Point of Sale (POS) Testing
Urwashi Priya
Posted On: November 30, 2023
![]() 212028 Views
212028 Views
![]() 11 Min Read
11 Min Read
The retail industry, including physical stores and e-commerce, have experienced significant shift. In the light of rapidly evolving technological developments, business owners emphasize the security of transactional data on the backend for processing and approval as well as a seamless user experience on the front end of their online platforms.
Think of a busy retail space, loaded shopping carts, and the thrill of a smooth checkout process. It is the outcome of a well tested and well-oiled Point of Sale (POS) system!
In this blog we will look at what a Point of Sale system is and why is it important. Furthermore, we shall look into the significance of POS Testing, how it is different from conventional software testing and finally, we wrap it up looking at some of the best practices for doing POS Testing.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
- What is a Point of Sale (POS) System?
- Consequences of a Failing Point of Sale(POS) System
- Importance of Point of Sale(POS) Testing
- Types of Point of Sale(POS) Testing
- Physical Components of POS Systems and How to Test Them?
- How is Point of Sale(POS) Testing Different?
- Challenges in Point of Sale(POS) Testing
- 8 Best Practices for Point of Sale(POS) Testing
- Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
What is a Point of Sale (POS) System?
Point of Sale(POS) system is a digital cash register in retail stores and restaurants. It helps calculate the total cost of the items, add tax, take payment, manage inventories, sales reports, customer data, and transactions. It serves as a central point where customers make payments for goods or services. Now the question arises, what is POS testing? We can think of it as meticulous quality control for the digital cash registers. POS testing is a practice of testing the functionalities of a POS System. It includes security, peripheral device connectivity, and payment processing, ensuring a dependable and error-free transaction experience for both consumers and companies.
Consequences of a Failing Point of Sale(POS) System
When a POS system fails, the consequences can be severe:
- Lost Sales: Transaction failures can result in lost sales, and customers may abandon their purchases due to delays or errors.
- Customer Frustration: Frustrated customers may avoid returning to a business with a malfunctioning POS system, impacting customer loyalty.
- Data Breaches: Security vulnerabilities can lead to data breaches, potentially causing severe financial and legal consequences.
- Operational Chaos: Businesses can experience overstocking or shortages when their POS system does not work.
Remember Target’s 2013 Data Breach? Target suffered a massive data breach due to vulnerabilities in its POS system. Hackers gained access to customer credit card data, affecting millions of customers. It teaches us that protecting POS systems is pivotal in ensuring customer data security and trust in the digital world.
Importance of Point of Sale(POS) Testing
POS testing ensures the smooth operation of Point of Sale systems. Let’s look at the crucial role of POS testing in maintaining system functionality.
- Transaction Accuracy: POS systems handle a high volume of transactions daily. POS testing ensures that they accurately calculate prices, apply discounts, and process various payment methods without errors.
- Data Security: Customer payment information and personal data are at stake. POS testing verifies that these systems are secure against data breaches and unauthorized access.
- Inventory Management: Many POS systems are integrated with inventory management. POS testing guarantees that inventory levels are accurately tracked and prevent discrepancies.
- Business Reputation: A well-functioning POS system enhances customer experience, enhancing a business’s reputation. It ensures that customers can complete transactions smoothly and without delays.
Types of Point of Sale(POS) Testing
The POS system operates at two levels, each requiring distinct types of testing:
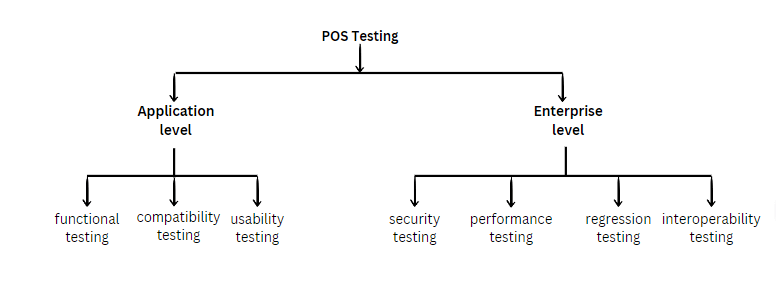
Application Level
At the application level, the testing primarily concentrates on the functionalities and user interface of the POS system. Different types of testing used at this level are:
- Functional Testing: Checks if the POS system functions as expected. Ensures core functionalities like item scanning, payment processing, and receipt generation work accurately without errors.
- Compatibility Testing: Checks compatibility with different hardware and software configurations. Ensures seamless operation with diverse hardware components and software environments, offering flexibility for businesses with varying equipment.
- Usability Testing: Evaluates the system’s user-friendliness and customer experience. Ensures the POS interface is intuitive, easy to navigate, and meets customer expectations, enhancing the checkout process and customer satisfaction.
Enterprise Level
At the enterprise level, the testing focuses on broader aspects like security, performance, and integration with external systems. Different types of testing used at this level are:
- Security Testing: Identifies vulnerabilities and weaknesses in the system’s security. Assesses the system’s resistance to data breaches and unauthorized access, ensuring customer payment information is encrypted and protected.
- Performance Testing: Evaluate the system’s performance under various conditions. Ensures the system can handle peak transaction loads without slowdown or crashes, optimizing performance and preventing delays during busy hours.
- Regression Testing: Verifies that updates or changes do not negatively impact existing functionalities. Maintains system stability and reliability by preventing new bugs or issues from being introduced with software updates.
- Interoperability Testing: Assesses how well the system integrates with external systems. Examines the integration with payment gateways, inventory management, and CRM systems, ensuring smooth communication and data exchange.
Take your Point of Sale (POS) testing strategies to the next level with Top 267+ Retail Test Cases.
Physical Components of POS System and How to Test Them?
Let’s explore the physical components of POS systems and their testing focus.
- Terminal: The POS terminal serves as the primary interface for transaction entry. Testing professionals validate the accuracy of product lists, pricing, offers, payment modes, verify the network connection, and update the operating system for software support.
- Display Pole: Display showcases the price of scanned items. Testing professionals verify the accuracy of the prices here and ensure these are in sync with the POS terminal.
- Barcode Reader: It is used to scan the product and perform backend checks. Testing professionals carefully check the system to make sure that all inventory items are scanned accurately, paying special attention to those without price tags. They also confirm that the scanning process is spot-on for items with the right price tags.
- Cash Register: This acts as the central location for cash transactions. When the point-of-sale operator chooses the cash payment option, the Cash Register opens automatically. A thorough validation of financial transactions is ensured by ensuring the Cash Register accurately records deposited/refunded amounts.
- Handheld Device: This facilitates wireless card payments. Testers verify the precision of manual amount entry, guaranteeing accuracy in every wireless card transaction.
- Printer: Printer is connected to terminals for receipt generation. It is tested for receipt printing precision, alignment, text, and font accuracy. Error handling scenarios, such as printer readiness and paper availability, including system responses during printer downtime mid-transaction.
- Magnetic Swipe Reader (MSR): It is designed for swiping payment cards. Testers validate balance checks, expiry dates, and payment transactions to ensure efficient initiation and prompt issuance of printed receipts.
How is Point of Sale(POS) Testing Different?
Point of Sale (POS) testing is distinct from conventional software testing processes due to its unique focus on customer-facing transactions and its critical role in a business’s daily operations.
| Aspect | POS Testing | Conventional Software Testing |
| Focus | Customer-facing transactions, payment processing, and system integration with peripheral devices. | Overall software functionality, including features, usability, and performance across different services. |
| Purpose | Ensures accuracy, efficiency, and security of point-of-sale operations. | Ensures software quality, reliability, and usability for the business’s end users. |
| Testing Focus | Customer experience, data security, and system performance under high transaction volumes. | Overall software behavior, identifying bugs, and ensuring user acceptance. |
| Compliance | Validates adherence to PCI DSS(Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard), ensuring secure handling of sensitive payment information. | Ensures compliance with industry standards and regulatory requirements, depending on the business domain. |
| Peripheral Devices | Tests integration with barcode scanners, receipt printers, and card readers. | Primarily focuses on software functionalities, and may not extensively test hardware integrations. |
| Criticality | Critical for businesses relying on POS systems for daily transactions, ensuring smooth customer experience; for example, a retail store. | Important for all software applications, but time-sensitiveness depends on the business domain. |
Whether it’s Point-of-Sale (POS) testing or conventional software testing, understanding the critical role testing plays in a product’s success is the key here. LambdaTest is an AI-powered test orchestration and execution platform that stands out as a leading cloud platform to test websites and mobile apps on more than 3000+ combinations of browsers, real devices, and operating systems. With LambdaTest’s Real Device Cloud, you can take the software testing experience even further by running tests on real devices to get a sense of how your product works on different types of devices.
Challenges in Point of Sale(POS) Testing
Let’s have a look at the challenges faced in POS testing:
- Diverse Hardware and Software Environments: POS systems need to work with a wide range of hardware components, such as barcode scanners, receipt printers, and various software environments, including different operating systems. Ensuring compatibility across this diversity is a significant challenge.
- Data Security Concerns: Given the sensitive nature of customer payment data, maintaining data security is a top priority. Testing for vulnerabilities and ensuring robust encryption is challenging but essential to protect customer information.
- Integration with External Systems: Interoperability with external systems like payment gateways and inventory management is critical.
- Scalability: As businesses(like retail stores, restaurants, and hotels) grow, the POS system must scale. Ensuring the system accommodates increasing products, customers, and transactions without performance degradation is a persistent challenge.
- Data Backup and Recovery: Testing the effectiveness of data backup and recovery processes to safeguard against data loss or hardware failures requires meticulous planning.
8 Best Practices for Point of Sale(POS) Testing
Let’s look at some of the best practices which one must adhere to for POS Testing:
- Clear Test Plan: Develop a well-structured test plan outlining the scope, objectives, and specific test cases for a comprehensive evaluation of the POS system.
- Realistic Test Data: Utilize diverse and real-world test data, including various product types, prices, and payment methods to replicate actual scenarios.
- End-to-end Testing: Ensure end-to-end testing that covers the complete sales process, from item scanning to payment processing and receipt generation, to evaluate the smooth operation of the entire system.
- User Acceptance Testing (UAT): Engage actual users or representatives of your target audience to conduct UAT. Their feedback is essential to validate the system’s user-friendliness and alignment with user expectations.
- Use Automation: Consider implementing test automation tools to streamline repetitive and regression testing, saving time and enhancing test coverage.
- Data Backup and Recovery Testing: Regularly verify the efficiency of data backup and recovery procedures to ensure critical data can be restored in case of hardware failures or data loss.
- Compliance Testing: If your business operates within a regulated industry, ensure that the POS system complies with industry-specific regulations and standards.
Conclusion
In exploring Point of Sale (POS) testing, we’ve uncovered its pivotal role in managing transactions, data security, and business inventory. Failing POS systems can lead to lost sales and data breaches. We’ve highlighted various POS testing types, challenges faced, and the best practices of POS testing. In a competitive market where customers demand smooth experiences, POS testing becomes the reason for success, assuring adaptability, data protection, and a good reputation for businesses.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the difference between POS System and POS Testing?
POS (Point of Sale) systems are used by businesses to streamline transactions, manage inventory, and enhance overall operational efficiency, while POS Testing focuses on validating the functionality and reliability of the POS system.
Where are POS Systems used?
POS Systems are used across diverse industries, including retail stores, restaurants, hospitality establishments, salons/spas, and service-oriented businesses.
Got Questions? Drop them on LambdaTest Community. Visit now