testing.
- Windows Automation: Tailored for GUI testing of Windows desktop applications.
- Simple Scripting: BASIC-like syntax simplifies writing automation scripts.
- Keyboard and Mouse Simulation: Mimics real user interactions reliably.
- Small Footprint: Lightweight and fast execution for desktop automation.
13. QF-Test
QF-Test is a stable and versatile automation tool for GUI testing across desktop, web, and mobile applications. It provides low-code scripting, broad technology coverage, reusable test cases, and detailed reporting. Its reliability and maintainability make it suitable for large-scale GUI test automation in enterprise environments, ensuring consistent quality across platforms.
Features:
- Broad Technology Coverage: Supports Java, web, desktop, and mobile GUI testing.
- Stable Component Recognition: Handles complex and dynamic UI structures effectively.
- Low-Code Scripting: Enables easy creation of GUI tests with minimal coding.
- Reusable Test Cases: Reduces effort by reusing GUI testing assets efficiently.
- Detailed Reporting: Provides insights into test execution, results, and GUI issues.
14. Functionize
Functionize is an AI-powered testing platform designed to make GUI automation more resilient and scalable. It combines natural language processing with cloud execution, allowing both testers and non-technical users to create, manage, and run tests at scale. By leveraging self-healing automation, Functionize minimizes script breakage and accelerates continuous testing.
Features:
- AI-Powered Self-Healing: Adapts tests automatically when UI elements change, reducing maintenance.
- Natural Language Test Creation: Write test cases in plain English without complex coding.
- Cloud-Native Execution: Run massive test suites in parallel across browsers and devices.
- Visual Testing: Validates layouts and rendering to ensure pixel-perfect user experiences.
- Seamless CI/CD Integration: Fits into existing pipelines for continuous delivery.
Selecting the Right GUI Testing Tool
You need a tool that aligns with your tech stack, scales with your testing needs, and integrates seamlessly into your CI/CD pipeline. Prioritize ease of use, adaptability to dynamic UIs, and reliable community or vendor support.
- Technology Stack: Ensure the tool supports your platform (web, mobile, desktop) and required frameworks.
- Skill Availability: Opt for no-code or low-code test automation tools if developer skills are limited.
- Ease of Maintenance: Prioritize self-healing or model-based tools to avoid brittle tests.
- CI/CD Compatibility: Choose UI testing tools that integrate smoothly with pipelines (e.g., CLI or Docker).
- Cost and License Model: Balance budget against required features, considering open-source vs. enterprise tools.
- Scalability and Parallelism: Select tools that support concurrent execution to accelerate testing cycles.
- Reporting and Analytics: Favor tools that provide clear, actionable insights for faster debugging.
Future of GUI Testing Tools
The future of GUI testing is evolving toward more intelligent, adaptive, and integrated solutions. AI and machine learning will increasingly enable self-healing tests, reducing maintenance when UI elements change. Cloud-native platforms will support massive parallel execution across browsers, devices, and operating systems, ensuring faster test cycles.
- AI-Powered Self-Healing: Tests adapt automatically to UI changes, reducing maintenance.
- Cloud-Native and Parallel Execution: Run large-scale tests across browsers, devices, and platforms simultaneously.
- Natural Language and Low-Code Testing: Enables test creation without deep coding skills.
- Advanced Visual Validation: Pixel-level and DOM-aware comparisons detect layout shifts and dynamic content issues.
- CI/CD and DevOps Integration: Continuous validation of GUIs in agile and DevOps pipelines.
- Cross-Platform and Emerging Tech Support: Extends to web, mobile, desktop, and future interfaces like AR/VR.
- Faster and Smarter Automation: Optimized workflows, analytics, and AI insights streamline GUI test processes.
Conclusion
GUI testing plays a vital role in quality assurance by connecting the developer’s logic with the user’s experience. It helps uncover interface issues that other testing layers may miss, ensures consistency across platforms, and protects the overall usability of your product.
To make GUI testing more effective, it’s important to balance manual and automated efforts while embedding tests into CI/CD pipelines for faster feedback and earlier issue detection. Choosing the right tools also makes UI testing more effective.
You can also take a look at these top UI automated testing tools to explore the best options available.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are GUI testing tools, and why are they important?
GUI testing tools validate the look, feel, and behavior of an application’s user interface. They ensure buttons, forms, menus, and workflows respond correctly across platforms. This is important because any flaw in the interface directly impacts usability, user experience, and customer satisfaction.
How are GUI testing tools different from functional testing tools?
Functional testing tools focus on validating business logic, APIs, and backend processes. GUI testing tools, on the other hand, deal with visual layouts, responsiveness, and interactions. They simulate real-user actions like clicks or inputs to confirm that applications deliver smooth and consistent user experiences.
Can GUI testing be fully automated?
While many repetitive scenarios can be automated, GUI testing cannot be completely automated. Visual aspects like usability, design appeal, or accessibility often require manual verification. The best approach is to combine automation for regression with manual testing for user-centric validation and exploratory scenarios.
Which platforms do GUI testing tools typically support?
Modern GUI testing tools support a wide range of platforms, including web, mobile, and desktop applications. Some also provide cross-browser and cross-device validation, ensuring consistency across operating systems. This broad support makes them essential for applications that need reliable, uniform experiences everywhere.
What are the main challenges in GUI testing?
The biggest challenges include frequent UI changes that break scripts, flaky tests caused by unstable environments, and the time-consuming maintenance of test cases. Additionally, ensuring accessibility compliance and achieving consistency across multiple platforms often requires extra effort and careful tool selection.
How do I choose the right GUI testing tool?
Choosing the right tool depends on factors like supported technology stack, team skill set, ease of test maintenance, scalability, and cost. Compatibility with CI/CD pipelines and strong reporting features should also be prioritized to make GUI testing more efficient and effective.
Do GUI testing tools support accessibility testing?
Some GUI testing tools provide built-in accessibility checks, while others integrate with accessibility-focused frameworks. These ensure applications are usable for people with disabilities, including screen reader users. With accessibility becoming a compliance requirement, many tools now emphasize inclusive design validation alongside functional checks.
Can GUI testing tools integrate with DevOps pipelines?
Yes, most GUI testing tools support DevOps integration through APIs, plugins, or CLI execution. This allows teams to embed GUI tests into CI/CD workflows, run them in parallel, and generate reports. Such integration promotes continuous testing and faster feedback during development cycles.
What are some emerging trends in GUI testing tools?
Emerging trends include AI-powered self-healing scripts that adapt to UI changes, vision-based validation for visual accuracy, and low-code/no-code test creation for non-technical users. Deeper integration with DevOps and cloud platforms is also shaping the future, making GUI testing smarter and more scalable.
Which are the most popular GUI testing tools today?
Widely used GUI testing tools include LambdaTest, Selenium, Cypress, Playwright and Puppeteer. Each offers unique strengths, such as Selenium’s open-source flexibility or Cypress’s developer-friendly design. The right choice depends on project requirements, supported platforms, team skills, and desired level of automation.
Author