Scale Your Automation Testing with AI
Run end-to-end parallel tests & reduce test execution time by 5x
Generate tests scripts using natural language with KaneAI
Accelerate your testing process with Autoheal, SmartWait & RCA
- Web Development
- Home
- /
- Learning Hub
- /
- Cypress run Command: A Step-by-Step Guide
Cypress run Command: A Step-by-Step Guide
Step-by-step guide to Cypress run command, flags, browser selection, test file execution, custom reports, and parallel testing.
Last Modified on: November 26, 2025
- Share:
Cypress is a widely adopted JavaScript-based end-to-end testing framework that provides intuitive APIs and powerful CLI commands, such as cypress run, to perform automated tests in a headless environment directly from the terminal. This functionality significantly enhances testing efficiency and streamlines the overall workflow.
Overview
The Cypress run command is used to execute Cypress tests from the command line in a headless or headed mode, outside the interactive Test Runner. It is primarily used for automation, such as in CI/CD pipelines, where running tests without the graphical interface is essential.
What Are Commonly Used Cypress run Flags?
Here are some Cypress run flags using which you can modify test execution, specify browsers, enable headless mode and streamline automated testing workflows efficiently.
- -browser, -b: Run Cypress in the specified browser, optionally providing a path. Cypress will attempt to use that browser automatically.
- --config, -c: Override default configuration settings for this test run, enabling customization of environment, behavior, and project-specific execution parameters efficiently.
- --config-file, -C: Specify the configuration file Cypress should use, allowing seamless switching between multiple project setups and different testing environments easily.
- --env, -e: Define environment variables for this specific test execution, allowing dynamic configuration without modifying the project’s source code directly or permanently.
- --headed: Display the browser while running tests instead of headless mode, enabling observation and debugging of each step during execution visually.
- --headless: Run tests without opening the browser interface, improving execution speed and using default behavior for standard automated `cypress run` workflows.
- --help, -h: Output usage instructions and display all available command flags, helping quickly understand proper options for running Cypress efficiently.
How to Perform Cypress Testing in a Specific Browser?
Cypress enables testing in specific browsers by selecting them in the Test Runner or specifying via command-line, ensuring accurate cross browser testing.
- Verify Installed Browsers: Run npx cypress open to launch the Test Runner. The dropdown in the top-right corner shows all detected browsers, allowing you to choose one for interactive testing. Useful for exploring and debugging tests interactively.
- Select Browser via Command Line: Use npx cypress run --browser <browser-name> to execute tests in a specific browser, e.g., Chrome or Firefox. Ideal for automated test execution in CI/CD pipelines.
- Use Headless Mode for Automation: Combine browser selection with headless execution using npx cypress run --browser edge --headless. Runs faster in CI and can reveal timing or animation issues not visible in headed mode.
- Validate Across Browsers: Do not assume identical behavior across browsers. Test critical workflows in multiple browsers to catch subtle differences in rendering, JavaScript execution, or CSS handling.
- Manage Browser Versions: Ensure consistency by using specific browser versions in CI environments. Minor version differences can impact test stability and reliability.
- Debug Browser-Specific Issues: Use headed mode to interactively inspect and debug tests when failures occur. Especially useful for browser-specific quirks.
What Is Cypress run Command?
The Cypress run command is a CLI utility used to execute all Cypress tests in a headless environment via the terminal. By default, it sequentially runs all test files located in the cypress/e2e/*.cy.js directory and displays a summary of the results, indicating which tests passed or failed.
To use the Cypress run command, ensure Cypress is installed locally in your project. Then, prefix the command with npx as shown below:
npx cypress runThis will execute all test cases found in the cypress/e2e/*.cy.js directory. The output will display a detailed report of the test execution, including individual test results and an overall summary.
New to Cypress? Check out this step-by-step Cypress tutorial.
Basic Flags Used With Cypress run Command
The Cypress run command comes with several CLI flags, such as --browser, --spec, --reporter, just to name a few, that allow you to customize how test cases are executed headlessly on the terminal when added with the cypress run command.
These flags enable you to extend the functionality of the Cypress run command by adding additional commands as flags to the end of the run command to perform more advanced operations via the terminal.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| --browser, -b | Run Cypress in the browser with the given name. If a file system path is supplied, Cypress will attempt to use the browser at that path. |
| --config, -c | Specify configuration. |
| --config-file, -C | Specify the configuration file. |
| --env, -e | Specify environment variables. |
| --headed | Displays the browser instead of running headlessly. |
| --headless | Hide the browser instead of running headed (default during cypress run). |
| --help, -h | Output usage information. |
| --key, -k | Specify your secret record key. |
| --no-exit | Keep Cypress open after tests in a spec file run. |
| --no-runner-ui | Hides the Cypress Runner UI. |
| --project, -P | Path to a specific project. |
| --quiet, -q | Reduce output to stdout. |
| --record | Whether to record the test run. |
| --reporter, -r | Specify a Mocha reporter. |
| --reporter-options, -o | Specify Mocha reporter options. |
| --runner-ui | Displays the Cypress Runner UI. Useful when Test Replay is enabled and you want the UI displayed for screenshots and video. |
| --spec, -s | Specify the spec files to run. |
| --tag, -t | Identify a run with a tag or tags. |
Note: Run tests across Windows, and macOS on latest Cypress versions. Try LambdaTest Now!
How to Run Cypress Tests in a Specific Browser?
You can clone the GitHub repository created for Cypress run command. It includes all code samples and configurations demonstrated throughout the guide.
By default, Cypress executes tests using the Electron browser when the cypress run command is invoked. However, you can specify a different browser using the --browser flag. Cypress will then run the tests in headless mode with the specified browser.
To use a specific browser, append the --browser flag followed by the browser name (e.g., Chrome, Firefox, Edge, etc.) to the command:
npx cypress run --browser chrome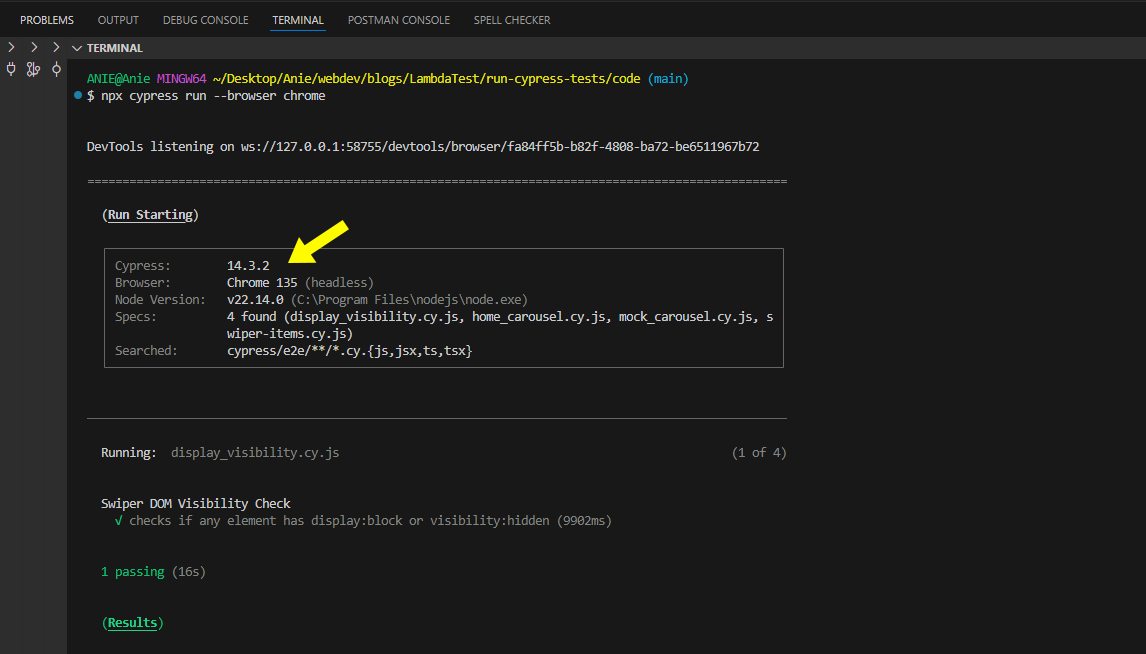
Here, the above command will execute the test in headless mode using Chrome as shown below.
You can run the above command in headed mode using the --headed command or npx cypress open.
npx cypress run --headed --browser firefox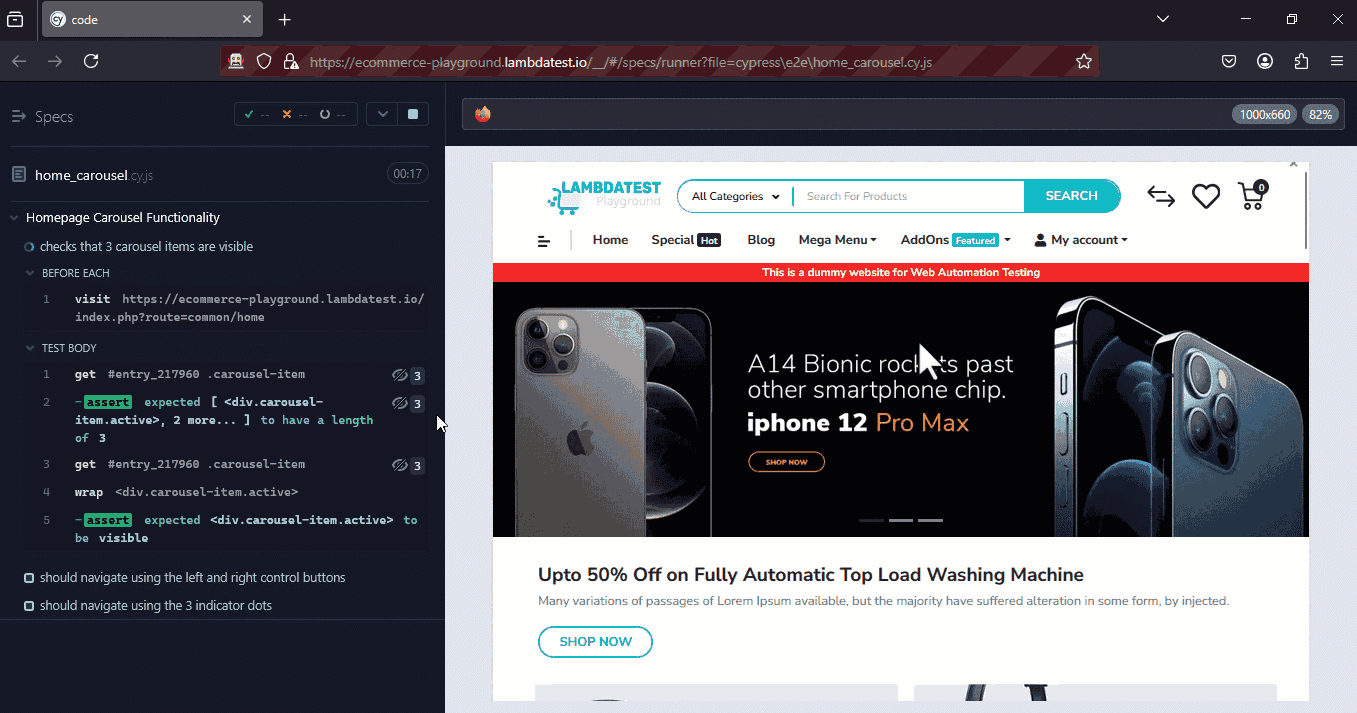
Make sure the chosen browser is installed on your local machine. You can verify the list of available browsers with the command below.
npx cypress infoHow to Run a Specific or Multiple Cypress Test Files?
By default, when the cypress run command is executed, Cypress runs all test files located in the cypress/e2e/*.cy.js directory sequentially, regardless of whether you're only interested in running a single file. This approach can be inefficient and time-consuming in cases where targeted testing is needed.
To address this, Cypress provides the --spec flag, which allows you to specify the exact test file (including its path) that you want to execute. When used, Cypress will run only the specified file and skip the rest.
For example, let’s run a test file located at cypress/e2e/swiper-items.cy.js. First, ensure the file exists and contains your test code: cypress/e2e/*.cy.js directory.
npx cypress run --spec cypress/e2e/swiper-items.cy.js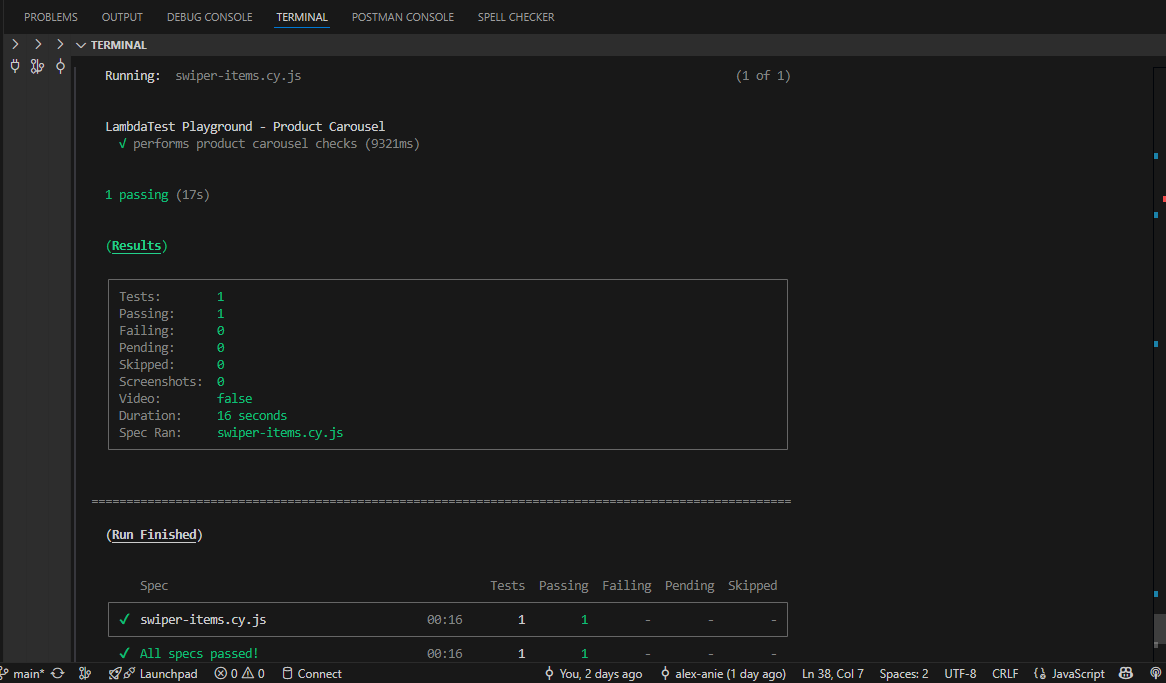
Then, run the test using the following command:
describe('LambdaTest Playground - Product Carousel', () => {
beforeEach(() => {
cy.visit('https://ecommerce-playground.lambdatest.io/')
})
it('performs product carousel checks', () => {
cy.get('.swiper-slide').then($items => {
cy.log(`Number of swiper items: ${$items.length}`)
})
cy.get('.price-new').should('exist').each($price => {
const text = $price.text()
expect(text.trim()).to.not.be.empty
expect(text).to.include('$')
})
cy.get('.swiper-slide img').should('be.visible').and($img => {
const src = $img.attr('src')
expect(src, 'Image src should exist').to.match(/^https?:///)
})
cy.get('h4.title .text-ellipsis-2').each($el => {
const text = $el.text().trim()
expect(text).to.not.be.empty
})
})
})This command will execute only the swiper-items.cy.js test file, reducing the time spent on executing all tests.
While this approach helps to target a specific test file, you can also target multiple files using a comma-separated list inside a double quote.
npx cypress run --spec "cypress/e2e/swiper-items.cy.js,cypress/e2e/home_carousel.cy.js"Here we are running swiper-items.cy.js and home_carousel.cy.js test files. Cypress will execute both files and ignore others.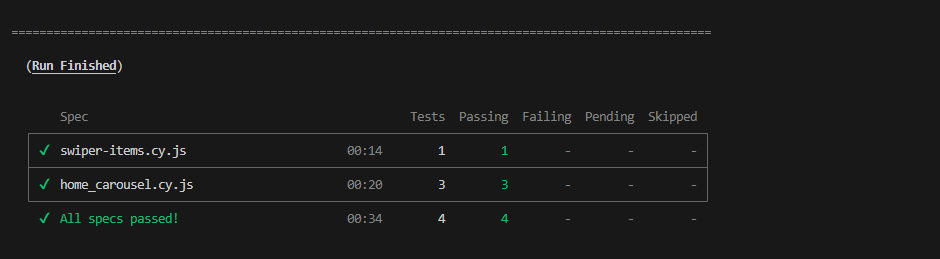
How to Generate Reports Using Cypress Custom Reporter?
When tests are executed via the terminal, for instance, using the cypress run command, the configured reporter captures the test results and formats them into reports, typically in HTML or JSON format.
Depending on the reporter you’re using, you might need to specify it with the --reporter flag, like so:
npx cypress run --reporter mocha-junit-reporterLet’s use the cypress-mochawesome-reporter package. This reporter does not require the --reporter flag explicitly when it's set up via your Cypress configuration. It automatically generates the report on completion of test execution.
Step 1: To install cypress-mochawesome-reporter, run:
npm install --save-dev cypress-mochawesome-reporterStep 2: Next, open your cypress.config.js file and configure the reporter as follows:
const { defineConfig } = require("cypress");
module.exports = defineConfig({
reporter: 'cypress-mochawesome-reporter',
reporterOptions: {
charts: true,
reportPageTitle: 'custom-title',
embeddedScreenshots: true,
inlineAssets: true,
},
e2e: {
setupNodeEvents(on, config) {
// implement node event listeners here
require('cypress-mochawesome-reporter/plugin')(on);
},
},
});
Step 3: Next, navigate to cypress/support/e2e.js directory and import cypress-mochawesome-reporter plugin.
import 'cypress-mochawesome-reporter/register';Step 4: Now, run the command below to automatically generate a Mochawesome report in the specified directory.
npx cypress runCypress will run all tests in the test directory, and as soon as all test execution is complete, Cypress will begin generating test reports using cypress-mochawesome-reporter.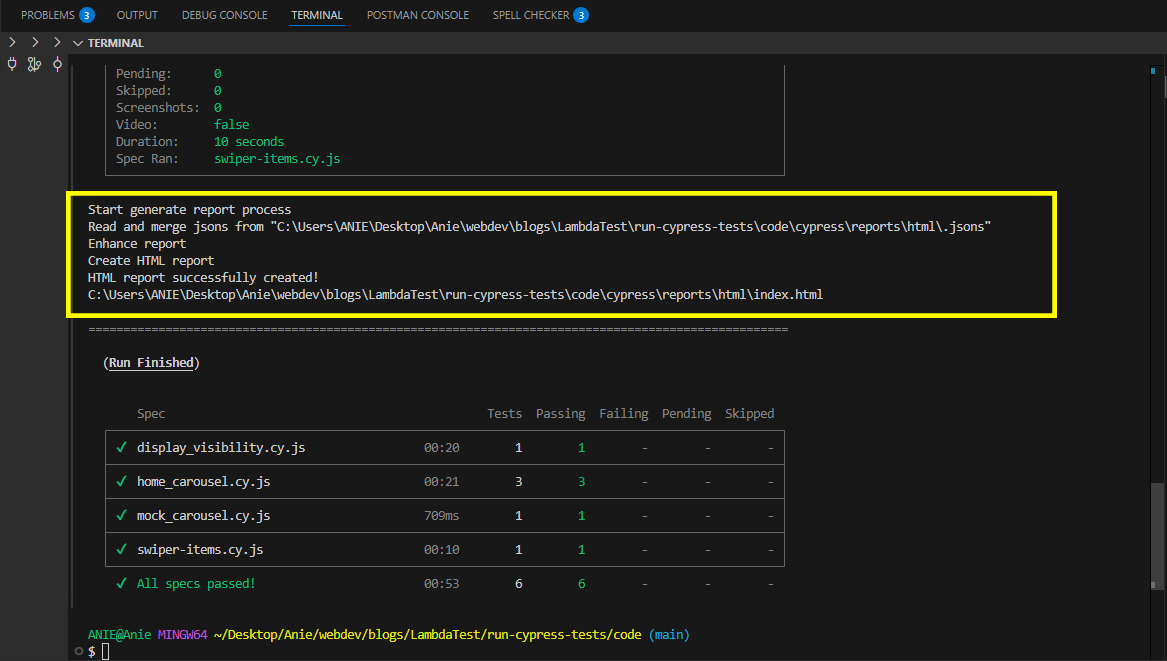
Next, locate the generated report file at cypress/report/html/index.html, click on the file, and open it in your default browser. Your reports should look as shown below.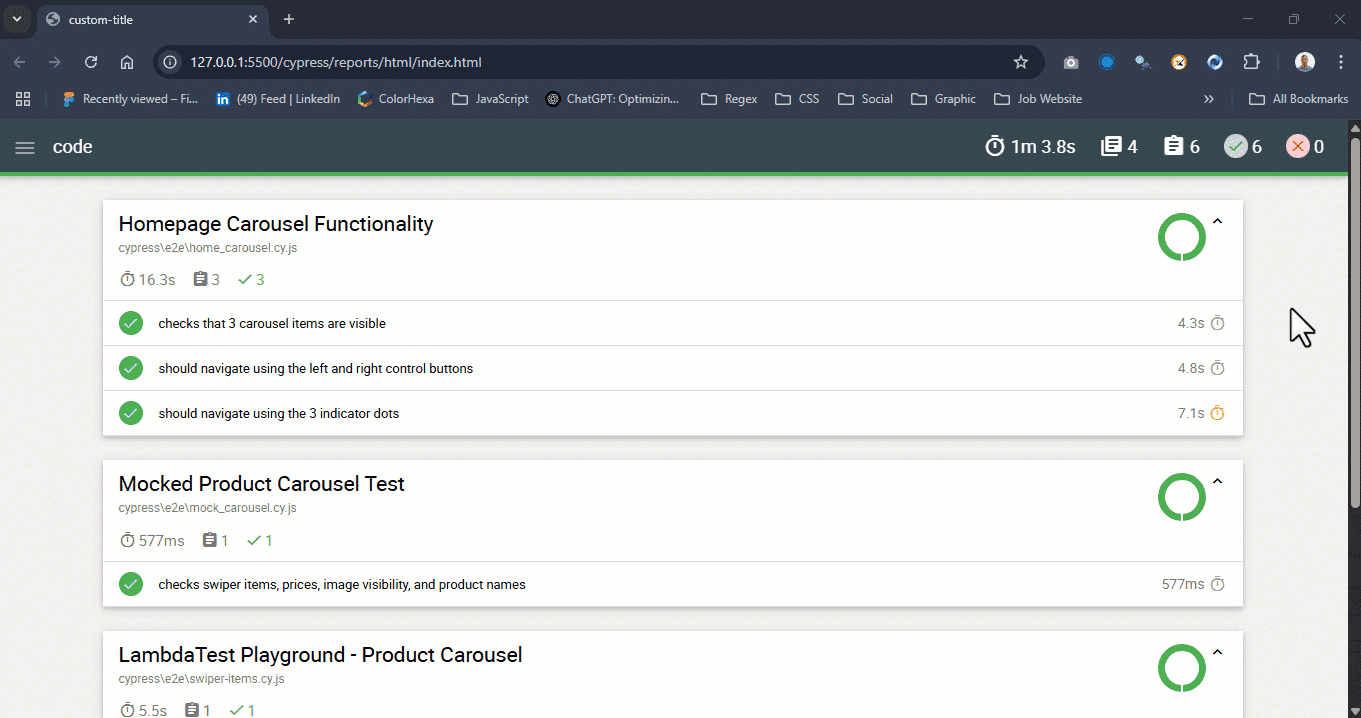
How to Run Cypress Tests in Parallel With LambdaTest?
Cloud-based testing platform like LambdaTest offers a scalable cloud that allows you to execute tests across multiple browsers in parallel. This approach significantly improves efficiency by enabling Cypress parallel testing, eliminating the need to run tests manually on each browser one at a time.
To begin, run the following command:
npm install -g lambdatest-cypress-cliThis installs the LambdaTest Cypress CLI globally. Once installed, initialize your project with:
lambdatest-cypress init --cv=14.3.2This will create the necessary LambdaTest configuration files and folders, including the lambdatest-config.json file. Open this file and enter your LambdaTest credentials (username and password).
You can find more details in this documentation on Cypress testing with LambdaTest.
To run Cypress tests on multiple browsers, you can define a browsers array in the lambdatest-config.json file, specifying the desired browser name, operating system, and version for execution on the LambdaTest cloud environment.
{
"lambdatest_auth": {
"username": "username",
"access_key": "accesskey"
},
"browsers": [
{
"browser": "Chrome",
"platform": "Windows 10",
"versions": [
"latest"
]
},
{
"browser": "Firefox",
"platform": "Windows 10",
"versions": [
"latest"
]
}
To run the tests, pass these parameters directly via the terminal using the --browser flag, as shown below:
lambdatest-cypress run --browsers "Windows 10:Chrome:latest,Windows 10:Firefox:latest"Here are the Cypress test results that you can notice on the LambdaTest Web Automation dashboard.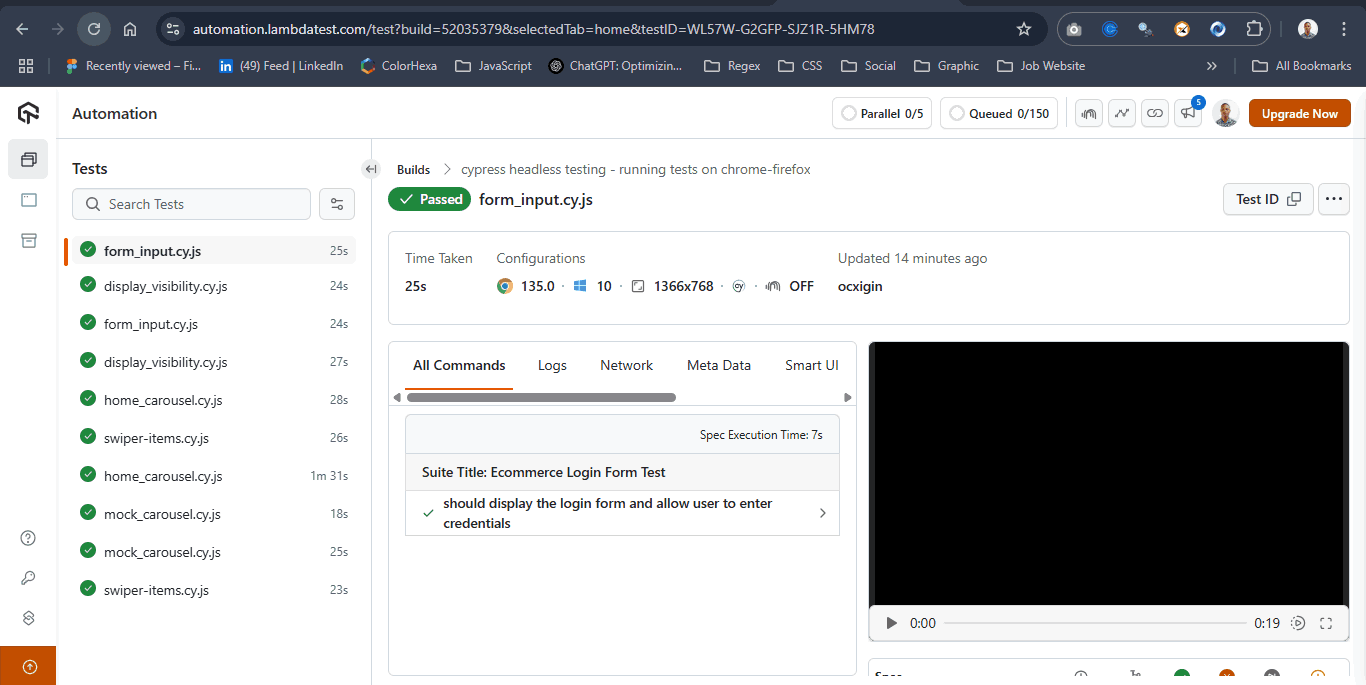
Conclusion
Bringing all these aspects together, mastering the Cypress run command is essential for creating a robust and efficient test automation workflow. Understanding the basic flags ensures you can tailor test runs to your project’s needs, while controlling the browser environment allows for accurate cross browser testing. Selecting specific test files or suites enhances efficiency by targeting only the relevant scenarios, reducing unnecessary execution time.
Integrating custom reporters provides clear, actionable insights from each run, helping teams quickly identify issues and track progress. Finally, leveraging parallel execution with platforms like LambdaTest dramatically accelerates test cycles, making large-scale automation practical and scalable. By combining these techniques, you gain full command over your Cypress tests, ensuring they are fast, reliable, and fully aligned with real-world project requirements.
Citations
- Cypress Command Line: https://docs.cypress.io/app/references/command-line
On This Page
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Did you find this page helpful?
More Related Hubs

Start your journey with LambdaTest
Get 100 minutes of automation test minutes FREE!!


