KaneAI - GenAI Testing Agent
Plan, author and evolve end to end automation test using natural language prompts.
- Testing Basics
- Home
- /
- Learning Hub
- /
- 50+ Automation Testing Interview Questions [Expert Answers]
50+ Automation Testing Interview Questions [Expert Answers]
Explore top Automation Testing Interview Questions covering frameworks, Selenium, CI/CD, AI trends, and real-world scenarios to prepare for 2026.
Last Modified on: December 4, 2025
- Share:
Automation testing is the backbone of modern software development, and with AI-driven tools rapidly reshaping QA, the skill demands for testers are evolving quickly. Companies are increasingly adopting self-healing scripts and autonomous testing systems, making these technologies standard expectations in automation roles.
This blog compiles the most important and frequently asked automation testing interview questions for 2026, covering the latest trends, AI-led capabilities, and real-world scenarios to help you walk into your next interview fully prepared and future-ready.
Overview
Automation Testing Interview Questions are designed to assess your knowledge of automation fundamentals, test frameworks, popular tools like Selenium, and real-world scenarios like dynamic element handling or CI/CD integration. Whether you’re preparing for a QA role or a DevOps-focused testing position, mastering these topics is essential.
1. Top Automation Testing Interview Questions (Fundamental to Expert)
- What is automation testing, and how does it differ from manual testing?
- What are the key benefits and limitations of automation testing?
- What are the different types of automation testing, and when should automation not be used?
- What are the six stages in the automation testing life cycle?
- What is the Page Object Model (POM), and why is it important for framework design?
- How do you handle test data management in automation frameworks?
- What are dynamic elements in Selenium, and how do you handle them using waits or XPath/CSS?
- What is the difference between continuous integration (CI) and continuous delivery (CD)?
- How do you identify and fix flaky tests in automation?
- What is the difference between horizontal and vertical scaling in cloud testing?
2. Real-World Scenario-Based Questions
- How do you handle scenarios where the application UI changes frequently?
- How do you implement data-driven testing when test data changes dynamically?
- How would you automate an end-to-end flow including login, form submission, and file upload?
- How do you run tests in parallel across multiple browsers and devices in the cloud?
- How do you maintain and scale a large automation test suite?
3. Modern Trends for 2026
- What is AI-powered automation, and how does it differ from traditional automation?
- How do self-healing test scripts work?
- How does AI improve visual testing and dynamic UI validation?
- How does AI help with test generation from natural language?
- What is intelligent test prioritization using machine learning?
Automation Testing Interview Questions
Note: We have compiled all Automation Testing Interview Questions List for you in a template format. Feel free to comment on it. Check it out now!!
Fundamentals of Automation Testing Interview Questions
Automation testing fundamentals help interviewers assess how well you understand the core concepts, tools, benefits, and limitations of test automation. These questions focus on essential knowledge every automation tester must master, including test types, frameworks, locators, CI/CD practices, and the role of automation in modern QA workflows.
1. What is Automation Testing?
Automation testing is a software testing strategy in which a tester programmatically runs tests using a tool or framework instead of manually executing test cases one by one. The primary goal is to save time, effort, and money on repetitive tests that don't change frequently. It helps teams achieve greater speed, reliability, and efficiency in their testing efforts.
Key Benefits:
- Faster test execution
- Increased test coverage
- Reduced human error
- Cost-effective for regression testing
- Enables continuous testing in CI/CD pipelines
2. What is the role of an Automation Tester?
An automation tester is responsible for designing, creating, and executing automated tests to ensure software works as expected. Their role involves understanding the application, building reliable test scripts, identifying defects early, and improving overall testing efficiency. They also maintain automation frameworks, optimize test coverage, and collaborate with developers and QA teams to deliver stable, high-quality releases faster and with fewer manual efforts.
3. What is the difference between Manual Testing and Automation Testing?
Manual Testing and Automation Testing are two core approaches in software quality assurance, each serving different needs. Here is a clear comparison table to help you understand the key differences between them, making it easier to evaluate Manual Testing vs Automation Testing effectively.
| Aspect | Manual Testing | Automation Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Execution | Performed by human testers | Executed using scripts and tools |
| Speed | Slower, especially for repetitive tasks | Faster and more efficient |
| Accuracy | Prone to human error | More precise and consistent |
| Cost/ROI | Lower upfront costs, higher long-term | Higher initial investment, long-term savings |
| Flexibility | Highly adaptable for exploratory testing | Better for stable, repetitive tests |
| Scalability | Limited by tester availability and time | Easily scales for large test suites |
| Best suited for | Exploratory testing, usability, ad-hoc tests | Regression testing, performance testing |
| Skill requirements | Testing expertise, domain knowledge | Programming and scripting skills |
4. What are the key benefits and limitations of automation testing?
Benefits:
- Speed and Efficiency: Execute hundreds of tests in minutes versus days manually
- Reusability: Scripts run across multiple builds and environments
- Coverage: Test more scenarios than feasible manually
- Continuous Testing: Integrate into CI/CD pipelines for instant feedback
- Cost Reduction: Studies show automation can reduce testing costs by 20-40% over 2-3 years
- Accuracy: Eliminate human errors in repetitive tasks
- Parallel Execution: Run tests simultaneously across browsers/devices
Limitations:
- High Initial Investment: Tools, framework development, training costs
- Maintenance Overhead: UI changes require script updates
- Cannot Replace Manual Testing: Misses usability issues, visual defects
- False Positives/Negatives: Flaky tests reduce trust
- Limited Creativity: Cannot perform exploratory testing
- Tool Dependency: Locked into specific tool ecosystems
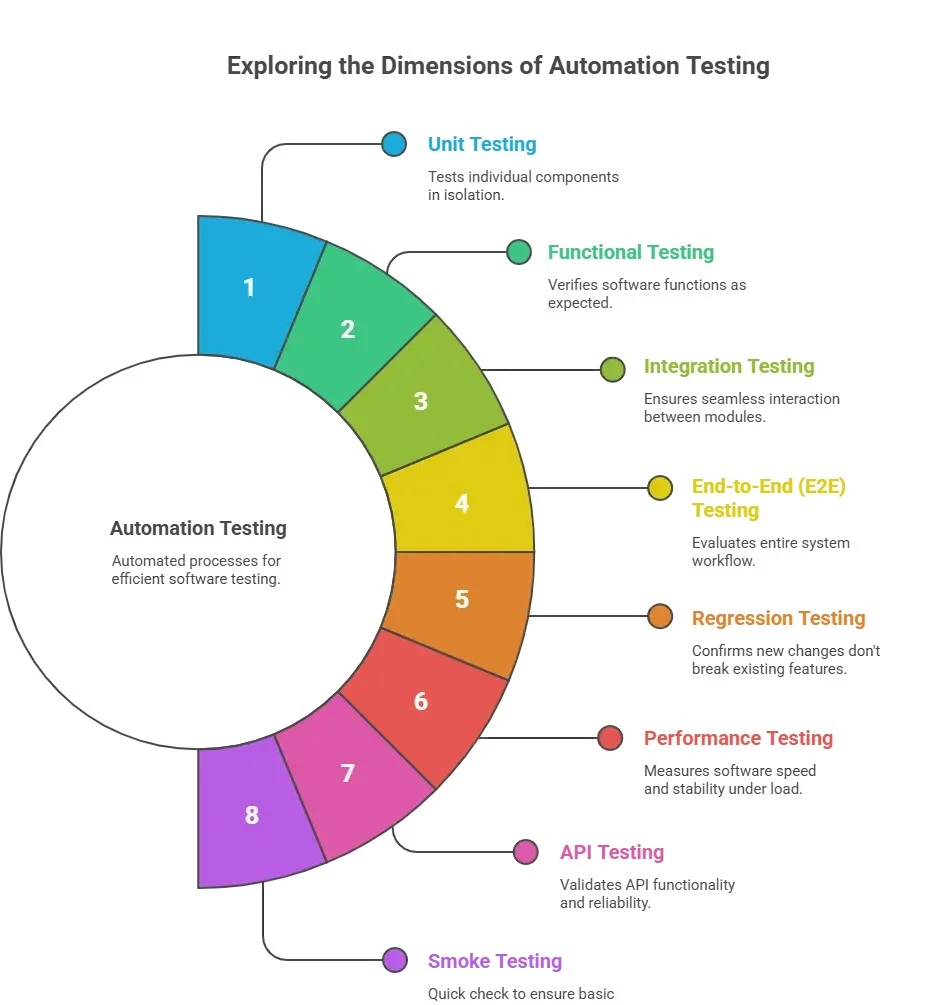
5. What are the different types of automation testing?
Automation testing includes several types of tests that help teams speed up validation, improve accuracy, and ensure software works as expected across different scenarios. Here are the main types:
- Unit Testing: This focuses on testing individual components or functions in isolation. It helps developers catch bugs early in the development cycle.
- Integration Testing: After units are combined, integration testing checks whether modules work together smoothly and share data correctly.
- Functional Testing: This ensures every feature behaves according to requirements. Tools like Selenium, Cypress, and Playwright are commonly used.
- End-to-End Testing: E2E tests simulate real user journeys, such as login, checkout, or form submission, to confirm the entire application workflow works from start to finish.
- Regression Testing: Whenever new changes or features are added, regression tests verify that existing functionality hasn’t broken. Automation makes this faster and more reliable.
- Performance Testing: This type measures speed, responsiveness, and stability under different loads. It includes load testing, stress testing, and scalability testing.
- API Testing: API automation validates endpoints, response data, performance, and security. It helps catch issues before they reach the UI layer.
- Smoke Testing: These quick tests act as a basic health check to confirm the core application is stable enough for deeper testing.
- Security Testing: Automation tools help detect vulnerabilities, validate authentication flows, and ensure data protection.
- Cross-Browser & Cross-Platform Testing: This ensures your application works consistently across multiple browsers, devices, and operating systems. Cloud platforms like LambdaTest make this easier.
6. What are the popular automation testing tools in the market?
An automation testing tool is a software application that automates the process of testing software applications. It allows testers to execute test cases automatically, eliminating manual testing and increasing testing efficiency and accuracy.
When selecting an automated testing tool, there are several factors to consider, such as your application, testing needs, and your team’s preferences. The popular automation testing tools in the market are:
7. What is the Robot Framework?
Robot Framework is an open-source automation framework used for both test automation and robotic process automation (RPA). It follows a keyword-driven approach, which makes test cases easy to read, write, and maintain, even for teams with less programming experience. It supports a wide range of libraries and tools, including Selenium, Appium, REST APIs, and database testing, allowing testers to automate web, mobile, and backend workflows. Because of its modular design and rich ecosystem, Robot Framework is widely used for end-to-end testing and scalable automation setups.
8. When should you NOT use Automation Testing?
There are certain cases where manual testing is preferred over automation testing:
- Short-term projects: When the project timeline is brief, and test creation would take longer than manual execution
- Ad-hoc testing: Unplanned testing that relies on the tester's intuition and creativity
- Exploratory testing: Requires human knowledge, experience, analytical skills, and creativity
- Usability testing: Evaluating user experience requires human judgment
- One-time test scenarios: When tests won't be repeated enough to justify automation effort
- Frequently changing UI: When the application interface changes, it constantly
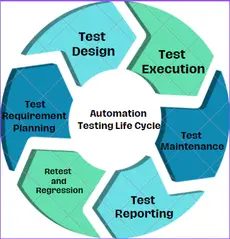
9. What are the 6 stages in the automation testing life cycle?
The automation testing life cycle consists of six key stages:
- Test Requirement Analysis: Identify what needs to be tested and define the overall automation strategy
- Test Design: Create and plan the test cases, test data, and conditions that will be automated
- Test Execution: Run the automated scripts to validate whether the application behaves as expected
- Test Maintenance: Update scripts when the application changes to keep tests stable and relevant
- Test Reporting: Share clear reports on test results, coverage, defects, and overall progress
- Retesting & Regression: Re-run tests to verify fixes and ensure existing features still work without issues
10. What is a Test Automation Framework?
A test automation framework is a structured set of guidelines and practices used in test automation to provide a standardized and efficient way to design, develop, and execute automated tests. It provides a foundation for the test automation process by defining how test scripts are organized, how test data is managed, and how test results are reported.
Read more about Best Test Automation Frameworks.
11. What are the Types of frameworks?
Different framework types suit various testing needs:
| Framework Type | Key Characteristics | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Linear (Record & Playback) | Sequential script execution, minimal planning | Small projects |
| Modular | Divides tests into independent modules based on abstraction | Applications with distinct components |
| Data-Driven | Separates test logic from test data | Multiple data scenarios |
| Keyword-Driven | Uses keywords to represent actions | Teams with limited coding knowledge |
| Hybrid | Combines multiple framework approaches | Complex projects |
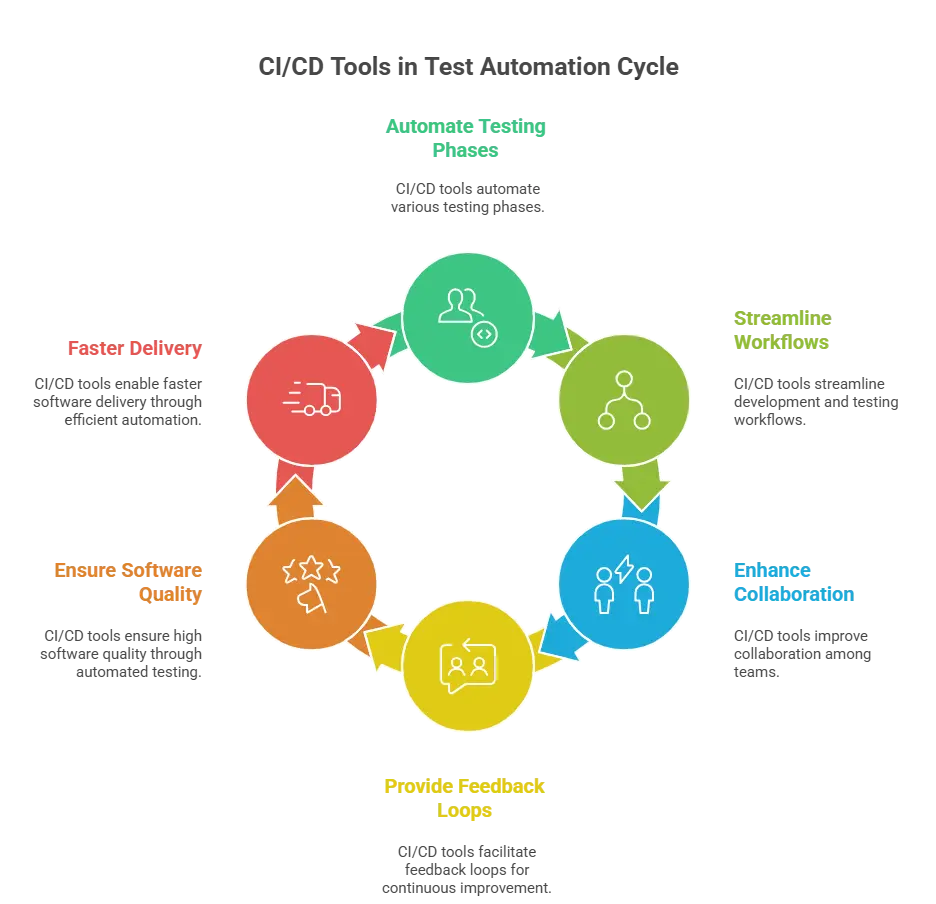
12. What role do CI/CD tools play in test automation?
CI/CD tools help test automation by:
- Auto-running tests on every code change to catch bugs early.
- Providing fast feedback so developers know immediately if something breaks.
- Supporting parallel test execution to speed up the testing process.
- Ensuring consistent test runs across different environments.
- Reducing manual effort by automating the entire build–test–deploy cycle.
- Improving code quality with continuous checks at every stage.
- Making releases more reliable by validating every change before deployment.
13. What is ROI in test automation, and how do you calculate it?
Return on Investment (ROI) measures whether automation efforts deliver value exceeding their costs.
Basic Formula:
ROI = (Savings - Investment) / Investment × 100%
- Savings = (Manual Testing Cost - Automated Testing Cost) × Number of Executions
- Investment = Tool Costs + Framework Development + Maintenance + Training
Example Calculation:
- Manual test suite execution: 100 hours @ $50/hour = $5,000
- Automated execution: 2 hours @ $50/hour = $100
- Initial automation investment: $20,000
- Executed 30 times in the first year
Savings = ($5,000 - $100) × 30 = $147,000 ROI = ($147,000 - $20,000) / $20,000 × 100% = 635%
Key Metrics to Track:
- Test execution time reduction
- Bug detection rate improvement
- Number of releases per quarter
- Team productivity increases
- Regression cycle time reduction
14. What is Selenium, and why is it popular in automation testing?
Selenium is an open-source framework used to automate web applications across different browsers and platforms. It allows testers to write scripts in multiple programming languages like Java, Python, C#, and JavaScript, and more, making it flexible for various projects.
Selenium is popular because it’s free, supports all major browsers, integrates well with CI/CD tools, and has a strong community. It also offers powerful components like WebDriver and Selenium Grid, which help teams run reliable tests and scale automation efficiently.
15. What are the various components of Selenium?
Selenium has four main components:
- Selenium IDE: A simple browser plugin used to record and replay test steps. It’s great for quick script creation without coding.
- Selenium RC: An older tool that’s now deprecated. Some legacy projects still use it, but it has been replaced by Selenium WebDriver.
- Selenium WebDriver: The most important part of Selenium. It lets you write automated tests in languages like Java, Python, and C#, and interacts directly with the browser for fast and reliable automation.
- Selenium Grid: Used for parallel testing by running tests across multiple machines, browsers, and environments simultaneously. This helps significantly reduce overall test execution time.
16. What is a Locator in Selenium, and what are the different types of Locators used in Selenium?
A locator in Selenium is a way to identify and find elements on a webpage so you can interact with them during automation. It helps Selenium understand which button to click, which field to type in, or which link to open.
The commonly used types of locators in Selenium are:
- ID: Finds an element using its unique ID attribute.
- Name: Locates elements based on the value of the name attribute.
- Class Name: Targets elements that share the same class value.
- Tag Name: Selects elements by their HTML tag, such as or .
- Link Text: Identifies links using their visible text.
- Partial Link Text: Finds links by matching part of the text.
- CSS Selector: A powerful and flexible way to locate elements using CSS patterns.
- XPath: A path-based method to locate elements anywhere in the HTML structure.
17. What is a page object model?
A Page Object Model (POM) is a design pattern used in automation testing where each page of an application is created as a separate class. This class stores the page’s elements and the actions you can perform on them. By keeping page details and test steps separate, POM makes tests easier to read, reduces repeated code, and simplifies updates when the UI changes.
18. What is a Test Script, and what is a Test Suite?
A test script is a set of detailed steps that check how a specific feature or action in an application should work. It includes the inputs, actions, and expected results.
A test suite is a collection of multiple test scripts grouped together to test a broader feature or an entire module. It helps run several related tests in an organized way to ensure everything works correctly.
19. What is regression Testing?
Regression testing is a software testing methodology that ensures that recent changes to a software application have not adversely affected its existing features. The primary goal of regression testing is to detect any bugs or issues that may have been introduced due to new code modifications, bug fixes, enhancements, or updates.
20. What is cross-browser testing, and why do we perform it?
Cross browser testing is a software testing methodology that ensures a web application works as intended consistently across different browsers, as web browsers can interpret and render web pages differently. The goal is to provide a consistent user experience for all users, regardless of their browsers.
With LambdaTest's Selenium Cloud Grid, cross-browser testing is efficient and scalable. Speed up the software release process and provide a top-notch user experience to your customers by testing web applications across 3000+ browsers, real devices, and operating systems.
21. What is the Automation Testing Life Cycle?
The Automation Testing Life Cycle is the step-by-step process used to plan, design, build, run, and maintain automated tests. It includes analyzing requirements, choosing a tool, creating a framework, writing scripts, executing them, reviewing results, and updating tests whenever the application changes.
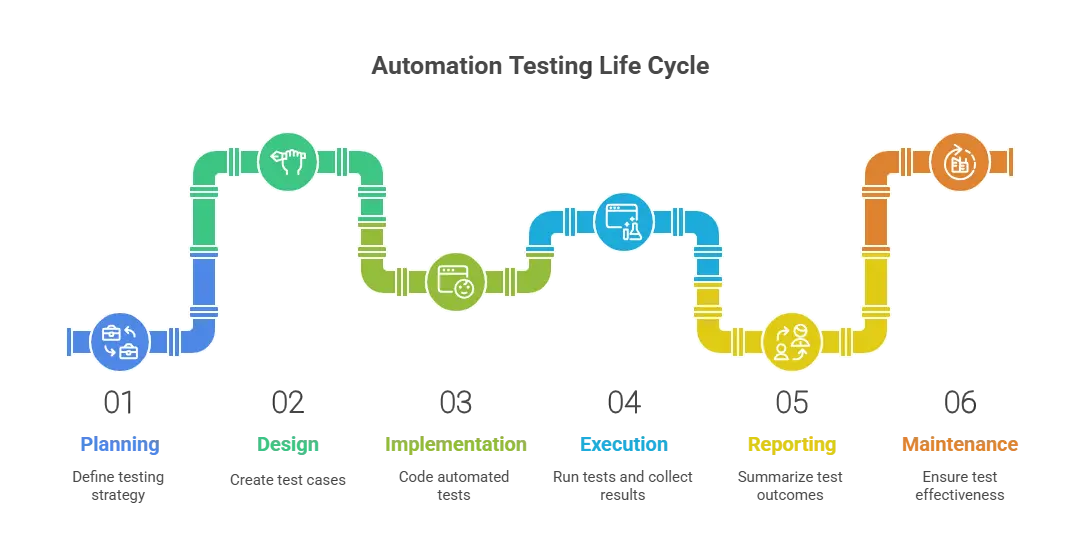
This cycle helps ensure testing is organized, fast, and consistent.
22. What is the Test Automation Pyramid, and why is it important in automation testing?
The Test Automation Pyramid is a concept that helps teams build a balanced and efficient test strategy. It shows how different types of tests should be distributed to get faster feedback, reduce flaky tests, and keep maintenance low.
- Unit Tests (Base of the Pyramid): Unit tests focus on testing individual components or functions in isolation. They are typically written by developers and cover small, specific pieces of code. Unit tests are fast, low-cost, and provide quick feedback, helping catch and fix issues early in development.
- Integration Tests (Middle of the Pyramid): Integration tests validate the interactions between various components or modules within an application. They ensure that different parts of the software work together. Integration tests are broader in scope than unit tests but narrower than UI tests.
- UI (User Interface) Tests (Top of the Pyramid): UI tests, also known as end-to-end tests, validate the functionality of the entire application from a user's perspective. They simulate user interactions with the application's graphical user interface. UI tests are slower, more complex, and more brittle and costly to maintain compared to unit and integration tests.
The pyramid is important because it encourages teams to rely more on fast, stable tests at the bottom and keep the slower, higher-level tests lightweight. This leads to faster releases, reduced costs, and a more stable automation framework.
Intermediate-Level Automation Testing Interview Questions
Intermediate automation testing questions focus on evaluating your ability to design scalable frameworks, implement POM, manage test data, handle dynamic elements, work with tools like TestNG, and apply best practices in real test automation pipelines. These questions help interviewers assess whether you can move beyond basic scripting and contribute to a maintainable, efficient automation ecosystem.
23. Explain your test automation framework architecture.
My test automation framework is designed to be modular, maintainable, and easy to scale. It follows a layered structure to keep the code organized and reusable.
- Test Scripts Layer: This is where the actual test cases live. Each script validates one feature or workflow and is written in a readable format for clarity.
- Page/Object Layer: Implements the Page Object Model (POM) to store all UI locators and reusable actions, reducing duplication and simplifying maintenance.
- Reusable Components/Utilities: Stores common functions like handling alerts, test data reading, wait utilities, logging, and screenshot capture to keep test scripts clean.
- Test Data Layer: Separates test data from scripts using JSON, Excel, CSV, or property files, enabling data-driven testing and easy reuse across test sets.
- Configurations Layer: Contains environment-specific settings such as URLs, credentials, and browser configs so the framework runs smoothly across setups.
- Test Runner/Orchestration Layer: Uses TestNG, JUnit, or Pytest to manage execution, grouping, parallel testing, and reporting. Also integrates with CI/CD pipelines.
- Reporting Layer: Generates detailed reports (like Allure or Extent Reports) with logs, screenshots, and status for each test step to speed up debugging.
- Integration Layer: Connects the framework with CI/CD tools, version control (Git), cloud testing platforms like LambdaTest, and notification systems like Slack or email.
Overall, the framework focuses on reusability, scalability, and maintainability so that tests are easy to build, run, and maintain as the application grows.
24. What is Page Object Model, and why is it important?
Page Object Model (POM) is a design pattern that creates an object repository for UI elements, separating test logic from page-specific code.
Without POM:
// LoginTest.java
driver.findElement(By.id("username")).sendKeys("testuser");
driver.findElement(By.id("password")).sendKeys("password123");
driver.findElement(By.id("loginButton")).click();
// CheckoutTest.java
driver.findElement(By.id("username")).sendKeys("testuser");
driver.findElement(By.id("password")).sendKeys("password123");
driver.findElement(By.id("loginButton")).click();
Problem: The Login code is duplicated. If the username locator changes, you must update every test.
With POM:
// LoginPage.java
public class LoginPage {
WebDriver driver;
By usernameField = By.id("username");
By passwordField = By.id("password");
By loginButton = By.id("loginButton");
public LoginPage(WebDriver driver) {
this.driver = driver;
}
public void login(String username, String password) {
driver.findElement(usernameField).sendKeys(username);
driver.findElement(passwordField).sendKeys(password);
driver.findElement(loginButton).click();
}
}
// LoginTest.java
LoginPage loginPage = new LoginPage(driver);
loginPage.login("testuser", "password123");
Benefits:
- Maintainability: Locator changes need updates in only one place
- Reusability: The Login method is used across all tests
- Readability: Tests read like user actions
- Reduced Duplication: DRY (Don't Repeat Yourself) principle
25. Explain the Page Object Model (POM) in Selenium.
The Page Object Model (POM) is a design pattern that is used to create object-oriented classes that serve as an interface to the web pages. This pattern promotes better maintainability, reusability, and readability in automation scripts. In POM, each web page in the application is represented as a class, and the elements of the page (buttons, text boxes, links, etc.) are represented as variables in that class.
- Why use POM?
- Separation of concerns: The automation script (test case) interacts with the page object class and does not need to know about the UI elements directly.
- Reusability: If there are changes to the page’s structure, you only need to update the page object class instead of the entire test script.
- Maintainability: It simplifies the process of modifying automation scripts since UI changes affect only the page object class and not the entire test suite.
In Selenium, the Page Object Model is implemented using annotations like @FindBy, and the elements are accessed using WebDriver methods such as getText(), click(), etc. By using this pattern, we create maintainable, scalable, and readable test code.
26. How do you handle test data management in your framework?
I keep test data separate from the test scripts by storing it in external files like JSON, Excel, or environment configs. The framework reads the data at runtime, making it easy to run the same test with multiple data sets. For dynamic scenarios, I generate test data through APIs or utility functions. I also maintain environment-specific data files and use cleanup steps to ensure each test starts with a consistent, reliable state.
27. What are Dynamic Elements? How do you handle dynamic elements on a web page using Selenium?
Dynamic elements are the elements on a web page with attributes or properties that can change dynamically during runtime. These changes may occur due to user interactions, updates in data, or other events triggered by the application.
The right strategies for locating and interacting with these elements are crucial during automation testing. With Selenium waits, XPaths, and JavaScript execution (using JavaScriptExecutor in Selenium Java or executescript() in Python), we can handle the execution of dynamic elements.
Some examples of dynamic elements are clocks and timers, live feeds, form autocomplete, interactive maps, real-time notifications, weather widgets, etc.
28. What is the difference between findElement and findElements in Selenium?
findElement is used when you want to locate a single web element on the page. It stops searching as soon as it finds the first match. If the element is not present, Selenium will throw a NoSuchElementException, which means the script will fail at that point.
findElements, on the other hand, searches for all elements that match the locator and returns them as a list. If no elements are found, it simply returns an empty list instead of throwing an error. This makes it useful when you want to check multiple items or verify if something exists without breaking the test.
Simple difference:
- findElement: returns the first matching element → throws error if nothing is found
- findElements: returns all matching elements as a list → returns an empty list if nothing is found
29. What is TestNG, and why do you use it?
TestNG is a testing framework designed to make test execution more structured, flexible, and efficient. It supports features like grouping tests, running tests in a specific order, data-driven testing, and generating detailed test reports.
You use TestNG because it simplifies the entire testing process. It helps manage complex test scenarios, allows parallel test execution, improves test organization through annotations, and provides clear reporting that makes it easier to understand failures and results. It’s widely used with Selenium because it makes automation testing faster, cleaner, and easier to maintain.
30. How does Selenium handle dropdowns?
Selenium uses the Select class to interact with dropdowns. It allows you to:
- Select options by visible text: dropdown.selectByVisibleText("Option 1")
- Select options by index: dropdown.selectByIndex(0)
- Select options by value: dropdown.selectByValue("value")
For multi-select dropdowns, you can use isMultiple() to check if it’s multi-select.
31. What is the purpose of the implicit wait in Selenium?
The purpose of an implicit wait in Selenium is to give the browser some extra time to load elements before the test throws an error. Since many elements don’t appear on the page immediately, implicit wait helps by telling Selenium to keep checking for the element for a set amount of time.
If the element shows up sooner, the test continues right away. If it doesn’t appear within the given time, then Selenium reports an error. This makes the test more stable and prevents failures caused by slow-loading elements.
32. What is the difference between “assert” and “verify” in Selenium?
The main difference lies in how the test behaves when a condition fails:
- Assert: When an assertion fails, the entire test stops at that point. This is used for checks that are essential for the remaining steps. For example, if the login page fails to load, there is no point in continuing further tests, so an assert is used. It ensures the test doesn’t continue with invalid or missing data.
- Verify: A verification allows the test to continue even if the condition fails. It records the failure but does not stop execution. This is helpful when the failed step is not critical and you still want to validate the rest of the scenario. For example, checking if a minor label or message is displayed.
In simple terms:
- Assert = Stop the test if the condition is false
- Verify = Continue the test even if the condition is false.
Advanced-Level Automation Testing Interview Questions
Advanced automation testing interviews focus on evaluating your ability to design scalable frameworks, integrate tests into CI/CD pipelines, optimize execution speed, and handle complex real-world testing challenges. These questions help assess your depth of technical expertise, problem-solving ability, and hands-on experience with modern automation tools and practices.
33. What is the difference between continuous integration (CI) and continuous delivery (CD)?
Continuous Integration (CI) is a development practice where developers integrate code into a shared repository frequently, ideally multiple times a day. This ensures that bugs are detected early in the development cycle. Automated tests are run on each integration to verify that the new code doesn’t break the application.
Continuous Delivery (CD) goes a step further, automating the deployment process. With CD, every change that passes automated testing can be deployed to production. This allows teams to release software more frequently and confidently. Both CI and CD improve the speed, quality, and reliability of the software development process.
| Feature | Continuous Integration (CI) | Continuous Delivery (CD) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Automatically integrate code changes and detect issues early | Ensure code is always in a deploy-ready state |
| Focus Area | Code integration, build, and unit testing | Release readiness, deployment pipeline automation |
| Primary Goal | Catch integration issues quickly | Deliver updates frequently and reliably |
| Process Trigger | Every code commit or merge | After CI passes successfully |
| Output | Tested and validated build | Deployable package ready for staging/production |
| Automation Level | Mainly build + test automation | End-to-end release automation (build → test → deploy) |
| Deployment | Not part of CI | Automated deployments to staging; production deployment may be manual or automated |
| Key Benefit | Reduces integration conflicts and improves developer workflow | Speeds up release cycles and improves delivery confidence |
| Tools | Jenkins, GitHub Actions, GitLab CI, CircleCI | Spinnaker, Argo CD, Octopus Deploy, AWS CodeDeploy |
34. How would you implement parallel test execution in Selenium?
Parallel test execution can significantly reduce test cycle times by running tests simultaneously across multiple browsers or machines. In Selenium, you can achieve parallel execution by using the following strategies:
- TestNG or JUnit: Both frameworks provide built-in support for parallel test execution through configuration. For instance, in TestNG, you can set the parallel attribute to tests or classes in your testng.xml file to run multiple tests or classes simultaneously.
- Selenium Grid: Selenium Grid allows you to run tests on different machines and browsers concurrently. It acts as a hub that manages multiple browser nodes.
- Cloud Services: Using cloud-based platforms like LambdaTest, which allows you to run parallel tests across thousands of real devices and browsers, scaling your test execution easily.
35. How do you handle alerts and pop-ups in Selenium?
In Selenium, browser alerts and popups can be managed using the Alert interface. Here's how to handle them:
- Accept: Use alert.accept() to accept the alert box.
- Dismiss: Use alert.dismiss() to dismiss a confirmation box.
- Get text: Use alert.getText() to retrieve the message from the alert.
- Send keys: For prompts, you can use alert.sendKeys("Your Text") to type into the alert box.
- Wait for Alert: To handle dynamic alerts, always use explicit waits like WebDriverWait to wait for the alert to appear before interacting with it.
36. Explain the concept of “Data-Driven Testing” in automation.
Data-Driven Testing (DDT) involves running the same test multiple times with different sets of data. This is useful for verifying how the application behaves with various input values. The test data is usually stored externally in Excel files, CSV files, or databases.
- Frameworks like TestNG or JUnit can integrate data sources to pass parameters into the test methods.
- Benefits: It allows you to cover a broader set of scenarios without duplicating code, and it helps in identifying edge cases and ensuring robustness in the application.
- Example: If testing a login page, data-driven testing can help you test different combinations of usernames and passwords.
37. What is the Page Factory in Selenium?
The Page Factory is an optimization of the Page Object Model (POM). It uses lazy initialization for web elements, meaning elements are initialized only when they are accessed, reducing overhead. This is achieved using the @FindBy annotation in Selenium.
- Advantages: It improves the maintainability of tests and makes the code more readable. It also avoids unnecessary delays since elements are only initialized when required.
Example:
@FindBy(id = "username")
private WebElement usernameField;38. How do you handle browser compatibility testing in automation?
Browser compatibility testing ensures that the web application works across all browsers and devices. Selenium helps automate this by running tests on different browsers using:
- Cross-Browser Testing: Use WebDriver’s DesiredCapabilities to specify which browser you want to test on.
- Selenium Grid or Cloud Platforms: Using tools like LambdaTest, you can test across 3,000+ browsers and 10,000+ real devices in parallel, significantly speeding up the testing process. This provides a more comprehensive testing approach, ensuring that your application functions well across different environments without manual intervention.
39. What are some best practices for writing automated test scripts?
Writing efficient, maintainable test scripts is key to successful automation. Some best practices include:
- Modularization: Break down tests into reusable methods and functions to avoid redundancy.
- Use of Waits: Implement explicit waits to ensure elements are available before interaction, and avoid using Thread.sleep(), which can introduce flakiness.
- Descriptive Naming Conventions: Use meaningful names for test methods and variables to make scripts easy to understand.
- Error Handling: Implement proper error handling and logging mechanisms to identify and troubleshoot test failures quickly.
- Version Control: Keep test scripts in version control systems like Git to manage changes and ensure collaboration across teams.
Expert-Level Automation Testing Interview Questions
Expert-level automation testing interviews focus on advanced concepts such as scaling strategies, handling flaky tests, managing real-world automation challenges, and implementing frameworks like BDD and TDD. These questions evaluate how well you apply automation skills to solve complex testing problems in modern, high-demand environments.
40. What is the role of automation in performance testing?
Automation plays a vital role in performance testing by simulating multiple users and measuring how the application performs under various conditions. Key benefits include:
- Simulating high traffic: Tools like JMeter and LoadRunner simulate thousands of users to test load capacity.
- Faster execution: Automated tests can be executed across different environments, providing quick feedback on performance.
- Identifying bottlenecks: Automation helps detect slow response times, errors, and system limitations.
- Scalability testing: It ensures the system can handle increased load without crashing.
Overall, automation ensures performance tests are consistent and repeatable, helping teams deliver scalable and high-performing applications.
41. What is the difference between horizontal and vertical scaling in cloud testing?
In cloud testing, scaling helps you handle different levels of load during test execution. There are two main ways to do this: horizontal scaling and vertical scaling.
- Horizontal Scaling (Scaling Out): This means adding more machines or instances instead of upgrading one. The load is spread across multiple servers, which is great when you need to run many tests in parallel across different browsers or devices.
- Vertical Scaling (Scaling Up): Here, you boost the power of a single machine by increasing its CPU, RAM, or storage. It’s helpful when certain tests need more processing power, but it’s limited by how much a single machine can handle.
Example: Tools like JMeter may rely on vertical scaling when simulating a high number of users from one powerful server.
42. How do you identify and fix flaky tests in automation?
Flaky tests are tests that fail sometimes and pass sometimes without any code change. They destroy trust in automation.
Common causes of flaky tests:
- Timing/synchronization issues
- Dynamic UI elements
- Network delays
- Race conditions
- Test data dependency
- Third-party API instability
How to fix them:
- Use explicit waits: Prefer WebDriverWait instead of thread.sleep() to avoid unnecessary delays
- Stabilize locators: Use robust CSS selectors instead of brittle XPath expressions
- Add retry logic: Implement retry mechanisms; platforms like LambdaTest HyperExecute offer built-in auto-retries
- Isolate test data: Prevent flaky behavior caused by shared-state or reused data
- Mock dependencies: Mock or stub external systems to reduce unpredictability
- Use visual locators: As a fallback when DOM-based selectors become unreliable
- Monitor flakiness: Track flaky trends using dashboards like LambdaTest Test Insights
43. How do you handle CAPTCHA in automation testing?
CAPTCHA (Completely Automated Public Turing test to tell Computers and Humans Apart) is designed to prevent automation, creating an inherent challenge.
Solutions:
1. Test Environment Bypass: Request developers to disable CAPTCHA in test environments (most common approach)
2. Test Accounts: Use special test accounts that skip CAPTCHA validation
3. API Testing: Test backend logic directly via APIs, bypassing UI-level CAPTCHA
4. Mock CAPTCHA: Implement a dummy CAPTCHA that always accepts a fixed response in test mode
5. Manual Intervention: Pause automation for a human to solve CAPTCHA (breaks automation flow)
6. Third-Party Services: Use OCR or CAPTCHA-solving services (expensive, unreliable, ethically questionable)
Best Practice: Collaborate with developers to implement environment-based CAPTCHA toggling rather than attempting to break security measures.
44. What is the difference between BDD (Behavior-Driven Development) and TDD (Test-Driven Development)?
The main differences between BDD and TDD are in their focus and execution:
BDD (Behavior-Driven Development):
- Focuses on the behavior of the application from the user’s perspective.
- Uses natural language constructs to describe the behavior, often in collaboration with non-developers (e.g., business analysts, product owners).
- Example: "Given that I am a user, when I click on the login button, then I should see the homepage."
TDD (Test-Driven Development):
- Focuses on writing tests for the application’s functionality before writing the actual code.
- The tests are more technical and focus on the code implementation.
- Example: "Write a test for a function to add two numbers."
BDD focuses on what should happen, while TDD focuses on how it should happen, making BDD more user-focused and TDD more developer-focused.
45. How is BDD implemented in tools like Cucumber or SpecFlow?
BDD is implemented in tools like Cucumber and SpecFlow by using Gherkin syntax, which allows tests to be written in a human-readable format. The process typically involves the following steps:
Cucumber:
- Defines behaviors in Gherkin language using "Given", "When", "Then" statements.
- These scenarios are written in .feature files and mapped to code using step definitions.
- Cucumber then executes the tests, checking if the system behaves as described.
SpecFlow:
- The .NET equivalent of Cucumber, used for BDD in C# environments.
- Uses the same Gherkin syntax for writing behavior scenarios.
- Step definitions are written in C# code, linking the Gherkin scenarios to the application behavior.
Both tools integrate with continuous testing frameworks and support collaboration between developers, testers, and non-technical stakeholders.
46. How do Gherkin language’s features enhance test collaboration?
Gherkin language enhances test collaboration by allowing tests to be written in plain English, making it accessible to all stakeholders, including business analysts, developers, and testers. Key features include:
- Readable syntax: Gherkin uses simple, natural language to describe system behavior, making it easy for non-technical stakeholders to understand and contribute.
- Collaborative approach: By using Gherkin, teams can collaboratively write acceptance criteria and test scenarios without needing technical knowledge, ensuring alignment between business goals and development.
- Automation-friendly: Gherkin scenarios are directly tied to executable code (via tools like Cucumber or SpecFlow), ensuring that the written behavior can be automatically tested.
Example: "Given I am a registered user, When I log in, Then I should be redirected to the dashboard."
Gherkin’s clear, simple syntax allows for better communication and collaboration across teams, ensuring that everyone is on the same page regarding system functionality and behavior.
Real-World Scenario-Based Questions
Real-world automation challenges go beyond basic scripting, which is why interviewers increasingly focus on scenario-based problem-solving. These questions evaluate how you handle dynamic data, UI changes, parallel execution, end-to-end flows, and large-scale test maintenance in practical automation environments.
47. How would you handle a scenario where the application UI frequently changes, and your automation tests are constantly breaking?
When the UI changes frequently, automation tests can become brittle. Here’s how to handle it:
- Use stable locators: Avoid using absolute XPath and prefer relative XPath or CSS selectors. Make sure locators are robust enough to handle small UI changes.
- Page Object Model (POM): Implement POM to separate the test scripts from the UI structure. This makes it easier to update the locators in a single place rather than in multiple test scripts.
- Smart waits: Use explicit waits to wait for elements to appear or change state instead of using fixed sleep times, which can be unreliable.
- Self-healing tests: Use AI-powered platforms like LambdaTest’s HyperExecute for auto-healing tests, which automatically detect and fix issues like broken locators.
This approach ensures tests are less prone to failure due to UI changes.
48. How would you implement data-driven testing in a scenario where test data changes dynamically during test execution?
To implement data-driven testing where test data changes dynamically:
- Externalize test data: Store test data in external sources like CSV files, Excel sheets, or databases that can be updated dynamically during execution.
- Parameterized tests: Use tools like TestNG or JUnit to pass dynamic test data to the test methods using annotations like @DataProvider or @Parameters.
- API calls for dynamic data: If data is fetched from an API, make API calls at the start of each test to retrieve the most up-to-date data for each execution.
- Validation: Ensure that each test validates the dynamic data against the expected results. For instance, if test data is expected to change, automate checks to verify if it’s being handled correctly.
This ensures that tests remain flexible and adapt to the dynamic nature of real-world data.
49. Imagine you have to automate end-to-end testing of a web application that involves login, form submission, and file upload. How would you design the test script?
Here’s how I would design an end-to-end automation test script for such a scenario:
- Step 1: Setup
- Initialize the test environment, like launching the browser and navigating to the login page.
- Use Selenium WebDriver for browser interaction, such as opening the browser and navigating to URLs.
- Step 2: Login
- Automate the login process using valid credentials (e.g., using sendKeys() for username and password, and click() for the login button).
- Handle potential alerts or pop-ups that might appear during login.
- Step 3: Form Submission
- Once logged in, navigate to the required form page.
- Automate form interactions, using WebDriver actions like sendKeys() to enter form data and click() for submission.
- Validate successful form submission by checking for confirmation messages or updated elements on the page.
- Step 4: File Upload
- For file uploads, use the sendKeys() method to select a file in the input field.
- If the file upload involves dragging and dropping, use actions like ActionBuilder to simulate the drag-and-drop feature.
- Step 5 Validation: After the form is submitted and the file is uploaded, validate each step to ensure the expected result (e.g., a success message, file confirmation).
This approach ensures a comprehensive test script that covers login, form submission, and file upload in a real-world scenario.
50. How would you handle parallel execution of tests across multiple browsers and devices in a cloud-based environment?
To handle parallel execution across multiple browsers and devices in a cloud-based environment:
- Use a cloud testing platform: Platforms like LambdaTest, which provide the ability to execute tests across 3,000+ real browsers and devices.
- Selenium Grid or Cloud Grid: Configure a Selenium Grid or use cloud-based grids that allow running tests in parallel on different browser-device combinations.
- TestNG for parallel execution: Use TestNG with the parallel="tests" or parallel="classes" attribute to run tests concurrently. This helps reduce the overall test execution time.
- CI/CD integration: Integrate the parallel execution setup into a CI/CD pipeline (e.g., Jenkins, GitHub Actions) to automatically trigger parallel tests after each code commit or on a schedule.
This method optimizes test execution time and ensures comprehensive cross-browser testing.
51. In a scenario where you are testing a large-scale web application with multiple modules, how would you approach test maintenance and ensure that your test suite is scalable?
For testing a large-scale web application with multiple modules:
- Modular Test Design: Use modular design principles where common functionality is abstracted into reusable functions or methods (e.g., login, navigation).
- Page Object Model (POM): Implement POM to manage locators and actions for each page in a separate class. This helps centralize test logic and reduces maintenance efforts when UI changes occur.
- Test Categorization: Categorize tests based on modules, features, or critical functionalities, and prioritize them based on importance and frequency of changes.
- Use Data-Driven Testing: Use data-driven and parameterized tests to run the same set of tests with different data sets without duplicating code.
- Regular Test Review and Refactoring: Regularly review and refactor your test scripts to ensure they remain efficient and maintainable as the application evolves.
- Cloud-based Test Execution: Use cloud-based platforms like LambdaTest for parallel execution across different environments, enabling quick feedback across modules without overwhelming resources.
This ensures that tests are scalable, reusable, and easy to maintain as the application grows.
Modern Trends in Automation Testing: What to Prepare for 2026
Automation testing is shifting toward AI-driven test creation, self-healing scripts, and intelligent automation workflows. These questions highlight the key modern trends you must prepare for in 2026.
52. What is AI-powered test automation, and how does it differ from traditional automation?
Traditional automation requires explicitly programmed instructions. AI-powered testing uses machine learning to make intelligent decisions, adapt to changes, and optimize test execution.
Key Differences:
| Aspect | Traditional Automation | AI-Powered Automation |
|---|---|---|
| Test Creation | Manual scripting | Natural language, AI generation |
| Element Location | Fixed locators | Self-healing locators |
| Maintenance | Manual updates for UI changes | Automatic adaptation |
| Test Optimization | Manual analysis | AI-driven prioritization |
| Defect Prediction | Reactive | Proactive prediction |
Real-World Applications:
- Self-Healing Test Scripts: AI detects when locators fail and automatically finds alternative selectors, enabling Self-Healing Test Automation. Example: If a button ID changes from
btn-submittosubmit-button, traditional automation fails, but AI analyzes visual attributes, position, and text to suggest or apply new locators. - Visual Testing with AI: AI compares screenshots intelligently, detecting visual differences while ignoring acceptable variations like timestamps or dynamic content.
- Test Generation from Requirements: NLP converts user stories into executable test cases. This allows teams to generate test cases with AI effortlessly. Example: For the requirement “As a user, I want to reset my password via email,” AI generates steps such as navigating to login, clicking Forgot Password, entering email, verifying email sent, using the reset link, updating password, and validating login.
- Navigate to the login page
- Click "Forgot Password"
- Enter email address
- Verify email sent
- Click the reset link
- Enter new password
- Verify login with the new password
- Intelligent Test Prioritization: ML models analyze code changes and predict which tests are likely to fail, ensuring high-risk tests run first.
Example: "As a user, I want to reset my password via email." AI generates test steps:
LambdaTest's KaneAI GenAI-native testing agent that understands natural language instructions, authors tests, and evolves them as applications change. You can describe test scenarios conversationally: "Test the checkout flow with a 10% discount code for first-time users," and KaneAI generates executable automation.
Conclusion
Automation testing is evolving fast, and this blog brings together the most relevant questions from fundamentals and framework design to CI/CD, Selenium, flaky test handling, and modern AI-driven practices. By understanding core concepts like the automation life cycle, Test Automation Pyramid, POM, cross-browser testing, and data-driven approaches, candidates can confidently handle both technical and scenario-based interview questions.
This guide also prepares you for the future with trends like autonomous testing, self-healing locators, visual validation, and AI-powered test generation, making it a complete resource for anyone aiming to excel in automation testing roles in 2026 and beyond.
On This Page
- Fundamentals of Automation Testing Interview Questions
- Intermediate-Level Automation Testing Interview Questions
- Advanced-Level Automation Testing Interview Questions
- Expert-Level Automation Testing Interview Questions
- Real-World Scenario-Based Questions
- Automation Testing Trends to Prepare for 2026
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Frequently asked questions
- Functional Automation – Tests core functionalities like login, forms, workflows.
- Regression Automation – Ensures new changes don't break existing features.
- Load Testing Automation – Checks performance under various load conditions.
- Smoke Testing Automation – Verifies basic app stability after each build.
- Selenium WebDriver: Script-based automation tool supporting multiple languages and browsers; ideal for complex test scenarios.
- Selenium IDE: Record-and-playback tool for beginners; suitable for simple, repetitive tests.
- Use XPath with
contains()for flexible element identification. - Use Explicit Waits (
WebDriverWait) to wait for visibility or presence. - Prefer stable locators like relative XPath and CSS selectors.
- Auto-generating test cases using NLP.
- Self-healing tests that auto-update broken locators.
- Flaky test detection for improved test stability.
- High-risk and business-critical areas.
- Repetitive tests such as regression suites.
- Areas requiring increased test coverage across multiple environments.
- Maintaining data in external sources (CSV, Excel, DBs).
- Using data-driven testing via TestNG, JUnit, etc.
- Using mock data or fixtures for predictable testing results.
Did you find this page helpful?
More Related Hubs

Start your journey with LambdaTest
Get 100 minutes of automation test minutes FREE!!

