How To Perform Localization Testing Of Websites & Apps
Salman Khan
Posted On: September 8, 2025
20 Min
Localization testing is now a business-critical need. According to MotionPoint’s 2025 report, 72% of internet users spend most of their time on websites in their native language, while over 75% of the global population speaks languages other than English. This clearly shows that users expect localized digital experiences, and businesses that fail to deliver risk losing trust and conversions.
In this blog, we’ll explore what localization testing is, why it matters, and how to perform it effectively for websites and apps.
- What is Localization Testing?
- Why is Localization Testing Important?
- When should you Perform Localization Testing?
- Types of Localization Testing
- Features of Localization Testing
- Benefits of Localization Testing
- Choosing the Right Localization Testing Tool based on your Needs
- How to Perform Localization Testing for Websites and Apps
- Challenges of Localization Testing
- Best practices of Localization Testing
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is Localization Testing?
Localization testing is the process of checking whether software works correctly for a specific region, language, or culture. Its main goal is to ensure that both the linguistic elements (like translations, dates, numbers, and currencies) and cultural aspects (such as images, colors, and formats) feel natural to local users. The short form for localization is L10n (where 10 represents the number of letters between “L” and “n”).
While the core functionality of the product usually remains the same, localization testing focuses on areas like the user interface, content, and overall user experience. It’s not just about making sure an app or website runs in different regions; it’s about making it feel personalized, relevant, and user-friendly for people in that specific location.
Why is Localization Testing Important?
Localization testing makes sure your product feels native in every market you enter. It is not just about translating words; it’s about checking that formats, flows, images, and legal text all make sense locally. Here’s why it matters:
- Builds user trust: People feel more comfortable when products use their own language and local formats.
- Improves user experience: Correct layouts, readable text, and smooth navigation reduce confusion.
- Ensures legal compliance: Local laws, privacy text, and terms must match each region’s rules.
- Prevents design issues: Different languages and directions (like RTL) can break UI if not tested.
- Boosts conversions: Local payment methods, address formats, and pricing reduce checkout errors.
- Avoid cultural mistakes: Icons, images, or colors should be appropriate for each market.
- Supports better visibility: Localized content improves search results and app store rankings.
- Provides accurate data: Correct regional settings make analytics and reporting reliable.
- Speeds up global rollout: A clear testing process helps launch in new markets faster
According to a survey, nearly 76% of online shoppers buy products with the information in their local language. Furthermore, 40% will never shop from websites in other languages. Therefore, customers are more inclined to stay with a localized product that fits them, while those who meet linguistic or cultural screw-ups are driven off.
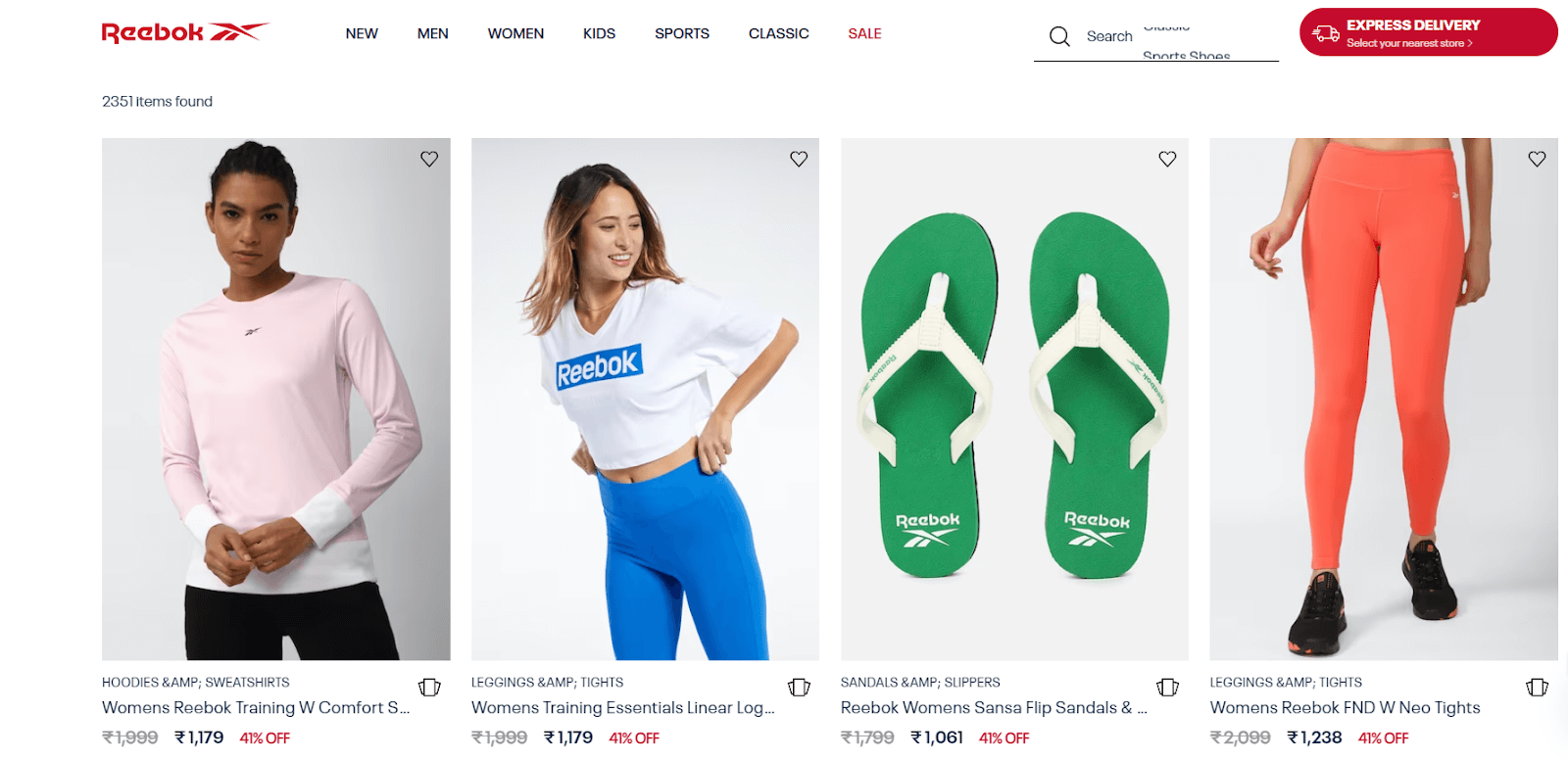
Translating words from one language to another isn’t always straightforward. Localization testing ensures that websites and apps avoid mistranslations and ambiguities by checking typography, images, and content accessibility for cultural accuracy.
While initial testing takes time, it reduces future costs and speeds up deployments, helping businesses enter new markets with a smoother user experience.
Read – Why Is It Important To Test Website From Different Country Locations?
When should you Perform Localization Testing?
Localization testing isn’t something you do just once; it needs to be carried out at key points in the software lifecycle to ensure your product feels natural and reliable for every market. Here are the reasons when you should perform localization testing:
- Before launch of a new product or feature: Run localization testing to make sure the product looks and works correctly in the target language and culture before it reaches users.
- When entering a new market: Always test when expanding to a new country or region to confirm that formats, currencies, and cultural elements are accurate.
- After major design or UI changes: If layouts, fonts, or visuals change, test again to ensure translated text still fits and the design works for all languages.
- When new content is added: Check new strings, promotional banners, or help pages to confirm they are properly translated and displayed.
- During regression testing before release: Include localization checks in your pre-release testing cycle to verify that no localized elements were broken by code changes.
- After system or platform updates: Test when browsers, operating systems, or mobile platforms release updates, since they may affect how text and characters display.
- When integrating third-party services: Validate payment gateways, address fields, or shipping tools in local settings to confirm they support all targeted locales.
- After compliance or policy changes: Test legal disclaimers, cookie banners, or consent flows to ensure they meet local regulatory requirements.
- If you notice unusual user behavior in specific regions: Use localization testing to investigate sudden drop-offs, payment failures, or customer complaints from a particular country.
- On a regular schedule: Even if no major changes occur, run periodic localization audits to keep the product consistent and trustworthy across all markets.
Types of Localization Testing
Here are the main types of localization testing that help ensure your software works correctly and feels natural for users in different regions.
- Linguistic Testing: Checks that the language used in the product is correct, natural, and free from grammar or translation errors.
- Functional Testing: Makes sure localized features like date, time, currency, and address formats work properly in each region.
- Visual/UI Testing: UI testing ensures that text fits well within the design, layouts don’t break, and the interface looks correct in all languages.
- Cultural Testing: Verifies that images, colors, symbols, and content are appropriate and respectful for the local culture.
- Compliance Testing: Confirms that the product meets local laws, regulations, and standards such as privacy or tax rules.
- Device and Browser Testing: Checks that the software runs smoothly on different devices, operating systems, and browser settings with local language packs.
- Accessibility Testing: Ensures localized content is usable for all users, including those relying on screen readers or other assistive tools.
- Content Format Testing: Validates localized emails, notifications, receipts, and other external content so they display correctly.
- Performance Testing: Measures whether the product remains fast and stable when handling different languages, scripts, or regional settings.
- Search and Store Testing: Makes sure app store listings, keywords, and in-product search results work well in the target language.
Features of Localization Testing
Here are some important features of localization testing that make software usable and reliable across different regions and languages.
- Language Accuracy: Ensures all text is translated correctly and sounds natural to native speakers.
- Regional Formats: Verifies dates, times, currencies, and numbers follow the local style.
- Input Validation: Checks that forms accept local names, phone numbers, and addresses without errors.
- User Interface Layout: Confirms that text fits properly on the screen without cutting off or overlapping.
- Right-to-Left Support: Makes sure apps and websites display correctly for languages like Arabic or Hebrew.
- Font Rendering: Tests if special characters and scripts display clearly across devices.
- Cultural Relevance: Validates that images, colors, and symbols are appropriate for the local audience.
- Payment and Compliance: Ensures local payment methods, taxes, and legal requirements are correctly applied.
- Location-Based Features: Checks maps, addresses, and time zones work for the region being tested.
- Search and Navigation: Confirms users can find content in their own language with accurate results.
- Notifications and Messages: Verifies that emails, SMS, and app alerts are localized and readable.
- Accessibility: Makes sure localized content is usable with screen readers and assistive tools.
- Performance in Local Regions: Tests that the app loads quickly and works smoothly in target countries.
- Fallback Handling: Ensures the system shows a default language when a translation is missing.
- Test Data Coverage: Uses real local examples of names, addresses, and special characters during testing.
Benefits of Localization Testing
Here are some major benefits of localization testing that help your software connect with users, perform smoothly across regions, and succeed in global markets.
- Better user experience: Your product looks and feels natural in every market, right words, right formats, right flow. When screens read correctly and actions make sense, people stay longer and use more features.
- Higher conversion and revenue: Prices, taxes, sizes, and offers appear in familiar formats. Checkout flows use local address, phone, and payment rules. Fewer surprises mean more completed purchases.
- Stronger brand trust: Correct tone, imagery, and examples show respect for local cultures. Users see a brand that “gets” them, which builds loyalty and word-of-mouth.
- Fewer production bugs: Testing catches issues like hard-coded strings, broken characters, and text overflow before release. Fixing these in pre-prod costs far less than hotfixes and rollbacks.
- Faster releases to new regions: A repeatable localization test suite (including pseudolocalization and locale smoke tests) speeds up approvals for each market. Teams can launch in weeks, not months.
- Lower support and refund rates: Clear messages, correct error texts, and valid local inputs reduce confusion. Support teams get fewer “Where do I add my postcode?” or “Why is my currency wrong?” tickets.
- Legal and policy compliance: Consent text, age gates, return policies, and disclosures follow local rules. You reduce risk of takedowns, fines, and app store rejections.
- Better search and store visibility: Localized copy, metadata, and microcopy improve search terms users actually type. App and web listings become easier to find in each language.
- Scalable engineering practices: Externalized strings, locale-aware formatting, and RTL checks become part of the pipeline. New locales plug into the same framework with minimal rework.
- Clear performance insights by region: With consistent tests per locale, teams can compare bounce rate, checkout completion, and task success across countries and quickly focus on improvements where they matter most.
Choosing the Right Localization Testing Tool based on your Needs
There are many factors to consider when selecting the best tool for your localization testing needs, such as:
- Check locale coverage: Make sure the tool supports multiple languages, regions, time zones, currencies, and date/number formats.
- Validate device and browser support: The tool should allow testing across real devices, browsers, and operating systems your users actually use.
- Confirm Unicode and script handling: Ensure proper rendering of special characters, right-to-left scripts, and complex languages.
- Look for pseudolocalization support: Choose a tool that can simulate text expansion and untranslated strings before real translations are added.
- Evaluate automation compatibility: Verify the tool works with your existing frameworks like Selenium, Appium, or Playwright.
- Check integration with your workflow: The tool should connect with your CI/CD pipeline, version control, and bug-tracking systems.
- Review reporting features: Opt for tools that provide clear screenshots, logs, and locale-based test reports for easy debugging.
- Assess security and compliance: Ensure data protection, encryption, and role-based access control, especially for enterprise use.
- Match to team size and maturity: Smaller teams may need simplicity and speed; larger enterprises may require advanced dashboards and audit trails.
- Run a pilot before adoption: Test the tool with a small set of localization test cases across critical locales to see if it meets your needs.
How to Perform Localization Testing for Websites and Apps
For instance, platforms like LambdaTest offer automated test orchestration with cross-browser testing on 10,000+ real devices and 3,000+ browsers from geolocations. This enables testing across more than 50 countries, ensuring a comprehensive evaluation of the user experience.
How to Perform Localization Testing for Websites
Here’s a brief guide on performing localization testing on LambdaTest for websites:
- In case you don’t have a LambdaTest account, visit the LambdaTest registration page and create one.
- Login to LambdaTest, and it will take you to the dashboard.
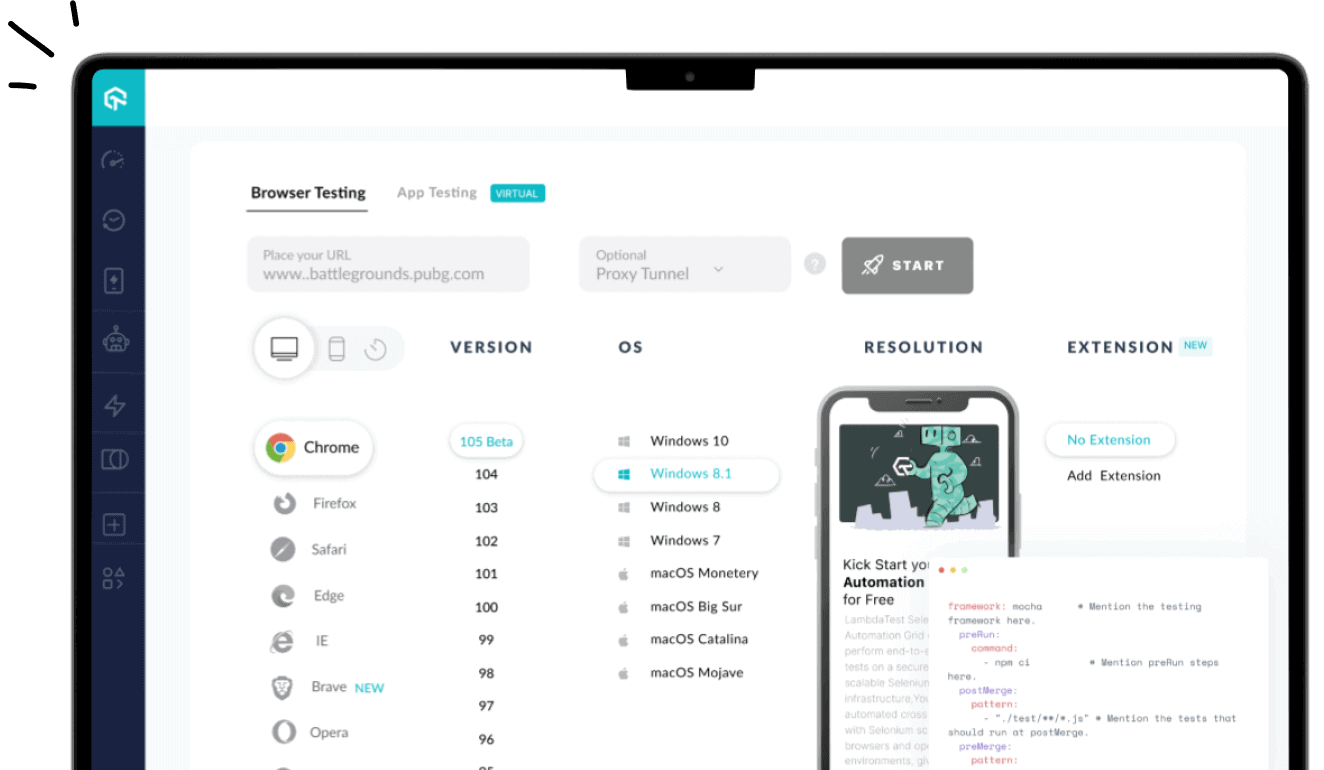
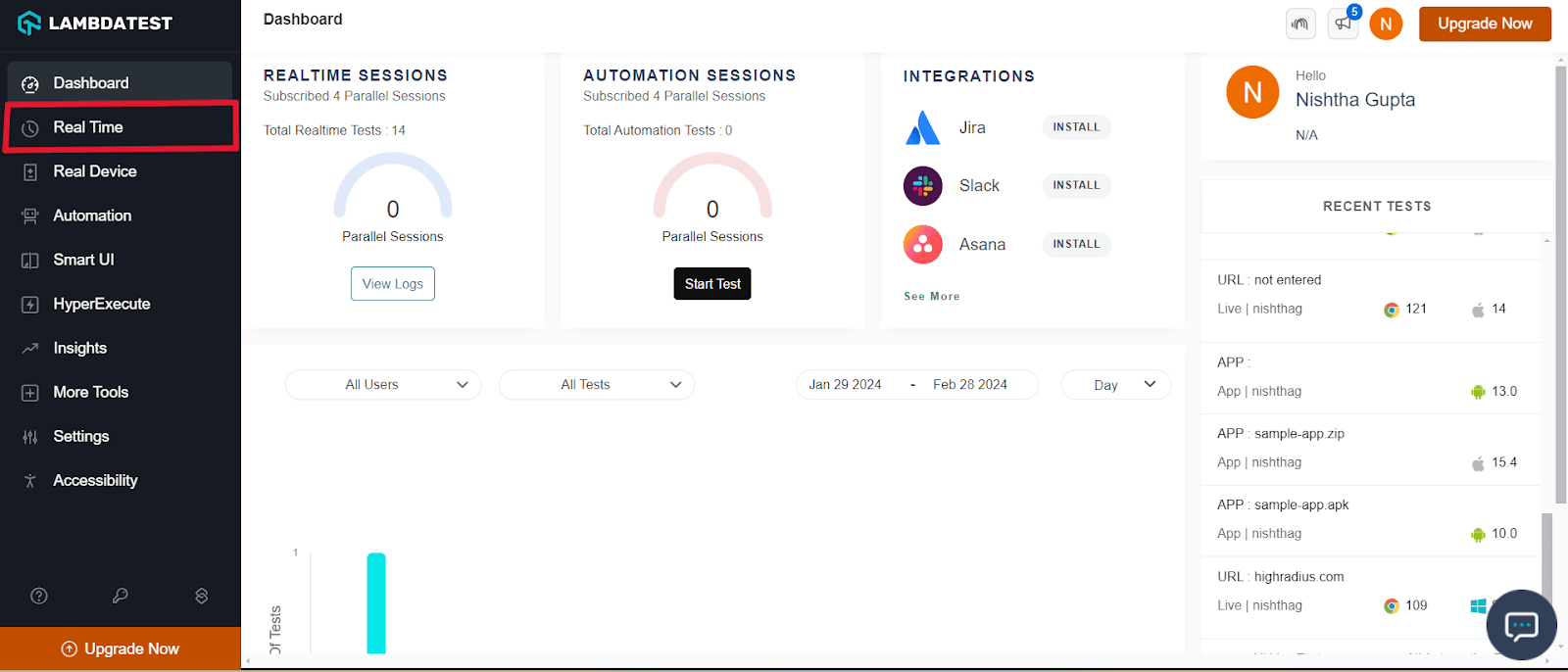
- From the left menu, select Real Time Testing.
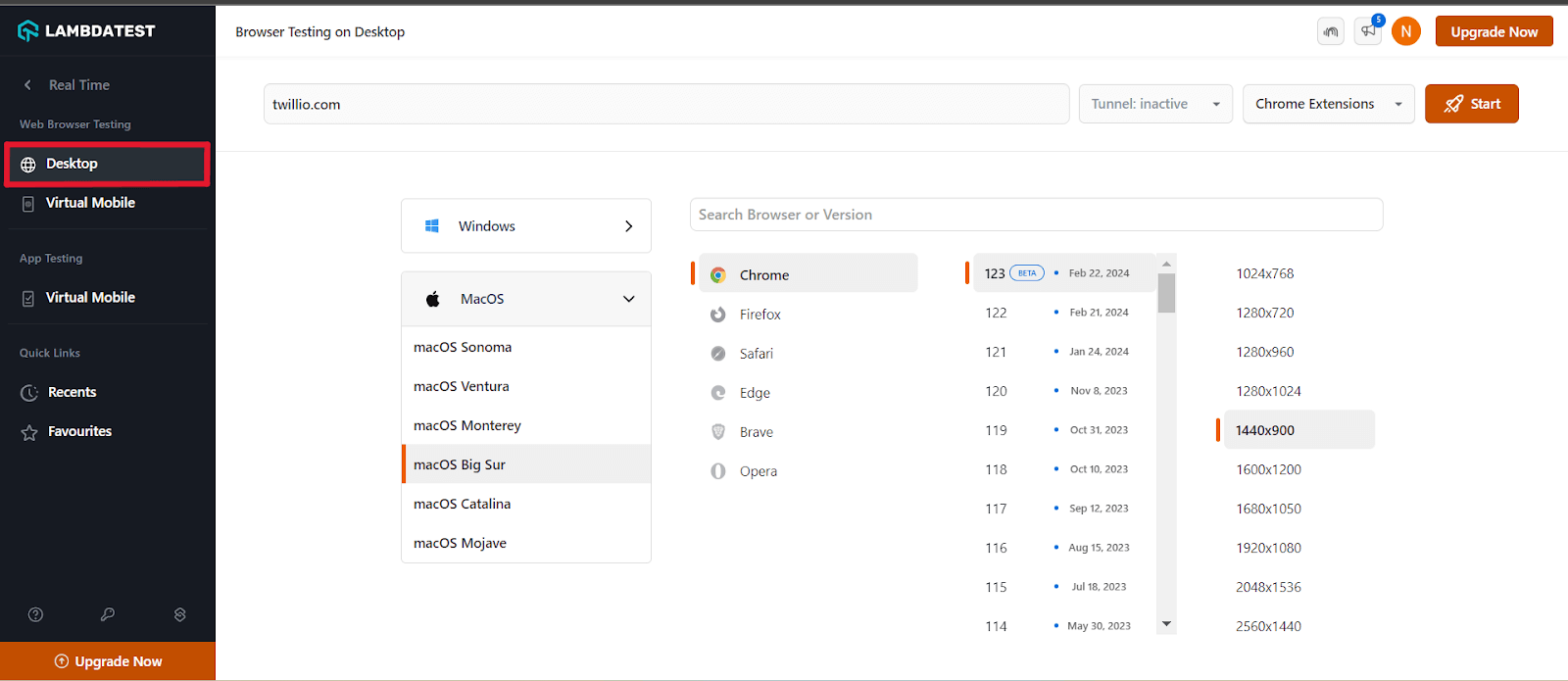
- Enter a test URL select the type of operating system (Desktop or Mobile), VERSION, OS, and RESOLUTION. Here we chose browser – Chrome 96 and OS – macOS Big Sur. Click START
- A new test session will open based on the select browser-OS combinations.
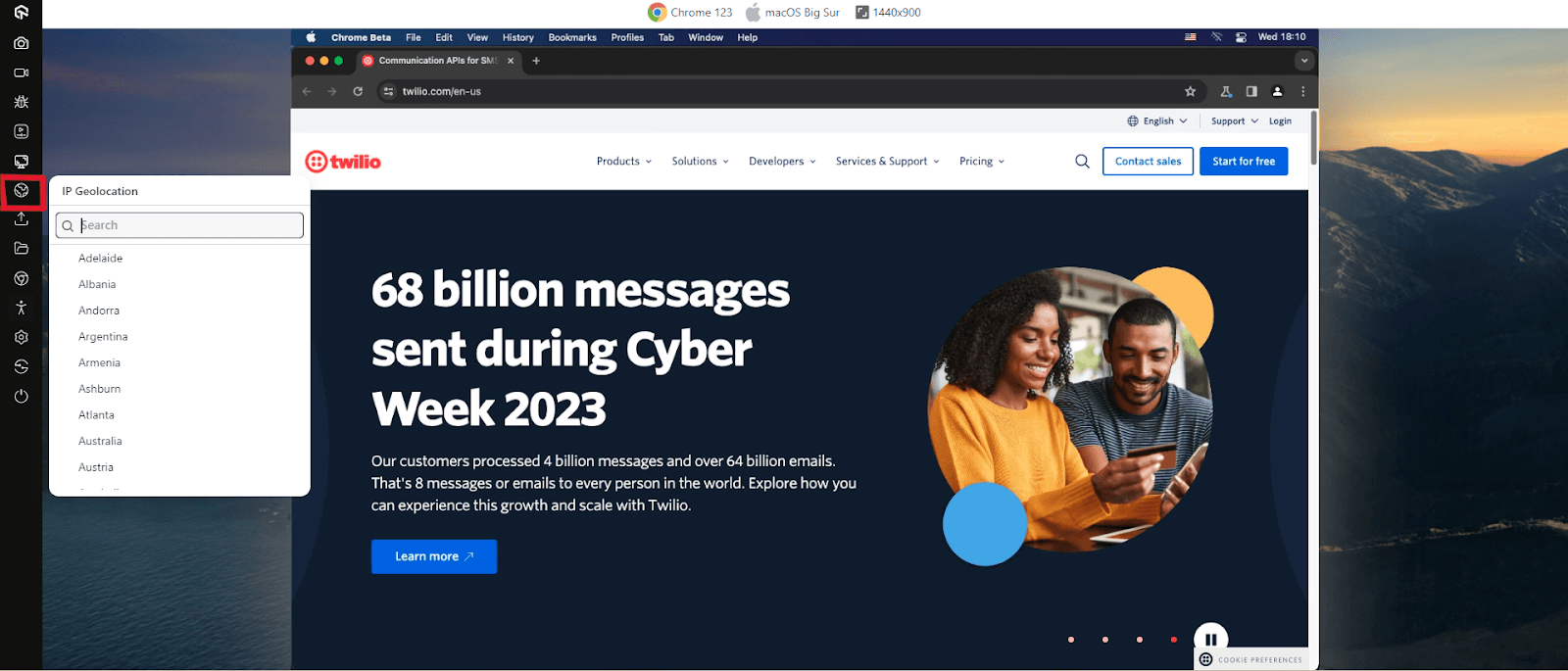
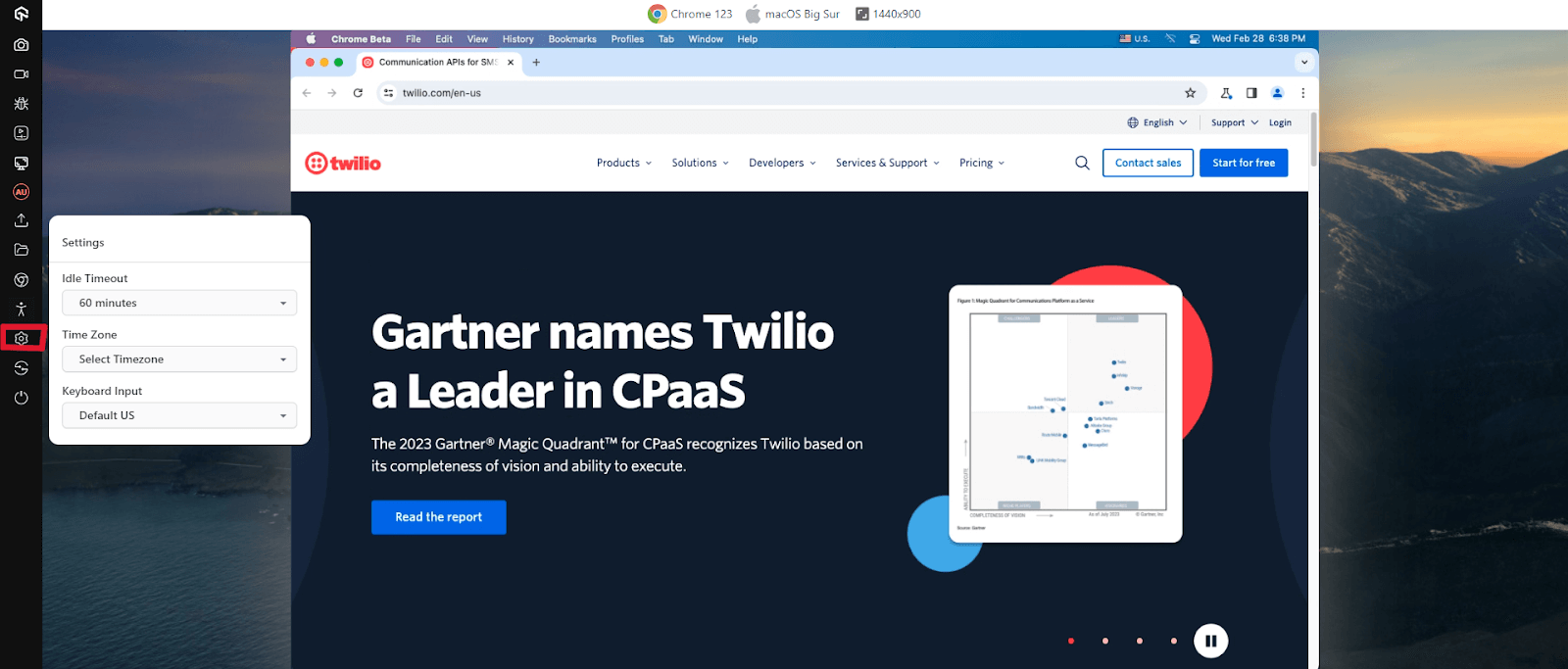
- From the left floating tool, click IP Geolocation.
- A list of countries will be displayed. Choose the desired country. In this example, we chose – Australia. Selecting the desired country will route you to the Australian IP address. By clicking on Settings, you can choose the idle timeout of the session and the timezone.
- Here is a quick video tutorial on performing real-time browser testing on LambdaTest.
- Localization requires the development of resources, the adaptation of services, and the time spent learning about market dynamics. This slows the time to market.
- Inadequate knowledge of the target locale’s language.
- If you have limited knowledge of the product, it can hinder your localization testing experience.
- Localization testing can be time-consuming as learning about different locations takes time.
- It utilizes too many internal resources as you can’t perform – 100% localization manually.
- Setting up and maintaining an in-house device lab can be cumbersome and often has scalability issues.
- Start with research: Understand your target audience, cultural nuances, and market requirements before building test cases. Accurate translations and cultural relevance should be at the core of your testing strategy.
- Test early, test often: Don’t wait until the end of development. Running localization tests early in the SDLC helps catch issues like text overflow or RTL layout problems before they become costly fixes. Combine automation (e.g., Selenium WebDriver) with manual checks for best results.
- Leverage user feedback and KPIs: Define success metrics for each market (e.g., downloads, transactions, sign-ups). Continuously analyze data and user feedback to refine localization efforts and improve ROI.
- Test across browsers and devices: Ensure compatibility on different browsers, devices, and operating systems. Cloud-based platforms like LambdaTest allow testing on 3000+ real browsers and devices under real-world conditions.
- Use pseudolocalization: Introduce pseudolocalization early to detect untranslated strings, text expansion, and encoding issues before real translations are integrated.
- Collaborate with native experts: Always involve native speakers or linguists to validate translations, cultural sensitivity, and usability. Automation is powerful, but human insight ensures true authenticity.
- Maintain continuous testing in CI/CD: Integrate localization testing into your pipelines so every release is validated across locales without slowing down delivery.
- Globalization testing ensures that software can handle multiple languages, scripts, and formats without breaking.
- Localization testing ensures the software is correctly adapted to a specific market or locale (e.g., correct translations, UI layouts, and cultural relevance).
In addition to online browser testing, it’s also crucial to perform a mobile friendly test of your localized websites and web applications. A responsive web design helps you deliver an ultimate mobile experience to users across the globe.
With LambdaTest mobile app testing, you can test mobile applications manually on Android emulators and iOS simulators and a real device cloud of 10,000+ devices and 3,000+ browsers combinations.
How to Perform Localization Testing for Apps
Shown below are the steps on how to test localization of apps.
1. In case you don’t have a LambdaTest account, visit the LambdaTest registration page and create one.
2. Login to LambdaTest, and it will take you to the dashboard.
3. From the left menu, select Real Time Testing.
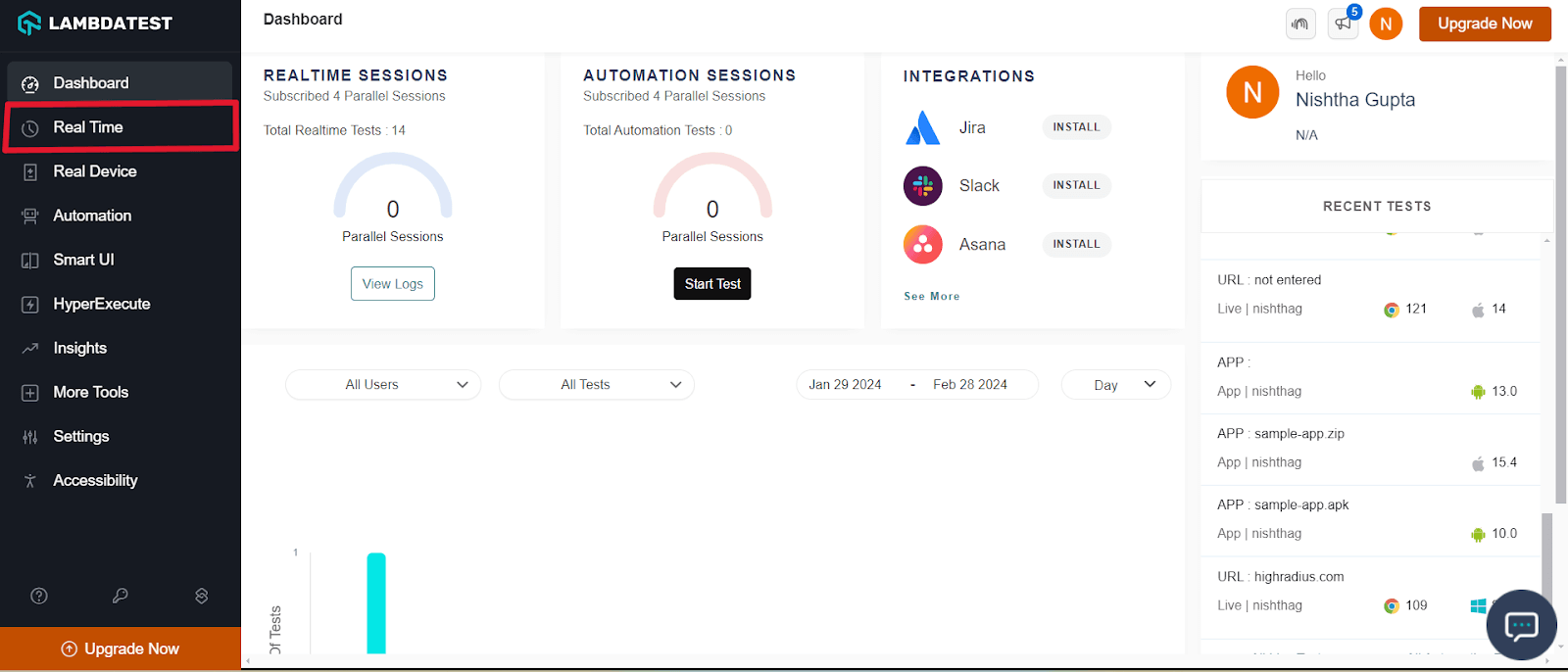
4. Go to Virtual Mobile and select the App Testing. Upload your application. We have used the sample app present here and choose OS type (Android or iOS), BRAND, and DEVICE/OS. Here we chose iPhone 15 Pro Max. Click START.
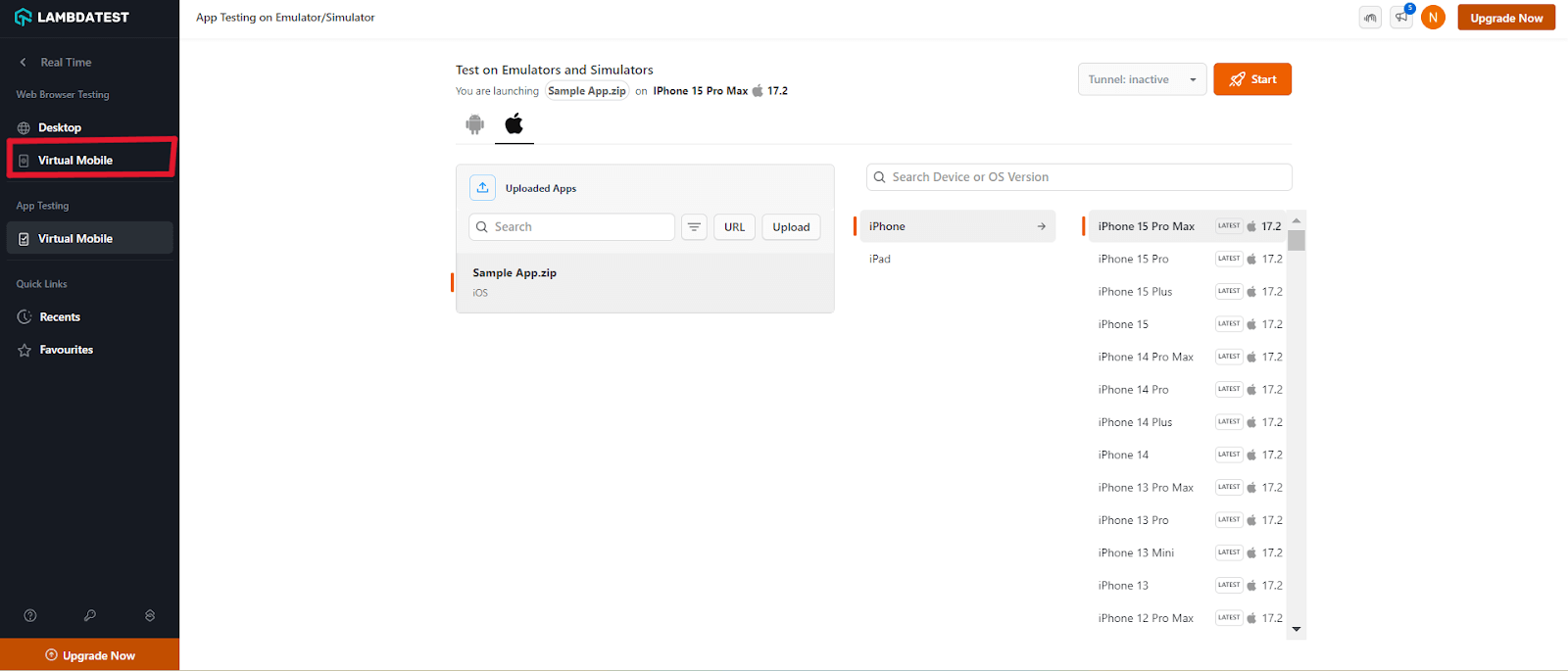
7. A test session will open based on the selected device-OS combinations.
8. From the left floating tool, click IP Geolocation. A dropdown menu will appear. Choose your desired country. In this example, we chose – Brazil.
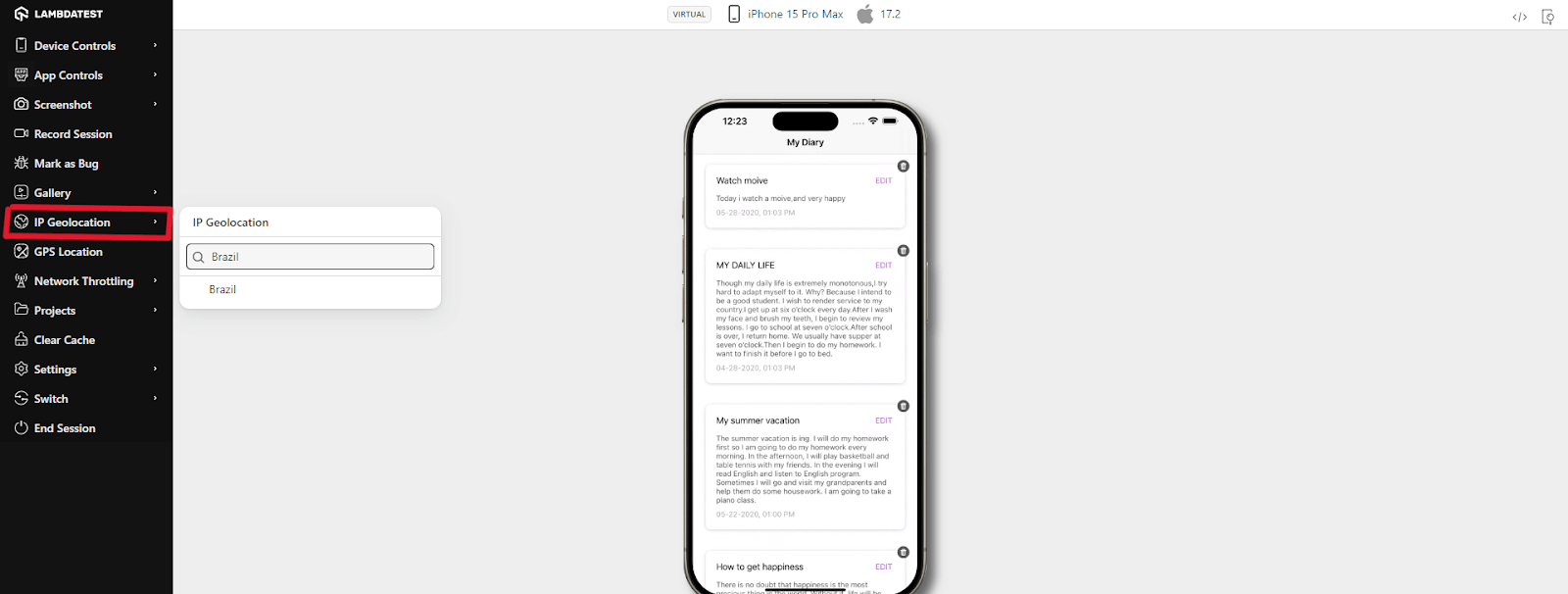
9. Selecting the desired country will route you to the Brazilian IP address.
Also, read – How To Test Mobile Applications Manually
Here is a quick video tutorial on performing mobile device cloud testing on LambdaTest.
You can also Subscribe to the LambdaTest YouTube Channel and stay updated with the latest tutorials around Selenium testing, Cypress testing, CI/CD, and more.
Challenges of Localization testing
Here are the following challenges of localization testing while performing software testing.
Best practices of Localization testing
Localization testing often comes with challenges such as long lead times, complex ROI measurement, and resource constraints. Following these best practices can help you overcome them:
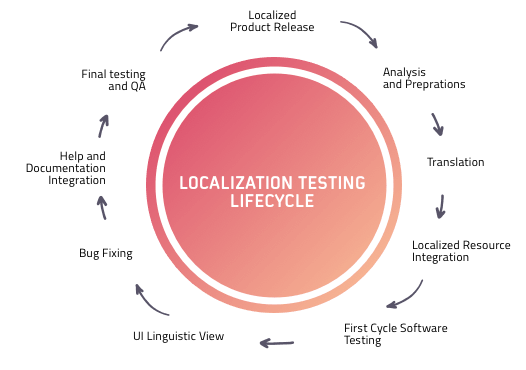
Read – Lessons For Writing Effective Test Cases
Conclusion
Website localization or mobile localization testing is more than checking translations, it ensures your product feels native, trustworthy, and usable in every market. By starting early, combining automation with human expertise, and testing across real devices and browsers, teams can avoid costly errors and deliver consistent experiences worldwide. With the right approach and tools like LambdaTest’s real device cloud and test orchestration platform, you can make localization testing faster, more reliable, and scalable.
Happy Testing!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is a localization tester?
A localization tester is a professional who verifies that a software application works correctly in different languages, regions, and cultures. They check translations, formats, UI layouts, and cultural elements to ensure the product feels native to local users.
What is localization with an example?
Localization is adapting software to a specific region or language. For example, an e-commerce app may display prices in U.S. dollars for American users but in euros for European users, along with region-specific date formats and tax rules.
Is localization testing functional or nonfunctional?
Localization testing is mainly considered nonfunctional testing because it focuses on usability, look-and-feel, and cultural accuracy rather than core business logic. However, it can include functional checks like payment methods and input validations specific to a locale.
How do you automate localization testing?
Localization testing can be automated by leveraging Selenium WebDriver. Localization automation testing is a type of non-functional testing in which the product’s localized version is cross-checked for a given cultural or locale settings.
What is globalization and localization testing in software testing?
Why is localization testing important in software development?
It helps businesses build trust, comply with local regulations, and improve adoption in new markets. Poor localization can hurt brand reputation and reduce conversions.
What are the key areas covered in localization testing?
It covers linguistic accuracy, date and currency formats, UI layout for different languages, right-to-left (RTL) support, input methods, and cultural relevance of images and symbols.
Can localization testing be automated?
Yes, parts of localization testing, like date formats, untranslated strings, and currency checks, can be automated using tools such as Selenium or Appium. However, linguistic and cultural validation usually requires human expertise.
What is pseudolocalization in localization testing?
Pseudolocalization is a technique where original text is replaced with fake but expanded characters (e.g., “Ŧĕśţ ŧęxţ”) to test how UI handles longer strings, encoding, and untranslated content before real translations are added.
What challenges are common in localization testing?
Common issues include text overflow, untranslated strings, encoding errors with special characters, broken RTL layouts, and culturally inappropriate visuals.
What tools are used for localization testing?
Popular options include Selenium, Appium, and Playwright for automation, along with cloud-based platforms like LambdaTest that provide access to 3000+ real browsers and 10,000+ devices for accurate locale testing.
Author