13 Best Android Emulators for Chromebook [2026]
Harish Rajora
Posted On: November 12, 2025
27 Min
Emulators for Chromebook are a great option if you want to run or test Android apps on your device. Chromebooks run on ChromeOS, which doesn’t natively support all Android apps, but these emulators can bridge that gap, allowing you to run or test your mobile apps seamlessly.
They also help you evaluate how your app behaves in different situations, like adjusting to larger screens, maintaining stability during regular use, or supporting features that may not fully work on ChromeOS. Using an emulator for Chromebook provides a more complete way to test your app without needing multiple physical devices.
Overview
Why Use Android Emulators on Chromebooks?
Android emulators let you test and refine apps without needing multiple physical Chromebooks. They help ensure consistent performance and compatibility across virtual devices.
What Are Some of the Best Android Emulators for Chromebooks?
Several Android emulators offer unique features for Chromebook users, helping test apps across different screen sizes, Android versions, and hardware setups. These tools make development and testing easier without needing multiple physical devices.
- LambdaTest: A cloud-based platform providing an online Android emulator with instant access to various screen sizes and Android versions for testing.
- Android Studio: IDE with built-in AVDs to test apps across configurable hardware profiles and Android versions on Chromebooks.
- Genymotion: Cloud and desktop emulator allowing precise customization of Android virtual devices for thorough Chromebook testing.
- Crosvm: Lightweight ChromeOS emulator supporting virtualization for efficient Android app testing on Chromebook hardware.
- Brunch Framework: Runs ChromiumOS on standard devices, creating Chromebook-like Android environments for development and app validation.
- ARChon: Chrome extension enabling APK execution in browsers, suitable for lightweight testing and debugging without full emulators.
- QEMU: Open-source emulator providing flexible Android virtualization and multi-architecture support for Chromebook testing.
- Appetize.io: Browser-based Android emulator allowing Chromebook users to upload APKs and run virtual devices without installation.
- MEmu Play: High-performance emulator optimized for gaming and app testing, supporting multiple instances on Chromebook hardware.
- Waydroid: Container-based Android emulator leveraging Linux Kernel for fast, direct hardware access and efficient app execution.
How to Choose the Right Emulator for Chromebooks?
Choosing the right emulator depends on your testing purpose, workflow, and Chromebook’s hardware capabilities. Consider these factors:
- Purpose of use: Identify whether you need it for testing apps, development, or gaming to select the most effective emulator.
- Platform type: Decide between cloud-based platforms or locally installed emulators for flexibility and resource management.
- Android version support: Ensure the emulator can handle the specific Android versions your app targets for compatibility testing.
- Hardware & resource needs: Check if your Chromebook can handle virtualization-heavy emulators or lightweight alternatives for smooth performance.
- Feature requirements: Determine if you need multi-instance support, device simulation, network throttling, or sensor testing.
- Ease of setup & maintenance: Some emulators need advanced setup, while others provide ready-to-use solutions with minimal configuration.
Do Emulators Really Match Real Device Testing?
Android emulators on Chromebooks allow app testing without physical devices but may not fully replicate real-world performance, gestures, sensors, or device-specific behavior. For precise testing, using a real device cloud like LambdaTest provides instant access to actual Chromebooks and Android devices, ensuring accurate app validation.
TABLE OF CONTENT
- Why Use Android Emulators?
- Best Android Emulators for Chromebooks
- LambdaTest
- Android Studio
- Genymotion
- ChromeOS Emulator (crosvm)
- ChromiumOS (Brunch Framework)
- ARChon
- QEMU
- Appetize.io
- MEmu Play
- Waydroid
- AirDroid Web
- BlueStacks
- ARC Welder
- Comparison of Chromebook Android Emulators
- Can You Run Android Emulators on Chromebooks?
- Choosing the Right Emulator
- Do Emulators Really Match Real Device?
- Use LambdaTest for Real Device Testing
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Why Use Android Emulators on Chromebooks?
Running an Android emulator on a Chromebook gives you access to virtual devices with different screen sizes, Android versions, and hardware configurations.
This allows you to:
- Behavior testing: Check how your app functions beyond ChromeOS limitations, including UI behavior and feature support.
- Feature validation: Test features that may not run natively on a Chromebook by using a full Android environment.
- Device profiles: Simulate multiple Android device configurations without relying on physical hardware.
- Large screen testing: Evaluate how your app adapts to Chromebook-sized displays, including layout behavior and performance.
For developers seeking accurate results, an Android emulator for Chromebooks provides a reliable way to test app performance, UI consistency, and compatibility across different Android environments, which isn’t always achievable through Play Store testing alone.
What Are Some of the Best Android Emulators for Chromebooks?
Exploring the best Android emulators for Chromebooks and their key features helps streamline mobile emulator for app testing. Emulators make it easier to test your app across different screen sizes, Android versions, and configurations without needing multiple physical devices, helping you ensure a smooth experience for Chromebook users.
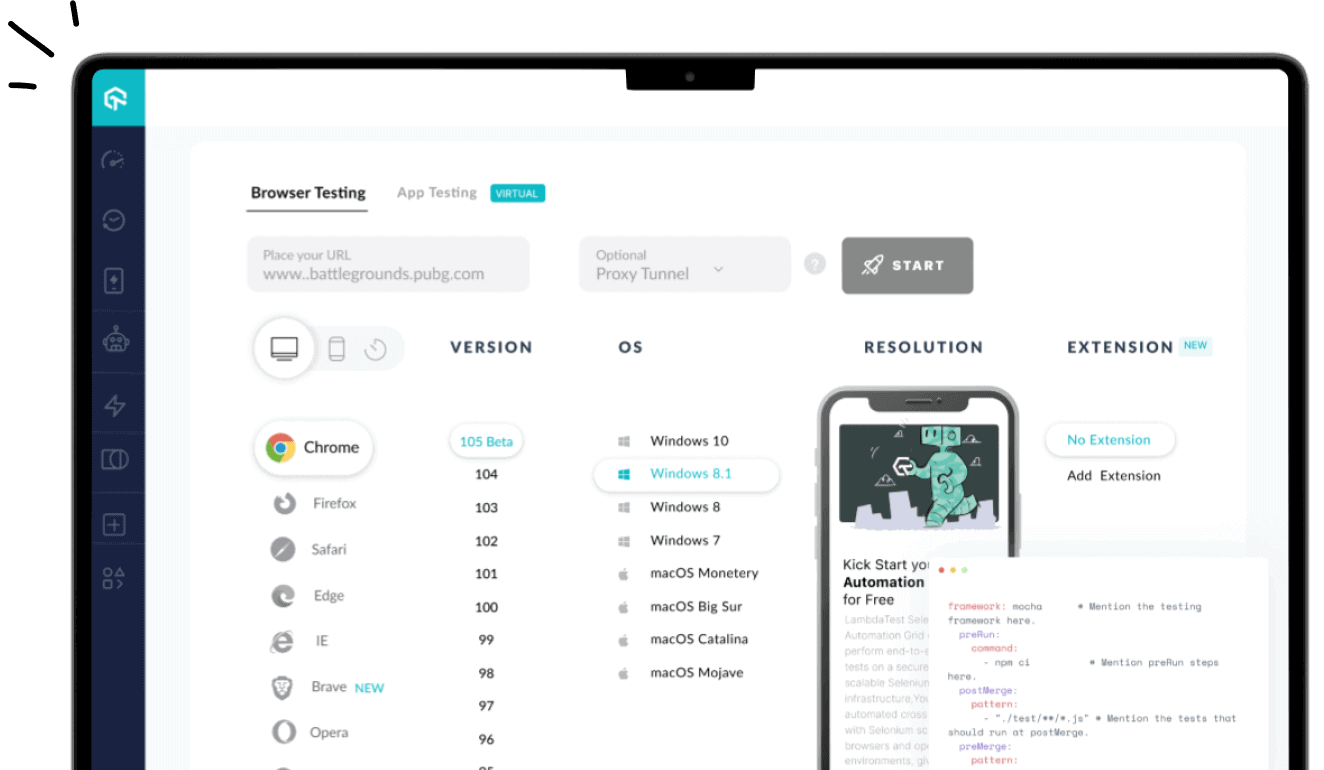
1. LambdaTest
LambdaTest is a cloud testing platform that enables you to perform mobile app testing on virtual devices, including Android apps on Chromebooks. It provides access to Android emulators online directly from your Chromebook, allowing you to test Android apps without the need for physical devices.
For small screens, you can test at 1366×768 resolution with a 14.0-inch display. For medium screens, LambdaTest supports 3840×2160 resolution on a 15.0-inch screen. On larger screens, testing is available at 1920×1080 resolution with a 17.0-inch screen. Refer to this ChromeOS testing guide.
Key features:
- Device Simulation: Emulate multiple Android devices and screen sizes directly on a Chromebook for accurate app testing environments.
- OS version flexibility: The emulator supports older Android versions (like 4.4) up to the latest (14.0), helping test app compatibility on Chromebooks.
- App Control: Install, launch, terminate, and uninstall APKs seamlessly within the emulator environment on Chromebook.
- Device Interaction: Simulate rotations, on-screen keyboard input, volume changes, shaking, and screen locking for realistic app behavior.
- Hardware Profile Simulation: Configure device RAM, CPU, and storage settings to mirror real Chromebook hardware in the emulator.
- App deployment: You can upload APKs and run them on any selected device virtually without requiring the physical device.
- Switch between OS types: Run tests across Android, iOS, and ChromeOS, while Chromebook users get optimized support for Android testing.
Test your Android apps on ChromeOS. Try LambdaTest Now!
2. Android Studio
Android Studio is a widely used IDE for Android development and can be installed on many Chromebooks via Linux (Beta). On compatible models with hardware virtualization, you may use its built‑in Android emulators for Chromebook to test apps across different Android versions and hardware profiles directly from ChromeOS.
Key features:
- Broad Android version compatibility: Android Studio allows Chromebook users to run AVDs across older, current, and preview Android versions efficiently.
- Hardware and sensor simulation: On Chromebooks, the emulator simulates accelerometer, GPS, orientation, network, and rotation for complete Android sensor testing.
- ChromeOS-supported system images: Chromebook users can utilize ChromeOS-specific system images from the SDK Manager to test apps on larger screens effectively.
- Configurable device profiles: Android Studio enables creating custom device profiles on Chromebooks with unique screen sizes, resolutions, RAM, and hardware configurations.
- Official and fast-release emulator builds: Chromebook users receive updated emulator versions and system images immediately because Android Studio is officially maintained by Google.
3. Genymotion
Genymotion is one of the leading emulators for Chromebooks, widely used for mobile testing and development. It offers multiple formats: as a SaaS-based emulator accessible via the cloud, as a device image for cloud platforms like AWS, and as a native desktop application for Windows, macOS, and Linux. When using it on a Chromebook, Genymotion’s SaaS version is ideal, specifically designed for automating tests on Android devices.
Key features:
- Custom device initialization: Provides options to define virtual device CPU, RAM, storage, screen resolution, and Android version precisely on Chromebooks.
- Automation integration: Supports integration with CI/CD pipelines, allowing Chromebook users to connect emulators with automated test frameworks directly.
- Multi-emulator management: The platform allows launching, configuring, and controlling multiple virtual Android devices simultaneously on a single Chromebook system.
- Sensor and network simulation: Provides configurable sensors, GPS, network speed, and device rotation for emulated Android devices on Chromebooks.
- Cloud-based device templates: Chromebook users can select from pre-configured cloud device images on Genymotion for rapid setup and standardized testing environments.
4. ChromeOS Emulator (crosvm)
Crosvm is a lightweight virtual machine monitor developed for ChromeOS, enabling developers to run an emulator for Chromebooks directly without physical devices. It allows Android virtual devices to simulate real hardware, including CPU, memory, storage, and GPU, ensuring accurate testing of apps on Chromebook-sized screens and proper interaction with ChromeOS features.
Key features:
- Hardware virtualization support: Enables you to utilize the host CPU, GPU, and memory efficiently for accurate testing.
- Device isolation: The emulator runs Android virtual devices in a sandbox, ensuring safe execution and preventing interference with ChromeOS operations.
- Integration with ChromeOS: Allows seamless execution of Android apps and emulators directly within ChromeOS without additional third-party software.
- Performance monitoring: Chromebooks using Crosvm can track CPU, memory, and I/O usage of Android emulators for optimization and troubleshooting.
- Custom VM configurations: Supports defining virtual CPU cores, RAM, and storage for precise Android emulator environments on Chromebook devices.
5. ChromiumOS (Brunch Framework)
Brunch Framework allows running ChromiumOS on non-ChromeOS devices, letting developers test the Android emulator for Chromebook-like environments effectively. It helps simulate Chromebook environments, deploy Android virtual devices, and validate app performance, responsiveness, and UI behavior without needing a physical Chromebook.
Key features:
- Cross-platform testing: Allows you to run ChromiumOS builds on standard laptops, ensuring effective app compatibility.
- ChromeOS-like environment: Emulators gain access to a simulated ChromeOS environment, replicating Chromebook behavior for accurate Android app testing.
- Kernel and driver support: Provides the necessary drivers and kernel modules to enable Android emulator execution in ChromiumOS virtual environments.
- Custom image deployment: Developers can install ChromiumOS images with Brunch, supporting various virtual devices and screen resolutions for emulator testing.
- Open-source development: Enables modifications and improvements, allowing testers to customize Android emulator environments for Chromebook-specific testing.
6. ARChon (ARChon Runtime for Chrome)
ARChon is a Chrome extension that allows running Android apps on Chromebooks by converting APK files to chromeos-apk. It works directly in the browser without installing a full emulator, making it one of the lightweight emulator for Chromebooks. While it does not offer pre-configured device profiles or hardware emulation, developers can run apps across different Chrome versions. ARChon is ideal for testing smaller apps or debugging browser-based behaviors without needing multiple Android devices.
Key features:
- Chrome extension-based emulator: Runs Android apps by installing a Chrome extension on Chromium-based browsers, including ChromeOS, Windows, macOS, and Linux.
- APK conversion requirement: Cannot run standard APK files directly and requires conversion into chromeos-apk format before execution on the emulator.
- No device selection: The platform does not provide pre-configured Android devices; developers must build and test binaries manually for each app version.
- Sandboxed execution: Android apps run within a Chrome sandbox environment, isolating the emulated instance from the host operating system.
- Cross-platform support: Allows Chromebook users to execute converted Android apps on multiple operating systems without installing additional emulator software.
7. QEMU
QEMU (Quick Emulator) is an open-source Android emulator for Chromebooks that provides virtualization and emulation of Android environments through Linux bindings. It enables developers to run Android applications on a virtualized system using Chromebook hardware without needing physical Android devices. QEMU supports multiple architectures and provides a flexible environment for testing and debugging Android apps on ChromeOS.
Key features:
- Full system emulation: Can emulate a complete Android environment on a Chromebook, simulating CPU, memory, and peripherals accurately.
- Multi-architecture support: Allow running x86, ARM, MIPS, and SPARC Android images seamlessly on Linux.
- Virtual disk management: Enables Chromebook users to create, modify, and manage virtual disks to store Android system images and app data efficiently.
- Snapshot support: Developers can save and restore system states in QEMU, allowing quick testing and rollback for Android apps on Chromebooks.
- Peripheral device integration: Allows integration of Chromebook hardware, like keyboard, mouse, and network interfaces, to Android virtual devices effectively.
8. Appetize.io
Appetize.io is a cloud-based platform that allows you to use emulators for Chromebooks to run apps directly in a browser. Users can upload APK files, select device profiles, and simulate Android devices without needing physical hardware, making it ideal for testing and validating apps on ChromeOS efficiently.
Key features:
- Browser-based access: Allows Chromebook users to launch Android emulators directly from a browser, eliminating the need for installation of local software.
- Multiple device simulation: Users can emulate different Android devices with varying screen sizes, resolutions, and OS versions for comprehensive testing.
- APK deployment support: Enables uploading and running APK files on the virtual Android devices directly from a Chromebook environment.
- Session configuration: You can set session parameters on Chromebooks, including device model, OS version, and runtime options for accurate app testing.
- Cloud-hosted environment: Runs entirely in the cloud, allowing Chromebook users to access consistent Android environments without relying on local system resources.
9. MEmu Play
MEmu Play enables users to run Android apps and games smoothly on their Chromebooks. Known for its compatibility and high-performance features, MEmu Play allows Chromebook users to experience Android with optimized gaming performance, including keymapping for keyboard and mouse control and enhanced frame rates for demanding applications.
Key features:
- Multi-instance support: Allows Chromebook users to run multiple Android emulator instances simultaneously for testing applications efficiently.
- Customizable hardware allocation: Users can set CPU cores, RAM, and graphics resources for each Android emulator instance directly on their Chromebook.
- Android version flexibility: The emulator supports multiple Android versions, enabling developers to run apps on different system images for accurate testing.
- Keyboard and mouse keymapping: Provides customizable keymapping to simulate touch inputs accurately for Android apps on Chromebook keyboards.
- High-performance rendering: The emulator optimizes frame rates and graphics rendering to ensure smooth Android app and game performance on Chromebooks.
10. Waydroid
Waydroid is an Android emulator for Chromebooks that runs in Linux mode. Using a container with direct hardware access requires some Linux Kernel adjustments during setup. It includes a minimal Android image based on LineageOS, providing improved performance and efficient app execution.
Key features:
- Containerized architecture: Uses container technology to run Android apps on Chromebooks without the heavy resource consumption of traditional virtual machines.
- Direct hardware access: Android applications in Waydroid can interact directly with the Chromebook hardware, enabling faster and more responsive performance.
- Minimal Android image: Uses a lightweight LineageOS-based Android image, reducing overhead while providing essential Android functionalities on Chromebooks.
- Linux-based integration: Runs within the Linux environment on Chromebooks, allowing seamless execution of Android apps alongside Linux applications.
- Performance optimization: The emulator leverages containerization and Linux Kernel access to deliver efficient Android app execution on Chromebook devices.
11. AirDroid Web
AirDroid Web is an application that can mirror the physical Android device connected to the platform. It just requires a QR code scan and works as a cast to a bigger screen, such as a Chromebook on a desktop.
Key features:
- Device mirroring via QR code: Users can mirror an Android device on a Chromebook by scanning a QR code quickly and securely.
- Cross-network device connection: AirDroid Web allows Android devices and Chromebooks to connect over the cloud, eliminating the need for the same local network.
- Chromebook-based control: Once mirrored, users can navigate Android apps using the Chromebook keyboard, mouse, and touchpad for precise interaction.
- Multiple device support: AirDroid Web can mirror up to five Android devices simultaneously to a Chromebook, enabling parallel testing and observation.
12. BlueStacks
BlueStacks is a powerful emulator for Chromebooks that works via a Chrome extension or cloud access. While widely used for gaming, it also allows developers and testers to install, run, and test Android applications directly on Chromebook devices. It supports multiple Android versions, keymapping, performance tuning, and customizable resource profiles, making it ideal for both app testing and casual use on ChromeOS.
Key features:
- Enhanced input controls: BlueStacks supports keymapping, mouse, and keyboard inputs on Chromebooks, providing precise control for Android applications and games.
- Cloud and ChromeOS installation: Chromebook users can access BlueStacks via a web platform or a Chrome extension for in-browser Android emulation.
- Automation rules with macros: BlueStacks allows users to automate sequences of actions with macros, streamlining repeated tasks and testing workflows on Chromebooks.
- Performance customization: Users can adjust memory, CPU allocation, and graphics settings on Chromebooks to optimize the emulator for Android applications.
13. ARC Welder
ARC Welder is an Android Runtime Chrome extension that serves as a lightweight emulator for Chromebooks, PC, Linux, and macOS. It just requires Google Chrome to be installed, eliminating the need to download and install heavy software on the system.
Key features:
- Chrome extension-based emulator: Runs as a Chrome extension, requiring no additional software installation to emulate Android applications on Chromebooks.
- Support for unhosted apps: Users can run unpublished or third-party APKs directly through ARC Welder without relying on Google Play Store distribution.
- Lightweight and fast execution: Provides low-resource emulation on Chromebook, enabling quick app launches and minimal lag during testing or use.
- Cross-platform: Supports Chromebook, Windows, Linux, and macOS, offering consistent Android runtime environments across multiple operating systems.
Best Android Emulators for Chromebook: Quick Comparison
Testing Android apps on Chromebooks can be challenging without the right emulator. The following table compares popular emulators based on type, setup, Android version support, device simulation, cloud availability, and best use cases.
| Emulators | Type | Android Version Support | Cloud Support | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LambdaTest | Cloud-based | 4.4 – 14 | ✅ | Quick cross-device testing without physical devices |
| Android Studio | Local IDE | Old, current, preview | ❌ | Full development & detailed app testing |
| Genymotion | Cloud & desktop | Multiple versions | ✅ | Automation & CI/CD, multi-device testing |
| ChromeOS Emulator (crosvm) | Local VM | Multiple versions | ❌ | Lightweight ChromeOS testing |
| ChromiumOS (Brunch Framework) | Local / cross-platform | Custom builds | ❌ | Chromebook-like Android environment testing |
| ARChon | Chrome extension | Depends on APK | ❌ | Lightweight app testing & debugging in browser |
| QEMU | Local emulator | Multiple architectures | ❌ | Flexible Android virtualization & debugging |
| Appetize.io | Cloud-based | Multiple versions | ✅ | Browser-based testing without installation |
| MEmu Play | Local / gaming-focused | Multiple versions | ❌ | High-performance gaming & app testing |
| Waydroid | Local container | Minimal LineageOS image | ❌ | Fast containerized Android execution |
| AirDroid Web | Browser-based / mirroring | Depends on device | ✅ | Device mirroring & interaction on Chromebook |
| BlueStacks | Local / cloud | Multiple versions | ✅ | Gaming, app testing, automation macros |
| ARC Welder | Chrome extension | Depends on APK | ❌ | Lightweight Android testing in Chrome |
Can You Run Android Emulators on Chromebooks?
Yes, you can run Android emulators on Chromebooks, but the experience depends on the Chromebook model and its hardware capabilities. ChromeOS already supports Android apps through the Google Play Store, so for basic app usage, you don’t need an emulator.
For development or testing, you can install Android Studio through Linux (Beta) and use its built-in emulator for Chromebooks. This works only if your Chromebook supports hardware virtualization and has sufficient RAM, since the emulator relies on Android Virtual Devices (AVDs) to create simulated Android environments.
An emulator is especially useful when you need to test your app on different device profiles, screen sizes, or Android versions, something that the Play Store environment alone cannot provide. For general users, most Android apps can be installed directly from the Play Store without needing an emulator.
How to Choose the Right Emulator for Chromebooks?
Selecting the right Android emulator for your Chromebook depends on your testing needs, development workflow, and system capabilities. With multiple options available, ranging from cloud-based platforms like LambdaTest and Appetize.io to local emulators such as Android Studio and Waydroid, it’s essential to evaluate key aspects before making a choice.
If you’re also working on Windows devices, many of the same principles apply. Android emulators for Windows, like BlueStacks, MEmu Play, or Genymotion, provide similar functionality, allowing app testing, development, or gaming, but are optimized for PC hardware and OS environments. This makes it easy to maintain consistency across platforms while testing your Android apps.
Consider the following factors:
- Purpose of use: Determine if you need the emulator primarily for app testing, development, or gaming. For instance, BlueStacks and MEmu Play are optimized for gaming, while LambdaTest and Android Studio are ideal for professional testing and development.
- Platform type: Decide between cloud-based emulators or local installation. Cloud-based emulators like LambdaTest or Appetize.io offer easy access without requiring hardware resources, while local options like Waydroid and QEMU provide full hardware integration and offline testing.
- Android version support: Ensure the emulator supports the Android versions relevant to your apps. Emulators like Android Studio and Genymotion allow testing across multiple versions, from older releases to the latest Android builds.
- Hardware and resource needs: Check your Chromebook’s hardware capabilities. Some emulators, such as Crosvm or Waydroid, leverage hardware virtualization for performance, while others, like ARC Welder, are lightweight and suitable for lower-spec devices.
- Feature Requirements: Identify the essential features you need, such as device simulation, sensor testing, network throttling, or multi-instance support. Platforms like LambdaTest and Genymotion offer extensive testing features, whereas ARChon and AirDroid Web are better suited for lightweight app testing or device mirroring.
- Ease of setup and maintenance: Some emulators require kernel modifications or complex setup (Waydroid, Brunch Framework), while cloud platforms and Chrome extensions (Appetize.io, ARC Welder) are ready to use with minimal configuration.
By evaluating your requirements across these areas, you can select an Android emulator for Chromebook that best matches your development or testing workflow, ensuring accurate app performance, compatibility, and productivity.
Do Emulators Really Match Real Device Testing?
Android emulators for Chromebooks provide a convenient way to run and test apps without needing physical devices. However, when it comes to precise results, an Android emulator for app testing may have limitations compared to real Chromebook hardware.
Emulators often cannot perfectly replicate performance, network behavior, touch gestures, sensors, or device-specific quirks found on actual Chromebooks. This can result in differences in app responsiveness, UI rendering, and overall functionality.
To overcome these challenges, you can use a LambdaTest real device cloud offers instant access to real Chromebooks and Android devices, helping developers and testers validate their apps in real-world conditions without maintaining a physical device lab.
Why Use LambdaTest for Real Device Testing for Chromebooks?
LambdaTest provides instant access to a wide range of Android devices without the need to maintain an in-house device lab. It helps developers and testers identify device-specific issues early, ensures apps perform consistently across models, and accelerates the release cycle by enabling remote and scalable testing. With LambdaTest, you can test on real devices from anywhere, ensuring your app delivers a seamless experience to all users.
Testing on real devices provides several key advantages over emulators:
- Extensive coverage: Test Android apps across multiple Chromebook models and Android versions to ensure compatibility.
- Real-time interaction: Experience app behavior on actual devices, including touch, multitasking, and hardware-specific interactions.
- Parallel testing: Run multiple tests on different Chromebooks simultaneously, reducing QA time.
- Accurate network simulation: Validate app performance under real network conditions like Wi-Fi, 4G, or 5G.
- Hardware & sensor accuracy: Test accelerometer, orientation, camera, and other sensors reliably on real devices.
- Automated testing support: Integrate with frameworks like Appium and Espresso to automate tests on Chromebooks.
Using emulators is helpful for early development or quick testing, but real device testing ensures your Android apps run smoothly on actual Chromebooks.
Testing Android apps on Chromebooks can be challenging without the right emulator. The following table compares popular emulators based on type, setup, Android version support, device simulation, cloud availability, and best use cases.
Conclusion
Android emulators for Chromebooks are a sought-after way to run and test Android applications on ChromeOS without purchasing a new device. From cloud-based options like LambdaTest to Chrome extensions like ARChon, each emulator has a different setup method and performs differently. The list above helps explore all these Android emulators for Chromebook so that a user, a tester, or a developer can select one that suits their needs, requirements, and projects the most.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can ARM apps run on x86 Chromebook emulators?
Yes, most emulators like Android Studio or Genymotion use ARM translation layers to run ARM apps on x86 virtual devices. Performance may be slower, and apps using native ARM libraries can sometimes crash or behave unexpectedly.
Do emulators match real Chromebook graphics?
Not exactly. Emulators simulate screen resolution and density but may not replicate GPU performance, color calibration, or refresh rates perfectly. UI-heavy or graphics-intensive apps should still be tested on actual devices for accurate results.
How do I handle keyboard and touch input differences?
Emulators map mouse clicks to taps and gestures. Multi-touch or pinch-zoom may be limited unless your Chromebook has a touchscreen. Some allow keyboard shortcuts to simulate gestures, but real-device testing may still be needed for precise interactions.
Can emulators test ChromeOS-specific integrations?
Partially. Features like drag-and-drop between apps, file system access, or ChromeOS notifications may not fully work. For testing interactions unique to ChromeOS, real devices provide more accurate results.
Do emulators affect app performance metrics like FPS or memory usage?
Yes. Emulators simulate hardware using your Chromebook’s CPU and GPU. Metrics like frame rate, memory, and battery consumption may differ from real devices, especially for graphics-heavy apps or apps running background tasks.
Can I test app notifications reliably on emulators?
Mostly. Push notifications work with Google Play Services, but background app restrictions or battery optimizations on real Chromebooks may behave differently than in emulators.
How do ChromeOS updates affect emulators?
Updates can impact Linux container settings, GPU acceleration, or networking. Some emulators may need reconfiguration or updates to work properly, so testing after OS updates is recommended.
Are cloud-based emulators reliable for testing local files?
Not fully. Cloud emulators cannot access your Chromebook’s local storage, which may affect apps that read or write files locally. Local emulators or Linux-based setups are better for this type of testing.
Can emulators be integrated into automated testing pipelines on Chromebooks?
Yes, but it’s more complex than on desktops. You need Linux container support (Crostini), headless emulator configuration, and networking setup. Once configured, emulators like Android Studio or Genymotion can run CI/CD tests.
Will running multiple emulators cause network issues?
Potentially. Each emulator runs its own virtual network. Running several simultaneously can cause IP or port conflicts, which may break server connections or app communication, especially for networked apps.
Author