TestNG Listeners In Selenium WebDriver With Examples
Ramit Dhamija
Posted On: May 30, 2019
15 Min
Chapters
- What Is TestNG Framework
- Install TestNG in Eclipse
- Create TestNG Project in Eclipse
- Create TestNG.xml File in Eclipse
- Using TestNG In Selenium
- First TestNG Automation Script
- Exception Tests in TestNG
- Parallel Test Execution in TestNG
- Assertions in TestNG
- Set Test Case Priority in TestNG
- TestNG Reporter Log
- Generating TestNG Reports
- Running JUnit Selenium Tests using TestNG
- Grouping Test Cases in TestNG
- Use DataProviders In TestNG
- Parameterization In TestNG
- TestNG Listeners
- TestNG Annotations
- Parallel Testing In Selenium With TestNG
- Appium With TestNG
There are different interfaces provided by Java that allow you to modify TestNG behavior. These interfaces are known as TestNG Listeners in Selenium WebDriver. They enable you to customize test logs or reports based on your project requirements.
Overview
What are TestNG Listeners?
TestNG Listeners are interfaces that allow you to listen to events during test execution. They provide hooks to customize test behavior, logging, reporting, or executing additional code before, after, or during tests.
What Are the Types of TestNG Listeners?
TestNG offers various listeners to monitor different aspects of test execution. Each listener serves a specific purpose, helping improve reporting, debugging, and test automation flexibility. Common types include:
- ITestListener: Monitors the test lifecycle events like start, success, failure, and skip, enabling custom reporting or logging actions.
- IAnnotationTransformer: Modifies test annotations dynamically at runtime to customize execution, priorities, or data-driven parameters programmatically.
- IInvokedMethodListener: Listens before and after each method invocation, allowing additional actions around test method execution for logging or validations.
- ISuiteListener: Tracks test suite start and finish events, enabling custom operations, reporting, or setup/teardown at the suite level.
- IReporter: Generates customized reports after test execution, summarizing suite results, failed tests, and execution statistics programmatically.
- IConfigurable: Allows configuration methods to access and modify test method details, providing fine-grained control during configuration execution.
- IExecutionListener: Notifies before and after the entire test run, enabling global setup, teardown, or logging at the framework level.
- IHookable: Allows overriding the test method execution dynamically, providing control to wrap test method calls for custom logic.
- IMethodInterceptor: Intercepts test methods before execution to change order, filter, or modify methods based on runtime conditions or data.
- IConfigurationListener: Monitors configuration method events like before/after suite, class, and method, enhancing logging and debugging capabilities.
Which TestNG Listeners In Selenium WebDriver Do You Use The Most?
In Selenium WebDriver projects, listeners like ITestListener, IReporter, and IInvokedMethodListener are commonly used. They help with reporting, logging, and handling test execution events efficiently. Commonly Used Listeners:
- ITestListener: Tracks test success, failure, or skip events with custom logs or screenshots.
- IReporter: Generates detailed, customized execution reports for all test suites.
- IInvokedMethodListener: Performs actions before or after each method, useful for capturing screenshots or detailed logging.
- IHookable: Controls the test method execution flow for advanced testing scenarios or additional validations.
What are TestNG Listeners?
TestNG listeners serve as vital components in the TestNG framework, offering a powerful mechanism to monitor and influence the progress of test executions. These listeners are specialized classes that facilitate enhanced control over test scenarios, enabling developers and testers to capture and respond to various events during test runs. With TestNG listeners, you can amplify test automation capabilities by customizing behavior, generating comprehensive reports, and implementing dynamic test management.
There are numerous TestNG listeners in Selenium WebDriver, some of them are used very frequently by the testing community & some are almost forgotten. In this TestNG tutorial, I will demonstrate the most popular TestNG listeners with examples but before that, let me enlist the various TestNG listeners in Selenium WebDriver.
- ITestListener
- IAnnotationTransformer
- IInvokedMethodListener
- ISuiteListener
- IReporter
- IConfigurable
- IExecutionListener
- IHookable
- IMethodInterceptor
- IConfigurationListener
With TestNG certification, you can challenge your skills in performing automated testing with TestNG and take your career to the next level.
Here’s a short glimpse of the TestNG certification from LambdaTest:
Frequently Used TestNG Listeners With Examples
Now, in this TestNG tutorial, let’s us first look into the most popular & widely used TestNG listeners with examples.
1. ITestListener
ITestListener is the most adopted TestNG listener in Selenium WebDriver. Providing you with an easy to implement interface through a normal Java class, where the class overrides every method declared inside the ITestListener. By using this TestNG listener in Selenium WebDriver, you can change the default behaviour of your test by adding different events to the methods. It also defines a new way of logging or reporting.
Following are some methods provided by this interface:
onStart: This method is invoked before any test method gets executed. This can be used to get the directory from where the tests are running.
onFinish: This method is invoked after all tests methods gets executed. This can be used to store information of all the tests that were run.
onTestStart: This method is invoked before any tests method is invoked. This can be used to indicate that the particular test method has been started.
onTestSkipped: This method is invoked when each test method is skipped. This can be used to indicate that the particular test method has been skipped.
onTestSuccess: This method is invoked when any test method gets succeeded. This can be used to indicate that the particular test method has successfully finished its execution.
onTestFailure: This method is invoked when any test method gets failed. This can be used to indicate that the particular test method has been failed. You can create an event of taking a screenshot which would show where the test has been failed.
onTestFailedButWithinSuccessPercentage: This method is invoked each time the test method fails but is within the success percentage mentioned. To implement this method, we use two attributes as a parameter of TestNG annotations i.e. successPercentage and invocationCount. The success percentage takes the value of success percentage and invocation count denotes the number of times that a particular test method would execute.
For example: @Test(successPercentage=60, invocationCount=5), in this annotation success percentage is 60% and invocation count is 5, that means out of 5 times if at least 3 times ((⅗)*100= 60) the test method gets passed, it would be considered as passed.
For every ITestListener method we usually pass the following arguments:
- “ITestResult” interface along with its instance “result” which describes the result of a test.
- “ITestContext” interface along with its instance “context” which describes the test context containing all the information of the given test run.
Note: If you want to trace your exception through ITestResult then you need to avoid try/catch handling.
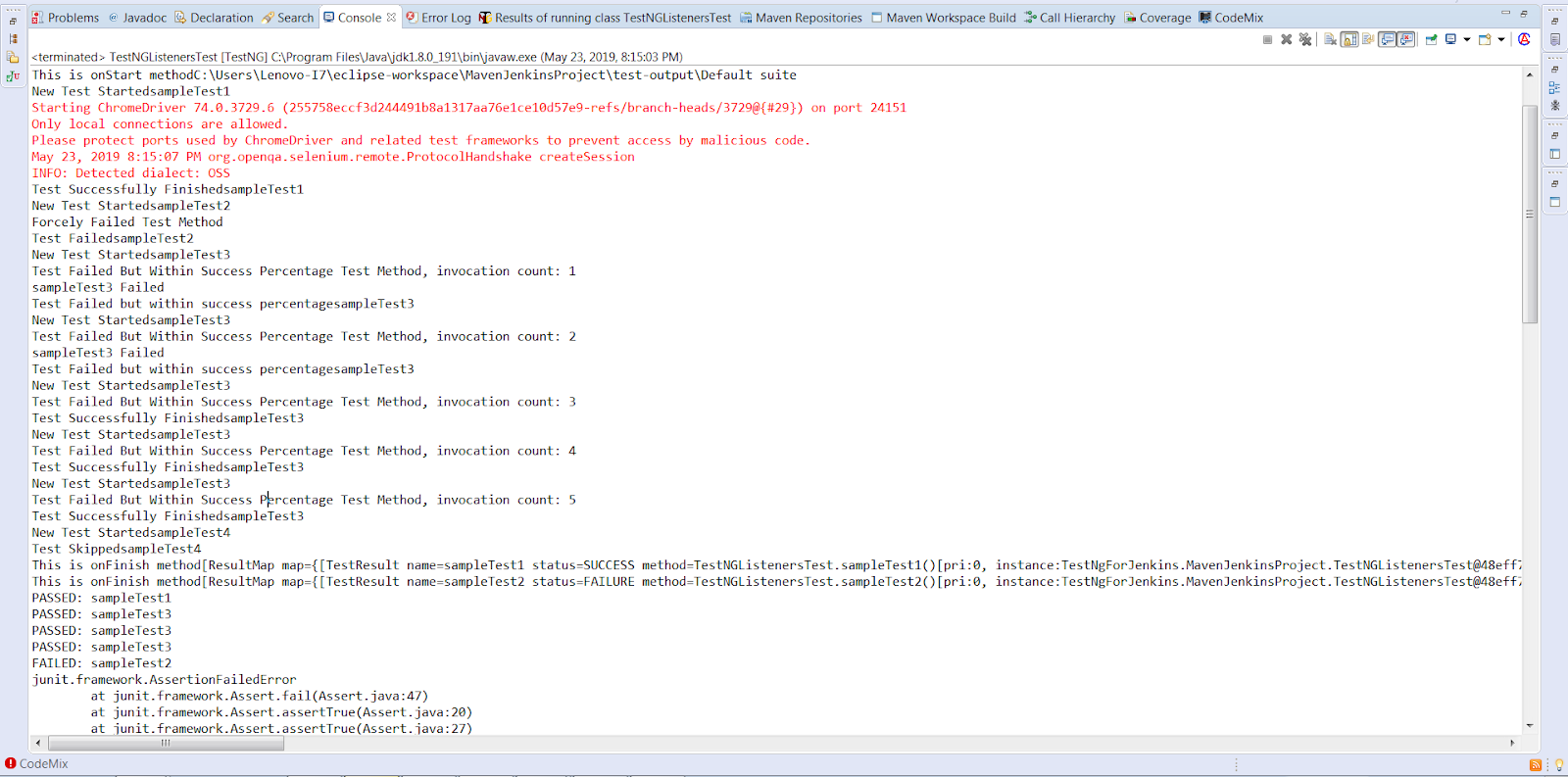
Now, in this TestNG tutorial for listeners, we will take a basic example code for running the test at the class level. Logs would get generated at a console and it would help you understanding which tests passed, failed and skipped.
The first class(ListentersBlog.java) would contain all the methods implemented by ITestListener interface:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 |
package TestNgListeners; import org.testng.ITestContext; import org.testng.ITestListener; import org.testng.ITestResult; public class ListenersBlog implements ITestListener { public void onTestStart(ITestResult result) { System.out.println("New Test Started" +result.getName()); } public void onTestSuccess(ITestResult result) { System.out.println("Test Successfully Finished" +result.getName()); } public void onTestFailure(ITestResult result) { System.out.println("Test Failed" +result.getName()); } public void onTestSkipped(ITestResult result) { System.out.println("Test Skipped" +result.getName()); } public void onTestFailedButWithinSuccessPercentage(ITestResult result) { System.out.println("Test Failed but within success percentage" +result.getName()); } public void onStart(ITestContext context) { System.out.println("This is onStart method" +context.getOutputDirectory()); } public void onFinish(ITestContext context) { System.out.println("This is onFinish method" +context.getPassedTests()); System.out.println("This is onFinish method" +context.getFailedTests()); } } |
Below is the code that includes the tests methods(TestNGListenersTest.java). Make sure you add a Listeners annotation just above your class name to implement the above added methods.
Syntax: @Listeners(PackageName.ClassName.class)
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 |
package TestNgListeners; import org.openqa.selenium.By; import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver; import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeDriver; import org.testng.SkipException; import org.testng.annotations.Listeners; import org.testng.annotations.Test; import junit.framework.Assert; @Listeners(TestNgListeners.ListenersBlog.class) public class TestNGListenersTest { @Test //Passing Test public void sampleTest1() throws InterruptedException { System.setProperty("webdriver.chrome.driver", "C:\\Users\\Lenovo-I7\\Desktop\\Selenium\\chromedriver.exe"); WebDriver driver = new ChromeDriver(); driver.get("https://www.apple.com/"); driver.manage().window().maximize(); driver.findElement(By.xpath("//*[@id=\'ac-globalnav\']/div/ul[2]/li[3]")).click(); Thread.sleep(2000); driver.findElement(By.cssSelector("#chapternav > div > ul > li.chapternav-item.chapternav-item-ipad-air > a")).click(); Thread.sleep(2000); driver.findElement(By.linkText("Why iPad")).click(); Thread.sleep(2000); driver.quit(); } @Test //Failing Test public void sampleTest2() throws InterruptedException { System.out.println("Forcely Failed Test Method"); Assert.assertTrue(false); } private int i = 0; @Test(successPercentage = 60, invocationCount = 5) //Test Failing But Within Success Percentage public void sampleTest3() { i++; System.out.println("Test Failed But Within Success Percentage Test Method, invocation count: " + i); if (i == 1 || i == 2) { System.out.println("sampleTest3 Failed"); Assert.assertEquals(i, 6); } } @Test //Skipping Test public void sampleTest4() { throw new SkipException("Forcely skipping the sampleTest4"); } } |
Console Output Screen:
Now, suppose you have multiple classes in your project, then adding TestNG Listeners in Selenium WebDriver to each class might be a pain. In such cases, you can create a test suite and add Listeners tag to your suite(xml file) instead of adding Listeners to each class.
Here is the example code(testng.xml) for running the test at the suite level :
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE suite SYSTEM "http://testng.org/testng-1.0.dtd"> <suite name="TestNG Listeners Suite" parallel="false"> <listeners> <listener class-name="TestNgListeners.ListenersBlog" /> </listeners> <test name="Test"> <classes> <class name="TestNgListeners.TestNGListenersTest" /> </classes> </test> </suite> |
2. IAnnotationTransformer
IAnnotationTransformer is an interface that provides a method “transform” which would get invoked by TestNG to modify the behaviour of Test annotation method in our test class.
The transform method provides various parameters:
- annotation: The annotation that would get read from the test class.
- testClass: If the annotation found on a class, this parameter would represent that same class.
- testConstructor: If the annotation found on a constructor, this parameter would represent that same constructor.
- testMethod: If the annotation found on a method, this parameter would represent that same method.
Note: At least one of the parameters will be non-null.
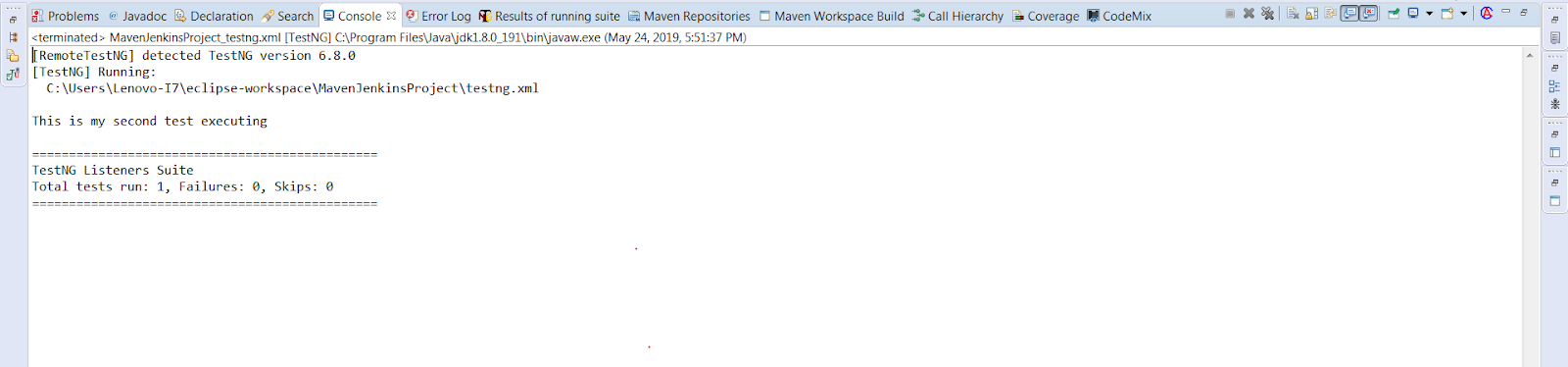
Below is the sample code that would be executed at the suite level. In this code, we have used a parameter “alwaysRun = true” in our Test annotation that indicates that the test method would always run even if the parameters on which the method depends fails. However, we would transform this behaviour of our test method through IAnnotationTransformer Listener which won’t allow the particular test method to get executed.
Listeners Class File:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 |
package TestNgListeners; import java.lang.reflect.Constructor; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import org.testng.IAnnotationTransformer; import org.testng.annotations.ITestAnnotation; public class AnnotationTransformers implements IAnnotationTransformer { public boolean isTestRunning(ITestAnnotation ins) { if(ins.getAlwaysRun()) { return true; } return false; } public void transform(ITestAnnotation annotation, Class testClass, Constructor testConstructor, Method testMethod) { if(isTestRunning(annotation)) { annotation.setEnabled(false); } } } |
Test Class File:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 |
package TestNgListeners; import org.testng.annotations.Listeners; import org.testng.annotations.Test; public class AnnotationTransformerTests { @Test(alwaysRun=true) public void test1() { System.out.println("This is my first test whose behaviour would get changed while executing"); } @Test public void test2() { System.out.println("This is my second test executing"); } } |
Console Output Screen:
3. IInvokedMethodListener
This interface allows you to perform some action before and after a method has been executed. This listener gets invoked for configuration and test methods. This TestNG listener in Selenium WebDriver works same as the ITestListerner and the ISuiteListerner. However, there is a difference that you should make a note of & that is, in IInvokedMethodListener, it makes the call before and after every method.
There are two methods to be implemented:
beforeInvocation(): This method is invoked prior every method.
afterInvocation(): This method is invoked post every method.
Here is sample code for this listener, implemented at class level.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 |
InvokedMethodListeners.java(includes listeners implemented methods) package TestNgListeners; import org.testng.IInvokedMethod; import org.testng.IInvokedMethodListener; import org.testng.ITestResult; public class InvokedMethodListeners implements IInvokedMethodListener { public void beforeInvocation(IInvokedMethod method, ITestResult testResult) { System.out.println("Before Invocation of: " + method.getTestMethod().getMethodName() + "of Class:" + testResult.getTestClass()); } public void afterInvocation(IInvokedMethod method, ITestResult testResult) { System.out.println("After Invocation of: " + method.getTestMethod().getMethodName() + "of Class:" + testResult.getTestClass()); } } |
File Name: InvokedMethodListenersTest.java (includes configuration and test methods)
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 |
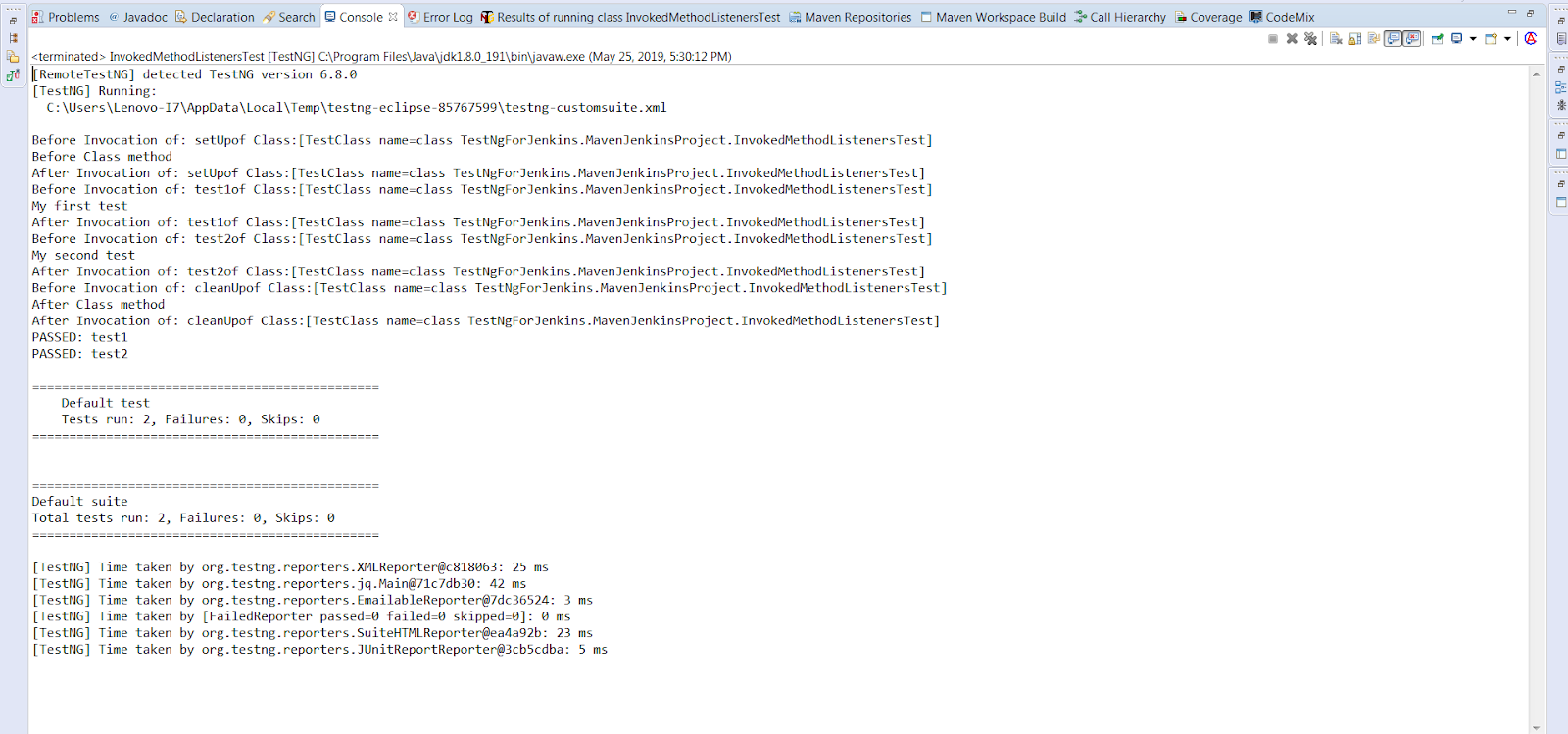
package TestNgListeners; import org.testng.annotations.AfterClass; import org.testng.annotations.BeforeClass; import org.testng.annotations.Listeners; import org.testng.annotations.Test; @Listeners(value=InvokedMethodListeners.class) public class InvokedMethodListenersTest { @Test public void test1() { System.out.println("My first test"); } @Test public void test2() { System.out.println("My second test"); } @BeforeClass public void setUp() { System.out.println("Before Class method"); } @AfterClass public void cleanUp() { System.out.println("After Class method"); } } |
Console Output Screen:
4. ISuiteListener
This TestNG listener in Selenium WebDriver is implemented at a suite level called ISuiteListener. It has 2 methods:
onStart: This method is invoked prior the test suite execution.
onFinish: This method is invoked post the test suite execution.
This listener basically listen to the events to have occurred before and after the execution of the suite.If the parent suite further contains child suites then child suites are executed before running the parent suite.
Step 1: Implementing ISuiteListener with normal java class and adding the unimplemented methods.
Class: SuiteListeners
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
package TestNgListeners; import org.testng.ISuite; import org.testng.ISuiteListener; public class SuiteListeners implements ISuiteListener { public void onStart(ISuite suite) { System.out.println("Suite executed onStart" + suite.getName()); } public void onFinish(ISuite suite) { System.out.println("Suite executed onFinish" + suite.getName()); } } |
Step 2: Creating two test classes to be added in two different child suites.
Class 1: SuiteListenersTests1
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 |
package TestNgListeners; import org.testng.annotations.AfterSuite; import org.testng.annotations.BeforeSuite; import org.testng.annotations.Test; public class SuiteListenersTests1 { @BeforeSuite public void test1() { System.out.println("BeforeSuite method in Suite1"); } @Test public void test2() { System.out.println("Main Test method 1"); } @AfterSuite public void test3() { System.out.println("AfterSuite method in Suite1"); } } |
Class 2: SuiteListenersTests2
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 |
package TestNgListeners; import org.testng.annotations.AfterSuite; import org.testng.annotations.BeforeSuite; import org.testng.annotations.Test; public class SuiteListenersTests2 { @BeforeSuite public void test1() { System.out.println("BeforeSuite method in Suite2"); } @Test public void test2() { System.out.println("Main Test method 2"); } @AfterSuite public void test3() { System.out.println("AfterSuite method in Suite2"); } } |
Step 3: Adding the test classes to the child suites.
Suite 1: Test Suite One.xml
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE suite SYSTEM "http://testng.org/testng-1.0.dtd"> <suite name="Test Suite One"> <test name="Test Method1"> <classes> <class name="TestNgListeners.SuiteListenersTests1"/> </classes> </test> </suite> |
Suite 2: Test Suite Two.xml
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE suite SYSTEM "http://testng.org/testng-1.0.dtd"> <suite name="Test Suite Two"> <test name="Test Method2"> <classes> <class name="TestNgListeners.SuiteListenersTests2"/> </classes> </test> </suite> |
Step 4: Creating a parent suite xml file that would combine other 2 defined suites along with the listeners class.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
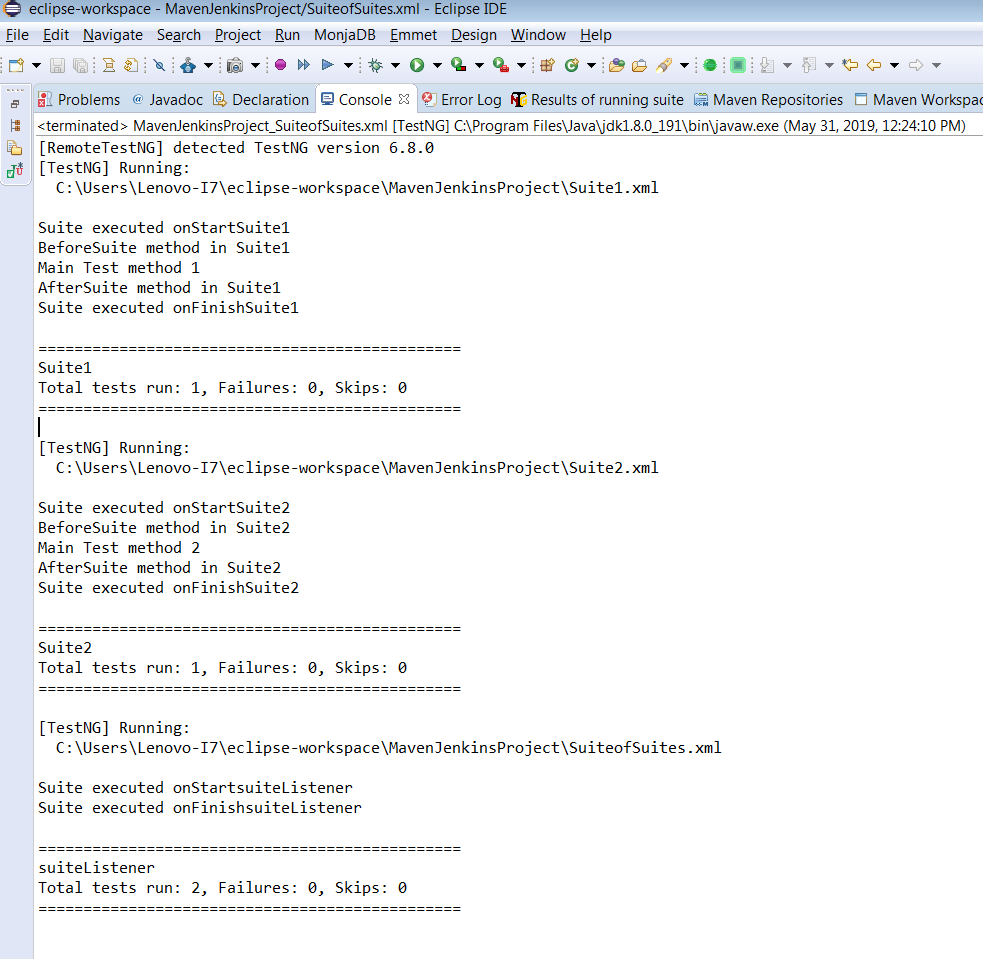
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE suite SYSTEM "http://testng.org/testng-1.0.dtd"> <suite name="suiteListener"> <listeners> <listener class-name="TestNgListeners.SuiteListeners"></listener> </listeners> <suite-files> <suite-file path="./Suite1.xml"> </suite-file> <suite-file path="./Suite2.xml"> </suite-file> </suite-files> </suite> |
Console Output Screen:
5. IReporter
This TestNG listener in Selenium WebDriver provides an interface which helps you to customize the test report generated by TestNG. It provides generateReport method which would get invoked after execution of all the suites. The method further contains three parameters:
- xmlSuite: it provides you with a list of multiple suites presented in the testng xml file that goes under execution.
- suites: This object represents a great deal of information about the classes, packages, test execution result, along with all the test methods. Basically, it represents detailed information around the suite after the final execution.
- outputDirectory: contains the output folder path where the report gets generated.
Below is the example of IReporterer listener at suite level.
File Name :ReporterListener.java
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 |
package TestNgListener; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; import org.testng.IReporter; import org.testng.ISuite; import org.testng.ISuiteResult; import org.testng.ITestContext; import org.testng.xml.XmlSuite; public class ReporterListener implements IReporter { public void generateReport(List xmlSuites, List suites, String outputDirectory) { for(ISuite isuite : suites) { Map<string, isuiteresult=""> suiteResults = isuite.getResults(); String sn = isuite.getName(); for(ISuiteResult obj : suiteResults.values()) { ITestContext tc = obj.getTestContext(); System.out.println("Passed Tests of" + sn + "=" + tc.getPassedTests().getAllResults().size()); System.out.println("Failed Tests of" + sn + "=" + tc.getFailedTests().getAllResults().size()); System.out.println("Skipped Tests of" + sn + "=" + tc.getSkippedTests().getAllResults().size()); } } } } </string,> |
File Name: ReporterTest.java
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 |
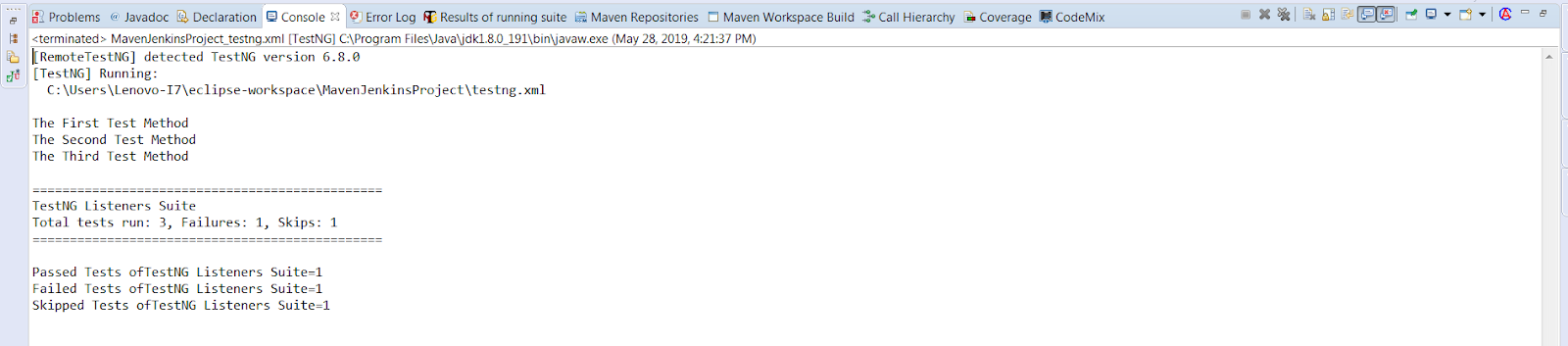
package TestNgListener; import org.testng.SkipException; import org.testng.annotations.Listeners; import org.testng.annotations.Test; import junit.framework.Assert; public class ReporterTest { @Test public void FirstTest() { System.out.println("The First Test Method"); Assert.assertTrue(true); } @Test public void SecondTest() { System.out.println("The Second Test Method"); Assert.fail("Failing this test case"); } @Test public void ThirdTest() { System.out.println("The Third Test Method"); throw new SkipException("Test Skipped"); } } |
Console Output Screen:
Not So Frequently Used TestNG Listeners In Selenium WebDriver
In this section, I will be highlighting those TestNG listeners which are not so renowned as the ones discussed in the previous section. I have avoided the practical demonstration of these TestNG listeners with their examples as they are rarely used. I will, however, help you understand their purpose.
6. IConfigurationListener
This TestNG listener in Selenium WebDriver is used to create an event only when the configuration method is passed, failed or skipped.
Below are the unimplemented methods provided by this listener:
- onConfigurationSuccess: It gets invoked when the configuration method gets succeeded.
- onConfigurationFailure: It gets invoked when the configuration method gets failed.
- onConfigurationSkip: As the name suggests, when your configuration method is skipped, it calls for onConfigurationSkip method.
7. IExecutionListener
This listener is used to keep track when the test or suite run start and finish. It provides two methods:
onExecutionStart: It is invoked before the suite or test starts running.
onExecutionFinish: It is invoked after the suite or test gets executed.
Note: It is not possible for this listener to prevent the execution but only to create events in some way. Also, you can provide more than one “IExecution” listener as you configure TestNG.
8. IHookable
This interface skips the invocation of test methods and provides a run method which gets invoked instead of each @Test method found. The test method is then invoked once the callBack() method of the IHookCallBack parameter is called.
IHookable listener is utilized when you wish to perform testing on classes which require JAAS authentication. This can be used to set permissions i.e. for whom the test method should run and when the test method should get skipped.
9. IMethodInterceptor
→To return the list of IMethodInstance, post-execution of TestNG.
→ To sort the list of test methods.
TestNG would execute the tests methods in the same order defined in the returned value.
IMethodInterceptor interface includes only one method to implement “intercept” which returns the modified list of test methods.
Example: One of the test methods SampleTestOne is to test the logs, so we grouped it in “LogCheck”.
Now, suppose we only want to run the LogCheck grouped tests and not the other tests, so, we have to provide an IMethodInterceptor listener that can eliminate the other tests and return only LogCheck grouped tests.
10. IConfigurable
The ICongurable listener is somewhat similar to IHookable listener. This interface skips the invocation of test methods and provides a run method which gets invoked instead of each configuration method found. The configuration method is then invoked once the callBack() method of the IConfigureCallBack parameter is called.
Which TestNG Listeners In Selenium WebDriver Do You Use The Most?
I hope this TestNG tutorial, helped you to realize which TestNG listeners are most suitable for your project requirements. Regarding the rarely used TestNG listeners, if there are any specific TestNG listener in Selenium that you find highly useful then feel free to share them in the comment section below. For an all in one session on performing a complete TestNG tutorial with Selenium you can checkout this video.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is TestNG and how is it different from JUnit?
TestNG is a testing framework for Java that supports advanced features like parallel execution, test dependencies, and data-driven testing. Unlike JUnit, which focuses mainly on unit tests, TestNG provides more flexibility and control over complex test suites and reporting.How do you control the order of test execution in TestNG?
You can control the test execution order using the priority attribute in the @Test annotation. Tests with lower priority values execute first. You can also use dependencies to ensure that specific tests run only after others complete successfully.What is parallel testing in TestNG?
Parallel testing enables simultaneous execution of multiple tests, classes, or methods. This helps reduce total execution time in large projects and can be configured easily in the TestNG XML file.What is a DataProvider in TestNG?
A DataProvider allows you to run a single test with multiple sets of data. It supports data-driven testing, enabling validation of functionality across different inputs without writing separate test cases.How does TestNG handle expected exceptions?
TestNG allows defining expected exceptions in the @Test annotation. If the specified exception occurs, the test passes, making it ideal for validating negative test scenarios and exception handling.What are test groups in TestNG?
Test groups help categorize test methods into logical sets like smoke, regression, or functional. You can run, include, or exclude specific groups using the TestNG XML configuration, making test management efficient.How are reports generated in TestNG?
TestNG automatically generates HTML and XML reports after each execution, summarizing passed, failed, and skipped tests. These reports give clear visibility into test outcomes and can be shared or customized further.How can you disable a test in TestNG?
You can temporarily disable a test by setting @Test(enabled = false). This prevents the test from running without removing its code, allowing you to skip unstable or unfinished tests easily.What are setup and teardown annotations in TestNG?
TestNG provides lifecycle annotations such as @BeforeMethod, @AfterMethod, @BeforeClass, and @AfterClass. These annotations help prepare test data, initialize resources, and perform cleanup after execution.What are test dependencies in TestNG?
Test dependencies let you specify that a test should execute only after certain other tests have passed. This ensures tests run in a logical order and prevents execution of dependent tests when prerequisites fail.Author