Scale Your Automation Testing with AI
Run end-to-end parallel tests & reduce test execution time by 5x
Generate tests scripts using natural language with KaneAI
Accelerate your testing process with Autoheal, SmartWait & RCA
- Automation
- Home
- /
- Learning Hub
- /
- How to Install Cypress Using Multiple Methods for E2E Testing
How to Install Cypress Using Multiple Methods for E2E Testing
Learn how to install Cypress using npm, Yarn, direct download, and advanced methods for fast and efficient E2E testing.
Last Modified on: December 6, 2025
- Share:
Cypress is a powerful test automation framework that runs directly in the browser, giving developers real-time visibility, control over test execution, and dependable results. Whether you're working with React, Angular, Vue.js, or any browser-based application, Cypress provides a smooth testing workflow and integrates easily with CI/CD pipelines. By learning how to install Cypress, you can quickly set up a testing environment and begin writing tests that enhance application quality and development efficiency.
Overview
How to Install Cypress Using Various Methods?
Cypress can be installed through multiple techniques, depending on how you manage dependencies and environments. You can use package managers, download binaries manually, or apply advanced configuration for controlled installations. Each method offers flexibility to fit different development setups.
- Using NPM: Install Cypress locally for a single project or globally for system-wide access. Local installation ensures project-specific version control. For a specific project, use the command npm install --save-dev cypress, and for setting up Cypress globally, use npm install -g cypress.
- Using Yarn: Install Cypress using Yarn for faster dependency resolution and caching. For project-specific installation, use yarn add --dev cypress.
- Direct Download: Download Cypress manually from the official releases page, extract it, and add it to your system PATH. This method is useful when package managers are unavailable or restricted.
- Advanced Installation Using CYPRESS_INSTALL_BINARY: Control binary installation behavior in CI/CD or custom setups. Skip download using CYPRESS_INSTALL_BINARY=0 npm install cypress, use a custom URL via CYPRESS_INSTALL_BINARY=https://custom-url.com/cypress.zip npm install cypress, or run npx cypress install for post-installation setup.
How to Initialize and Configure Your First Cypress Project ?
Setting up a Cypress project provides a ready-to-use environment for end-to-end testing. By combining Cypress with a lightweight backend like Express, you can test UI, navigation, and API interactions reliably in a local or cloud setup.
- Initialize Your Project: Create a new Node.js project and install required dependencies with npm init -y and npm install express to prepare your backend server.
- Configure package.json Scripts: Add scripts for development, headless tests, and combined server + Cypress execution to simplify workflow and automation.
- Install and Initialize Cypress: Run npx cypress open to initialize Cypress, automatically creating folders for fixtures, tests, plugins, and support files.
- Update Cypress Configuration: Set cypress.config.js with your base URL, timeouts, viewport, and environment variables to ensure Cypress interacts correctly with your Express server.
- Start the Express Server: Run the backend using npm run dev with nodemon for auto-reload so Cypress can access live routes, forms, and APIs.
- Write Your First Test: Create test files in cypress/e2e/ using the Gherkin-like structure with commands such as cy.visit(), cy.get(), and cy.contains() to validate UI and navigation.
- Run Tests via CLI or Test Runner: Use npx cypress run for headless execution or npx cypress open to interactively run and debug tests with the Cypress Test Runner.
How to Get Started With Cypress Installation?
The first step toward setting up a powerful end-to-end testing environment is installing Cypress, and before you begin, make sure your system meets the following requirements.
System Requirements:
- Operating System: Supports Windows 10+ and macOS 10.15+ to maintain compatibility across modern development environments.
- Linux Support: Works with Linux systems like Ubuntu 18.04+, CentOS 7+, and Fedora 21+ for reliable cross-platform Cypress usage support.
- Minimum Hardware Requirements: Requires a minimum of 4GB RAM and 2GB free disk space to maintain stable Cypress performance during test execution sessions.
- 64-bit System Required: Needs a 64-bit operating system to fully support Cypress processes, browsers, and efficient end-to-end testing operations running smoothly.
- Modern CPU Recommended: Requires a modern CPU with hardware acceleration capabilities for fast browser rendering and smooth Cypress test execution throughout projects.
Having these in place ensures a smooth setup process and allows Cypress to run efficiently without compatibility issues. Once everything is ready, you can proceed to install Cypress and start running tests without delays. To get started smoothly, follow a Cypress tutorial and gain deeper insights, from setup to running your first Cypress tests.
What Are the Prerequisites for Installing Cypress?
Before you proceed to install Cypress, make sure your development environment is properly configured. Certain tools and software need to be set up beforehand to ensure smooth installation, test execution, and efficient test development. Preparing these prerequisites in advance will save time and help prevent configuration issues during the Cypress setup process.
- Node.js Installation: Cypress supports Node.js 14 and above, but Node.js 16+ is recommended for best compatibility. To check your current Node.js version:
node --versionnpm --version - macOS (Homebrew): Homebrew offers an easy way to install and manage Node.js on macOS. Use the following command to install:
brew install nodechoco install nodejssudo apt install nodejs npm- Visual Studio Code: Recommended with extensions like Cypress Snippets or Cypress Helper for autocompletion and ready-made code templates.
- WebStorm: Offers built-in support for Cypress, including intelligent code assistance and test integration.
Note: Run Cypress tests across 3000+ real desktop browsers and OS combinations.. Try LambdaTest Today!
How to Install Cypress?
There are several methods to install Cypress, allowing you to choose the method that best fits your project setup and workflow:
- Using NPM
- Using Yarn
- Direct Download
- Advanced Installation Using CYPRESS_INSTALL_BINARY
We’ll cover each method in detail so you can easily select the approach that works best for your project and start testing with Cypress quickly.
Using NPM
The most common method for installing Cypress is through npm, Node.js's default package manager. Navigate to your project directory in the terminal and run the installation command.
- For Local Installation: For project-specific use, it’s best to install Cypress locally as a development dependency. This keeps it isolated to your project and avoids affecting other projects. Follow the command given :
npm install --save-dev cypressThis approach ensures that Cypress is installed as a development dependency, making it available only during development and testing phases while keeping your production bundle clean.
npm install -g cypressNote: Global installation is generally not recommended for team projects as it can lead to version inconsistencies.
Using Yarn
Yarn is an alternative package manager for JavaScript projects that many developers prefer for its speed and reliability features. To install Cypress using Yarn, navigate to your project directory and execute the following command.
yarn add --dev cypressThis command functions similarly to npm but leverages Yarn's enhanced dependency resolution and caching mechanisms for potentially faster installation times.
Direct Download
Cypress offers direct download alternatives on their website for cases where npm or Yarn installations are not possible. This method is useful in environments with restricted internet access, corporate networks with specific security policies, or when you need a specific version not available through package managers.
To download directly:
- Visit the Cypress releases page.
- Download the appropriate version for your operating system
- Extract the archive to your desired location.
- Add the Cypress binary to your system PATH.
Extracting the downloaded archive and adding the executable to your system PATH allows global access. While direct downloads provide flexibility, they require manual updates and do not integrate as seamlessly with project dependency management.
Advanced Installation Using CYPRESS_INSTALL_BINARY
The CYPRESS_INSTALL_BINARY environment variable provides advanced control over the Cypress installation process, especially useful in CI/CD environments or when working with custom binary distributions.
This method allows you to specify alternative download locations, use cached binaries, or skip binary downloads entirely when using pre-installed versions.
- Install Cypress without downloading the binary: If Cypress is already installed globally or through other means, execute:
CYPRESS_INSTALL_BINARY=0 npm install cypressCYPRESS_INSTALL_BINARY=https://custom-url.com/cypress.zip npm install cypressCYPRESS_INSTALL_BINARY=0 npm install cypressWhen you skip binary installation, you'll need to install it later using:
npx cypress installThis installation method is particularly valuable in Docker environments, corporate networks with proxy requirements, or when implementing custom distribution strategies. You can also use this approach to install specific versions or custom builds of Cypress that may not be available through standard package managers.
How To Set Up Your First Project?
When you first install Cypress, it automatically creates a folder structure in your project, including subdirectories for fixtures, tests (e2e), plugins, and support files. The cypress.config.js file serves as the main configuration, allowing you to customize behavior, set base URLs, configure timeouts, and define environment variables.
Creating your first Cypress test is straightforward and follows familiar testing patterns, giving you a complete environment to start writing end-to-end tests immediately.
Why Is Express Needed?:
Express is used to create a lightweight backend server that serves as the application Cypress will test. Without a server or web application, Cypress cannot perform end-to-end tests. Express allows you to:
- Serve multiple pages with navigation.
- Handle user management functionality.
- Provide a contact form and API endpoints.
- Add interactive elements with data-cy attributes for Cypress to interact with.
- Quickly set up a backend for testing without heavy frameworks.
By combining Cypress with Express, you have a complete testable environment for both front-end and back-end workflows.
Express provides a lightweight backend environment, allowing Cypress to perform end-to-end tests on a real application. Without a server, Cypress cannot interact with your app’s pages, forms, or API endpoints. Using Express, you can quickly set up a backend for testing without heavy frameworks, giving you a complete, testable environment for both front-end and back-end workflows.
You can reference a ready-made example here: server.js on GitHub
Installing Express Dependencies
To get started with Express, first open your project directory in a code editor and initialize it. Then, install the necessary dependencies to set up a lightweight backend server for your Cypress tests.
- Initialize Project: Open your project directory in your code editor, and initialize the project.
npm init -ynpm install express{
"name": "cypress-installation”
"version": "1.0.0",
"main": "server.js",
"scripts": {
"test": "cypress open",
"start": "node server.js",
"dev": "nodemon server.js",
"test:headless": "cypress run",
"cy:open": "cypress open",
"cy:run": "cypress run",
"test:full": "concurrently "npm run start" "wait-on http://localhost:3000 && cypress run""
},
"keywords": [],
"author": "",
"license": "ISC",
"description": "",
"dependencies": {
"express": "^5.1.0"
}
}npx cypress openSelect E2E Testing and click Continue. Cypress automatically creates the folder structure and configuration files for you.
This command automatically creates the following structure for your project:
your-project/
│
├── cypress/
│ ├── e2e/
│ │ └── spec.cy.js
│ │
│ ├── fixtures/
│ │ └── example.json
│ │
│ └── support/
│ ├── commands.js
│ └── e2e.js
│
├── cypress.config.js
└── package.jsonCypress Configuration Files
cypress.config.js is the main file, and this file controls core Cypress behavior, test settings, base URLs, timeouts, and environment variables. It acts as the central place to manage how Cypress runs and interacts with your application. Configuring this file properly ensures smoother execution when you install Cypress and begin writing tests.
const { defineConfig } = require("cypress");
module.exports = defineConfig({
e2e: {
setupNodeEvents(on, config) {
// implement node event listeners here
},
},
});
cypress/support/e2e.js - Global configuration and behavior:
This file manages shared behaviors, global hooks, and reusable functions that apply to all Cypress tests. It allows you to import and register custom commands, improving readability and reducing repetitive code.
With import './commands', you centralize utility actions for smoother test execution after you install Cypress.
// You can read more here:
// https://on.cypress.io/configuration
// ***********************************************************
// Import commands.js from the cypress/support/ folder using ES2015 syntax:
import './commands' Updating Cypress Configuration
After you install Cypress and generate the default project structure, you must configure it to interact with your Express server. Updating the configuration file ensures Cypress knows where your application is running and how to handle test execution smoothly.
Update your cypress.config.js to point to your Express app:
const { defineConfig } = require('cypress')
module.exports = defineConfig({
e2e: {
baseUrl: 'http://localhost:3000',
viewportWidth: 1280,
viewportHeight: 720,
defaultCommandTimeout: 10000,
setupNodeEvents(on, config) {
// implement node event listeners here
},
env: {
apiUrl: 'http://localhost:3000/api'
}
}
})Starting Your Express Server
Once your configuration is set, the next step is to run the Express server so Cypress can interact with the application during testing. Starting the server ensures your routes, UI elements, and API endpoints are live and ready to be tested end-to-end.
Make sure you install nodemon, using npm install --save-dev nodemon, then run your Express server in one terminal:
npm run devYour Express server will start at http://localhost:3000 with auto-reload enabled. This gives Cypress a live application to test against.
Writing a Basic Cypress Test
With your server running and configuration complete, you can now create your first test case in Cypress. This initial test helps validate routing, UI visibility, and user interactions, forming the foundation for more advanced automation as you continue to install Cypress and scale your testing suite.
In your Cypress folder, create an e2e folder, navigate to the folder, and create your first test: your first test in cypress/e2e/first-test.cy.js:
describe("My First Test", () => {
it("Visits the app root url", () => {
cy.visit("/");
cy.get("h1").contains("Welcome to Cypress Testing App");
cy.get("[data-cy=get-started-btn]").should("be.visible");
});
it("Checks navigation", () => {
cy.visit("/");
cy.get("nav").should("be.visible");
cy.get("nav a").should("have.length", 4);
// Test navigation to users page
cy.get("nav a").contains("Users").click();
cy.url().should("include", "/users");
cy.contains("h1", "User Management");
});
it("Tests user management functionality", () => {
cy.visit("/users");
// Add a new user
cy.get("[data-cy=user-name]").type("Test User");
cy.get("[data-cy=user-email]").type("test@example.com");
cy.get("[data-cy=add-user-btn]").click();
// Verify user was added
cy.contains("Test User").should("be.visible");
});
});Running Cypress Tests
Once you install Cypress and write a test script, you can execute your suites directly through the terminal or the Cypress Test Runner. Running tests helps validate application flow, UI behavior, APIs, and navigation under different environments and browsers.
Below are multiple ways to execute Cypress tests efficiently.
- Command Line Interface: Run Cypress directly from the terminal for faster automation and continuous integration workflows.
- Run all tests in headless mode: Executes every test without opening the Cypress UI for quick automated runs.
# Run all tests
npx cypress run# Run specific test file
npx cypress run --spec "cypress/e2e/first-test.cy.js"# Run tests in specific browser
npx cypress run --browser chrome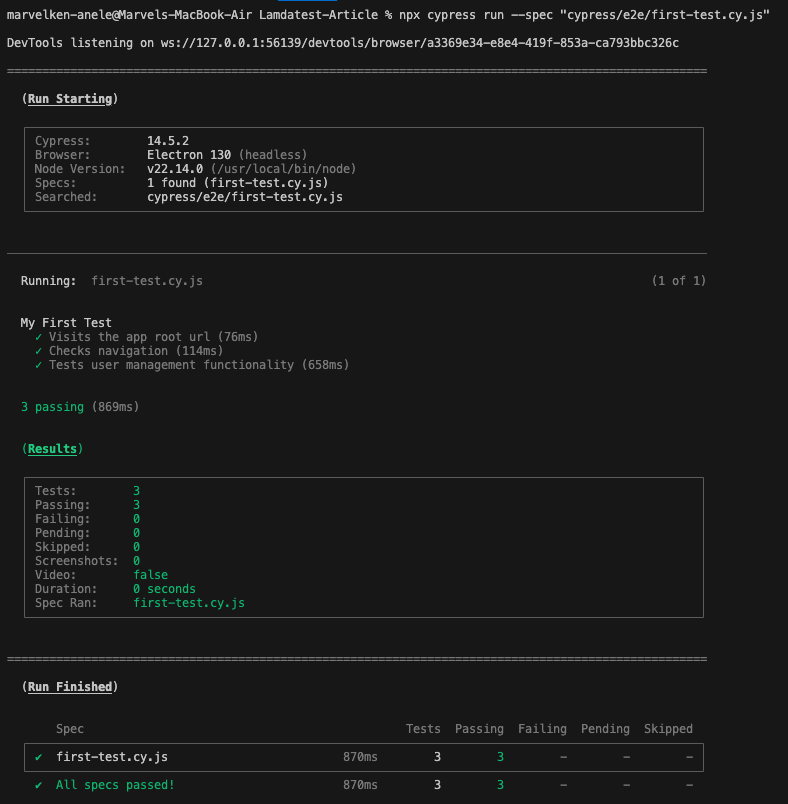
- Launch the Test Runner: The Cypress Test Runner provides an interactive interface to view and execute your tests in real time. It helps you quickly identify issues and debug your application as tests run.
npx cypress open- The Test Runner provides:
- Real-time test execution for instant feedback.
- Interactive debugging with pause and step-through controls.
- Time-travel debugging to inspect past UI states.
- Network request inspection for API behavior verification.
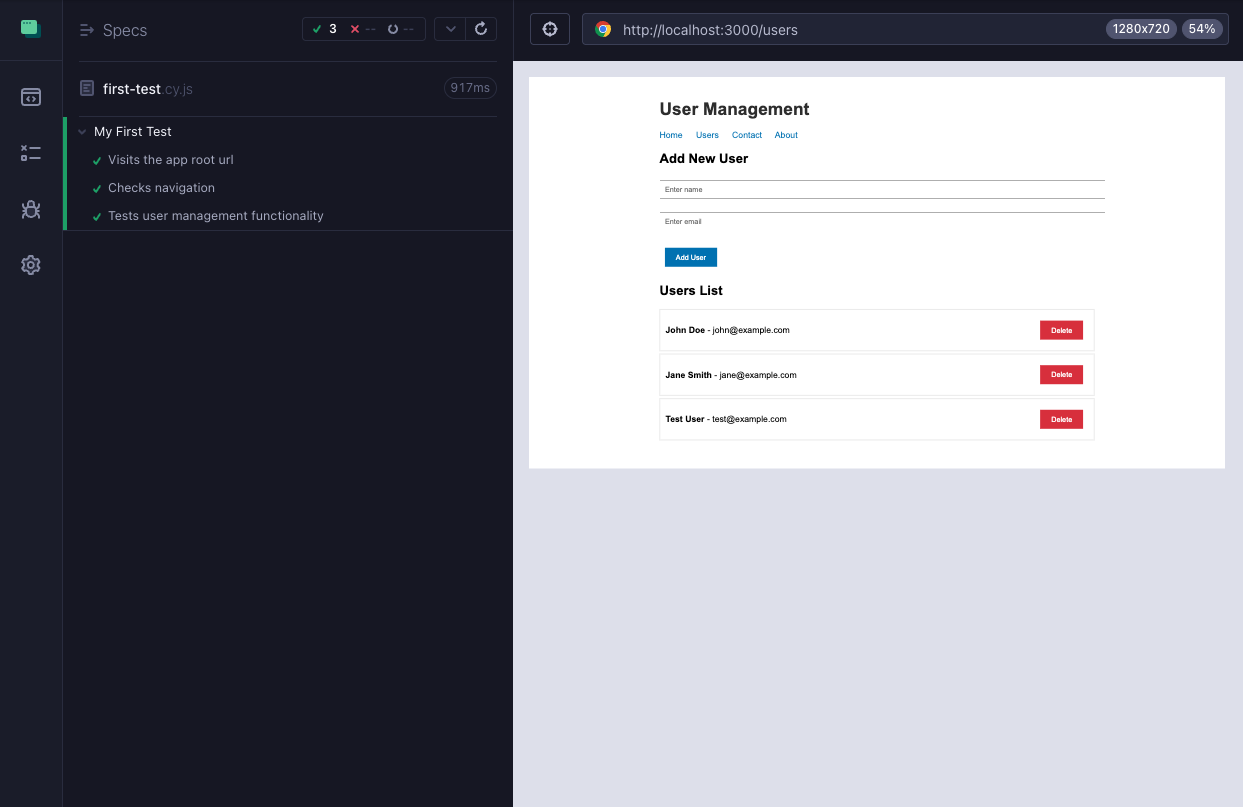
How to Perform Cypress Tests at Scale With Cypress CLI?
Running Cypress in the cloud is the most effective approach for scaling tests.LambdaTest is a cloud testing platform that allows you to perform manual and automated Cypress testing at scale across 3000+ browsers and OS combinations, offering parallel execution, stable performance, and seamless scalability, far beyond what local setups can support.
Before integrating the Cypress test script with LambdaTest, you'll need to follow the steps:
- Create .env file: Securely store your LambdaTest credentials by creating a .env file in the root of your project. Add the following values:
LT_USERNAME="<your_username>"
LT_ACCESS_KEY="<your_access_key>"# Install LambdaTest Cypress CLI
sudo npm install -g lambdatest-cypress-cli# Configure authentication
lambdatest-cypress init{
"lambdatest_auth": {
"username": "<Your LambdaTest Username>",
"access_key": "<Your LambdaTest Access Key>"
},
"browsers": [
{
"browser": "Chrome",
"platform": "Windows 10",
"versions": ["latest"]
},
{
"browser": "Firefox",
"platform": "macOS Big Sur",
"versions": ["latest"]
}
],
"run_settings": {
"cypress_version": "13.x",
"build_name": "Sample Cypress Tests",
"parallels": 2,
"specs": "./cypress/e2e/**/*.cy.js"
},
"tunnel_settings": {
"tunnel": true,
"tunnel_name": "cypress-tunnel"
}
}Note: The tunnel is set to true here because we're testing a local Express server running on localhost:3000. The tunnel creates a secure connection allowing LambdaTest's cloud browsers to access your local application.
By defining multiple browsers and OS combinations in your configuration, you enable cross-browser testing with Cypress directly through LambdaTest. Instead of relying solely on local browser availability, you can run your Cypress suite across Chrome, Firefox, Edge, Safari, and various operating systems, providing wider coverage and more reliable results in real-world environments.
Running Your Tests
Once your LambdaTest configuration is set, you can begin executing your Cypress test suite directly in the cloud. This allows tests to run independently of local machine limitations and ensures consistent execution across real browser environments.
- Run tests through LambdaTest cloud: Execute your Cypress tests on the LambdaTest infrastructure:
# Terminal 2: Execute tests on LambdaTest cloud
lambdatest-cypress run --specs "./cypress/e2e/**/*.cy.js"# Run tests against deployed app (no tunnel needed)
lambdatest-cypress run --specs "./cypress/e2e/**/*.cy.js" --tunnel falseOutput:
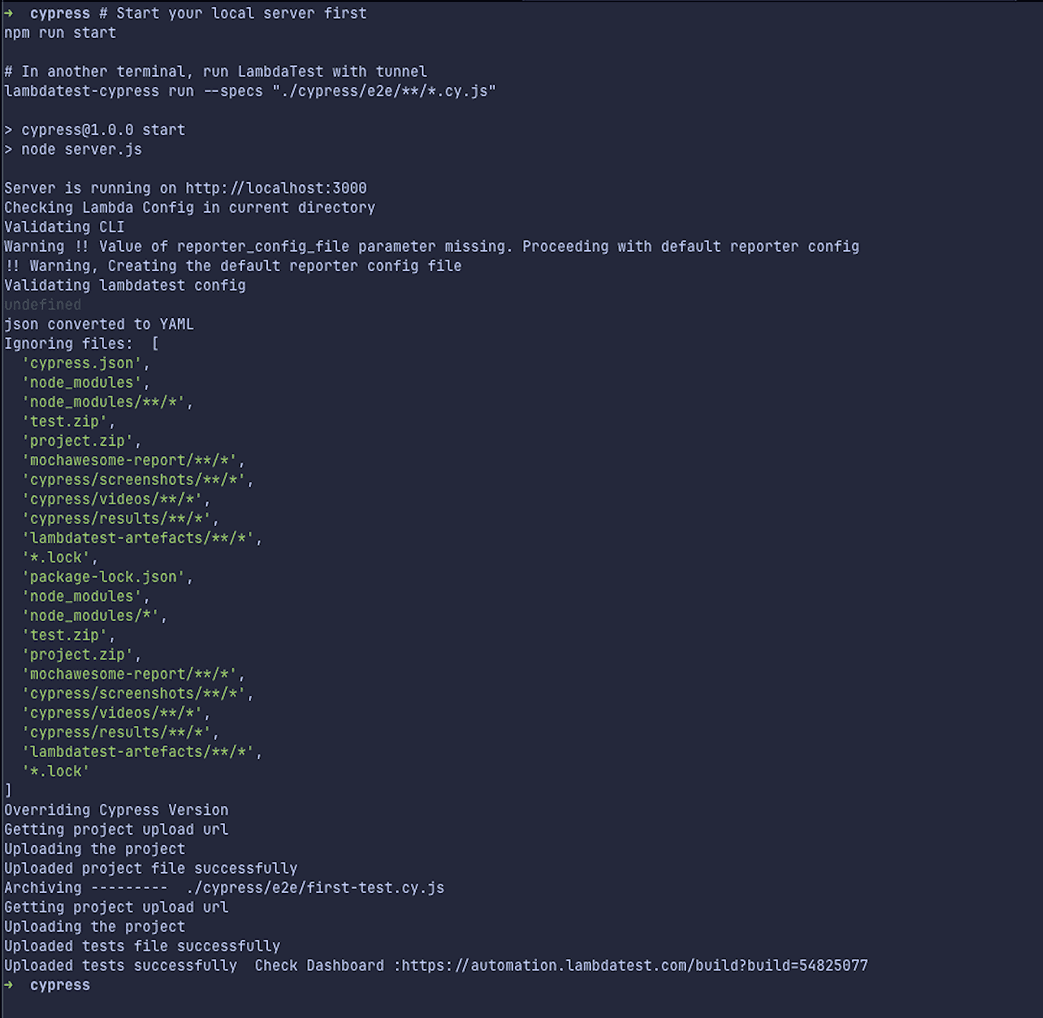
Result:
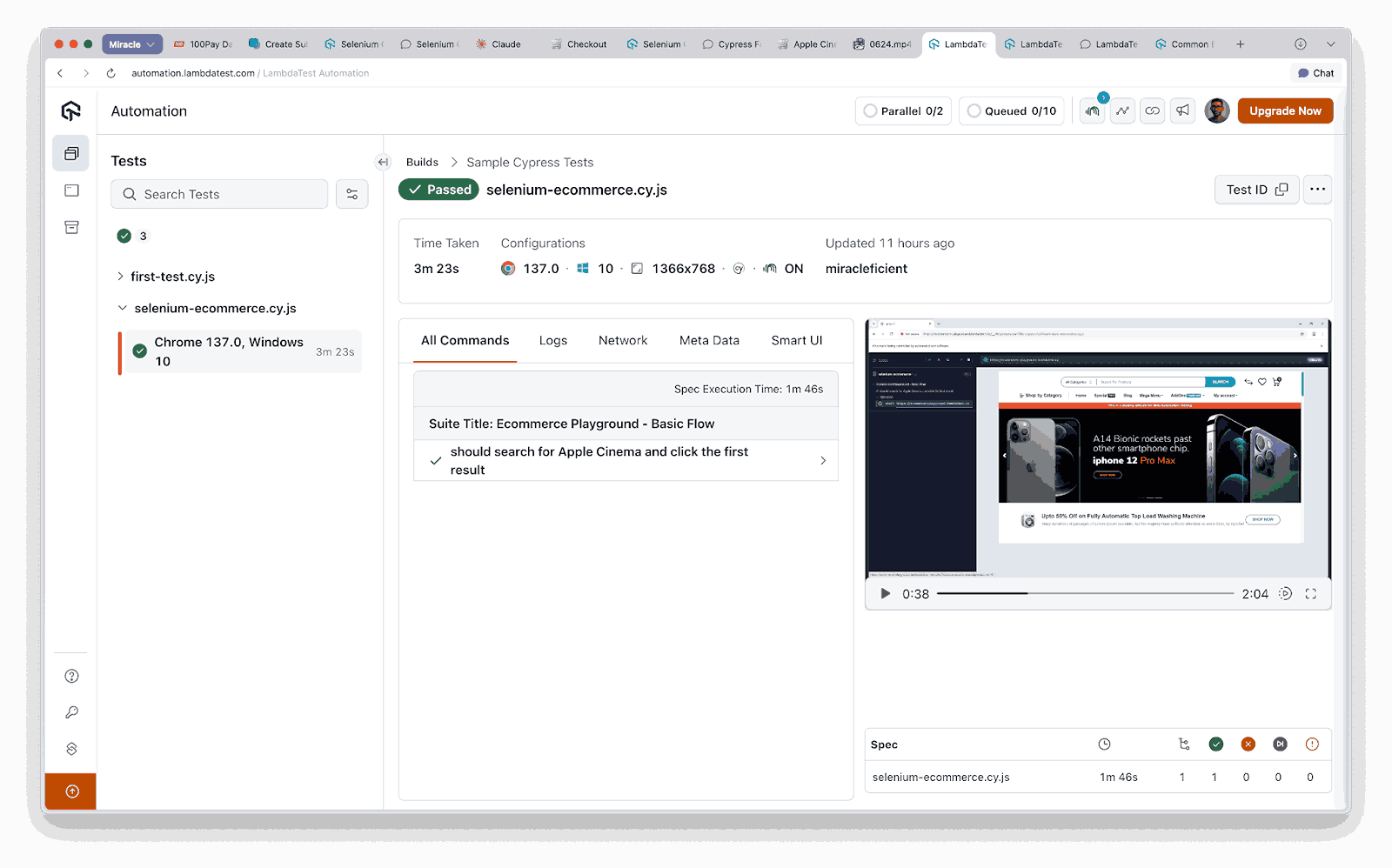
Now that you have successfully executed Cypress tests on a single browser and operating system, you can take the next step toward faster execution by enabling Cypress parallel testing. This allows multiple test specs to run simultaneously, reducing overall execution time and improving efficiency as your test suite grows.
Running Tests in Parallel
Execute tests across multiple browsers simultaneously:
# Run with maximum parallelism
lambdatest-cypress run --parallels 10
# Run specific test suite
lambdatest-cypress run --specs "./cypress/e2e/checkout/**/*.cy.js"Result:
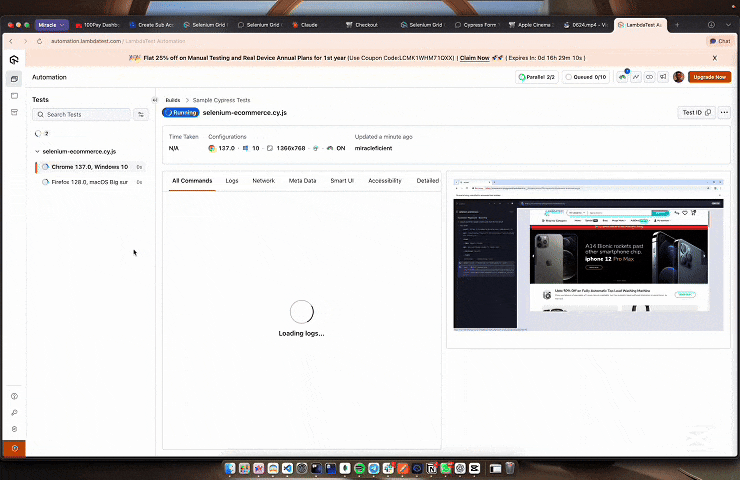
To get started with Cypress automation, follow this support documentation on Cypress testing with LambdaTest.
Best Practices to Follow to Install Cypress
Writing Cypress tests is more than getting them to pass; it's also about creating a sustainable testing strategy. These practices help avoid common issues that lead to flaky tests and future maintenance problems.
Test Organization
A well-organized test suite makes it easy to diagnose failures and add new coverage. Poor organization leads to duplicate tests and confusion about test purposes.
Structure tests for maintainability:
// Group related tests
describe('User Authentication', () => {
beforeEach(() => {
cy.visit('/login')
})
describe('Valid Credentials', () => {
it('should login successfully', () => {
// test implementation
})
})
describe('Invalid Credentials', () => {
it('should show error message', () => {
// test implementation
})
})
})Performance Optimization
Test execution speed will directly impact developer productivity and CI/CD efficiency. To optimize test execution speed, you can do these:
// Use data attributes for reliable selectors
cy.get('[data-cy=submit-button]').click()
// Avoid unnecessary waits
cy.get('.loading').should('not.exist')
// Use aliases for repeated elements
cy.get('.user-menu').as('userMenu')
cy.get('@userMenu').click()Reporting & Analytics
Test reporting provides visibility into your test suite's performance over time. Proper reporting configuration helps teams identify patterns in failures and make more informed decisions about test improvements.
You can implement comprehensive reporting this way:
// cypress.config.js
module.exports = defineConfig({
e2e: {
reporter: 'mochawesome',
reporterOptions: {
reportDir: 'cypress/reports',
overwrite: false,
html: false,
json: true
}
}
})Conclusion
Installing and configuring Cypress involves ensuring system prerequisites, selecting the right installation method, and setting up your testing environment. By first taking the time to install Cypress correctly, you can take full advantage of local testing with fast feedback, real-time debugging, and an excellent development experience.
However, to achieve scalable, cross-browser testing, cloud platforms like LambdaTest are highly beneficial. Combining local Cypress testing with cloud-based execution provides a robust strategy, rapid development cycles locally and comprehensive, parallel testing across multiple browsers and environments in the cloud. This ensures both developer productivity and reliable, thorough test coverage for modern web applications.
Citations
- Cypress Official Documentation: https://docs.cypress.io/
- Cypress Installation Guide: https://docs.cypress.io/guides/getting-started/installing-cypress
- Advanced Installation Options: https://docs.cypress.io/app/references/advanced-installation
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Did you find this page helpful?
More Related Hubs

Start your journey with LambdaTest
Get 100 minutes of automation test minutes FREE!!


