Cypress Automation Tutorial: E2E Testing with Cypress
Sachin
Posted On: July 1, 2021
![]() 288420 Views
288420 Views
![]() 16 Min Read
16 Min Read
The demand for Cypress automation testing has increased exponentially with the need to deliver products faster to the market. As per the State of JS survey 2021, Cypress awareness has climbed from 74% in 2020 to 83% in 2021 with 92% satisfaction. Cypress has emerged as a prominent tool for web automation testing in recent years addressing fundamental issues faced by modern web applications. Now Selenium testing has been widely accepted for web automation testing. Which often triggers a debate around Selenium vs Cypress, however, this article isn’t just about resolving the Selenium vs Cypress debate. This is going to be on help you perform Cypress automation testing like a pro.
In this Cypress tutorial, we talk about the Cypress test automation framework that is fundamentally and architecturally different from the Selenium test automation. How to set up and install Cypress and finally, run Cypress automation testing over hundreds of browsers and operating systems using the LambdaTest Cypress cloud.
TABLE OF CONTENT
Introduction To Cypress Automation Testing Framework
Cypress is a purely JavaScript-based front-end testing framework that lets you easily write powerful and flexible tests for your web applications. It enables advanced testing options for both unit tests and integration tests with benefits such as easy test configuration, convenient reporting, intuitive dashboard experience, and more.
As Cypress supports only JavaScript, it is widely accepted by the developer community. It also has a huge following (around 32K GitHub stars) from developers and QA engineers since the time was publicly released for the community.
So why Cypress automation is considered an alternative to Selenium?
Let’s take a look at the architectural differences between Cypress and Selenium and how Cypress is resolving the problems faced in modern-day web application testing.
Get the best out of your Cypress tests with LambdaTest’s online Cypress automation tool. Check out how you can execute your Cypress test scripts using LambdaTest’s online cloud.
Understanding Selenium Architecture
Selenium WebDriver is a powerful tool for developers that lets you perform automation tests across different browsers. This architecture includes a Selenium server that runs your tests, browser driver corresponding to the browser (under test), and ‘N’ number of clients that communicate with the server, typically in the language supported by the Selenium framework.
Shown below is the top-level architecture diagram of the Selenium 3 framework:
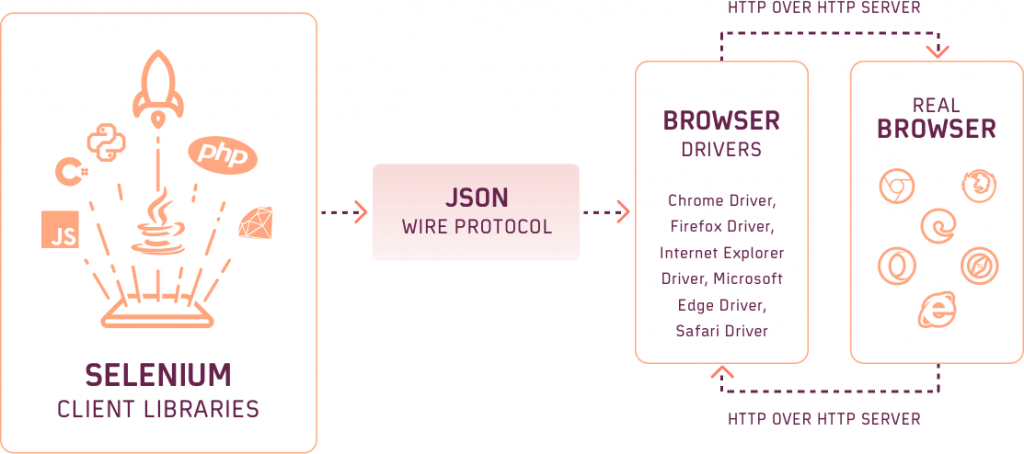
As of writing this blog, Selenium 4 is in the beta stage and open to use for the community. Selenium 4 is W3C compliant which means that test flakiness will be significantly reduced with Selenium 4. A couple of features of Selenium 3 are deprecated in Selenium 4, you can make sure to check what is new in Selenium 4 and what is deprecated in it.
Read – How To Upgrade From Selenium 3 To Selenium 4?
Now, let’s dive into Cypress architecture and its breakthrough features to understand the difference with Selenium.
Understanding Cypress Architecture
Cypress is an open-source testing framework based on JavaScript that supports web application testing. Unlike Selenium, Cypress automation testing works completely on a real browser without the need for driver binaries. The automated code and application code share the same platform, which gives complete control over the application under test.
To describe the backend story of Cypress test automation, let’s have a look at its high-level architecture.
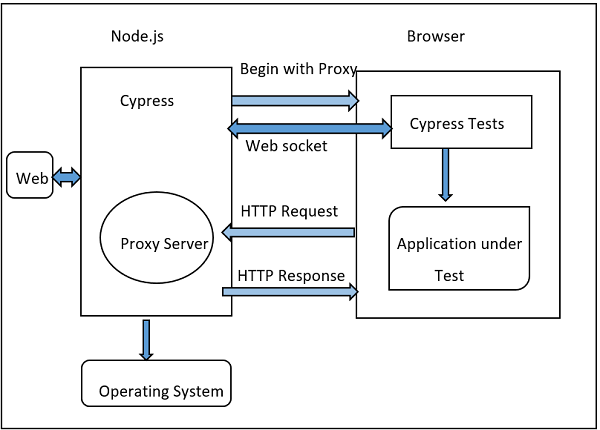
Cypress automation testing runs on NodeJS server, which communicates with the test runner(Browser) instrumentalized by Cypress to run the application (one of the iframe) and test code(another iframe) in the same event loop.
Here’s quick video if you have doubts regarding how to handle iframes in Cypress.
This in turn allows the Cypress automation testing code to mock and even change the JavaScript object on the fly. This is one of the primary reasons why Cypress automation testing is expected to execute faster than corresponding Selenium test automation.
Watch this video to learn how Cypress can be used to automate accessibility testing.
Key benefits of using Cypress test automation framework:
- Cypress is easy to set up.
- Cypress has an in-built wait for requests feature that eliminates the need to configure additional waits.
- There is no need for driver binaries in Cypress automation testing and execution happens on the real browser.
- Since test code and application run in the same browser, it can access application JS objects.
- Cypress automation testing lets you change code and execute the same on the fly .
- It provides dashboard support for detailed reporting.
- It supports parallel test execution.
- It has support for BDD and TDD style testing.
- Cypress tests are less flaky due to the auto-wait features supported by the framework.
- At each step, screen grabs that show the test behavior are captured. These can be super helpful in debugging issues with the tests.
- Detailed documentation and thriving community.
Read- Selenium vs. Cypress – Which Is Better in 2021?
Setting Up Cypress Automation Testing
Cypress requires Node JS (>= 12) to be pre-installed on the machine. It is bundled into a singleton package which can be added to your node_modules with npm or yarn using the following commands:
npm install cypress
OR
yard add cypress.
Note: Make sure you have initialized your folder with npm init or package.json file is created under your project folder.
Once Cypress packages are added to your project directory, you should be able to see the cypress folder added to your project with pre-added tests for sample testing.
Cypress Test runner
To open Cypress test runner and view the pre-added tests, run the following command on the terminal:
npx cypress open
If you manage commands through package.json, then you might write it under scripts that would look something as shown below. In that case, use the following command:
npm run cy:open
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
{ ... "scripts":{ "cy:open":"cypress open", ... } ... } |
Once you execute the command, the test runner would show up as seen below:
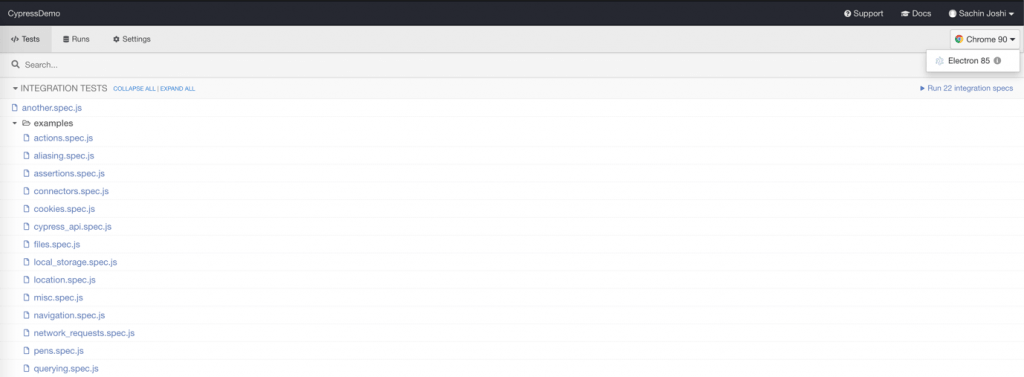
As in the above screenshot, you can choose to run the specific test by selecting one or run all at the root folder. You can also run the tests by selecting a browser via CLI:
npx cypress run -- --browser chrome
Additionally, to run specific file use:
npx cypress run -- --browser chrome --spec ''
Sample Code
actions.spec.js file is written with Mocha style and uses Cypress built-in commands to launch and interact with the browser. If you’re new to Mocha, you can refer to this Mocha tutorial.
List of a few commands that we would be using is shown below:
- cy.visit() – Launch a browser with the URL provided as the argument
- cy.get() – Get the elements using CSS-selectors
- type()- Enter the value in input boxes
- {keyCommand} like “{enter}” – Write keyboard actions
- Asserts command – Cypress automation testing uses its own BDD style of assertions inspired by likes of Chai
There are a whole bunch of advanced commands around Cypress API, which you can check on the Cypress official website.
For demonstration of Cypress test automation, we use the Kitchen Sink example which is available on the official GitHub of Cypress.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 |
describe('Actions', () => { beforeEach(() => { cy.visit('https://example.cypress.io/commands/actions') }) // https://on.cypress.io/interacting-with-elements it('.type() - type into a DOM element', () => { // https://on.cypress.io/type cy.get('.action-email') .type('fake@email.com').should('have.value', 'fake@email.com') // .type() with special character sequences .type('{leftarrow}{rightarrow}{uparrow}{downarrow}') .type('{del}{selectall}{backspace}') // .type() with key modifiers .type('{alt}{option}') //these are equivalent .type('{ctrl}{control}') //these are equivalent .type('{meta}{command}{cmd}') //these are equivalent .type('{shift}') // Delay each keypress by 0.1 sec .type('slow.typing@email.com', { delay: 100 }) .should('have.value', 'slow.typing@email.com') cy.get('.action-disabled') // Ignore error checking prior to type // like whether the input is visible or disabled .type('disabled error checking', { force: true }) .should('have.value', 'disabled error checking') }) it('.focus() - focus on a DOM element', () => { // https://on.cypress.io/focus cy.get('.action-focus').focus() .should('have.class', 'focus') .prev().should('have.attr', 'style', 'color: orange;') }) } |
Here is the execution snapshot of the test running on the Chrome browser:
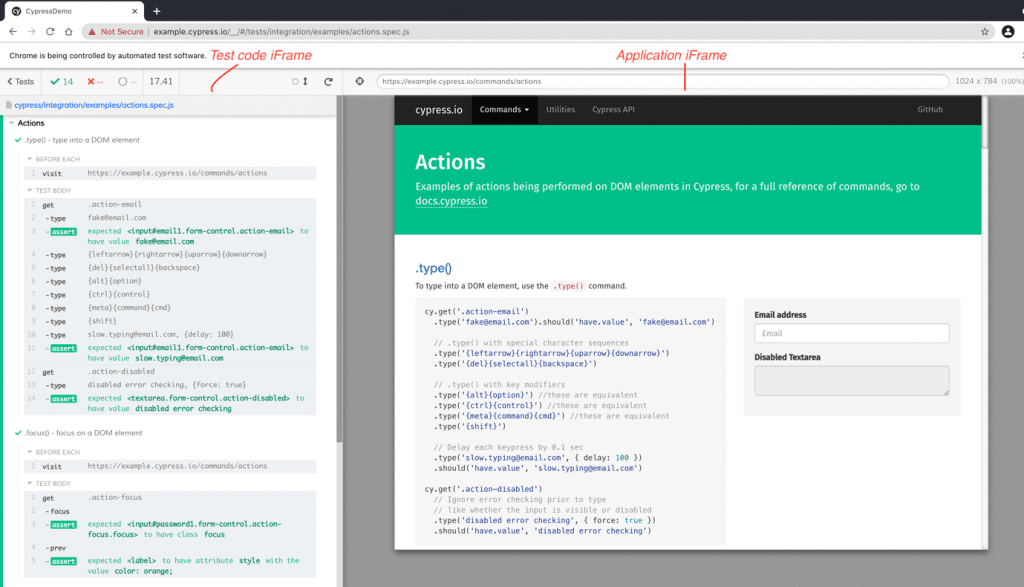
Defaults to Spec reporter in the console output:
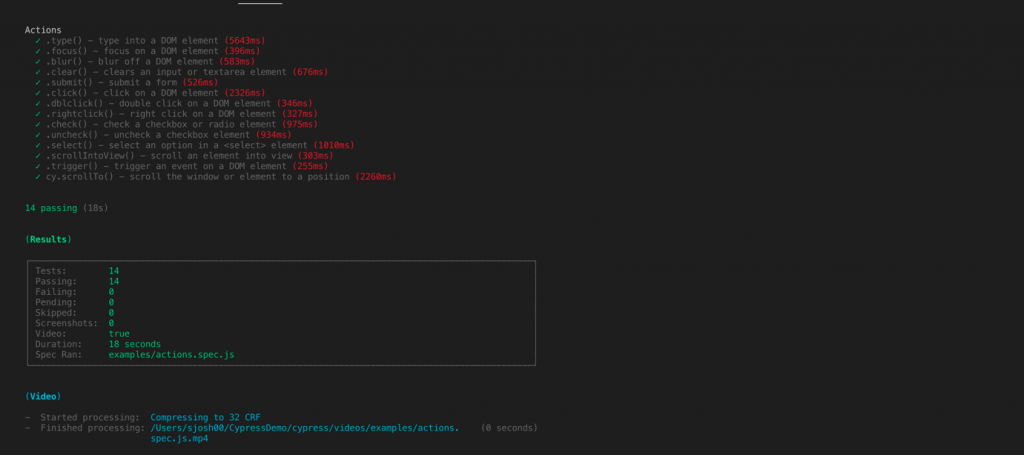
The amazing part to notice about execution is that it auto records your test execution and stores it as a .mp4 file for viewing or sharing with other members in the team.
Dashboard services of Cypress test automation framework
While test runner does a wonderful job of running tests and storing the recorded session for execution, Cypress automation testing provides more amazing features through its paid services. The paid services are completely optional for use but CI integration and parallelization of test runs stand out from the rest.
Some of the key features of dashboard services include:
- Allows tests to run parallel with CI setup.
- Allows tests to be grouped and run for multilevel environments or browsers.
- Easily integrates with CI tools.
- Provides insights into your historical runs.
- Auto balancing feature to reduce the load on CI servers.
Read – Top CI/CD Tools
Configuring test to run in the dashboard
For running tests in Dashboard services, we need to create an account on Cypress Dashboard. Follow the below steps for creating a projectId and record key.
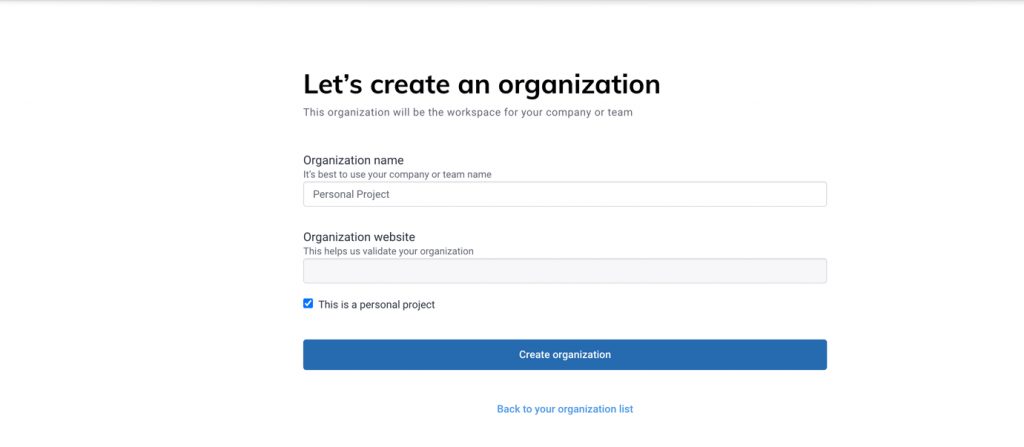
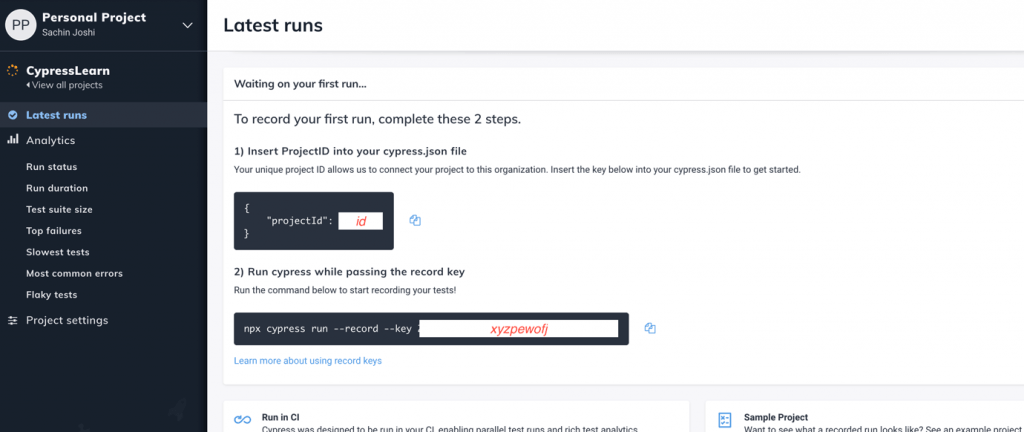
Add your projectId on the cypress.json file:
|
1 2 3 |
{ "projectId": "" } |
Execute tests on Cypress Dashboard with:
npx cypress run --record --key
Try your free Cypress UI automation testing online.
Setup Cypress Automation Testing with Cloud-based Selenium Grid
While the Cypress testing framework does let you run tests in parallel, achieving optimal browser coverage is impossible when running tests on a local setup. For optimal browser coverage, you need to upgrade your test infrastructure to a Grid-based system so that you can leverage Cypress framework for performing Cypress UI testing on different browsers and operating systems.
The need for a cloud-based cross browser testing platform like LambdaTest can help resolve the underlying problems to a great extent. Let’s now write a simple Cypress automation testing and see it in action on the LambdaTest platform.
In this guide for setting up the Cypress test automation framework, we’ll also explore how to seamlessly integrate Cypress-docker containers for efficient testing. Learn more about Cypress-docker here.
Step 1: Create a new spec file.
Create a new spec file google.spec.js under /cypress/integration folder. In the test code, we are searching Cypress on Google and verifying the results containing Cypress as a keyword.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
describe('Search Cypress on Google',()=>{ it('Open google site',()=>{ cy.visit('https://www.google.com/') }) it('search cypress term in search bar',()=>{ cy.get('[name="q"]').should('be.enabled').type('Cypress{enter}') }) it('Check the results of search',()=>{ cy.get('#search').should('be.visible') cy.get('#search').contains('Cypress').should('be.visible') }) }) |
Step 2: Install the LambdaTest Cypress CLI:
LambdaTest Cypress CLI enables cross browser testing with Cypress. It lets you test your application across different browsers without any hiccups!
Install lamdatest-cypress cli package using npm install lambdatest-cypress-cli under the project root directory. Once installed, lambdatest-config.json is created using the npx lambdatest-cypress-cli init command, which looks like below:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 |
{ "lambdatest_auth": { "username": "", "access_key": "" }, "browsers": [ { "browser": "Chrome", "platform": "Windows 10", "versions": [ "90.0" ] }, { "browser": "Firefox", "platform": "macOS Big Sur", "versions": [ "82.0" ] } ], "run_settings": { "cypress_config_file": "cypress.json", "build_name": "LambdaCypress", "parallels": 1, "specs": "./cypress/integration/*.spec.js", "ignore_files": "", "npm_dependencies": { "cypress": "6.1.0" }, "feature_file_suppport": false }, "tunnel_settings": { "tunnel": false, "tunnelName": null } } |
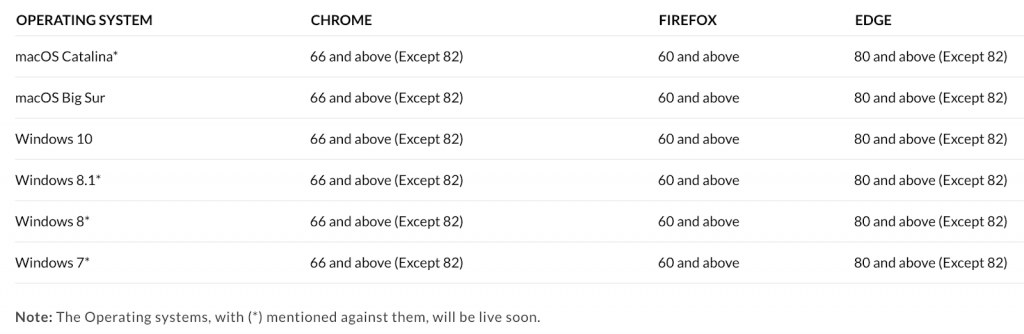
In the above config file, we are specifying browsers Chrome and Firefox with the desired versions and platform configurations. As of writing this blog, LambdaTest supports the following browsers and platforms for Cypress E2E testing:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
{ "name": "cypressdemo", "version": "1.0.0", "description": "", "main": "index.js", "scripts": { "test": "cypress open", "cy:run": "cypress run", "record": "cypress run --record --key ", "lambdarun":"lambdatest-cypress run" }, "keywords": [], "author": "", "license": "ISC", "dependencies": { "cypress": "^5.6.0", "lambdatest-cypress-cli": "^2.0.4", "typescript": "^4.1.3" } } |
Run the tests using npm run lambdatest to see the tests in action on the LambdaTest Grid.
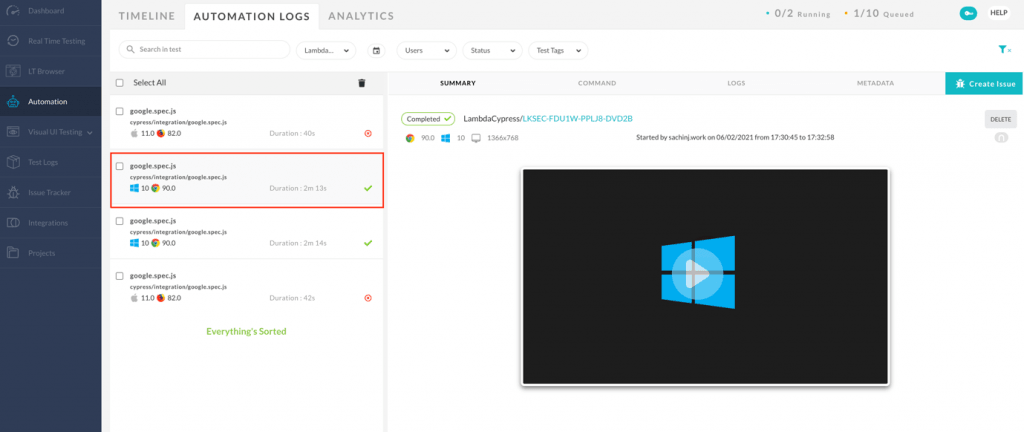
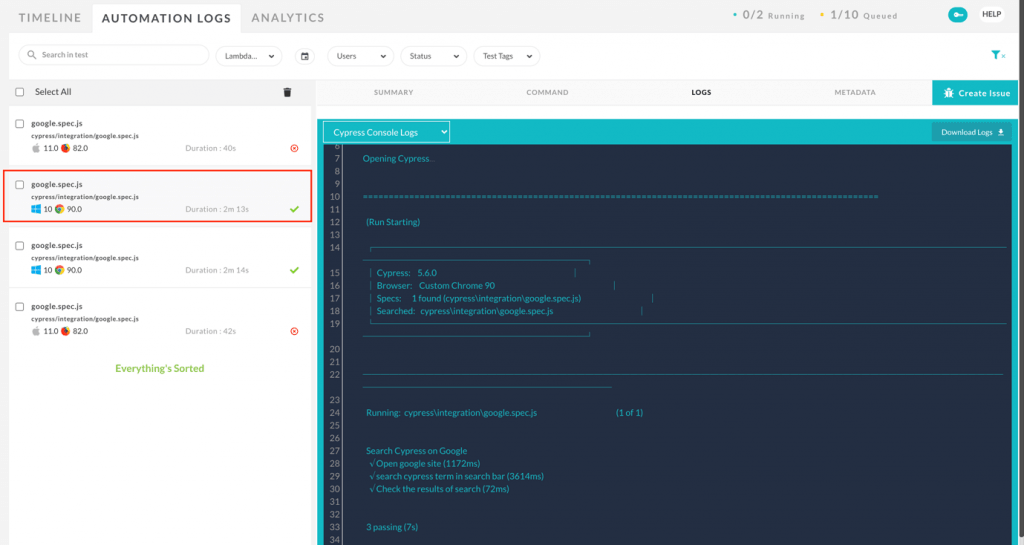
You can also view the execution logs in LambdaTest results under the ‘Automation Logs’ option.
My recommendations to folks looking for a reliable automation cloud testing framework are:
- If your applications are built with modern UI frameworks and need component-based test support, then you might think to switch to Cypress eventually (if not on a priority).
- Switch to Cypress automation testing if current tests show flakiness and have to be revamped for betterment.
- If you are building a new automated framework that works hand in hand with development and deployment, then a POC on Cypress automation testing is worth a try!
Read – How To Perform Cypress Testing At Scale With LambdaTest
Wrapping Up Cypress Tutorial
Trim down your test cycles by executing Cypress parallel testing online with LambdaTest. In this Cypress tutorial, we covered the basics of the Cypress test automation framework and how its modern architecture resolves the problems faced in modern web automation testing.
We also looked into its open-source test runner and paid Dashboard services and tried our hands-on with Cypress tests on cloud-based grid LamdaTest. It helps perform cross browser testing with Cypress, along with running tests in parallel on a reliable and scalable cloud grid.
Take this certification to showcase your expertise with end-to-end testing using Cypress automation testing and stay one step ahead.
Here’s a short glimpse of the Cypress 101 certification from LambdaTest:
Happy Testing!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Cypress?
Cypress is a web application testing framework for Node.js that makes it easier to write end-to-end tests for your applications. The problem that Cypress solves is that most of the frameworks that are used for this purpose, do not support end-to-end testing. Those kinds of tests covers the behavior of your app from outside, through DOM.
What is Cypress automation framework?
Cypress automation framework is a Node.js based framework written in Javascript and designed to be painless and easy to use. It has an intuitive command-line interface and aims to be the “framework” for your website or web app’s integration and acceptance testing.
What is Cypress used for?
Cypress is a JavaScript end-to-end testing framework used to automate and test web applications. It offers fast, reliable, and interactive testing capabilities, allowing developers to write tests in an easy-to-understand manner, making it popular for front-end web development.
What is Cypress automation framework?
Cypress automation framework is a Node.js based framework written in Javascript and designed to be painless and easy to use. It has an intuitive command-line interface and aims to be the “framework” for your website or web app’s integration and acceptance testing.
Is Cypress easier to learn than Selenium?
Cypress is generally considered easier to learn than Selenium. It has a simpler API, better documentation, and a more intuitive testing approach. Additionally, Cypress eliminates the need for complex setups and provides an interactive and user-friendly testing experience.
How fast is Cypress compared to Selenium?
Cypress is significantly faster than Selenium due to its architecture. Cypress runs directly in the browser and operates within the same event loop as the application, resulting in faster test execution and reduced flakiness compared to Selenium’s remote WebDriver communication.
Why use Cypress for API testing?
Cypress is advantageous for API testing due to its ability to handle both front-end and back-end testing within a single framework. It provides a simple and intuitive API for making HTTP requests, asserting responses, and manipulating data, making it efficient and convenient for comprehensive API testing.
Is Cypress used for backend testing?
Cypress is primarily designed for front-end testing, focusing on automating and testing web applications in the browser. While Cypress can make API requests and perform backend interactions, its main strength lies in end-to-end testing of the user interface and user experience. For comprehensive backend testing, specialized tools and frameworks such as Postman, Jest, or Mocha are typically more commonly used.
Does Cypress use Selenium?
No, Cypress does not use Selenium. It is a separate end-to-end testing framework built on a different architecture, offering faster and more reliable testing for web applications.
Got Questions? Drop them on LambdaTest Community. Visit now